Antigua on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
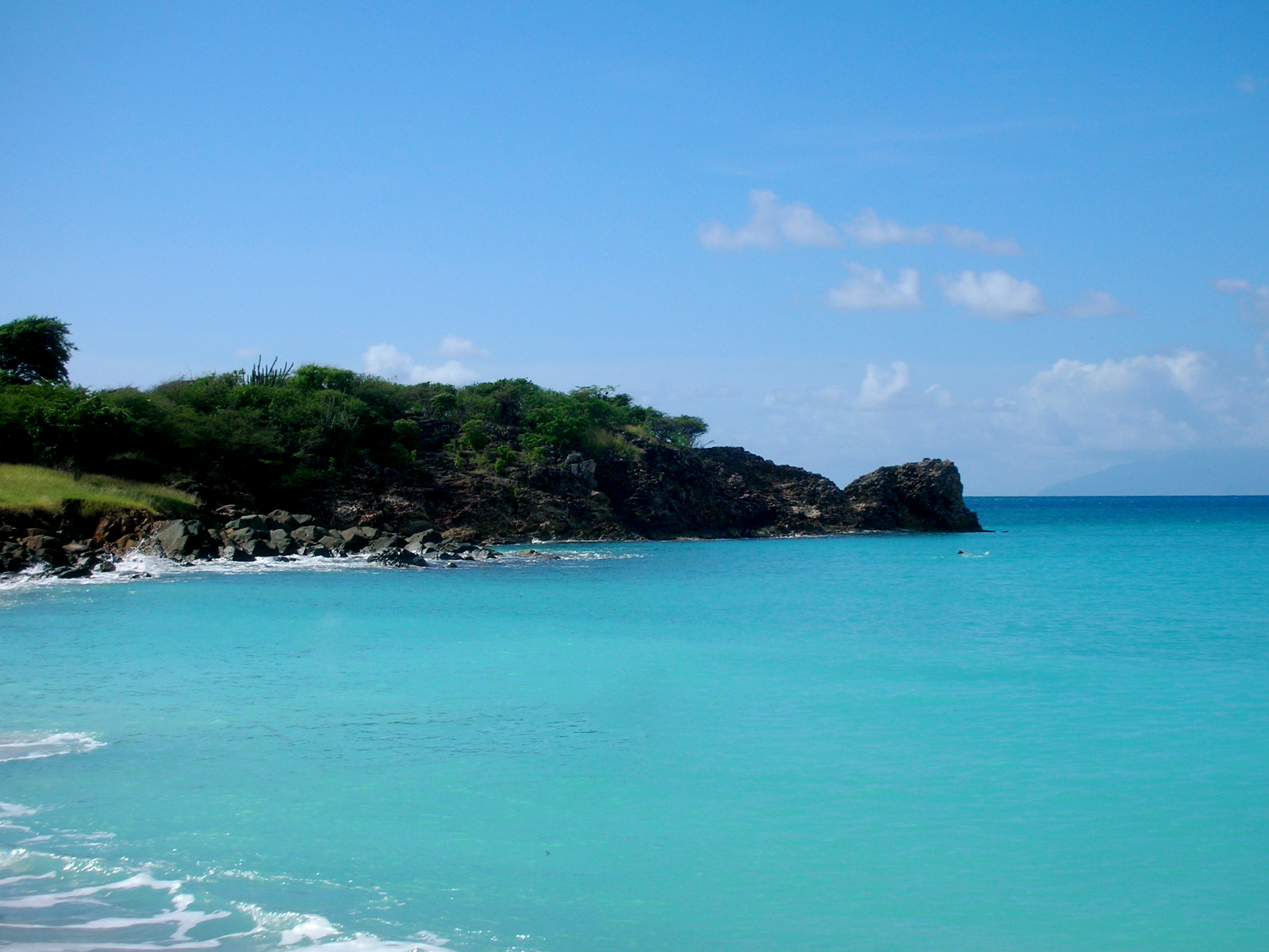 Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the
Antigua ( ), also known as Waladli or Wadadli by the native population, is an island in the
Judaism and Christian Art: Aesthetic Anxieties from the Catacombs to Colonialism
'' Accessed 23 September 2011. The name ''Waladli'' comes from the indigenous inhabitants and means approximately "our own". The island's perimeter is roughly and its area . Its


Arawaks
and
. Watson points out that the Caribs had a much more warlike culture than the Arawak. The indigenous people of the West Indies built excellent sea vessels, which they used to sail the Atlantic and Caribbean resulting in much of the South American and the Caribbean islands being populated by the Arawak and Carib. Their descendants live throughout South America, particularly Brazil, Venezuela and Colombia. According to ''A Brief History of the Caribbean'', infectious diseases introduced from Europe, high rates of malnutrition and enslavement led to a rapid population decline among the Caribbean's native population. There are some differences of opinions as to the relative importance of these causes.
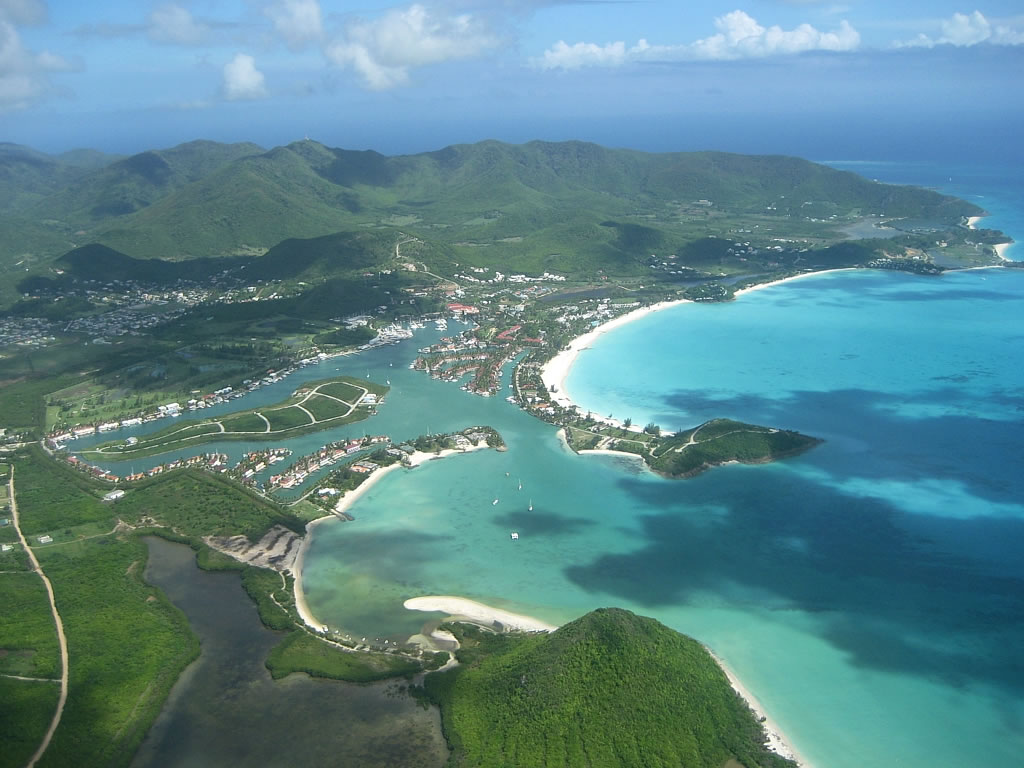


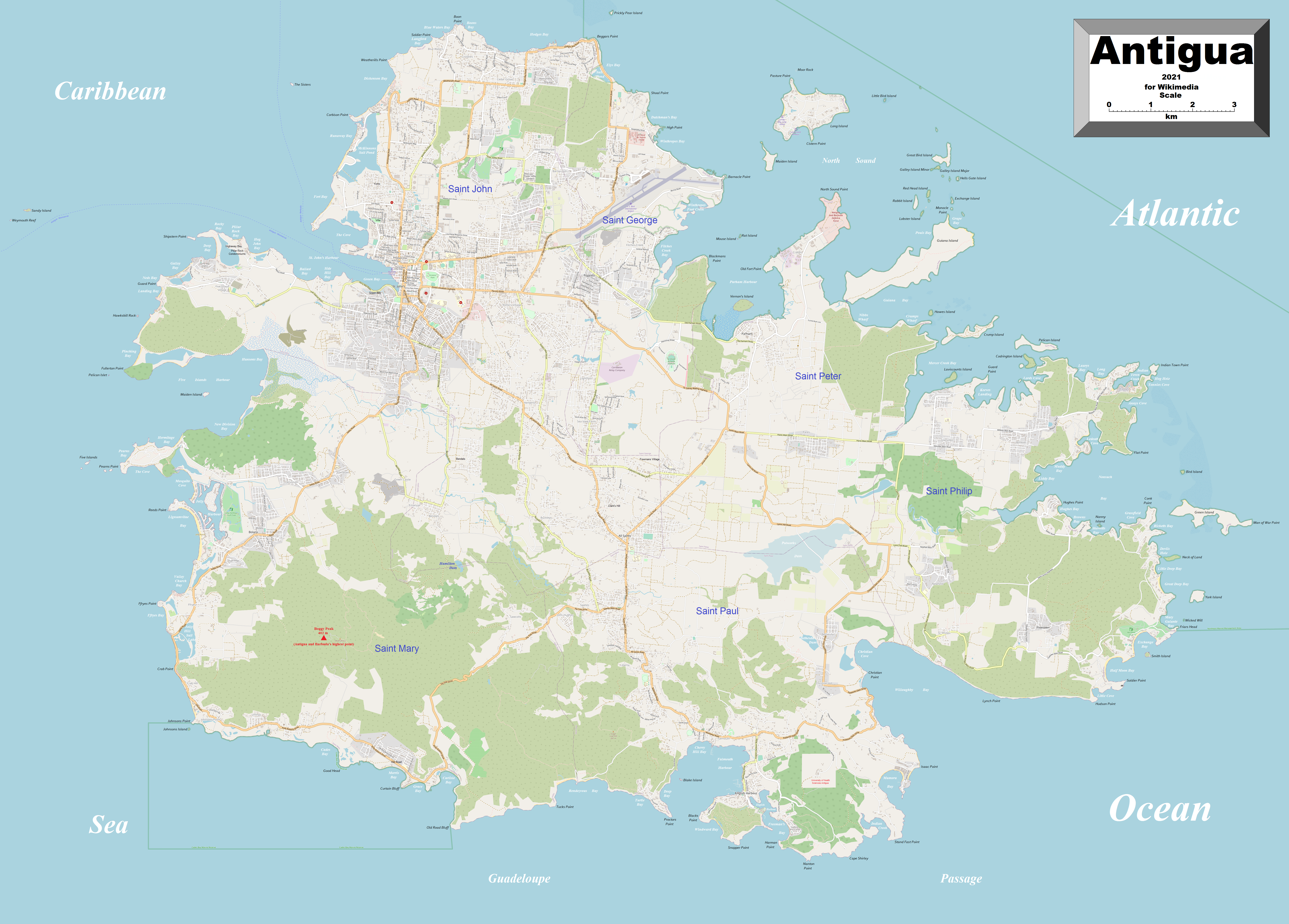 Located in the Leeward Islands Antigua has an area of with of coastline. The highest elevation on the island is .
Various natural points, capes, and beaches around the island include: Boon Point, Beggars Point, Parham, Willikies, Hudson Point, English Harbour Town, Old Road Cape, Johnson's Point, Ffryes Point, Jennings, Five Islands, and Yepton Beach, and Runaway Beach.
Several natural harbours are formed by these points and capes, including: Fitches Creek Bay, between Beggars Point and Parham; Nonsuch Bay between Hudson Point and Willikies; Willoughby Bay, between Hudson Point and English Harbour Town; English Harbour leading into English Harbour Town; Falmouth Harbour recessing into Falmouth; Rendezvous Bay between Falmouth and Old Road Cape; Five Islands Harbour, between Jennings and Five Islands; and Green Bay, the main harbour at St. John's, between Yepton Beach and Runaway Beach.
Located in the Leeward Islands Antigua has an area of with of coastline. The highest elevation on the island is .
Various natural points, capes, and beaches around the island include: Boon Point, Beggars Point, Parham, Willikies, Hudson Point, English Harbour Town, Old Road Cape, Johnson's Point, Ffryes Point, Jennings, Five Islands, and Yepton Beach, and Runaway Beach.
Several natural harbours are formed by these points and capes, including: Fitches Creek Bay, between Beggars Point and Parham; Nonsuch Bay between Hudson Point and Willikies; Willoughby Bay, between Hudson Point and English Harbour Town; English Harbour leading into English Harbour Town; Falmouth Harbour recessing into Falmouth; Rendezvous Bay between Falmouth and Old Road Cape; Five Islands Harbour, between Jennings and Five Islands; and Green Bay, the main harbour at St. John's, between Yepton Beach and Runaway Beach.
''
Antigua Nice
(The Antigua Nice article was extracted by D.V. Nicholson's writings for the Antigua Historic Sites and Conservation Commission.)
*''The Life of Horatio Lord Nelson'' by Robert Southeybr>Project Gutenberg free book
*The ''
Article on Antiguan real estate.
Government of Antigua and BarbudaBeaches Of AntiguaAntigua Barbuda Department of TourismAntigua Tourism Guide
*
Embassy of Antigua and Barbuda in Madrid
- His Excellenc
Dr. Dario Item
is the Head of Mission.
Honorary Consulate General of Antigua and Barbuda in the Principality of MonacoAntigua & Barbuda Official Business Hub
{{Authority control Islands of Antigua and Barbuda Former English colonies 1630s establishments in the Caribbean 1632 establishments in the British Empire 1632 establishments in North America
Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc be ...
. It is one of the Leeward Islands in the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
region and the main island of the country of Antigua and Barbuda. Antigua and Barbuda became an independent state within the Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the C ...
on 1 November 1981.
''Antigua'' means "ancient" in Spanish after an icon
An icon () is a religious work of art, most commonly a painting, in the cultures of the Eastern Orthodox, Oriental Orthodox, and Catholic churches. They are not simply artworks; "an icon is a sacred image used in religious devotion". The mos ...
in Seville Cathedral, "" — St. Mary of the Old Cathedral.Kessler, Herbert L. & Nirenberg, David. Judaism and Christian Art: Aesthetic Anxieties from the Catacombs to Colonialism
'' Accessed 23 September 2011. The name ''Waladli'' comes from the indigenous inhabitants and means approximately "our own". The island's perimeter is roughly and its area . Its
population
Population typically refers to the number of people in a single area, whether it be a city or town, region, country, continent, or the world. Governments typically quantify the size of the resident population within their jurisdiction usi ...
was 83,191 (at the 2011 Census). The economy is mainly reliant on tourism, with the agricultural sector serving the domestic market.
Over 22,000 people live in the capital city, St. John's. The capital is situated in the north-west and has a deep harbour which is able to accommodate large cruise ships. Other leading population settlements are All Saints (3,412) and Liberta (2,239), according to the 2001 census.
English Harbour on the south-eastern coast provides one of the largest deep water, protected harbors in the Eastern Caribbean. It is the site of a restored British colonial naval station named "Nelson's Dockyard
Nelson's Dockyard is a cultural heritage site and marina in English Harbour, located in Saint Paul Parish on the island of Antigua, in Antigua and Barbuda.
It is part of Nelson's Dockyard National Park, which also contains Clarence House and Shi ...
" after Vice-Admiral The 1st Viscount Nelson. English Harbour and the neighbouring village of Falmouth are yachting and sailing destinations and provisioning centres. During Antigua Sailing Week
Antigua Sailing Week is a week long yacht regatta held in the waters off English Harbour, St Pauls Antigua. It is one of Antigua's most notable events. Founded in 1967, it is cited as one of the top regattas in the world with 100 yachts, 1500 parti ...
, at the end of April and beginning of May, an annual regatta brings a number of sailing vessels and sailors to the island to take part in sporting events. Every December for the past 60 years, Antigua has been home to one of the largest charter yacht shows, welcoming super-yachts from around the world.
On 6 September 2017, the Category 5 Hurricane Irma destroyed 90 percent of the buildings on the island of Barbuda and the entire population was evacuated to Antigua.
History


Early Antiguans
The first inhabitants were the Guanahatabey people. Eventually, theArawak
The Arawak are a group of indigenous peoples of northern South America and of the Caribbean. Specifically, the term "Arawak" has been applied at various times to the Lokono of South America and the Taíno, who historically lived in the Greate ...
migrated from the mainland, followed by the Carib. Prior to European colonization, Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
was the first European to visit Antigua, in 1493.
The Arawak were the first well-documented group of indigenous people to settle Antigua. They paddled to the island by canoe (''piragua'') from present-day Venezuela
Venezuela (; ), officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela ( es, link=no, República Bolivariana de Venezuela), is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in th ...
, pushed out by the Carib, another indigenous people. The Arawak introduced agriculture to Antigua and Barbuda. Among other crops, they cultivated the Antiguan "black" pineapple. They also grew corn, sweet potatoes (white with firmer flesh than the bright orange "sweet potato" grown in the United States), chili pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for ...
s, guava, tobacco, and cotton.
Some of the vegetables listed, such as corn and sweet potatoes, continue to be staples of Antiguan cuisine. Colonists took them to Europe, and from there, they spread around the world. For example, a popular Antiguan dish, ''dukuna'' (), is a sweet, steamed dumpling made from grated sweet potatoes, flour and spices. Another staple, ''fungi'' (), is a cooked paste made of cornmeal and water.
Most of the Arawak left Antigua about A.D. 1100. Those who remained were raided by the Carib coming from Venezuela. According to ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'', the Caribs' superior weapons and seafaring prowess allowed them to defeat most Arawak nations in the West Indies. They enslaved some and cannibalised others. See also ''The Catholic Encyclopedia'' entries forArawaks
and
. Watson points out that the Caribs had a much more warlike culture than the Arawak. The indigenous people of the West Indies built excellent sea vessels, which they used to sail the Atlantic and Caribbean resulting in much of the South American and the Caribbean islands being populated by the Arawak and Carib. Their descendants live throughout South America, particularly Brazil, Venezuela and Colombia. According to ''A Brief History of the Caribbean'', infectious diseases introduced from Europe, high rates of malnutrition and enslavement led to a rapid population decline among the Caribbean's native population. There are some differences of opinions as to the relative importance of these causes.
British

Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
named the island "Antigua" in 1493 in honour of the "Virgin of the Old Cathedral" ( es, La Virgen de la Antigua) found in Seville Cathedral in southern Spain. On his 1493 voyage, honouring a vow, he named many islands after different aspects of St. Mary
Mary; arc, ܡܪܝܡ, translit=Mariam; ar, مريم, translit=Maryam; grc, Μαρία, translit=María; la, Maria; cop, Ⲙⲁⲣⲓⲁ, translit=Maria was a first-century Jewish woman of Nazareth, the wife of Joseph and the mother of ...
, including Montserrat and Guadeloupe.
In 1632, a group of English colonists left St Kitts to settle on Antigua. Christopher Codrington, an Englishman, established the first permanent English settlement on the island. Antigua rapidly developed as a profitable sugar colony. For a large portion of Antigua's history, the island was considered Britain's "Gateway to the Caribbean". It was on the major sailing routes among the region's resource-rich colonies. Lord Horatio Nelson, a major figure in Antigua's history, arrived in the late 18th century to defend the island's commercial shipping prowess.
Slavery
Sugar became Antigua's main crop in about 1674, when Christopher Codrington (c. 1640–1698) settled at Betty's Hope plantation. He came from Barbados, bringing the latest sugar technology with him. Betty's Hope, Antigua's first full-scale sugar plantation, was so successful that other planters turned from tobacco to sugar. This resulted in their importing slaves to work the sugar cane crops. According to ''A Brief History of the Caribbean'', many West Indian colonists initially tried to use locals as slaves. These groups succumbed easily to disease and/or malnutrition, and died by the thousands. The enslaved Africans adapted better to the new environment and thus became the number-one choice of unpaid labour; they also provided medical services and skilled labour, including carpentry, for their masters. However, the West African slave population in the Caribbean also had a high mortality rate, which was offset by regular imports of very high numbers of new slaves from West and Central Africa. Sugar cane was one of the most gruelling and dangerous crops slaves were forced to cultivate. Harvesting cane required backbreaking long days in sugar cane fields under the hot island sun. Sugar cane spoiled quickly after harvest, and the milling process was slow and inefficient, forcing the mill and boiling house to operate 24 hours a day during harvest season. Sugar mills and boiling houses were two of the most dangerous places for slaves to work on sugar plantations. In mills wooden or metal rollers were used to crush cane plants and extract the juices. Slaves were at risk of getting their limbs stuck and ripped off in the machines. Similarly, in sugar boiling houses slaves worked under extremely high temperatures and at the risk of being burned in the boiling sugar mixture or getting their limbs stuck. Today, collectors prize the uniquely designed colonial furniture built by West Indian slaves. Many of these works feature what are now considered "traditional" motifs, such as pineapples, fish and stylized serpents. By the mid-1770s, the number of slaves had increased to 37,500, up from 12,500 in 1713. The white population, in contrast, had fallen from 5,000 to below 3,000. The slaves lived in wretched and overcrowded conditions and could be mistreated or even killed by their owners with impunity. The Slave Act of 1723 made arbitrary murder of slaves a crime, but did not do much to ease their lives. Unrest against enslavement among the island's enslaved population became increasingly common. In 1729, a man named Hercules washung, drawn and quartered
To be hanged, drawn and quartered became a statutory penalty for men convicted of high treason in the Kingdom of England from 1352 under King Edward III (1327–1377), although similar rituals are recorded during the reign of King Henry III ( ...
and three others were burnt alive, for conspiring to kill the slave owner Nathaniel Crump and his family. In 1736, an enslaved man called "Prince Klaas" (whose slave name was Court) allegedly planned to incite a slave rebellion on the island. Court was crowned "King of the Coromantees" in a pasture outside the capital of St. John's. The coronation appeared to be just a colourful spectacle but was, for the enslaved people, a ritual declaration of war on the colonists. From information obtained from other slaves, the colonists discovered the plot and implemented a brutal crackdown on suspected rebels. Prince Klaas and four accomplices were caught and executed on the breaking wheel
The breaking wheel or execution wheel, also known as the Wheel of Catherine or simply the Wheel, was a torture method used for public execution primarily in Europe from antiquity through the Middle Ages into the early modern period by breakin ...
. (However, some doubts exist about Court's guilt.) Six of the rebels were hanged in chains and starved to death, and another 58 were burnt at the stake
Death by burning (also known as immolation) is an execution and murder method involving combustion or exposure to extreme heat. It has a long history as a form of public capital punishment, and many societies have employed it as a punishment f ...
. The site of these executions is now the Antiguan Recreation Ground.
The American War of Independence
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
in the late 18th century disrupted the Caribbean sugar trade. At the same time, public opinion in Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
gradually turned against slavery. "Traveling ... at slavery's end, osephSturge and homasHarvey (1838 ...) found few married slaves residing together or even on the same estate. Slaveholders often counted as 'married' only those slaves with mates on the estate." Great Britain abolished the slave trade in 1807, and all existing slaves were emancipated
Emancipation generally means to free a person from a previous restraint or legal disability. More broadly, it is also used for efforts to procure economic and social rights, political rights or equality, often for a specifically disenfranchi ...
in 1834.
Horatio, Lord Nelson
Horatio Nelson (who was created 1st Viscount Nelson in 1801) was Senior Naval Officer of the Leeward Islands from 1784 to 1787 on . During his tenure, he tried to enforce the Navigation Acts. These acts prohibited trade with the newly formed United States of America. Most of the merchants in Antigua depended upon trading with the USA, so many of them despised Captain Nelson. As a result, he was unable to get a promotion for some time after his stint on the island. Unlike the Antiguan merchants, Nelson had a positive view of the controversial Navigation Acts:The Americans were at this time trading with our islands, taking advantage of the register of their ships, which had been issued while they were British subjects. Nelson knew that, by the Navigation Act, no foreigners, directly or indirectly, are permitted to carry on any trade with these possessions. He knew, also, that the Americans had made themselves foreigners with regard to England; they had disregarded the ties of blood and language when they acquired the independence which they had been led on to claim, unhappily for themselves, before they were fit for it; and he was resolved that they should derive no profit from those ties now. Foreigners they had made themselves, and as foreigners they were to be treated.Nelson said: "The Antiguan Colonists are as great rebels as ever were in America, had they the power to show it." A dockyard started in 1725, to provide a base for a squadron of British ships whose main function was to patrol the West Indies and thus maintain Britain's sea power, was later named "Nelson's Dockyard" in his honour. While Nelson was stationed on Antigua, he frequently visited the nearby island of Nevis, where he met and married a young widow, Fanny Nisbet, who had previously married the son of a plantation family on Nevis.
1918 labour unrest
Following the foundation of the Ulotrichian Universal Union, a friendly society which acted as a trade union (which were banned), the sugar cane workers were ready to confront the plantation owners when they slashed their wages. The cane workers went on strike and rioted when their leaders were arrested.Independence
In 1968, with Barbuda and the tiny island of Redonda as dependencies, Antigua became an associated state of the Commonwealth, and in November 1981 it was disassociated from Britain.U.S. government presence
Commissioned, 9 August 1956, the Naval Facility (NAVFAC) Antigua was one of the shore terminal stations that were part of theSound Surveillance System
The Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) was a submarine detection system based on passive sonar developed by the United States Navy to track Soviet Navy, Soviet submarines. The system's true nature was classified with the name and acronym SOSUS them ...
(SOSUS) and the Integrated Undersea Surveillance System (IUSS), which were used to track Soviet submarines. NAVFAC Antigua was decommissioned 4 February 1984.
From 1958 through 1960 the United States installed the Missile Impact Location System The Missile Impact Location System or Missile Impact Locating System (MILS)Both full names are found in references. is an ocean acoustic system designed to locate the impact position of test missile nose cones at the ocean's surface and then the pos ...
(MILS) in the Atlantic Missile Range, later the Eastern Range, to localize the splashdowns of test missile nose cones. MILS was developed and installed by the same entities that had completed the first phase of the Atlantic SOSUS system. A MILS installation consisting of both a target array for precision location and a broad ocean area system for good positions outside the target area was installed at Antigua, downrange. The island was the second downrange MILS installation with the furthest being downrange at Ascension Island
Ascension Island is an isolated volcanic island, 7°56′ south of the Equator in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is about from the coast of Africa and from the coast of South America. It is governed as part of the British Overseas Territory of ...
.
Until July 7, 2015, the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
maintained a small base near the airport, designated Detachment 1, 45th Operations Group, 45th Space Wing (known as Antigua Air Station). The mission provided high rate telemetry data for the Eastern Range and its space launches. The unit was deactivated due to US government budget cuts and the property given to the Antiguan Government.
Demographics
Census Data
These figures do not include the island of Barbuda. Source:
Geography
 Located in the Leeward Islands Antigua has an area of with of coastline. The highest elevation on the island is .
Various natural points, capes, and beaches around the island include: Boon Point, Beggars Point, Parham, Willikies, Hudson Point, English Harbour Town, Old Road Cape, Johnson's Point, Ffryes Point, Jennings, Five Islands, and Yepton Beach, and Runaway Beach.
Several natural harbours are formed by these points and capes, including: Fitches Creek Bay, between Beggars Point and Parham; Nonsuch Bay between Hudson Point and Willikies; Willoughby Bay, between Hudson Point and English Harbour Town; English Harbour leading into English Harbour Town; Falmouth Harbour recessing into Falmouth; Rendezvous Bay between Falmouth and Old Road Cape; Five Islands Harbour, between Jennings and Five Islands; and Green Bay, the main harbour at St. John's, between Yepton Beach and Runaway Beach.
Located in the Leeward Islands Antigua has an area of with of coastline. The highest elevation on the island is .
Various natural points, capes, and beaches around the island include: Boon Point, Beggars Point, Parham, Willikies, Hudson Point, English Harbour Town, Old Road Cape, Johnson's Point, Ffryes Point, Jennings, Five Islands, and Yepton Beach, and Runaway Beach.
Several natural harbours are formed by these points and capes, including: Fitches Creek Bay, between Beggars Point and Parham; Nonsuch Bay between Hudson Point and Willikies; Willoughby Bay, between Hudson Point and English Harbour Town; English Harbour leading into English Harbour Town; Falmouth Harbour recessing into Falmouth; Rendezvous Bay between Falmouth and Old Road Cape; Five Islands Harbour, between Jennings and Five Islands; and Green Bay, the main harbour at St. John's, between Yepton Beach and Runaway Beach.
Fauna
The Antiguan racer is among the rarest snakes in the world. The Lesser Antilles are home to four species of racers. All four have undergone severe range reductions; at least two subspecies are extinct and another, ''A. antiguae'', now occupies only 0.1 percent of its historical range. Griswold's ameiva (''Ameiva griswoldi'') is a species of lizard in the genus Ameiva. It is endemic to Antigua and Barbuda. It is found on both islands.Administrative divisions
The island is divided into six civilparish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one or ...
es: St. George, Saint Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupat ...
, Saint Philip, Saint Paul, Saint Mary, and Saint John. The parishes have no type of local government.
Economy
The country's official currency is theEast Caribbean dollar
The Eastern Caribbean dollar ( symbol: EC$; code: XCD) is the currency of all seven full members and one associate member of the Organisation of Eastern Caribbean States (OECS). The successor to the British West Indies dollar, it has existed si ...
. Given the dominance of tourism, many prices in tourist-oriented businesses are shown in US dollars. The EC dollar is pegged to the US dollar at a varied rate and averages about US$1 = EC$2.7.
Tourism
Antigua's economy relies largely on tourism, and the island is promoted as a luxury Caribbean escape. Many hotels and resorts are located around the coastline. The island's single airport, VC Bird Airport, is served by several major airlines, including Virgin Atlantic,British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London, England, near its main hub at Heathrow Airport.
The airline is the second largest UK-based carrier, based on fleet size and passengers ...
, American Airlines
American Airlines is a major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the largest airline in the world when measured by fleet size, scheduled passengers carried, and revenue passeng ...
, United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
, Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia. The airline, along ...
, Caribbean Airlines, Air Canada, WestJet, and JetBlue. There is regular air service to Barbuda.
Education
Antigua has two international primary/secondary schools: CCSET International, which offers the Ontario Secondary School Diploma, and Island Academy, which offers the International Baccalaureate. There are also many other private schools but these institutions tend to follow the same local curriculum (CXCs) as government schools. The island of Antigua currently has two foreign-owned for-profitoffshore medical school An offshore medical school is a medical school that caters "primarily to foreign (American and Canadian citizens) students, wishing to practice medicine in the US and Canada" according to the World Bank, compared to local schools that focus on the ...
s, the American University of Antigua
American University of Antigua (AUA) is a private, international medical school located in Antigua and Barbuda.
History
AUA was co-founded by Neal S. Simon, a lawyer and former president of Ross University. AUA began instruction in 2002. I ...
(AUA), founded in 2004, and The University of Health Sciences Antigua (UHSA), founded in 1982. The island's medical schools cater mostly to foreign students but contribute to the local economy and health care.
Online gambling
Antigua was one of the first nations to legalize, license, and regulate online gambling and is a primary location for incorporation of online gambling companies. Some countries, most notably the United States, argue that if a particular gambling transaction is initiated outside the country of Antigua and Barbuda, then that transaction is governed by the laws of the country where the transaction was initiated. This argument was brought before the WTO and was deemed incorrect. In 2006, the United States Congress voted to approve the Unlawful Internet Gambling Enforcement Act which criminalized the operations of offshore gambling operators which take wagers from American-based gamblers. This was a ''prima facie'' violation of the GATS treaty obligations enforced by the WTO, resulting in a series of rulings unfavourable to the US. On 21 December 2007, an Article 22 arbitration panel ruled that the United States' failure to comply with WTO rules would attract a US$21 million sanction. The WTO ruling was notable in two respects: First, although technically a victory for Antigua, the $21 million was far less than the US$3.5 billion which had been sought; one of the three arbitrators was sufficiently bothered by the propriety of this that he issued a dissenting opinion. Second, a rider to the arbitration ruling affirmed the right of Antigua to take retaliatory steps in view of the prior failure of the US to comply with GATS. These included the rare, but not unprecedented, right to disregard intellectual property obligations to the US. Antigua's obligations to the US in respect of patents, copyright, and trademarks are affected. In particular, Berne Convention copyright is in question, and also material not covered by the Berne convention, including TRIPS accord obligations to the US. Antigua may thus disregard the WIPO treaty on intellectual property rights, and therefore the US implementation of that treaty (the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, or DMCA)—at least up to the limit of compensation. Since there is no appeal to the WTO from an Arbitration panel of this kind, it represents the last legal word from the WTO on the matter. Antigua is therefore able to recoup some of the claimed loss of trade by hosting (and taxing) companies whose business model depends on immunity from TRIPS provisions. Software company SlySoft was based in Antigua, allowing it to avoid nations with laws that are tough on anti-circumvention of technological copyright measures, in particular the DMCA in the United States.Banking
Swiss American Bank Ltd., later renamed Global Bank of Commerce, Ltd, was formed in April 1983 and became the first offshore international financial institution governed by the International Business Corporations, Act of 1982 to become a licensed bank in Antigua. The bank was later sued by the United States for failure to release forfeited funds from one of its account holders. Swiss American Bank was founded by Bruce Rappaport. Stanford International Bank was formed by Allen Stanford in 1986 in Montserrat where it was called Guardian International Bank. On 17 February 2009, the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission charged Allen Stanford,Laura Pendergest-Holt
Laura Pendergest-Holt (born July 23, 1973) is a convicted Ponzi scheme perpetrator, financier, and former chief investment officer of Stanford Financial Group, who was charged with a civil charge of fraud on February 17, 2009. On May 12, 2009, Pen ...
and James Davis with fraud in connection with the bank's US$8 billion certificate of deposit (CD) investment scheme that offered "improbable and unsubstantiated high interest rates". This led the federal government to freeze the assets of the bank and other Stanford entities. On 27 February 2009, Pendergest-Holt was arrested by federal agents in connection with the alleged fraud. On that day, the SEC said that Stanford and his accomplices operated a "massive Ponzi scheme", misappropriated billions of investors' money and falsified the Stanford International Bank's records to hide their fraud. "Stanford International Bank's financial statements, including its investment income, are fictional," the SEC said."New SEC Complaint Says Stanford Ran Ponzi Scheme"''
The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published ...
'', 27 February 2009.
Antigua Overseas Bank (AOB) was part of the ABI Financial Group and was a licensed bank in Antigua. On 13 April 2012, AOB was placed into receivership by the government of Antigua.
On 27 November 2018, Scotiabank, the leading commercial bank on the island, announced plans to sell its banking operations in Antigua and 9 other non-core Caribbean markets to Republic Financial Holdings Limited.
Sport
The major Antiguan sport iscricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by st ...
. Vivian ("Viv") Richards is one of the most famous Antiguans, who played for, and captained, the West Indies cricket team. Richards scored the fastest Test century at the Antigua Recreation Ground, it was also the venue at which Brian Lara twice broke the world record for an individual Test innings (375 in 1993/94, 400 not out in 2003/04). Antigua was the location of a 2007 Cricket World Cup site, on a new Recreation Ground constructed on an old cane field in the north of the island. Both football (soccer) and basketball are becoming popular among the island youth. There are several golf courses in Antigua. Daniel Bailey was the first athlete to win a global world medal at the 2010 IAAF World Indoor Championships.
Being surrounded by water, sailing is one of the most popular sports with Antigua Sailing Week and Antigua Classic Yacht Regatta being two of the region's most reputable sailing competitions. Hundreds of yachts from around the world compete around Antigua each year. Sport fishing is also a very popular sport with several big competitions held yearly. Windsurfing was very popular until kite-surfing came to the island. Kitesurfing or kite-boarding is very popular at Jabbawock Beach.
Notable residents
*Curtly Ambrose
Sir Curtly Elconn Lynwall Ambrose KCN (born 21 September 1963) is an Antiguan former cricketer who played 98 Test matches for the West Indies. Widely acknowledged as one of the greatest fast bowlers of all time, he took 405 Test wickets ...
, legendary West-Indian cricketer
* Giorgio Armani, Italian fashion designer; owns a home near Deep Bay
* Calvin Ayre, billionaire founder of internet gambling company Bodog Entertainment Group
*Silvio Berlusconi
Silvio Berlusconi ( ; ; born 29 September 1936) is an Italian media tycoon and politician who served as Prime Minister of Italy in four governments from 1994 to 1995, 2001 to 2006 and 2008 to 2011. He was a member of the Chamber of Deputies f ...
, former Italian Prime Minister
* Richard Branson, Virgin Atlantic mogul
*Mehul Choksi
Mehul Chinubhai Choksi (born 5 May 1959) is a fugitive Indian-born businessman living in Antigua and Barbuda, who is wanted by the Indian judicial authorities for criminal conspiracy, criminal breach of trust, cheating and dishonesty including ...
, an Indian alleged scamster, diamond merchant and owner of Gitanjali Jewelers
* Eric Clapton, established an Antiguan drug treatment centre; has a home on the south of the island
* Melvin Claxton, Pulitzer Prize-winning journalist
* Timothy Dalton, actor of James Bond fame
*Heather Doram
Heather Doram is an Antiguan artist, actor, activist and educator, who is the designer of Antigua & Barbuda's national costume. In 2002 she was awarded the Grand Cross of the Most Illustrious Order of Merit (Antigua) in recognition of her lifet ...
, artist, activist and educator, who designed the Antiguan and Barbudan national costume.
*Ken Follett
Kenneth Martin Follett, (born 5 June 1949) is a British author of thrillers and historical novels who has sold more than 160 million copies of his works.
Many of his books have achieved high ranking on best seller lists. For example, in the ...
, the author of '' Eye of the Needle'', owns a house on Jumby Bay
Long Island also known as Jumby Bay is an island off the northeast coast of Antigua. It is located off the northern tip of the Parham Peninsula, about from ''Dutchman Bay'' on Antigua. It is the fifth largest island of Antigua and Barbuda.
Fl ...
*Marie-Elena John
Marie-Elena John is a Caribbean writer whose novel, '' Unburnable'', was published in 2006. She is an Africanist, development and women’s rights specialist, currently serving as the Senior Racial Justice Lead at UN Women.
Biography
John was bor ...
, Antiguan writer and former African Development Foundation
The United States African Development Foundation (USADF) is an independent United States government agency that provides grants of up to $250,000 for operational assistance, enterprise expansion and market linkage to early stage agriculture, e ...
specialist. Her debut novel, '' Unburnable'', was selected Best Debut of 2006 by ''Black Issues Book Review
''Black Issues Book Review'' was a bimonthly magazine published in New York City, U.S., in which books of interest to African-American readers were reviewed. It was published from 1999 until 2007.
History and profile
''Black Issues Book Review'' ...
''
*S. D. Jones
Conrad Efraim (March 30, 1945 – October 26, 2008) was an Antiguan professional wrestler best known by his ring name, Special Delivery Jones or S. D. Jones (sometimes referred to as S. D. "Special Delivery" Jones) from his time (1974–1990) in ...
, professional wrestler known as "Special Delivery Jones" in the WWE in the 1970s and 1980s
*Phil Keoghan
Philip John Keoghan ( ; born 31 May 1967) is a New Zealand television personality, best known for hosting the American version of ''The Amazing Race'' on CBS, since its 2001 debut. He is the creator and host of '' No Opportunity Wasted'', whi ...
, host of ''The Amazing Race
''The Amazing Race'' is an adventure reality game show franchise in which teams of two people race around the world in competition with other teams. The ''Race'' is split into legs, with teams tasked to deduce clues, navigate themselves in fore ...
'', lived here during part of his childhood
* Jamaica Kincaid, novelist famous for her writings about life on Antigua. Her 1988 book ''A Small Place
''A Small Place'' is a work of creative nonfiction published in 1988 by Jamaica Kincaid. A book-length essay drawing on Kincaid's experiences growing up in Antigua, it can be read as an indictment of the Antiguan government, the tourist industry ...
'' was banned under the Vere Bird administration
* Robin Leach of Lifestyles of the Rich and Famous
''Lifestyles of the Rich and Famous'' is an American television series that aired in syndication from 1984 to 1995. The show featured the extravagant lifestyles of wealthy entertainers, athletes, socialites and magnates.
It was hosted by Rob ...
fame.
* Archibald MacLeish, poet and (U.S.) Librarian of Congress.
* Rachel Lambert Mellon, horticulturist and philanthropist, has owned a compound in Antigua's Half Moon Bay since the 1950s.
*Fred Olsen
Fredrich Olsen (1891–1986) was a British-born American chemist remembered as the inventor of ball propellant and as a donor or seller to the art antiquities collections of Yale University, the University of Illinois, and the Massachusetts Inst ...
(1891–1986), inventor of the ball propellant manufacturing process
* Mary Prince, abolitionist and autobiographer, who wrote ''The History of Mary Prince'' (1831), the first account of the life of a Black woman to be published in the United Kingdom.
* Viv Richards, West Indian cricket legend; the Sir Vivian Richards Stadium in Antigua was named in his honour
* Richie Richardson, former West-Indies cricket team captain
* Andy Roberts, the first Antiguan to play Test cricket for the West Indies. He was a member of the West Indies teams that won the 1975 and 1979 World Cups.
* Andriy Mykolayovych Shevchenko, former Ukrainian footballer and politician.
* Peter Stringfellow, British nightclub owner
* Thomas J. Watson Jr., CEO of IBM
* Oprah Winfrey, talk-show host
See also
* Barbuda Land Acts * Bibliography of Antigua and Barbuda * Chief Justices * Geology of Antigua and Barbuda *Guns for Antigua
The Guns for Antigua scandal was a political scandal involving the shipment of Israeli-made weapons through Antigua to the Medellin drug cartel in Colombia. The affair was exposed by the Louis Blom-Cooper Royal Commission, following the discover ...
*Index of Antigua and Barbuda-related articles
Index (or its plural form indices) may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Fictional entities
* Index (''A Certain Magical Index''), a character in the light novel series ''A Certain Magical Index''
* The Index, an item on a Halo megastru ...
* List of Antiguans and Barbudans
* Outline of Antigua and Barbuda
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
Antigua Nice
(The Antigua Nice article was extracted by D.V. Nicholson's writings for the Antigua Historic Sites and Conservation Commission.)
*''The Life of Horatio Lord Nelson'' by Robert Southeybr>Project Gutenberg free book
*The ''
Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
''
*''Veranda Magazine'', Island Flourish: West Indian Furnishings by Dana Micucci, March – April 2004
*''A Brief History of the Caribbean from the Arawak and the Carib to the Present'', by Jan Rogozinski, Penguin Putnam, Inc September 2000Article on Antiguan real estate.
Further reading
*External links
Government of Antigua and Barbuda
*
Embassy of Antigua and Barbuda in Madrid
- His Excellenc
Dr. Dario Item
is the Head of Mission.
Honorary Consulate General of Antigua and Barbuda in the Principality of Monaco
{{Authority control Islands of Antigua and Barbuda Former English colonies 1630s establishments in the Caribbean 1632 establishments in the British Empire 1632 establishments in North America