Amissville, Virginia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Amissville ( ) is an unincorporated community in Rappahannock County in the U.S. commonwealth of Virginia. It is located on
 Amissville was also the site of a sharp cavalry fight in November 1862, at Corbin's Crossroads, when Gen.
Amissville was also the site of a sharp cavalry fight in November 1862, at Corbin's Crossroads, when Gen.
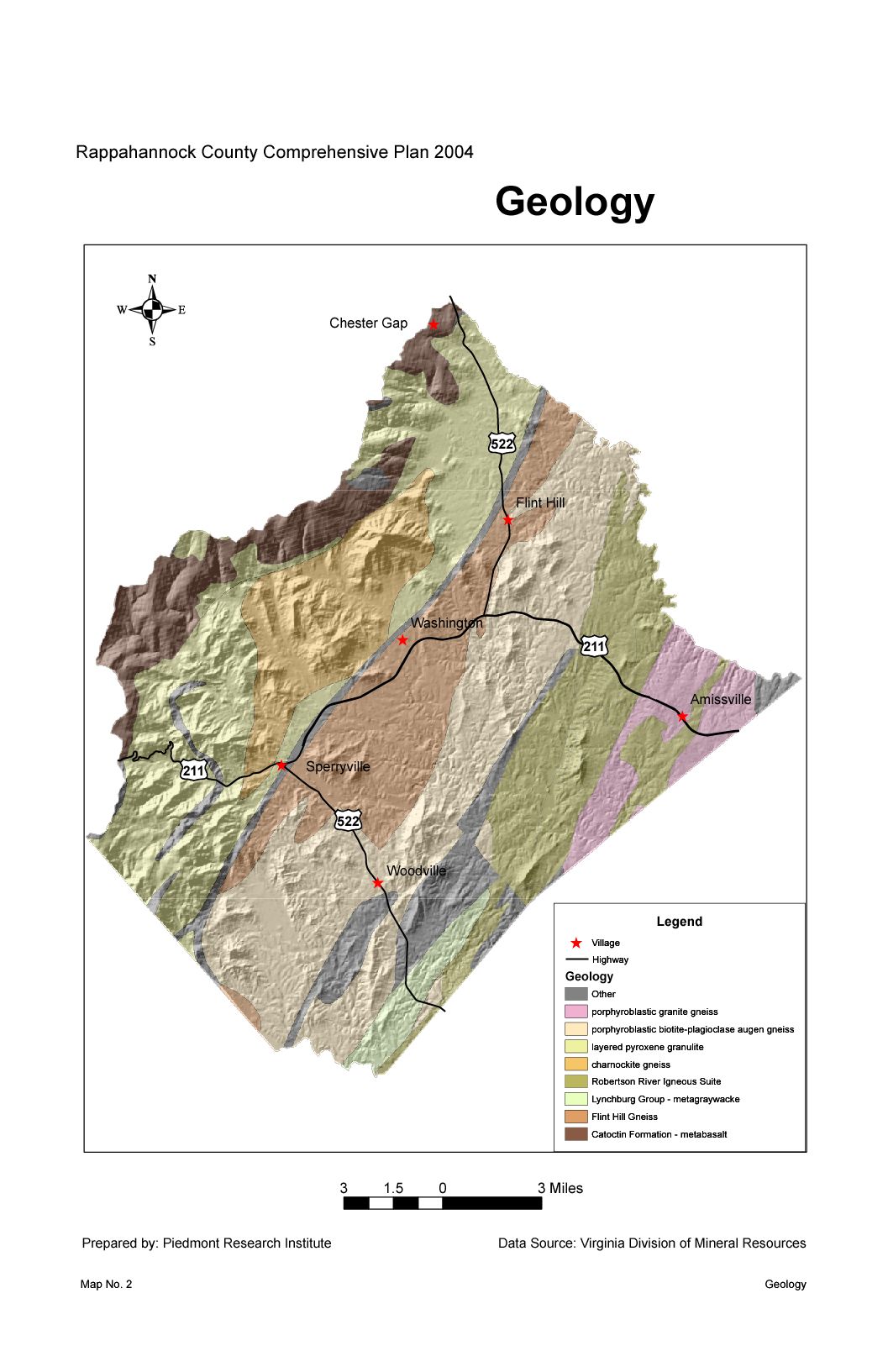 The geology of Amissville and the surrounding vicinity consists of several units. Predominant and oldest (approximately 704 million years old, +/- 5 million years, based on the U- Pb
The geology of Amissville and the surrounding vicinity consists of several units. Predominant and oldest (approximately 704 million years old, +/- 5 million years, based on the U- Pb
Amissville.com
{{authority control Unincorporated communities in Rappahannock County, Virginia Unincorporated communities in Virginia Populated places established in 1810 1810 establishments in Virginia
U.S. Route 211
U.S. Route 211 (US 211) is a spur of US 11 in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known for most of its length as Lee Highway, the U.S. Highway runs from Interstate 81 (I-81) and Virginia State Route 211 (SR 211) in New Market east to US 15 Business, ...
about halfway between Warrenton and the small town of Washington, Virginia
The town of Washington, Virginia, is a historic village located in the eastern foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains near Shenandoah National Park. The entire town is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district, Wa ...
.
The Locust Grove/R.E. Luttrell Farmstead and Meadow Grove Farm are listed on the National Register of Historic Places.
History
The land on which the village of Amissville is now situated was part of the 5.3 million acre Northern Neck Proprietary owned in the 1700s by Thomas Fairfax, 6th Lord Fairfax of Cameron. In 1649 King Charles II of England, then in exile in France after the execution of his father, Charles I, had given this unmapped and unsettled region to seven loyal supporters. By 1688 the proprietary was owned solely by Thomas Lord Culpeper whose only child married Thomas 5th Lord Fairfax in 1690. They acquired the proprietary on the death of Lord Culpeper and the region became synonymous with the Fairfax name. In 1719, Thomas 6th Lord Fairfax inherited the land. During 1747 to 1766, Lord Fairfax granted land that encompassed the area of today's Amissville to five individuals: Thomas Burk received 200 acres, Samuel Scott received 270 acres and 470 acres, James Genn received two grants of 400 acres each, Gabriel Jones received 380 acres, and Philip Edward Jones received 452 acres. It is widely believed that individuals with surnames Amiss and Bayse received land grants from Lord Fairfax in the Amissville area. However, there are no grants to anyone with these surnames recorded in the Virginia Colonial land grant books maintained by the Library of Virginia. Rather, Joseph Amiss and Edmond Bayse purchased existing land grants. On 14 July 1766 Joseph Amiss purchased, for 40 pounds, the 380 acres that had been granted to Gabriel Jones. On 15 October 1770 Edmond Bayse purchased, for 90 pounds, the 800 acres that had been granted to James Genn. On 1 July 1794, Joseph Amiss distributed his land and slaves as gifts to his three living sons William, Philip, and Thomas, and his grandsons William (son of William) and John (son of Thomas). In return, Joseph and his wife Constant were given a life estate to the property (10)Constant is believed to have been a daughter of Gabriel Jones. The sons and grandsons and their children purchased additional land in the Amissville area. On 20 April 1778, Edmond Bayse gave his son Elijamon 190 acres of the 800 acres that Edmond had acquired in 1770. This was the northern part of the 800 acres, located adjacent to today's Route 211. Although Elijamon sold this land in 1789, he and his children acquired other land in the Amissville area and became major landowners. The post office was established on 2 October 1810, with Thomas Amiss as its first postmaster. In 1854, Amissville was described as a small post-village with about 75 inhabitants.US Civil War
Amissville is near the site of a minor action on July 24, 1863, involving George A. Custer's Michigan Brigade ofcavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry in ...
following the Confederate loss at Gettysburg. Longstreet's corps and Gen. A. P. Hill
Ambrose Powell Hill Jr. (November 9, 1825April 2, 1865) was a Confederate general who was killed in the American Civil War. He is usually referred to as A. P. Hill to differentiate him from another, unrelated Confederate general, Daniel Harvey H ...
's corps were retreating from Pennsylvania through the Chester Gap
Chester Gap, sometimes referred to as Happy Creek Gap for the creek that runs down its western slope, is a wind gap in the Blue Ridge Mountains on the border of Rappahannock County, Fauquier County and Warren County in Virginia. The gap is tra ...
and south on the Richmond Road towards Culpeper. Custer and his troops traveled from their headquarters and camp near Amissville and attacked with cavalry and artillery
Artillery is a class of heavy military ranged weapons that launch munitions far beyond the range and power of infantry firearms. Early artillery development focused on the ability to breach defensive walls and fortifications during sieges, ...
from the southern slope of Battle Mountain (about 5 miles southwest of the village), but his forces were vastly outnumbered and after a brisk and severe fight, forced to retreat north and east over Battle Mountain back to Amissville. Two of Custer's men were awarded the Medal of Honor
The Medal of Honor (MOH) is the United States Armed Forces' highest military decoration and is awarded to recognize American soldiers, sailors, marines, airmen, guardians and coast guardsmen who have distinguished themselves by acts of valor ...
in 1893 for their part in capturing Confederate artillery at Battle Mountain. Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain were named not for the military engagement but for the Bataille family which lived near the two elevations in the 1700s. Bataille was later corrupted to Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain, the names they bear today.
J.E.B. Stuart
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a United States Army officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials o ...
's Confederate cavalry were heading to Culpeper County
Culpeper County is a county located along the borderlands of the northern and central region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, the population was 52,552. Its county seat and only incorporated community is C ...
following the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union ...
in Maryland. At Corbin's crossroads, during the fight, Gen. Stuart narrowly escaped death when he turned his head and a Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''U ...
bullet clipped off half of his moustache. The site of the engagement is about 3/4 of a mile south of the present village of Amissville.
In late August 1862, Gen. Stuart and his cavalry were scouting around Maj. Gen. John Pope's Federal Army of Virginia
The Army of Virginia was organized as a major unit of the Union Army and operated briefly and unsuccessfully in 1862 in the American Civil War. It should not be confused with its principal opponent, the Confederate Army of ''Northern'' Virginia, ...
, elements of which were moving towards Thoroughfare Gap
''Thoroughfare Gap'' is the fifth studio album by American singer-songwriter Stephen Stills, released in 1978. It was a critical and commercial disappointment that only charted at number 84 in the US. This album is now available as a three-alb ...
in Fauquier County
Fauquier is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 72,972. The county seat is Warrenton.
Fauquier County is in Northern Virginia and is a part of the Washington metropolitan area.
History
In 160 ...
. Gen. Stuart and his cavalry reached Amissville on August 22, and turned back to surround Pope's army. In an attack near Catlett's Station, Gen. Stuart's men captured Gen. Pope's overcoat and military papers.
Climate
The climate in this area is characterized by hot, humid summers and generally mild to cool winters. According to the Köppen Climate Classification system, Amissville has a humid subtropical climate, abbreviated "Cfa" on climate maps.Geology
 The geology of Amissville and the surrounding vicinity consists of several units. Predominant and oldest (approximately 704 million years old, +/- 5 million years, based on the U- Pb
The geology of Amissville and the surrounding vicinity consists of several units. Predominant and oldest (approximately 704 million years old, +/- 5 million years, based on the U- Pb zircon
Zircon () is a mineral belonging to the group of nesosilicates and is a source of the metal zirconium. Its chemical name is zirconium(IV) silicate, and its corresponding chemical formula is Zr SiO4. An empirical formula showing some of the ...
geochronology dating method, coinciding with the initial rifting
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-graben w ...
of the supercontinent Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probabl ...
) is the Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is pre ...
alkali feldspar
Feldspars are a group of rock-forming aluminium tectosilicate minerals, also containing other cations such as sodium, calcium, potassium, or barium. The most common members of the feldspar group are the ''plagioclase'' (sodium-calcium) feldspa ...
granitic
A granitoid is a generic term for a diverse category of coarse-grained igneous rocks that consist predominantly of quartz, plagioclase, and alkali feldspar. Granitoids range from plagioclase-rich tonalites to alkali-rich syenites and from quartz ...
rock of the Robertson River Igneous Suite
Suite may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
*Suite (music), a set of musical pieces considered as one composition
** Suite (Bach), a list of suites composed by J. S. Bach
** Suite (Cassadó), a mid-1920s composition by Gaspar Cassadó
** ''Suite ...
. This includes felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
complex material such as biotite
Biotite is a common group of phyllosilicate minerals within the mica group, with the approximate chemical formula . It is primarily a solid-solution series between the iron-endmember annite, and the magnesium-endmember phlogopite; more alumi ...
, hornblende-biotite, magnetite
Magnetite is a mineral and one of the main iron ores, with the chemical formula Fe2+Fe3+2O4. It is one of the oxides of iron, and is ferrimagnetic; it is attracted to a magnet and can be magnetized to become a permanent magnet itself. With the ...
, and alkali
In chemistry, an alkali (; from ar, القلوي, al-qaly, lit=ashes of the saltwort) is a basic, ionic salt of an alkali metal or an alkaline earth metal. An alkali can also be defined as a base that dissolves in water. A solution of ...
granitic rock
Rock most often refers to:
* Rock (geology), a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals or mineraloids
* Rock music, a genre of popular music
Rock or Rocks may also refer to:
Places United Kingdom
* Rock, Caerphilly, a location in Wales ...
including rhyolite
Rhyolite ( ) is the most silica-rich of volcanic rocks. It is generally glassy or fine-grained (aphanitic) in texture, but may be porphyritic, containing larger mineral crystals ( phenocrysts) in an otherwise fine-grained groundmass. The miner ...
on the eastern slopes of Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain.
Battle Mountain and Little Battle Mountain are the only mountains in Rappahannock County which are known to be volcanic in origin, and are among the oldest visibly intact extinct volcanoes in Virginia. White quartz boulders
In geology, a boulder (or rarely bowlder) is a rock fragment with size greater than in diameter. Smaller pieces are called cobbles and pebbles. While a boulder may be small enough to move or roll manually, others are extremely massive.
In c ...
and smaller fragments are common on and around Battle Mountain, a result of molten silica that was contained in the rhyolite lava and granitic magma that formed the volcano.
The Robertson River Igneous Suite extends from south of Laurel Mills (originating near Charlottesville
Charlottesville, colloquially known as C'ville, is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia. It is the county seat of Albemarle County, which surrounds the city, though the two are separate legal entities. It is named after Queen Ch ...
) and runs north-northeast through Hackleys Crossroad and beyond in a band approximately four kilometers wide. Precambrian coarse leucogneiss and fine-grained gneiss prevails from the eastern edge of the Amissville, Rappahannock County area from north of the Amissville post office and U.S. Route 211
U.S. Route 211 (US 211) is a spur of US 11 in the U.S. state of Virginia. Known for most of its length as Lee Highway, the U.S. Highway runs from Interstate 81 (I-81) and Virginia State Route 211 (SR 211) in New Market east to US 15 Business, ...
and south to Viewtown. Flint Hill Gneiss, a light to dark-gray quartz monzonite gneiss is predominate from Ben Venue and west to Massies Corner and extending further into Rock Mills and the town of Washington, Virginia
The town of Washington, Virginia, is a historic village located in the eastern foothills of the Blue Ridge Mountains near Shenandoah National Park. The entire town is listed on the National Register of Historic Places as a historic district, Wa ...
.
A fine-grained Precambrian arkosic
Arkose () or arkosic sandstone is a detrital sedimentary rock, specifically a type of sandstone containing at least 25% feldspar.
Arkosic sand is sand that is similarly rich in feldspar, and thus the potential precursor of arkose.
Quartz is c ...
sandstone and conglomerate, which Aaron Mountain is composed of, occurs on the contact between the Flint Hill Gneiss starting approximately two kilometers west of Laurel Mills and running north-northeast along a narrow band (starting out at approximately 1 kilometer wide and tapering down to 100 meters) in contact with the Robertson River Igneous Suite, terminating just south of U.S. Route 211. The creeksides and river bottoms of the Thorton River, Battle Run and the Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the enti ...
and their smaller tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage ...
are all composed of Quaternary Period
The Quaternary ( ) is the current and most recent of the three periods of the Cenozoic Era in the geologic time scale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). It follows the Neogene Period and spans from 2.58 million years ...
alluvium
Alluvium (from Latin ''alluvius'', from ''alluere'' 'to wash against') is loose clay, silt, sand, or gravel that has been deposited by running water in a stream bed, on a floodplain, in an alluvial fan or beach, or in similar settings. Alluv ...
including stratified, unconsolidated
Soil consolidation refers to the mechanical process by which soil changes volume gradually in response to a change in pressure. This happens because soil is a two-phase material, comprising soil grains and pore fluid, usually groundwater. Whe ...
gray to grayish-yellow sand, silt and local gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone.
Gravel is classifi ...
s.
Notes
References
External links
Amissville.com
{{authority control Unincorporated communities in Rappahannock County, Virginia Unincorporated communities in Virginia Populated places established in 1810 1810 establishments in Virginia