Antipodal hotspot on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of
A mantle plume is a proposed mechanism of
 The chemical and isotopic composition of basalts found at hotspots differs subtly from mid-ocean-ridge basalts. These basalts, also called ocean island basalts (OIBs), are analysed in their radiogenic and stable isotope compositions. In radiogenic isotope systems the originally subducted material creates diverging trends, termed mantle components. Identified mantle components are DMM (depleted mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) mantle), HIMU (high U/Pb-ratio mantle), EM1 (enriched mantle 1), EM2 (enriched mantle 2) and FOZO (focus zone). This geochemical signature arises from the mixing of near-surface materials such as subducted slabs and continental sediments, in the mantle source. There are two competing interpretations for this. In the context of mantle plumes, the near-surface material is postulated to have been transported down to the core-mantle boundary by subducting slabs, and to have been transported back up to the surface by plumes. In the context of the Plate hypothesis, subducted material is mostly re-circulated in the shallow mantle and tapped from there by volcanoes.
Stable isotopes like Fe are used to track processes that the uprising material experiences during melting.
The processing of oceanic crust, lithosphere, and sediment through a subduction zone decouples the water-soluble trace elements (e.g., K, Rb, Th) from the immobile trace elements (e.g., Ti, Nb, Ta), concentrating the immobile elements in the oceanic slab (the water-soluble elements are added to the crust in island arc volcanoes).
The chemical and isotopic composition of basalts found at hotspots differs subtly from mid-ocean-ridge basalts. These basalts, also called ocean island basalts (OIBs), are analysed in their radiogenic and stable isotope compositions. In radiogenic isotope systems the originally subducted material creates diverging trends, termed mantle components. Identified mantle components are DMM (depleted mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) mantle), HIMU (high U/Pb-ratio mantle), EM1 (enriched mantle 1), EM2 (enriched mantle 2) and FOZO (focus zone). This geochemical signature arises from the mixing of near-surface materials such as subducted slabs and continental sediments, in the mantle source. There are two competing interpretations for this. In the context of mantle plumes, the near-surface material is postulated to have been transported down to the core-mantle boundary by subducting slabs, and to have been transported back up to the surface by plumes. In the context of the Plate hypothesis, subducted material is mostly re-circulated in the shallow mantle and tapped from there by volcanoes.
Stable isotopes like Fe are used to track processes that the uprising material experiences during melting.
The processing of oceanic crust, lithosphere, and sediment through a subduction zone decouples the water-soluble trace elements (e.g., K, Rb, Th) from the immobile trace elements (e.g., Ti, Nb, Ta), concentrating the immobile elements in the oceanic slab (the water-soluble elements are added to the crust in island arc volcanoes).
 The most prominent thermal contrast known to exist in the deep (1000 km) mantle is at the core-mantle boundary at 2900 km. Mantle plumes were originally postulated to rise from this layer because the hotspots that are assumed to be their surface expression were thought to be fixed relative to one another. This required that plumes were sourced from beneath the shallow asthenosphere that is thought to be flowing rapidly in response to motion of the overlying tectonic plates. There is no other known major thermal boundary layer in the deep Earth, and so the core-mantle boundary was the only candidate.
The base of the mantle is known as the D″ layer, a seismological subdivision of the Earth. It appears to be compositionally distinct from the overlying mantle and may contain partial melt.
Two very broad,
The most prominent thermal contrast known to exist in the deep (1000 km) mantle is at the core-mantle boundary at 2900 km. Mantle plumes were originally postulated to rise from this layer because the hotspots that are assumed to be their surface expression were thought to be fixed relative to one another. This required that plumes were sourced from beneath the shallow asthenosphere that is thought to be flowing rapidly in response to motion of the overlying tectonic plates. There is no other known major thermal boundary layer in the deep Earth, and so the core-mantle boundary was the only candidate.
The base of the mantle is known as the D″ layer, a seismological subdivision of the Earth. It appears to be compositionally distinct from the overlying mantle and may contain partial melt.
Two very broad,
 The plume hypothesis has been tested by looking for the geophysical anomalies predicted to be associated with them. These include thermal, seismic, and elevation anomalies. Thermal anomalies are inherent in the term "hotspot". They can be measured in numerous different ways, including surface heat flow, petrology, and seismology. Thermal anomalies produce anomalies in the speeds of seismic waves, but unfortunately so do composition and partial melt. As a result, wave speeds cannot be used simply and directly to measure temperature, but more sophisticated approaches must be taken.
Seismic anomalies are identified by mapping variations in wave speed as seismic waves travel through Earth. A hot mantle plume is predicted to have lower seismic wave speeds compared with similar material at a lower temperature. Mantle material containing a trace of partial melt (e.g., as a result of it having a lower melting point), or being richer in Fe, also has a lower seismic wave speed and those effects are stronger than temperature. Thus, although unusually low wave speeds have been taken to indicate anomalously hot mantle beneath hotspots, this interpretation is ambiguous. The most commonly cited seismic wave-speed images that are used to look for variations in regions where plumes have been proposed come from seismic tomography. This method involves using a network of seismometers to construct three-dimensional images of the variation in seismic wave speed throughout the mantle.
The plume hypothesis has been tested by looking for the geophysical anomalies predicted to be associated with them. These include thermal, seismic, and elevation anomalies. Thermal anomalies are inherent in the term "hotspot". They can be measured in numerous different ways, including surface heat flow, petrology, and seismology. Thermal anomalies produce anomalies in the speeds of seismic waves, but unfortunately so do composition and partial melt. As a result, wave speeds cannot be used simply and directly to measure temperature, but more sophisticated approaches must be taken.
Seismic anomalies are identified by mapping variations in wave speed as seismic waves travel through Earth. A hot mantle plume is predicted to have lower seismic wave speeds compared with similar material at a lower temperature. Mantle material containing a trace of partial melt (e.g., as a result of it having a lower melting point), or being richer in Fe, also has a lower seismic wave speed and those effects are stronger than temperature. Thus, although unusually low wave speeds have been taken to indicate anomalously hot mantle beneath hotspots, this interpretation is ambiguous. The most commonly cited seismic wave-speed images that are used to look for variations in regions where plumes have been proposed come from seismic tomography. This method involves using a network of seismometers to construct three-dimensional images of the variation in seismic wave speed throughout the mantle.
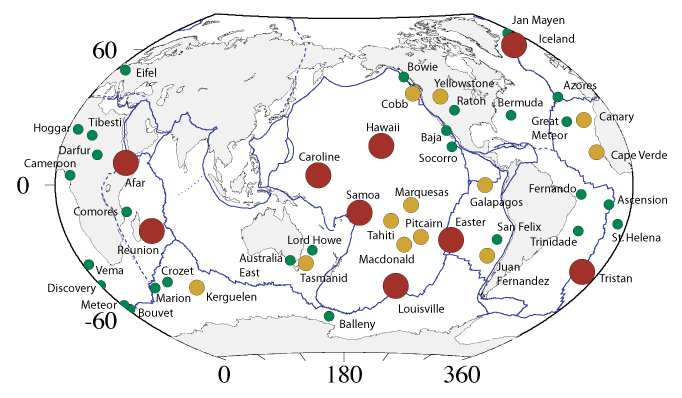 Mantle plumes have been suggested as the source for
Mantle plumes have been suggested as the source for
 Beginning in the early 2000s, dissatisfaction with the state of the evidence for mantle plumes and the proliferation of
Beginning in the early 2000s, dissatisfaction with the state of the evidence for mantle plumes and the proliferation of
Seismic-tomography image of Yellowstone mantle plumeLarge Igneous Provinces CommissionMantleplumes.org: mantle-plume skeptic website
– managed and maintained by
convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
within the Earth's mantle
Earth's mantle is a layer of silicate rock between the crust and the outer core. It has a mass of 4.01 × 1024 kg and thus makes up 67% of the mass of Earth. It has a thickness of making up about 84% of Earth's volume. It is predominantly so ...
, hypothesized to explain anomalous volcanism. Because the plume head partially melts on reaching shallow depths, a plume is often invoked as the cause of volcanic hotspots, such as Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
or Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, and large igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s such as the Deccan
The large Deccan Plateau in southern India is located between the Western Ghats and the Eastern Ghats, and is loosely defined as the peninsular region between these ranges that is south of the Narmada river. To the north, it is bounded by the ...
and Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
. Some such volcanic regions lie far from tectonic plate boundaries, while others represent unusually large-volume volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called a ...
near plate boundaries.
Concepts
Mantle plumes were first proposed by J. Tuzo Wilson in 1963 and further developed by W. Jason Morgan in 1971 and 1972. A mantle plume is posited to exist where super-heated material forms ( nucleates) at the core-mantle boundary and rises through the Earth's mantle. Rather than a continuous stream, plumes should be viewed as a series of hot bubbles of material. Reaching the brittle upperEarth's crust
Earth's crust is Earth's thin outer shell of rock, referring to less than 1% of Earth's radius and volume. It is the top component of the lithosphere, a division of Earth's layers that includes the crust and the upper part of the mantle. The ...
they form diapirs
A diapir (; , ) is a type of igneous intrusion in which a more mobile and ductily deformable material is forced into brittle overlying rocks. Depending on the tectonic environment, diapirs can range from idealized mushroom-shaped Rayleigh–T ...
. These diapirs are "hotspots" in the crust. In particular, the concept that mantle plumes are fixed relative to one another and anchored at the core-mantle boundary would provide a natural explanation for the time-progressive chains of older volcanoes seen extending out from some such hotspots, for example, the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain
The Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain is a mostly undersea mountain range in the Pacific Ocean that reaches above sea level in Hawaii. It is composed of the Hawaiian ridge, consisting of the islands of the Hawaiian chain northwest to Kure Atoll, ...
. However, paleomagnetic
Paleomagnetism (or palaeomagnetismsee ), is the study of magnetic fields recorded in rocks, sediment, or archeological materials. Geophysicists who specialize in paleomagnetism are called ''paleomagnetists.''
Certain magnetic minerals in rock ...
data show that mantle plumes can also be associated with Large Low Shear Velocity Provinces (LLSVPs) and do move relative to each other.
The current mantle plume theory is that material and energy from Earth's interior are exchanged with the surface crust in two distinct and largely independent convective flows:
* as previously theorized and widely accepted, the predominant, steady state plate tectonic regime driven by upper mantle convection
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle as convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface.
The Earth's surface lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere and the two form ...
, mainly the sinking of cold plates of lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years ...
back into the asthenosphere
The asthenosphere () is the mechanically weak and ductile region of the upper mantle of Earth. It lies below the lithosphere, at a depth between ~ below the surface, and extends as deep as . However, the lower boundary of the asthenosphere is ...
.
* the punctuated, intermittently dominant mantle overturn regime driven by plume convection that carries heat upward from the core-mantle boundary in a narrow column. This second regime, while often discontinuous, is periodically significant in mountain building and continental breakup.
The plume hypothesis was simulated by laboratory experiments in small fluid-filled tanks in the early 1970s. Thermal or compositional fluid-dynamical plumes produced in that way were presented as model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
s for the much larger postulated mantle plumes. Based on these experiments, mantle plumes are now postulated to comprise two parts: a long thin conduit connecting the top of the plume to its base, and a bulbous head that expands in size as the plume rises. The entire structure resembles a mushroom. The bulbous head of thermal plumes forms because hot material moves upward through the conduit faster than the plume itself rises through its surroundings. In the late 1980s and early 1990s, experiments with thermal models showed that as the bulbous head expands it may entrain some of the adjacent mantle into the head.
The size and occurrence of mushroom mantle plumes can be predicted by the transient instability theory of Tan and Thorpe. The theory predicts mushroom-shaped mantle plumes with heads of about 2000 km diameter that have a critical time (time from onset of heating of the lower mantle to formation of a plume) of about 830 million years for a core mantle heat flux
Heat flux or thermal flux, sometimes also referred to as ''heat flux density'', heat-flow density or ''heat flow rate intensity'' is a flow of energy per unit area per unit time. In SI its units are watts per square metre (W/m2). It has both a ...
of 20 mW/m2, while the cycle time (the time between plume formation events) is about 2000 million years. The number of mantle plumes is predicted to be about 17.
When a plume head encounters the base of the lithosphere, it is expected to flatten out against this barrier and to undergo widespread decompression melting to form large volumes of basalt magma. It may then erupt onto the surface. Numerical modelling predicts that melting and eruption will take place over several million years. These eruptions have been linked to flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s, although many of those erupt over much shorter time scales (less than 1 million years). Examples include the Deccan traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flo ...
in India, the Siberian traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
of Asia, the Karoo-Ferrar
The Karoo and Ferrar Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs) are two large igneous provinces in Southern Africa and Antarctica respectively, collectively known as the Karoo-Ferrar, Gondwana,E.g. or Southeast African LIP, associated with the initial break- ...
basalts/dolerites in South Africa and Antarctica, the Paraná and Etendeka traps
The Paraná-Etendeka traps (or Paraná and Etendeka Plateau; or Paraná and Etendeka Province) comprise a large igneous province that includes both the main Paraná traps (in Paraná Basin, a South American geological basin) as well as the smal ...
in South America and Africa (formerly a single province separated by opening of the South Atlantic Ocean), and the Columbia River basalts
The Columbia River Basalt Group is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt province on Earth, covering over mainly eastern Oregon and Washington, western Idaho, and part of northern Nevada. The basalt grou ...
of North America. Flood basalts in the oceans are known as oceanic plateaus, and include the Ontong Java plateau
The Ontong Java Plateau (OJP) is a massive oceanic plateau located in the southwestern Pacific Ocean, north of the Solomon Islands.
The OJP was formed around (Ma) with a much smaller volcanic event around 90 Ma. Two other southwestern Pacifi ...
of the western Pacific Ocean and the Kerguelen Plateau
The Kerguelen Plateau (, ), also known as the Kerguelen–Heard Plateau, is an oceanic plateau and a large igneous province (LIP) located on the Antarctic Plate, in the southern Indian Ocean. It is about to the southwest of Australia and is ...
of the Indian Ocean.
The narrow vertical conduit, postulated to connect the plume head to the core-mantle boundary, is viewed as providing a continuous supply of magma to a hotspot. As the overlying tectonic plate moves over this hotspot, the eruption of magma from the fixed plume onto the surface is expected to form a chain of volcanoes that parallels plate motion. The Hawaiian Islands
The Hawaiian Islands ( haw, Nā Mokupuni o Hawai‘i) are an archipelago of eight major islands, several atolls, and numerous smaller islets in the North Pacific Ocean, extending some from the island of Hawaii in the south to northernmost ...
chain in the Pacific Ocean is the archetypal example. It has recently been discovered that the volcanic locus of this chain has not been fixed over time, and it thus joined the club of the many type examples that do not exhibit the key characteristic originally proposed.
The eruption of continental flood basalts is often associated with continental rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
and breakup. This has led to the hypothesis that mantle plumes contribute to continental rifting and the formation of ocean basins.
Chemistry, heat flow and melting
 The chemical and isotopic composition of basalts found at hotspots differs subtly from mid-ocean-ridge basalts. These basalts, also called ocean island basalts (OIBs), are analysed in their radiogenic and stable isotope compositions. In radiogenic isotope systems the originally subducted material creates diverging trends, termed mantle components. Identified mantle components are DMM (depleted mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) mantle), HIMU (high U/Pb-ratio mantle), EM1 (enriched mantle 1), EM2 (enriched mantle 2) and FOZO (focus zone). This geochemical signature arises from the mixing of near-surface materials such as subducted slabs and continental sediments, in the mantle source. There are two competing interpretations for this. In the context of mantle plumes, the near-surface material is postulated to have been transported down to the core-mantle boundary by subducting slabs, and to have been transported back up to the surface by plumes. In the context of the Plate hypothesis, subducted material is mostly re-circulated in the shallow mantle and tapped from there by volcanoes.
Stable isotopes like Fe are used to track processes that the uprising material experiences during melting.
The processing of oceanic crust, lithosphere, and sediment through a subduction zone decouples the water-soluble trace elements (e.g., K, Rb, Th) from the immobile trace elements (e.g., Ti, Nb, Ta), concentrating the immobile elements in the oceanic slab (the water-soluble elements are added to the crust in island arc volcanoes).
The chemical and isotopic composition of basalts found at hotspots differs subtly from mid-ocean-ridge basalts. These basalts, also called ocean island basalts (OIBs), are analysed in their radiogenic and stable isotope compositions. In radiogenic isotope systems the originally subducted material creates diverging trends, termed mantle components. Identified mantle components are DMM (depleted mid-ocean ridge basalt (MORB) mantle), HIMU (high U/Pb-ratio mantle), EM1 (enriched mantle 1), EM2 (enriched mantle 2) and FOZO (focus zone). This geochemical signature arises from the mixing of near-surface materials such as subducted slabs and continental sediments, in the mantle source. There are two competing interpretations for this. In the context of mantle plumes, the near-surface material is postulated to have been transported down to the core-mantle boundary by subducting slabs, and to have been transported back up to the surface by plumes. In the context of the Plate hypothesis, subducted material is mostly re-circulated in the shallow mantle and tapped from there by volcanoes.
Stable isotopes like Fe are used to track processes that the uprising material experiences during melting.
The processing of oceanic crust, lithosphere, and sediment through a subduction zone decouples the water-soluble trace elements (e.g., K, Rb, Th) from the immobile trace elements (e.g., Ti, Nb, Ta), concentrating the immobile elements in the oceanic slab (the water-soluble elements are added to the crust in island arc volcanoes). Seismic tomography
Seismic tomography or seismotomography is a technique for imaging the subsurface of the Earth with seismic waves produced by earthquakes or explosions. P-, S-, and surface waves can be used for tomographic models of different resolutions based on ...
shows that subducted oceanic slabs sink as far as the bottom of the mantle transition zone
The transition zone is part of the Earth's mantle, and is located between the lower mantle and the upper mantle, between a depth of 410 and 660 km (250 to 400 mi). The Earth's mantle, including the transition zone, consists primarily o ...
at 650 km depth. Subduction to greater depths is less certain, but there is evidence that they may sink to mid-lower-mantle depths at about 1,500 km depth.
The source of mantle plumes is postulated to be the core-mantle boundary at 3,000 km depth. Because there is little material transport across the core-mantle boundary, heat transfer must occur by conduction, with adiabatic gradients above and below this boundary. The core-mantle boundary is a strong thermal (temperature) discontinuity. The temperature of the core is approximately 1,000 degrees Celsius higher than that of the overlying mantle. Plumes are postulated to rise as the base of the mantle becomes hotter and more buoyant.
Plumes are postulated to rise through the mantle and begin to partially melt on reaching shallow depths in the asthenosphere by decompression melting
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma ...
. This would create large volumes of magma. This melt rises to the surface and erupts to form hotspots.
The lower mantle and the core
large low-shear-velocity provinces
Large low-shear-velocity provinces, LLSVPs, also called LLVPs or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle (the region surrounding the outer core) of Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave ve ...
exist in the lower mantle under Africa and under the central Pacific. It is postulated that plumes rise from their surface or their edges. Their low seismic velocities were thought to suggest that they are relatively hot, although it has recently been shown that their low wave velocities are due to high density caused by chemical heterogeneity.
Evidence for the theory
Some common and basic lines of evidence cited in support of the theory are linear volcanic chains,noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
es, geophysical
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' some ...
anomalies, and geochemistry
Geochemistry is the science that uses the tools and principles of chemistry to explain the mechanisms behind major geological systems such as the Earth's crust and its oceans. The realm of geochemistry extends beyond the Earth, encompassing th ...
.
Linear volcanic chains
The age-progressive distribution of the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain has been explained as a result of a fixed, deep-mantle plume rising into the upper mantle, partly melting, and causing a volcanic chain to form as the plate moves overhead relative to the fixed plume source. Other hotspots with time-progressive volcanic chains behind them includeRéunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island o ...
, the Chagos-Laccadive Ridge, the Louisville Ridge
The Louisville Ridge, also known as the Louisville Seamount Chain, is an underwater chain of over 70 seamounts located in the Southwest portion of the Pacific Ocean. As one of the longest seamount chains on Earth it stretches some Vanderkluysen, ...
, the Ninety East Ridge
The Ninety East Ridge (also rendered as Ninetyeast Ridge, 90E Ridge or 90°E Ridge) is a mid-ocean ridge on the Indian Ocean floor named for its near-parallel strike along the 90th meridian at the center of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is approxima ...
and Kerguelen
The Kerguelen Islands ( or ; in French commonly ' but officially ', ), also known as the Desolation Islands (' in French), are a group of islands in the sub-Antarctic constituting one of the two exposed parts of the Kerguelen Plateau, a large ...
, Tristan
Tristan ( Latin/Brythonic: ''Drustanus''; cy, Trystan), also known as Tristram or Tristain and similar names, is the hero of the legend of Tristan and Iseult. In the legend, he is tasked with escorting the Irish princess Iseult to wed ...
, and Yellowstone
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellow ...
.
While there is evidence that the chains listed above are time-progressive, it has been shown that they are not fixed relative to one another. The most remarkable example of this is the Emperor chain, the older part of the Hawaii system, which was formed by migration of the hotspot in addition to the plate motion. Another example is the Canary Islands in the northeast of Africa in the Atlantic Ocean.
Noble gas and other isotopes
Helium-3 is a primordial isotope that formed in theBig Bang
The Big Bang event is a physical theory that describes how the universe expanded from an initial state of high density and temperature. Various cosmological models of the Big Bang explain the evolution of the observable universe from the ...
. Very little is produced, and little has been added to the Earth by other processes since then. Helium-4
Helium-4 () is a stable isotope of the element helium. It is by far the more abundant of the two naturally occurring isotopes of helium, making up about 99.99986% of the helium on Earth. Its nucleus is identical to an alpha particle, and cons ...
includes a primordial component, but it is also produced by the natural radioactive decay of elements such as uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
and thorium
Thorium is a weakly radioactive metallic chemical element with the symbol Th and atomic number 90. Thorium is silvery and tarnishes black when it is exposed to air, forming thorium dioxide; it is moderately soft and malleable and has a high ...
. Over time, helium in the upper atmosphere is lost into space. Thus, the Earth has become progressively depleted in helium, and 3He is not replaced as 4He is. As a result, the ratio 3He/4He in the Earth has decreased over time.
Unusually high 3He/4He have been observed in some, but not all, hotspots. This is explained by plumes tapping a deep, primordial reservoir in the lower mantle, where the original, high 3He/4He ratios have been preserved throughout geologic time.
Other elements, e.g. osmium
Osmium (from Greek grc, ὀσμή, osme, smell, label=none) is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, ...
, have been suggested to be tracers of material arising from near to the Earth's core, in basalts at oceanic islands. However, so far conclusive proof for this is lacking.
Geophysical anomalies
Seismic waves
A seismic wave is a wave of acoustic energy that travels through the Earth. It can result from an earthquake, volcanic eruption, magma movement, a large landslide, and a large man-made explosion that produces low-frequency acoustic energy. ...
generated by large earthquakes enable structure below the Earth's surface to be determined along the ray path. Seismic waves that have traveled a thousand or more kilometers (also called teleseismic waves) can be used to image large regions of Earth's mantle. They also have limited resolution, however, and only structures at least several hundred kilometers in diameter can be detected.
Seismic tomography images have been cited as evidence for a number of mantle plumes in Earth's mantle. There is, however, vigorous on-going discussion regarding whether the structures imaged are reliably resolved, and whether they correspond to columns of hot, rising rock.
The mantle plume hypothesis predicts that domal topographic uplifts will develop when plume heads impinge on the base of the lithosphere. An uplift of this kind occurred when the north Atlantic Ocean opened about 54 million years ago. Some scientists have linked this to a mantle plume postulated to have caused the breakup of Eurasia and the opening of the north Atlantic, now suggested to underlie Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
. Current research has shown that the time-history of the uplift is probably much shorter than predicted, however. It is thus not clear how strongly this observation supports the mantle plume hypothesis.
Geochemistry
Basalts found at oceanic islands are geochemically distinct frommid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a div ...
basalt (MORB). Ocean island basalt
Ocean island basalt (OIB) is a volcanic rock, usually basaltic in composition, erupted in oceans away from tectonic plate boundaries. Although ocean island basaltic magma is mainly erupted as basalt lava, the basaltic magma is sometimes modified b ...
(OIB) is more diverse compositionally than MORB, and the great majority of ocean islands are composed of alkali basalt
Alkali basalt or alkali olivine basalt is a dark-colored, porphyritic volcanic rock usually found in oceanic and continental areas associated with volcanic activity, such as oceanic islands, continental rifts and volcanic fields. Alkali basalt ...
enriched in sodium and potassium relative to MORB. Larger islands, such as Hawaii or Iceland, are mostly tholeiitic
The tholeiitic magma series is one of two main magma series in subalkaline igneous rocks, the other being the calc-alkaline series. A magma series is a chemically distinct range of magma compositions that describes the evolution of a mafic magma ...
basalt, with alkali basalt limited to late stages of their development, but this tholeiitic basalt is chemically distinct from the tholeiitic basalt of mid-ocean ridges. OIB tends to be more enriched in magnesium, and both alkali and tholeiitic OIB is enriched in trace incompatible element In petrology and geochemistry, an incompatible element is one that is unsuitable in size and/or charge to the cation sites of the minerals of which it is included. It is defined by the partition coefficient between rock-forming minerals and melt b ...
s, with the light rare earth elements showing particular enrichment compared with heavier rare earth elements. Stable isotope ratio
The term stable isotope has a meaning similar to stable nuclide, but is preferably used when speaking of nuclides of a specific element. Hence, the plural form stable isotopes usually refers to isotopes of the same element. The relative abunda ...
s of the elements strontium
Strontium is the chemical element with the symbol Sr and atomic number 38. An alkaline earth metal, strontium is a soft silver-white yellowish metallic element that is highly chemically reactive. The metal forms a dark oxide layer when it is e ...
, neodymium
Neodymium is a chemical element with the symbol Nd and atomic number 60. It is the fourth member of the lanthanide series and is considered to be one of the rare-earth metals. It is a hard, slightly malleable, silvery metal that quickly tarn ...
, hafnium
Hafnium is a chemical element with the symbol Hf and atomic number 72. A lustrous, silvery gray, tetravalent transition metal, hafnium chemically resembles zirconium and is found in many zirconium minerals. Its existence was predicted by Dmitri M ...
, lead
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, ...
, and osmium
Osmium (from Greek grc, ὀσμή, osme, smell, label=none) is a chemical element with the symbol Os and atomic number 76. It is a hard, brittle, bluish-white transition metal in the platinum group that is found as a trace element in alloys, ...
show wide variations relative to MORB, which is attributed to the mixing of at least three mantle components: HIMU with a high proportion of radiogenic lead, produced by decay of uranium and other heavy radioactive elements; EM1 with less enrichment of radiogenic lead; and EM2 with a high 87Sr/86Sr ratio. Helium in OIB shows a wider variation in the 3He/4He ratio than MORB, with some values approaching the primordial value.
The composition of ocean island basalts is attributed to the presence of distinct mantle chemical reservoirs formed by subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, ...
of oceanic crust. These include reservoirs corresponding to HUIMU, EM1, and EM2. These reservoirs are thought to have different major element compositions, based on the correlation between major element compositions of OIB and their stable isotope ratios. Tholeiitic OIB is interpreted as a product of a higher degree of partial melting in particularly hot plumes, while alkali OIB is interpreted as a product of a lower degree of partial melting in smaller, cooler plumes.
Seismology
In 2015, based on data from 273 large earthquakes, researchers compiled a model based on full waveform tomography, requiring the equivalent of 3 million hours of supercomputer time. Due to computational limitations, high-frequency data still could not be used, and seismic data remained unavailable from much of the seafloor. Nonetheless, vertical plumes, 400 C hotter than the surrounding rock, were visualized under many hotspots, including thePitcairn
The Pitcairn Islands (; Pitkern: '), officially the Pitcairn, Henderson, Ducie and Oeno Islands, is a group of four volcanic islands in the southern Pacific Ocean that form the sole British Overseas Territory in the Pacific Ocean. The four i ...
, Macdonald, Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands ( Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands ( Manono and Apolima); ...
, Tahiti
Tahiti (; Tahitian ; ; previously also known as Otaheite) is the largest island of the Windward group of the Society Islands in French Polynesia. It is located in the central part of the Pacific Ocean and the nearest major landmass is Austra ...
, Marquesas
The Marquesas Islands (; french: Îles Marquises or ' or '; Marquesan: ' (North Marquesan) and ' (South Marquesan), both meaning "the land of men") are a group of volcanic islands in French Polynesia, an overseas collectivity of France in t ...
, Galapagos, Cape Verde
, national_anthem = ()
, official_languages = Portuguese
, national_languages = Cape Verdean Creole
, capital = Praia
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, demonym ...
, and Canary
Canary originally referred to the island of Gran Canaria on the west coast of Africa, and the group of surrounding islands (the Canary Islands). It may also refer to:
Animals Birds
* Canaries, birds in the genera '' Serinus'' and ''Crithagra'' ...
hotspots. They extended nearly vertically from the core-mantle boundary (2900 km depth) to a possible layer of shearing and bending at 1000 km. They were detectable because they were 600–800 km wide, more than three times the width expected from contemporary models. Many of these plumes are in the large low-shear-velocity provinces
Large low-shear-velocity provinces, LLSVPs, also called LLVPs or superplumes, are characteristic structures of parts of the lowermost mantle (the region surrounding the outer core) of Earth. These provinces are characterized by slow shear wave ve ...
under Africa and the Pacific, while some other hotspots such as Yellowstone were less clearly related to mantle features in the model.
The unexpected size of the plumes leaves open the possibility that they may conduct the bulk of the Earth's 44 terawatts of internal heat flow from the core to the surface, and means that the lower mantle convects less than expected, if at all. It is possible that there is a compositional difference between plumes and the surrounding mantle that slows them down and broadens them.
Suggested mantle plume locations
 Mantle plumes have been suggested as the source for
Mantle plumes have been suggested as the source for flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
s. These extremely rapid, large scale eruptions of basaltic magmas have periodically formed continental flood basalt provinces on land and oceanic plateaus in the ocean basins, such as the Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps is a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). It is one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. It consists of numerous layers of solidified flo ...
, the Siberian Traps
The Siberian Traps (russian: Сибирские траппы, Sibirskiye trappy) is a large region of volcanic rock, known as a large igneous province, in Siberia, Russia. The massive eruptive event that formed the traps is one of the largest ...
the Karoo-Ferrar
The Karoo and Ferrar Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs) are two large igneous provinces in Southern Africa and Antarctica respectively, collectively known as the Karoo-Ferrar, Gondwana,E.g. or Southeast African LIP, associated with the initial break- ...
flood basalts of Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
, and the largest known continental flood basalt, the Central Atlantic magmatic province
The Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the ...
(CAMP).
Many continental flood basalt events coincide with continental rifting. This is consistent with a system that tends toward equilibrium: as matter rises in a mantle plume, other material is drawn down into the mantle, causing rifting.
Alternative hypotheses
In parallel with the mantle plume model, two alternative explanations for the observed phenomena have been considered: the plate hypothesis and the impact hypothesis.The plate hypothesis
 Beginning in the early 2000s, dissatisfaction with the state of the evidence for mantle plumes and the proliferation of
Beginning in the early 2000s, dissatisfaction with the state of the evidence for mantle plumes and the proliferation of ad hoc hypotheses
In science and philosophy, an ''ad hoc'' hypothesis is a hypothesis added to a theory in order to save it from being falsified. Often, ''ad hoc'' hypothesizing is employed to compensate for anomalies not anticipated by the theory in its unmodifi ...
drove a number of geologists, led by Don L. Anderson, Gillian Foulger, and Warren B. Hamilton, to propose a broad alternative based on shallow processes in the upper mantle and above, with an emphasis on plate tectonics as the driving force of magmatism.
The plate hypothesis suggests that "anomalous" volcanism results from lithospheric extension that permits melt to rise passively from the asthenosphere beneath. It is thus the conceptual inverse of the plume hypothesis because the plate hypothesis attributes volcanism to shallow, near-surface processes associated with plate tectonics, rather than active processes arising at the core-mantle boundary.
Lithospheric extension is attributed to processes related to plate tectonics. These processes are well understood at mid-ocean ridges, where most of Earth's volcanism occurs. It is less commonly recognised that the plates themselves deform internally, and can permit volcanism in those regions where the deformation is extensional. Well-known examples are the Basin and Range Province in the western USA, the East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of ...
valley, and the Rhine Graben. Under this hypothesis, variable volumes of magma are attributed to variations in chemical composition (large volumes of volcanism corresponding to more easily molten mantle material) rather than to temperature differences.
While not denying the presence of deep mantle convection and upwelling in general, the plate hypothesis holds that these processes do not result in mantle plumes, in the sense of columnar vertical features that span most of the Earth's mantle, transport large amounts of heat, and contribute to surface volcanism.
Under the umbrella of the plate hypothesis, the following sub-processes, all of which can contribute to permitting surface volcanism, are recognised:
*Continental break-up;
*Fertility at mid-ocean ridges;
*Enhanced volcanism at plate boundary junctions;
*Small-scale sublithospheric convection;
*Oceanic intraplate extension;
*Slab tearing and break-off;
*Shallow mantle convection;
*Abrupt lateral changes in stress at structural discontinuities;
*Continental intraplate extension;
*Catastrophic lithospheric thinning;
*Sublithospheric melt ponding and draining.
The impact hypothesis
In addition to these processes,impact event
An impact event is a collision between astronomical objects causing measurable effects. Impact events have physical consequences and have been found to regularly occur in planetary systems, though the most frequent involve asteroids, comets or ...
s such as ones that created the Addams crater on Venus and the Sudbury Igneous Complex in Canada are known to have caused melting and volcanism. In the impact hypothesis, it is proposed that some regions of hotspot volcanism can be triggered by certain large-body oceanic impacts which are able to penetrate the thinner oceanic lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust and the portion of the upper mantle that behaves elastically on time scales of up to thousands of years or ...
, and flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reac ...
volcanism can be triggered by converging seismic energy focused at the antipodal point
In mathematics, antipodal points of a sphere are those diametrically opposite to each other (the specific qualities of such a definition are that a line drawn from the one to the other passes through the center of the sphere so forms a true d ...
opposite major impact sites. Impact-induced volcanism has not been adequately studied and comprises a separate causal category of terrestrial volcanism with implications for the study of hotspots and plate tectonics.
Comparison of the hypotheses
In 1997 it became possible using seismic tomography to image submerging tectonic slabs penetrating from the surface all the way to the core-mantle boundary. For theHawaii hotspot
The Hawaii hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the H ...
, long-period seismic body wave diffraction tomography provided evidence that a mantle plume is responsible, as had been proposed as early as 1971. For the Yellowstone hotspot
The Yellowstone hotspot is a volcanic hotspot in the United States responsible for large scale volcanism in Idaho, Montana, Nevada, Oregon, and Wyoming, formed as the North American tectonic plate moved over it. It formed the eastern Snake Riv ...
, seismological evidence began to converge from 2011 in support of the plume model, as concluded by James et al., "we favor a lower mantle plume as the origin for the Yellowstone hotspot." Data acquired through Earthscope
Earthscope was an National Science Foundation (NSF) funded earth science program that, from 2003-2018, used geological and geophysical techniques to explore the structure and evolution of the North American continent and to understand the process ...
, a program collecting high-resolution seismic data throughout the contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
has accelerated acceptance of a plume underlying Yellowstone.
Although there is thus strong evidence that at least these two deep mantle plumes rise from the core-mantle boundary, confirmation that other hypotheses can be dismissed may require similar tomographic evidence for other hotspots.
See also
* * * * *References
External links
* by Facts In Motion.Seismic-tomography image of Yellowstone mantle plume
– managed and maintained by
Gillian R. Foulger Gillian may refer to:
Places
* Gillian Settlement, Arkansas, an unincorporated community
People
Gillian (variant Jillian) is an English feminine given name, frequently shortened to Gill.
It originates as a feminine form of the name Julian, Julio ...
.
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mantle Plume
Geodynamics