anticyclonic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
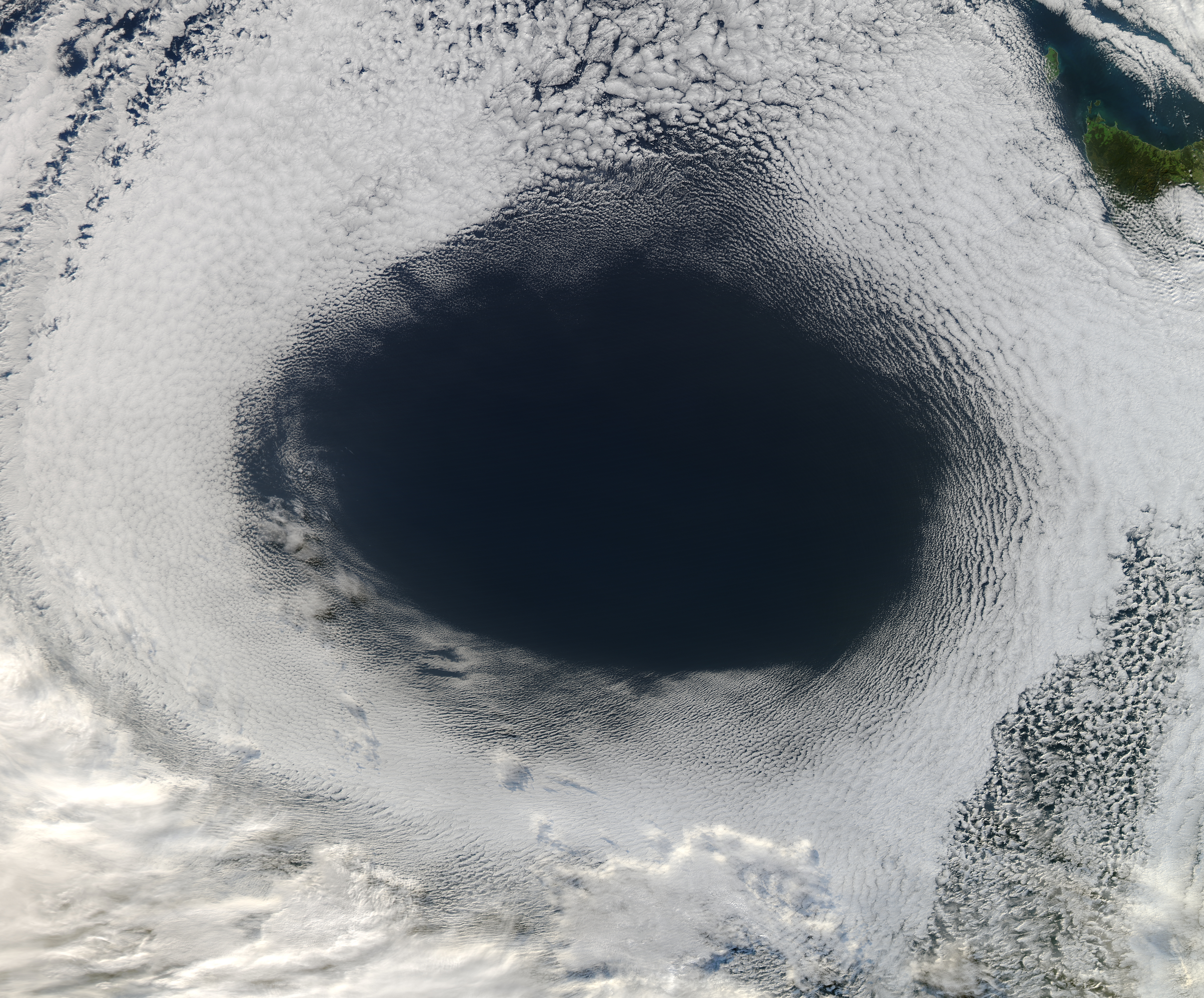
 An anticyclone is a
An anticyclone is a
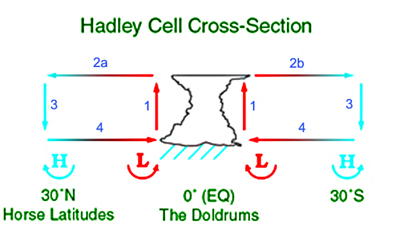
 Heating of the earth near the equator forces upward motion and convection along the
Heating of the earth near the equator forces upward motion and convection along the
 High-pressure systems are frequently associated with light winds at the surface and
High-pressure systems are frequently associated with light winds at the surface and
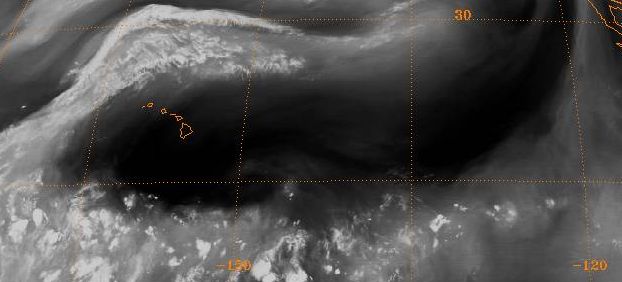
 The circulation around mid-level (altitude) ridges, and the air subsidence at their center, act to steer tropical cyclones around and out their periphery. Due to the subsidence within this type of system, a ''
The circulation around mid-level (altitude) ridges, and the air subsidence at their center, act to steer tropical cyclones around and out their periphery. Due to the subsidence within this type of system, a ''
Subject: A15) How do tropical cyclones form?
 On weather maps, high-pressure centers are associated with the letter H in English, within the isobar with the highest pressure value. On constant-pressure upper-level charts, anticyclones are located within the highest height line contour.Glossary of Meteorology (2009)
On weather maps, high-pressure centers are associated with the letter H in English, within the isobar with the highest pressure value. On constant-pressure upper-level charts, anticyclones are located within the highest height line contour.Glossary of Meteorology (2009)
High
.
Intertropical Convergence Zone photo
- NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Tropical cyclone meteorology

 An anticyclone is a
An anticyclone is a weather
Weather is the state of the atmosphere, describing for example the degree to which it is hot or cold, wet or dry, calm or stormy, clear or cloudy. On Earth, most weather phenomena occur in the lowest layer of the planet's atmosphere, the ...
phenomenon
A phenomenon ( : phenomena) is an observable event. The term came into its modern philosophical usage through Immanuel Kant, who contrasted it with the noumenon, which ''cannot'' be directly observed. Kant was heavily influenced by Gottfrie ...
defined as a large-scale circulation of wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
s around a central region of high atmospheric pressure, clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
and counterclockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to a cyclone
In meteorology, a cyclone () is a large air mass that rotates around a strong center of low atmospheric pressure, counterclockwise in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere as viewed from above (opposite to an an ...
). Effects of surface-based anticyclones include clearing skies as well as cooler, drier air. Fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
can also form overnight within a region of higher pressure.
Mid-tropospheric systems, such as the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a high-press ...
, deflect tropical cyclones around their periphery and cause a temperature inversion
In meteorology, an inversion is a deviation from the normal change of an atmospheric property with altitude. It almost always refers to an inversion of the air temperature lapse rate, in which case it is called a temperature inversion. Nor ...
inhibiting free convection near their center, building up surface-based haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon in which dust, smoke, and other dry particulates suspended in air obscure visibility and the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classificati ...
under their base. Anticyclones aloft can form within warm-core lows such as tropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
s, due to descending cool air from the backside of upper troughs such as polar highs, or from large-scale sinking such as a subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a high-press ...
.
The evolution of an anticyclone depends upon variables such as its size, intensity, and extent of moist convection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the c ...
, as well as the Coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
.
History
Sir Francis Galton
Sir Francis Galton, FRS FRAI (; 16 February 1822 – 17 January 1911), was an English Victorian era polymath: a statistician, sociologist, psychologist, anthropologist, tropical explorer, geographer, inventor, meteorologist, prot ...
first discovered anticyclones in the 1860s. Preferred areas within a synoptic flow pattern in higher levels of the dips in the Rossby wave
Rossby waves, also known as planetary waves, are a type of inertial wave naturally occurring in rotating fluids. They were first identified by Sweden-born American meteorologist Carl-Gustaf Arvid Rossby. They are observed in the atmospheres an ...
pattern. High-pressure systems are alternatively referred to as anticyclones. Their circulation is sometimes referred to as cum sole. Subtropical high-pressure zones form under the descending portion of the Hadley cell
The Hadley cell, named after George Hadley, is a global-scale tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward at a height of 10 to 15 kilometers above the earth's surface, descending in the subtropics ...
circulation. Upper-level high-pressure areas lie over tropical cyclones due to their warm core nature.
Surface anticyclones form due to downward motion through the troposphere, the atmospheric layer where weather occurs. Preferred areas within a synoptic flow pattern in higher levels of the troposphere are beneath the western side of troughs. On weather maps, these areas show converging winds (isotachs), also known as confluence
In geography, a confluence (also: ''conflux'') occurs where two or more flowing bodies of water join to form a single channel. A confluence can occur in several configurations: at the point where a tributary joins a larger river (main stem); o ...
, or converging height lines near or above the level of non-divergence, which is near the 500 hPa pressure surface about midway up the troposphere. Because they weaken with height, these high-pressure systems are cold.
Subtropical ridge
 Heating of the earth near the equator forces upward motion and convection along the
Heating of the earth near the equator forces upward motion and convection along the monsoon trough
The monsoon trough is a portion of the Intertropical Convergence Zone in the Western Pacific,Bin WangThe Asian Monsoon.Retrieved 2008-05-03. as depicted by a line on a weather map showing the locations of minimum sea level pressure, and as such, ...
or intertropical convergence zone
The Intertropical Convergence Zone (ITCZ ), known by sailors as the doldrums or the calms because of its monotonous windless weather, is the area where the northeast and the southeast trade winds converge. It encircles Earth near the thermal ...
. The divergence over the near-equatorial trough leads to air rising and moving away from the equator and to the poles aloft. As air moves towards the mid-latitudes, it cools and sinks leading to subsidence near the 30° parallel of both hemispheres. This circulation known as the Hadley cell
The Hadley cell, named after George Hadley, is a global-scale tropical atmospheric circulation that features air rising near the equator, flowing poleward at a height of 10 to 15 kilometers above the earth's surface, descending in the subtropics ...
forms the subtropical ridge. Many of the world's deserts are caused by these climatological high-pressure area
A high-pressure area, high, or anticyclone, is an area near the surface of a planet where the atmospheric pressure is greater than the pressure in the surrounding regions. Highs are middle-scale meteorological features that result from interpl ...
s. Because these anticyclones strengthen with height, they are known as warm core ridges.
Formation aloft
The development of anticyclones aloft occurs in warm core cyclones such astropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
s when latent heat caused by the formation of cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s is released aloft increasing the air temperature; the resultant thickness of the atmospheric layer increases high pressure aloft which evacuates their outflow.
Structure
In the absence of rotation, thewind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
tends to blow from areas of high pressure to areas of low pressure. The stronger the pressure difference (pressure gradient) between a high-pressure system and a low-pressure system, the stronger the wind. The coriolis force
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
caused by Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
's rotation gives winds within high-pressure systems their clockwise circulation in the northern hemisphere (as the wind moves outward and is deflected right from the center of high pressure) and anticlockwise circulation in the southern hemisphere (as the wind moves outward and is deflected left from the center of high pressure). Friction with land slows down the wind flowing out of high-pressure systems and causes wind to flow more outward (more ageostrophically) from the center.
Effects
Surface-based systems
 High-pressure systems are frequently associated with light winds at the surface and
High-pressure systems are frequently associated with light winds at the surface and subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope mov ...
of air from higher portions of the troposphere
The troposphere is the first and lowest layer of the atmosphere of the Earth, and contains 75% of the total mass of the planetary atmosphere, 99% of the total mass of water vapour and aerosols, and is where most weather phenomena occur. Fro ...
. Subsidence will generally warm an air mass by adiabatic (compressional) heating. Thus, high pressure typically brings clear skies. Because no clouds are present to reflect sunlight during the day, there is more incoming solar radiation
Solar irradiance is the power per unit area ( surface power density) received from the Sun in the form of electromagnetic radiation in the wavelength range of the measuring instrument.
Solar irradiance is measured in watts per square metre ...
and heating so temperatures rise rapidly near the surface. At night, the absence of clouds means that outgoing longwave radiation
Outgoing Long-wave Radiation (OLR) is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths from 3–100 μm emitted from Earth and its atmosphere out to space in the form of thermal radiation. It is also referred to as up-welling long-wave radiation an ...
(i.e. heat energy from the surface) is not blocked, allowing the escape of heat and giving cooler diurnal low temperatures in all seasons. When surface winds become light, the subsidence produced directly under a high-pressure system can lead to a buildup of particulates in urban areas under the high pressure, leading to widespread haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon in which dust, smoke, and other dry particulates suspended in air obscure visibility and the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classificati ...
. If the surface level relative humidity
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity dep ...
rises towards 100 percent overnight, fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
can form.
The movement of continental arctic air masses to lower latitudes produces strong but vertically shallow high-pressure systems. The surface level, sharp temperature inversion
Inversion or inversions may refer to:
Arts
* , a French gay magazine (1924/1925)
* ''Inversion'' (artwork), a 2005 temporary sculpture in Houston, Texas
* Inversion (music), a term with various meanings in music theory and musical set theory
* ...
can lead to areas of persistent stratocumulus
A stratocumulus cloud, occasionally called a cumulostratus, belongs to a genus-type of clouds characterized by large dark, rounded masses, usually in groups, lines, or waves, the individual elements being larger than those in altocumulus, and th ...
or stratus cloud
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds characterized by horizontal layering with a uniform base, as opposed to convective or cumuliform clouds that are formed by rising thermals. More specifically, the term ''stratus'' is used to describe flat, h ...
, colloquially known as anticyclonic gloom. The type of weather brought about by an anticyclone depends on its origin. For example, extensions of the Azores high pressure may bring about anticyclonic gloom during the winter because they pick up moisture as they move over the warmer oceans. High pressures that build to the north and move southwards often bring clear weather because they are cooled at the base (as opposed to warmed) which helps prevent clouds from forming.
Once arctic air moves over an unfrozen ocean, the air mass modifies greatly over the warmer water and takes on the character of a maritime air mass, which reduces the strength of the high-pressure system. When extremely cold air moves over relatively warm oceans, polar low
A polar low is a mesoscale, short-lived atmospheric low pressure system (depression) that is found over the ocean areas poleward of the main polar front in both the Northern and Southern Hemispheres, as well as the Sea of Japan. The systems usu ...
s can develop. However, warm and moist (or maritime tropical) air masses which move poleward from tropical sources are slower to modify than arctic air masses.
Mid-tropospheric systems
 The circulation around mid-level (altitude) ridges, and the air subsidence at their center, act to steer tropical cyclones around and out their periphery. Due to the subsidence within this type of system, a ''
The circulation around mid-level (altitude) ridges, and the air subsidence at their center, act to steer tropical cyclones around and out their periphery. Due to the subsidence within this type of system, a ''cap
A cap is a flat headgear, usually with a visor. Caps have crowns that fit very close to the head. They made their first appearance as early as 3200 BC. Caps typically have a visor, or no brim at all. They are popular in casual and informal se ...
'' can develop which inhibits free convection and hence mixing of the lower with the middle level troposphere. This limits thunderstorms
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are somet ...
and other low-pressure weather activity near their centers and traps low-level pollutants such as ozone
Ozone (), or trioxygen, is an inorganic molecule with the chemical formula . It is a pale blue gas with a distinctively pungent smell. It is an allotrope of oxygen that is much less stable than the diatomic allotrope , breaking down in the l ...
as haze
Haze is traditionally an atmospheric phenomenon in which dust, smoke, and other dry particulates suspended in air obscure visibility and the clarity of the sky. The World Meteorological Organization manual of codes includes a classificati ...
under their base, which is a significant problem in large urban centers during summer months such as Los Angeles, California
Los Angeles ( ; es, Los Ángeles, link=no , ), often referred to by its initials L.A., is the List of municipalities in California, largest city in the U.S. state, state of California and the List of United States cities by population, sec ...
and Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley o ...
.
Upper tropospheric systems
The existence of upper-level (altitude) high pressure allows upper leveldivergence
In vector calculus, divergence is a vector operator that operates on a vector field, producing a scalar field giving the quantity of the vector field's source at each point. More technically, the divergence represents the volume density of ...
which leads to surface convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
. If a capping mid-level ridge does not exist, this leads to free convection and the development of showers and thunderstorms if the lower atmosphere is humid. Because a positive feedback
Positive feedback (exacerbating feedback, self-reinforcing feedback) is a process that occurs in a feedback loop which exacerbates the effects of a small disturbance. That is, the effects of a perturbation on a system include an increase in th ...
loop develops between the convective tropical cyclone and the upper level high, the two system are strengthened. This loop stops once ocean temperatures cool to below ,Chris Landsea
Christopher William "Chris" Landsea is an American meteorologist, formerly a research meteorologist with the Hurricane Research Division of the Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory at NOAA, and now the Science and Operations Offic ...
Subject: A15) How do tropical cyclones form?
National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
. Retrievon 2008-06-08. reducing the thunderstorm activity, which then weakens the upper-level high-pressure system.
Importance to global monsoon regimes
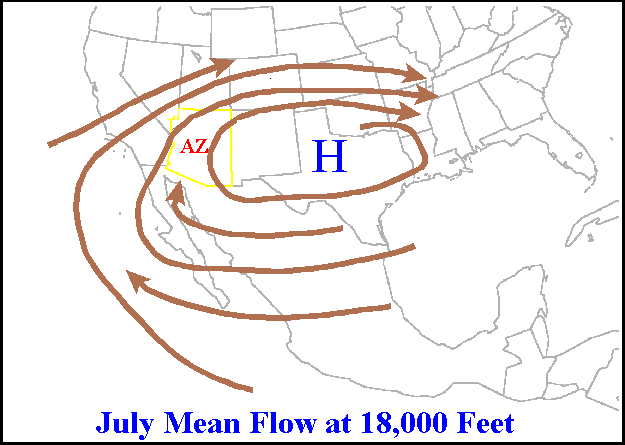
When the subtropical ridge in the Northwest Pacific is stronger than in other areas, it leads to a wetmonsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
season for Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
. The subtropical ridge position is linked to how far northward monsoon moisture and thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are some ...
s extend into the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. Typically, the subtropical ridge across North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
migrates far enough northward to begin monsoon conditions across the Desert Southwest
The Southwestern United States, also known as the American Southwest or simply the Southwest, is a geographic and cultural region of the United States that generally includes Arizona, New Mexico, and adjacent portions of California, Colorado, ...
from July to September. When the subtropical ridge is farther north than normal towards the Four Corners
The Four Corners is a region of the Southwestern United States consisting of the southwestern corner of Colorado, southeastern corner of Utah, northeastern corner of Arizona, and northwestern corner of New Mexico. The Four Corners area ...
, thunderstorms of the New Mexican Monsoon
The North American monsoon, variously known as the Southwest monsoon, the Mexican monsoon, the New Mexican monsoon, or the Arizona monsoon is a pattern of pronounced increase in thunderstorms and rainfall over large areas of the southwestern Un ...
can spread northward into Arizona
Arizona ( ; nv, Hoozdo Hahoodzo ; ood, Alĭ ṣonak ) is a state in the Southwestern United States. It is the 6th largest and the 14th most populous of the 50 states. Its capital and largest city is Phoenix. Arizona is part of the Fou ...
and New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. When suppressed to the south, the atmosphere dries out across the Desert Southwest, causing a break in the monsoon regime.
Depiction on weather maps
 On weather maps, high-pressure centers are associated with the letter H in English, within the isobar with the highest pressure value. On constant-pressure upper-level charts, anticyclones are located within the highest height line contour.Glossary of Meteorology (2009)
On weather maps, high-pressure centers are associated with the letter H in English, within the isobar with the highest pressure value. On constant-pressure upper-level charts, anticyclones are located within the highest height line contour.Glossary of Meteorology (2009)High
.
American Meteorological Society
The American Meteorological Society (AMS) is the premier scientific and professional organization in the United States promoting and disseminating information about the atmospheric, oceanic, and hydrologic sciences. Its mission is to advance th ...
. Retrieved on 2009-02-16.
Extraterrestrial versions
On Jupiter, there are two examples of an extraterrestrial anticyclonic storm; theGreat Red Spot
The Great Red Spot is a persistent high-pressure region in the atmosphere of Jupiter, producing an anticyclonic storm that is the largest in the Solar System. Located 22 degrees south of Jupiter's equator, it produces wind-speeds up to 432&nb ...
and the recently formed Oval BA
The atmosphere of Jupiter is the largest planetary atmosphere in the Solar System. It is mostly made of molecular hydrogen and helium in roughly solar proportions; other chemical compounds are present only in small amounts and include methane, ...
on Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest in the Solar System. It is a gas giant with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined, but slightly less than one-thousand ...
. They are powered by smaller storms merging unlike any typical anticyclonic storm that happens on Earth where water powers them. Another theory is that warmer gases rise in a column of cold air, creating a vortex as is the case of other storms that include Anne's Spot Anne's Spot refers to a reddish-colored anticyclonic oval in Saturn's atmosphere, observed in 1980 and 1981 at 55°S by the '' Voyager'' space probes.
It was probably also observed in 2004 at about 53°S by the Cassini orbiter Cassini may refer to: ...
on Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
and the Great Dark Spot
The Great Dark Spot (also known as GDS-89, for Great Dark Spot, 1989) was one of a series of dark spots on Neptune similar in appearance to Jupiter's Great Red Spot. In 1989, GDS-89 was the first Great Dark Spot on Neptune to be observed by NASA' ...
on Neptune. Anticyclones had also been detected near the poles of Venus.
See also
* Anticyclonic storm *Anticyclonic tornado
An anticyclonic tornado is a tornado which rotates in a clockwise direction in the Northern Hemisphere and a counterclockwise direction in the Southern Hemisphere. The term is a naming convention denoting the anomaly from normal rotation which is ...
*Atmosphere of Earth
The atmosphere of Earth is the layer of gases, known collectively as air, retained by Earth's gravity that surrounds the planet and forms its planetary atmosphere. The atmosphere of Earth protects life on Earth by creating pressure allowing fo ...
*Atmospheric circulation
Atmospheric circulation is the large-scale movement of air and together with ocean circulation is the means by which thermal energy is redistributed on the surface of the Earth. The Earth's atmospheric circulation varies from year to year, bu ...
*Atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibars, ...
*Great Smog of London
The Great Smog of London, or Great Smog of 1952, was a severe air pollution event that affected London, England, in December 1952. A period of unusually cold weather, combined with an anticyclone and windless conditions, collected airborne poll ...
* Barometric ridge
*Block (meteorology)
Blocks in meteorology are large-scale patterns in the atmospheric pressure field that are nearly stationary, effectively "blocking" or redirecting migratory cyclones. They are also known as blocking highs or blocking anticyclones.Glossary of Me ...
* North American High
*Ocean gyre
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of circulating ocean currents, particularly those involved with large wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determi ...
*Pressure system
A pressure system is a peak or lull in the sea level pressure distribution. The surface pressure at sea level varies minimally, with the lowest value measured and the highest recorded . High- and low-pressure systems evolve due to interactio ...
References
External links
Intertropical Convergence Zone photo
- NASA Goddard Space Flight Center
{{Authority control Meteorological phenomena Tropical cyclone meteorology