Alawite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Alawis, Alawites ( ar, علوية ''Alawīyah''), or pejoratively Nusayris ( ar, نصيرية ''Nuṣayrīyah'') are an ethnoreligious group that lives primarily in
 The origin of the genetics of Alawites is disputed. Local folklore suggests that they are descendants of the followers of the eleventh Imam, Hasan al-Askari (d. 873) and his pupil, Ibn Nusayr (d. 868). During the 19th and 20th centuries, some Western scholars believed that Alawites were descended from ancient
The origin of the genetics of Alawites is disputed. Local folklore suggests that they are descendants of the followers of the eleventh Imam, Hasan al-Askari (d. 873) and his pupil, Ibn Nusayr (d. 868). During the 19th and 20th centuries, some Western scholars believed that Alawites were descended from ancient
 After the end of World War I and the fall of the Ottoman Empire, Syria and Lebanon were placed by the
After the end of World War I and the fall of the Ottoman Empire, Syria and Lebanon were placed by the
 When the French began to occupy Syria in 1920, an Alawite State was created in the coastal and mountain country comprising most Alawite villages; the French justified this by citing differences between the "backwards" mountain people and the mainstream Sunnis. The division also intended to protect the Alawite people from more-powerful majorities, such as the Sunnis.
The French also created microstates, such as Greater Lebanon for the Maronite Christians and
When the French began to occupy Syria in 1920, an Alawite State was created in the coastal and mountain country comprising most Alawite villages; the French justified this by citing differences between the "backwards" mountain people and the mainstream Sunnis. The division also intended to protect the Alawite people from more-powerful majorities, such as the Sunnis.
The French also created microstates, such as Greater Lebanon for the Maronite Christians and  In 1939, the Sanjak of Alexandretta (now
In 1939, the Sanjak of Alexandretta (now
 Syria became independent on 17 April 1946. In 1949, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Syria experienced a number of military coups and the rise of the Ba'ath Party.
In 1958, Syria and Egypt were united by a political agreement into the
Syria became independent on 17 April 1946. In 1949, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Syria experienced a number of military coups and the rise of the Ba'ath Party.
In 1958, Syria and Egypt were united by a political agreement into the
Return of the Pink Panthers?
" ''Mideast Monitor''. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008. issued a
 Alawites and their beliefs have been described as "secretive""Alawi Islam"
Alawites and their beliefs have been described as "secretive""Alawi Islam"
Globalsecurity.org (Yaron Friedman, for example, in his scholarly work on the sect, has written that the Alawi religious material quoted in his book came only from "public libraries and printed books" since the "sacred writings" of the Alawi "are kept secret"); some tenets of the faith are kept secret from most Alawi and known only to a select few, Friedman, ''Nuṣayrī-ʿAlawīs'', 2010: p.xii they have therefore been described as a mystical sect. Alawite beliefs have never been confirmed by their modern religious authorities.'Abd al‑Latif al‑Yunis, Mudhakkirat al‑Duktur 'Abd al‑Latif al‑Yunis, Damascus: Dar al‑'Ilm, 1992, p. 63. Alawites tend to conceal their beliefs ('' taqiyya'') due to historical persecution.
 Other beliefs and practices include: the consecration of wine in a secret form of
Other beliefs and practices include: the consecration of wine in a secret form of
 Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime. Joshua Landis, director of the Center for Middle East Studies, writes that Hafiz al-Assad "tried to turn Alawites into 'good' (read Sunnified) Muslims in exchange for preserving a modicum of secularism and tolerance in society". On the other hand, Al-Assad "declared the Alawites to be nothing but Twelver Shiites".Syrian comment. Asad's Alawi dilemma
Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime. Joshua Landis, director of the Center for Middle East Studies, writes that Hafiz al-Assad "tried to turn Alawites into 'good' (read Sunnified) Muslims in exchange for preserving a modicum of secularism and tolerance in society". On the other hand, Al-Assad "declared the Alawites to be nothing but Twelver Shiites".Syrian comment. Asad's Alawi dilemma
8 October 2004 In a paper, "Islamic Education in Syria", Landis wrote that "no mention" is made in Syrian textbooks (controlled by the Al-Assad regime) of Alawites, Druze, Ismailis or Shia Islam; Islam was presented as a monolithic religion. Ali Sulayman al-Ahmad, chief judge of the Baathist Syrian state, has said:
 To avoid confusion with the ethnic-Turkish and Kurdish
To avoid confusion with the ethnic-Turkish and Kurdish
Levant
The Levant () is an approximate historical geographical term referring to a large area in the Eastern Mediterranean region of Western Asia. In its narrowest sense, which is in use today in archaeology and other cultural contexts, it is ...
and follows Alawism, a sect of Islam that originated from Shia Islam
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
. The Alawites revere Ali (Ali ibn Abi Talib), considered the first Imam of the Twelver school
A school is an educational institution designed to provide learning spaces and learning environments for the teaching of students under the direction of teachers. Most countries have systems of formal education, which is sometimes co ...
. The group is believed to have been founded by Ibn Nusayr
Abū Shuʿayb Muḥammad ibn Nuṣayr al-Numayri ( ar, أبو شعيب محمد بن نصير النميري), died after 868, was considered by his followers as the representative () of the tenth Twelver Imam, Ali al‐Hadi and of the eleventh ...
during the 9th century. Ibn Nusayr was a disciple of the tenth Twelver Imam, Ali al-Hadi and of the eleventh Twelver Imam, Hasan al-Askari. For this reason, Alawites are also called ''Nusayris''.
Surveys suggest Alawites represent an important portion of the Syrian population and are a significant minority in the Hatay Province of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
and northern Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
. There is also a population living in the village of Ghajar in the Golan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. Alawites form the dominant religious group on the Syrian coast and towns near the coast, which are also inhabited by Sunni
Sunni Islam () is the largest branch of Islam, followed by 85–90% of the world's Muslims. Its name comes from the word '' Sunnah'', referring to the tradition of Muhammad. The differences between Sunni and Shia Muslims arose from a dis ...
s, Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, and Ismailis. They are often confused with the Alevis
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, ...
, a distinct religious sect in Turkey.
Alawites identify as a separate ethnoreligious group. The Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
is only one of their holy books and texts, and their interpretation thereof has very little in common with the Shia
Shīʿa Islam or Shīʿīsm is the second-largest branch of Islam. It holds that the Islamic prophet Muhammad designated ʿAlī ibn Abī Ṭālib as his successor (''khalīfa'') and the Imam (spiritual and political leader) after him, mos ...
Muslim interpretation but is in accordance with the early Batiniyya
Batiniyya ( ar, باطنية, Bāṭiniyyah) refers to groups that distinguish between an outer, exoteric ('' zāhir'') and an inner, esoteric ('' bāṭin'') meaning in Islamic scriptures. The term has been used in particular for an allegoristic ...
and other '' ghulat'' sects. Alawite theology and rituals break from mainstream Shia Islam in several important ways. For one, the Alawites drink wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
as Ali's transubstantiated essence in their rituals; while other Muslims abstain from alcohol, Alawites are encouraged to drink socially in moderation. Finally, some of them believe in reincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the philosophical or religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new life in a different physical form or body after biological death. Resurrectio ...
, but it is not essential in their doctrine.
Alawites have historically kept their beliefs secret from outsiders and non-initiated Alawites, so rumours about them have arisen. Arabic accounts of their beliefs tend to be partisan (either positively or negatively). Friedman, ''Nuṣayrī-ʿAlawīs'', 2010: p.68 However, since the early 2000s, Western scholarship on the Alawite religion has made significant advances. Friedman, ''Nuṣayrī-ʿAlawīs'', 2010: p.67 At the core of Alawite belief is a divine triad, comprising three aspects of the one God. These aspects, or emanations, appear cyclically in human form throughout history.
The establishment of the French Mandate of Syria
The Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon (french: Mandat pour la Syrie et le Liban; ar, الانتداب الفرنسي على سوريا ولبنان, al-intidāb al-fransi 'ala suriya wa-lubnān) (1923−1946) was a League of Nations mandate foun ...
marked a turning point in Alawi history. It gave the French the power to recruit Syrian civilians into their armed forces for an indefinite period and created exclusive areas for minorities, including the Alawite State. The Alawite State was later dismantled, but the Alawites continued to be a significant part of the Syrian Armed Forces. Since Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad ', , (, 6 October 1930 – 10 June 2000) was a Syrian statesman and military officer who served as President of Syria from taking power in 1971 until his death in 2000. He was also Prime Minister of Syria from 1970 to 1 ...
took power through the 1970 Corrective Movement, the government has been dominated by a political elite led by the Alawite al-Assad family. During the Islamist uprising in Syria in the 1970s and 1980s, the establishment came under pressure. Even greater pressure has resulted from the Syrian Civil War.
Etymology
In older sources, Alawis are often called "Ansaris". According toSamuel Lyde
Samuel Lyde (1825–1860) was an English writer and Church of England missionary who worked in Syria in the 1850s and wrote a pioneering book on the Alawite sect. In 1856, he sparked months of anti-Christian rioting in Ottoman Palestine when, d ...
, who lived among the Alawites during the mid-19th century, this was a term they used among themselves. Other sources indicate that "Ansari" is simply a Western error in the transliteration of "Nusayri". However, the term "Nusayri" had fallen out of currency by the 1920s, as a movement led by intellectuals within the community during the French Mandate
Mandate most often refers to:
* League of Nations mandates, quasi-colonial territories established under Article 22 of the Covenant of the League of Nations, 28 June 1919
* Mandate (politics), the power granted by an electorate
Mandate may also r ...
sought to replace it with the modern term "Alawi".
They characterised the older name (which implied "a separate ethnic and religious identity") as an "invention of the sect's enemies", ostensibly favouring an emphasis on "connection with mainstream Islam"—particularly the Shia branch. As such, "Nusayri" is now generally regarded as antiquated, and has even come to have insulting and abusive connotations. The term is frequently employed as hate speech by Sunni fundamentalists fighting against Bashar al-Assad
Bashar Hafez al-Assad, ', Levantine pronunciation: ; (, born 11 September 1965) is a Syrian politician who is the 19th president of Syria, since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the ...
's government in the Syrian civil war, who use its emphasis on Ibn Nusayr in order to insinuate that Alawi beliefs are "man-made" and not divinely inspired.
Recent research has shown that the Alawi appellation was used by the sect's adherents since the 11th century. The following quote from Alkan (2012) illustrates this point: "In actual fact, the name 'Alawī' appears as early as in an 11th century Nuṣayrī tract (…). Moreover, the term 'Alawī' was already used at the beginning of the 20th century. In 1903 the Belgian-born Jesuit and Orientalist Henri Lammens (d. 1937) visited a certain Ḥaydarī-Nuṣayrī sheikh Abdullah in a village near Antakya and mentions that the latter preferred the name 'Alawī' for his people. Lastly, it is interesting to note that in the above-mentioned petitions of 1892 and 1909 the Nuṣayrīs called themselves the 'Arab Alawī people' (ʿArab ʿAlevī ṭāʾifesi) 'our ʿAlawī Nuṣayrī people' (ṭāʾifatunā al-Nuṣayriyya al-ʿAlawiyya) or 'signed with Alawī people' (ʿAlevī ṭāʾifesi imżāsıyla). This early self-designation is, in my opinion, of triple importance. Firstly, it shows that the word 'Alawī' was always used by these people, as ʿAlawī authors emphasize; secondly, it hints at the reformation of the Nuṣayrīs, launched by some of their sheikhs in the 19th century and their attempt to be accepted as part of Islam; and thirdly, it challenges the claims that the change of the identity and name from 'Nuṣayrī' to 'ʿAlawī' took place around 1920, in the beginning of the French mandate in Syria (1919–1938)."The Alawites are distinct from the '' Alevi'' religious sect in Turkey, although the terms share a common etymology and pronunciation.
Genealogical origin theories
 The origin of the genetics of Alawites is disputed. Local folklore suggests that they are descendants of the followers of the eleventh Imam, Hasan al-Askari (d. 873) and his pupil, Ibn Nusayr (d. 868). During the 19th and 20th centuries, some Western scholars believed that Alawites were descended from ancient
The origin of the genetics of Alawites is disputed. Local folklore suggests that they are descendants of the followers of the eleventh Imam, Hasan al-Askari (d. 873) and his pupil, Ibn Nusayr (d. 868). During the 19th and 20th centuries, some Western scholars believed that Alawites were descended from ancient Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
ern peoples such as the Arameans, Canaanites
{{Cat main, Canaan
See also:
* :Ancient Israel and Judah
Ancient Levant
Hebrew Bible nations
Ancient Lebanon
0050
Ancient Syria
Wikipedia categories named after regions
0050
Phoenicia
Amarna Age civilizations ...
, Hittites
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
, and Mardaites. Many prominent Alawite tribes are also descended from 13th century settlers from Sinjar.
In his Natural History, Book V, Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
said:
The "Tetrarchy of the Nazerini" refers to the western region, between the Orontes and the sea, which consists of a small mountain range called An-Nusayriyah Mountains bordered with a valley running from south-east to north-west known as " Al-Ghab plain"; the region was populated by a portion of Syrians, who were called Nazerini. However, scholars are reluctant to link between Nazerini and Nazarenes. Yet, the term "Nazerini" can be possibly connected to words which include the Semitic triliteral root
The roots of verbs and most nouns in the Semitic languages are characterized as a sequence of consonants or "radicals" (hence the term consonantal root). Such abstract consonantal roots are used in the formation of actual words by adding the vowe ...
''n-ṣ-r'' such as the subject ''naṣer'' in Eastern Aramaic which means "''keeper of wellness''".
History
Ibn Nusayr and his followers are considered the founders of the religion. After the death of the Eleventh Imam, al-Askari, problems emerged in the Shia Community concerning his succession, and then Ibn Nusayr claimed to be the Bab and Ism of the deceased Imam and that he received his secret teachings. Ibn Nusayr and his followers development seems to be one of many other early ghulat mystical Islamic sects, and were apparently excommunicated by the Shia representatives of the 12th Hidden Imam. The Alawites were later organised during Hamdanid rule in northern Syria (947–1008) by a follower of Muhammad ibn Nusayr known as al-Khaṣībī, who died in Aleppo about 969, after a rivalry with the Ishaqiyya sect, which claimed also to have the doctrine of Ibn Nusayr. The embrace of Alawism by the majority of the population in the Syrian coastal mountains was likely a protracted process occurring over several centuries. Modern research indicates that after its initial establishment in Aleppo, Alawism spread to Sarmin, Salamiyah,Homs
ar, حمصي, Himsi
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_t ...
and Hama
Hama ( ar, حَمَاة ', ; syr, ܚܡܬ, ħ(ə)mɑθ, lit=fortress; Biblical Hebrew: ''Ḥamāṯ'') is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial ...
before becoming concentrated in low-lying villages west of Hama, including Baarin, Deir Shamil, and Deir Mama, the Wadi al-Uyun valley, and in the mountains around Tartus
)
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium&n ...
and Safita.
In 1032, al-Khaṣībī's grandson and pupil, Abu Sa'id Maymun al-Tabarani (d. 1034), moved to Latakia (then controlled by the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
). Al-Tabarani succeeded his mentor al-Jilli of Aleppo as head missionary in Syria and became "the last definitive scholar of Alawism", founding its calendar and giving Alawite teachings their final form, according to the historian Stefan Winter. Al-Tabarani influenced the Alawite faith through his writings and by converting the rural population of the Syrian Coastal Mountain Range. Winter argues that while it is likely the Alawite presence in Latakia dates to Tabarani's lifetime, it is unclear if Alawite teachings spread to the city's mountainous hinterland, where the Muslim population generally leaned toward Shia Islam, in the eleventh century. In the early part of the century, the Jabal al-Rawadif (part of the Syrian Coastal Mountains around Latakia) were controlled by the local Arab chieftain Nasr ibn Mushraf al-Rudafi, who vacillated between alliance and conflict with Byzantium. There is nothing in the literary sources indicating al-Rudafi patronized the Alawites. To the south of Jabal al-Rawadif, in the Jabal Bahra, a 13th-century Alawite treatise mentions the sect was sponsored by the Banu'l-Ahmar, Banu'l-Arid, and Banu Muhriz
The Banu Muhriz were an Arab princely family that controlled the fortresses of Marqab (Margat), Kahf and Qadmus in the late 11th and early 12th centuries.
The family is credited by a 13th-century Alawite treatise for patronizing the budding Al ...
, three local families who controlled fortresses in the region in the 11th and 12th centuries. From this southern part of the Syrian coastal mountain range, a significant Alawite presence developed in the mountains east of Latakia and Jableh
)
, settlement_type = City
, motto =
, image_skyline = Jableh Collage.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = General view of city and port • Roman Amphitheater• Al ...
during the Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
period (1260s—1516).
According to Bar Hebraeus, many Alawites were killed when the Crusaders initially entered Syria in 1097; however, they tolerated them when they concluded they were not a truly Islamic sect. They even incorporated them within their ranks, along with the Maronites
The Maronites ( ar, الموارنة; syr, ܡܖ̈ܘܢܝܐ) are a Christian ethnoreligious group native to the Eastern Mediterranean and Levant region of the Middle East, whose members traditionally belong to the Maronite Church, with the lar ...
and Turcopoles. Two prominent Alawite leaders in the following centuries, credited with uplifting the group, were Shaykhs al-Makzun (d. 1240) and al-Tubani (d. 1300), both originally from Mount Sinjar in modern Iraq.
In the 14th century, the Alawites were forced by Mamluk sultan Baibars to build mosques in their settlements, to which they responded with token gestures described by the Muslim traveller Ibn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berber Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, largely in the Muslim ...
.
Ottoman Empire
During the reign of Sultan Selim I, of the Ottoman Empire, the Alawites would again experience significant persecution; especially in Aleppo when a massacre occurred in theGreat Mosque of Aleppo
The Great Mosque of Aleppo ( ar, جَـامِـع حَـلَـب الْـكَـبِـيْـر, ''Jāmi‘ Ḥalab al-Kabīr'') is the largest and one of the oldest mosques in the city of Aleppo, Syria. It is located in al-Jalloum district of the ...
on 24 April 1517. The massacre was known as the "Massacre of the Telal" ( ar, مجزرة التلل) in which the corpses of thousands of victims accumulated as a tell located west of the castle. The horrors of the massacre which caused the immigration of the survivors to the coastal region are documented at the National and University Library
The National and University Library (french: Bibliothèque nationale et universitaire; abbreviated BNU) is a public library in Strasbourg, France. It is located on Place de la République, the former ''Kaiserplatz'', and faces the '' Palais du ...
in Strasbourg
Strasbourg (, , ; german: Straßburg ; gsw, label= Bas Rhin Alsatian, Strossburi , gsw, label= Haut Rhin Alsatian, Strossburig ) is the prefecture and largest city of the Grand Est region of eastern France and the official seat of the ...
, the manuscript is reserved as a letter sent by an Ottoman commander to Sultan Selim I:
The Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
took aggressive actions against Alawites, due to their alleged “treacherous activities” as “they had long history of betraying the Muslim governments due to their mistrust towards Sunnis.” The Alawis rose up against the Ottomans on several occasions, and maintained their autonomy in their mountains.
In his book, '' Seven Pillars of Wisdom'', T. E. Lawrence wrote:
During the 18th century, the Ottomans employed a number of Alawite leaders as tax collectors under the '' iltizam'' system. Between 1809 and 1813, Mustafa Agha Barbar
Mustafa Agha Barbar El Korek (1767 – 28 April 1835) was an Ottoman Syrian statesman and military officer who was governor of the Ottoman province of Tripoli, ruling between 1800–08, 1810–20 and 1821-35.
Name
The middle word in his name, Ag ...
, the governor of Tripoli, attacked the Kalbiyya Alawites with "marked savagery." Some Alawites supported Ottoman involvement in the Egyptian-Ottoman Wars of 1831–1833 and 1839–1841, and had careers in the Ottoman army or as Ottoman governors. Moreover, they even initiated the Alawite revolt (1834–35)
The Alawis, Alawites ( ar, علوية ''Alawīyah''), or pejoratively Nusayris ( ar, نصيرية ''Nuṣayrīyah'') are an ethnoreligious group that lives primarily in Levant and follows Alawism, a sect of Islam that originated from Shia Isla ...
against the Egyptian rule of the region, which was later suppressed by the Governor of Homs.
By the mid-19th century, the Alawite people, customs and way of life were described by Samuel Lyde
Samuel Lyde (1825–1860) was an English writer and Church of England missionary who worked in Syria in the 1850s and wrote a pioneering book on the Alawite sect. In 1856, he sparked months of anti-Christian rioting in Ottoman Palestine when, d ...
, an English missionary among them, as suffering from nothing except a gloomy plight. The 19th century historian Elias Saleh described the Alawites as living in a "state of ignorance" and having the negative traits of "laziness, lying, deceitfulness, inclination to robbery and bloodshed, and backstabbing". By the 1870s, Alawite bandits were impaled on spikes and left on crossroads as a warning, according to the historian Joshua Landis.
Early in the 20th century, the mainly-Sunni Ottoman leaders were bankrupt and losing political power; the Alawites were poor peasant
A peasant is a pre-industrial agricultural laborer or a farmer with limited land-ownership, especially one living in the Middle Ages under feudalism and paying rent, tax, fees, or services to a landlord. In Europe, three classes of peasa ...
s.
French Mandate period
League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference th ...
under the French Mandate for Syria and the Lebanon. On 15 December 1918, Alawite leader Saleh al-Ali called for a meeting of Alawite leaders in the town of Al-Shaykh Badr
Al-Shaykh Badr ( ar, الشيخ بدر, also spelled ''Sheikh Bader'') is a city in Syria, administratively belonging to Tartus Governorate. Al-Shaykh Badr has an altitude of 536 meters. As of 2008, it had a population of 47,982. Its inhabitant ...
, urging them to revolt and expel the French from Syria.
When French authorities heard about the meeting, they sent a force to arrest Saleh al-Ali. He and his men ambushed and defeated the French forces at Al-Shaykh Badr, inflicting more than 35 casualties. After this victory, al-Ali began organising his Alawite rebels into a disciplined force, with its own general command and military ranks.
The Al-Shaykh Badr skirmish began the Syrian Revolt of 1919
The Alawite revolt (also called the Shaykh Saleh al-Ali Revolt) was a rebellion, led by Shaykh Saleh al-Ali against the French authorities of the Occupied Enemy Territory Administration and later as part of the Franco-Syrian War against the new ...
. Al-Ali responded to French attacks by laying siege to (and occupying) al-Qadmus, from which the French had conducted their military operations against him. In November, General Henri Gouraud mounted a campaign against Saleh al-Ali's forces in the An-Nusayriyah Mountains. His forces entered al-Ali's village of Al-Shaykh Badr, arresting many Alawi leaders; however, Al-Ali fled to the north. When a large French force overran his positions, he went underground.
Despite these instances of opposition, the Alawites mostly favoured French rule and sought its continuation beyond the mandate period.
Alawite State
Jabal al-Druze
Jabal al-Druze ( ar, جبل الدروز, ''jabal ad-durūz'', ''Mountain of the Druze''), officially Jabal al-Arab ( ar, جبل العرب, links=no, ''jabal al-ʿarab'', ''Mountain of the Arabs''), is an elevated volcanic region in the As-Suw ...
for the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
. Aleppo and Damascus were also separate states.Longrigg, Stephen Hemsley. ''Syria and Lebanon Under French Mandate''. London: Oxford University Press, 1958. Under the Mandate, many Alawite chieftains supported a separate Alawite nation, and tried to convert their autonomy into independence.
The French Mandate Administration encouraged Alawites to join their military forces, in part to provide a counterweight to the Sunni majority (which was more hostile to their rule). According to a 1935 letter by the French minister of war, the French considered the Alawites and the Druze
The Druze (; ar, دَرْزِيٌّ, ' or ', , ') are an Arabic-speaking esoteric ethnoreligious group from Western Asia who adhere to the Druze faith, an Abrahamic, monotheistic, syncretic, and ethnic religion based on the teachings of ...
the only " warlike races" in the Mandate territories. Between 1926 and 1939, the Alawites and other minority groups provided the majority of the locally recruited component of the Army of the Levant
The Army of the Levant (french: Armée du Levant) identifies the armed forces of France and then Vichy France which occupied, and were in part recruited from, the French Mandated territories in the Levant during the interwar period and early W ...
- the designation given to the French military forces garrisoning Syria and the Lebanon.
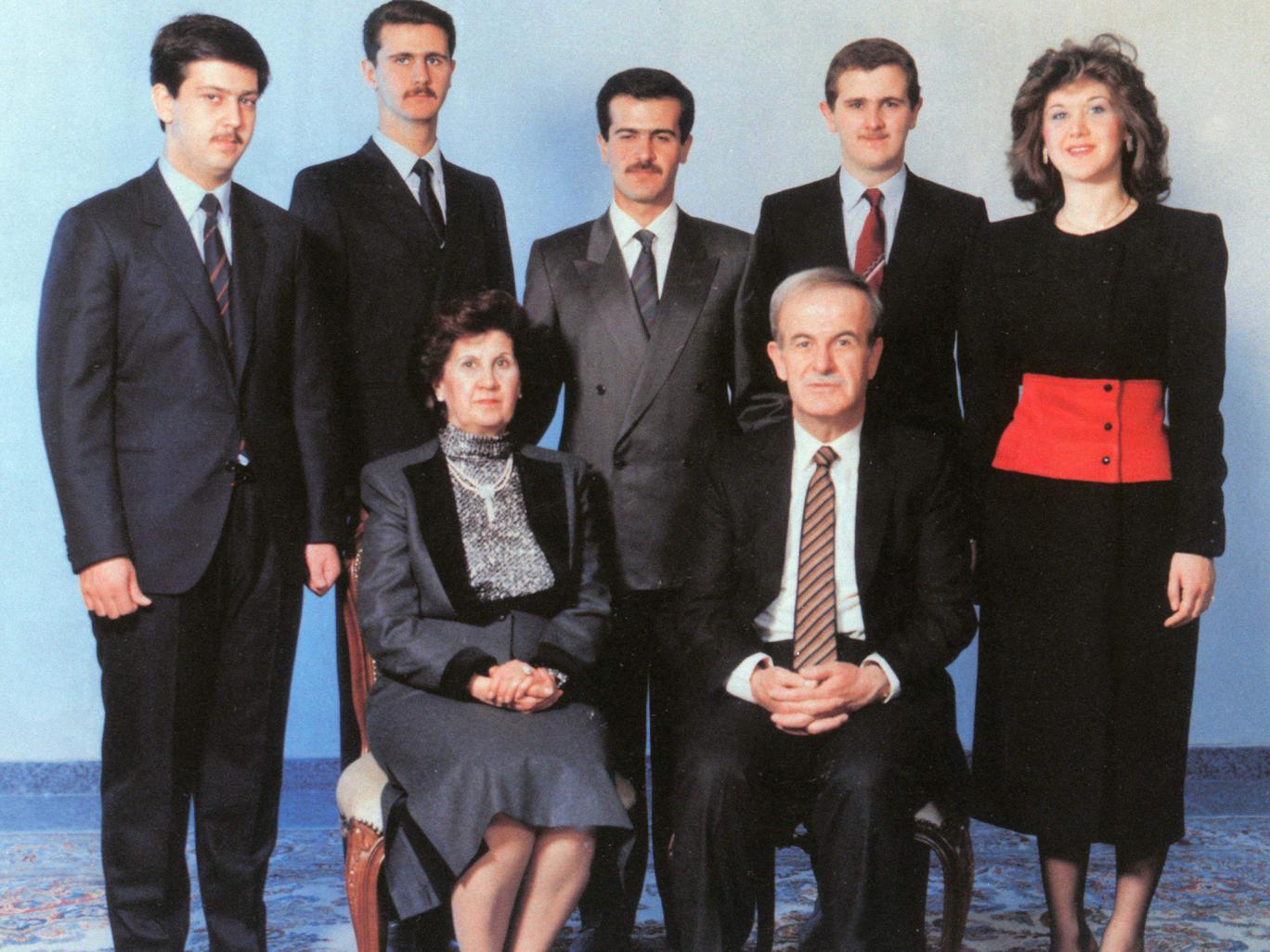
The region was home to a mostly-rural, heterogeneous population. The landowning families and 80 percent of the population of the port city of Latakia were Sunni Muslim; however, in rural areas 62 percent of the population were Alawite peasants. According to some researchers, there was considerable Alawite separatist sentiment in the region, their evidence is a 1936 letter signed by 80 Alawi leaders addressed to the French Prime Minister which said that the "Alawite people rejected attachment to Syria and wished to stay under French protection". Among the signatories was Sulayman Ali al-Assad
Ali ibn Sulayman al-Assad ( né al-Wahsh ; 1875 – 1963) was a Syrian farmer, tribal leader, and religious authority best known as the father of former Syrian President Hafez al-Assad and grandfather of current Syrian President Bashar al-Assa ...
, father of Hafez al-Assad.Khoury, Philip S. ''Syria and the French Mandate: The Politics of Arab Nationalism, 1920–1945''. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1987. However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. Even during this time of increased Alawite rights, the situation was still so bad for the group that many women had to leave their homes to work for urban Sunnis.
In May 1930, the Alawite State was renamed the Government of Latakia in one of the few concessions by the French to Arab nationalists before 1936. Nevertheless, on 3 December 1936 the Alawite State was re-incorporated into Syria as a concession by the French to the National Bloc (the party in power in the semi-autonomous Syrian government). The law went into effect in 1937.Shambrook, Peter A. ''French Imperialism in Syria, 1927–1936''. Reading: Ithaca Press, 1998.
 In 1939, the Sanjak of Alexandretta (now
In 1939, the Sanjak of Alexandretta (now Hatay
Hatay Province ( tr, Hatay ili, ) is the southernmost province of Turkey. It is situated almost entirely outside Anatolia, along the eastern coast of the Levantine Sea. The province borders Syria to its south and east, the Turkish province ...
) contained a large number of Alawites. The Hatayan land was given to Turkey by the French after a League of Nations plebiscite
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of ...
in the province. This development greatly angered most Syrians; to add to Alawi contempt, in 1938, the Turkish military went into İskenderun and expelled most of the Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Armenian population. Before this, the Alawite Arabs and Armenians comprised most of the province's population. Zaki al-Arsuzi
Zaki al-Arsuzi ( ar, زكي الأرسوزي, Zakī al-Arsūzī; June 18992 July 1968) was a Syrian philosopher, philologist, sociologist, historian, and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and i ...
, a young Alawite leader from Iskandarun province in the Sanjak of Alexandretta who led the resistance to the province's annexation by the Turks, later became a co-founder of the Ba'ath Party
The Arab Socialist Baʿath Party ( ar, حزب البعث العربي الاشتراكي ' ) was a political party founded in Syria by Mishel ʿAflaq, Ṣalāḥ al-Dīn al-Bītār, and associates of Zaki al-ʾArsūzī. The party espoused ...
with Eastern Orthodox Christian schoolteacher Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq ( ar, ميشيل عفلق, Mīšīl ʿAflaq, , 9 January 1910 – 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociologist and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its politica ...
and Sunni politician Salah ad-Din al-Bitar
Salah al-Din al-Bitar ( ar, صلاح الدين البيطار, Ṣalāḥ ad-Dīn al-Biṭār; 1 January 1912 – 21 July 1980) was a Syrian politician who co-founded the Arab Ba'ath Party with Michel Aflaq in the early 1940s. As student ...
.
After World War II, Sulayman al-Murshid
Sulayman al-Murshid ( ar, سليمان المرشد; 1907 – 16 December 1946) was a Syrian Alawi religious figure, political leader, and the founder of al-Murshidyah religious sect.
Early beginnings
Sulayman al-Murshid was born as Sulayman Yunu ...
played a major role in uniting the Alawite province with Syria. He was executed by the Syrian government in Damascus on 12 December 1946, only three days after a political trial.
After Syrian independence
 Syria became independent on 17 April 1946. In 1949, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Syria experienced a number of military coups and the rise of the Ba'ath Party.
In 1958, Syria and Egypt were united by a political agreement into the
Syria became independent on 17 April 1946. In 1949, after the 1948 Arab–Israeli War, Syria experienced a number of military coups and the rise of the Ba'ath Party.
In 1958, Syria and Egypt were united by a political agreement into the United Arab Republic
The United Arab Republic (UAR; ar, الجمهورية العربية المتحدة, al-Jumhūrīyah al-'Arabīyah al-Muttaḥidah) was a sovereign state in the Middle East from 1958 until 1971. It was initially a political union between Eg ...
. The UAR lasted for three years, breaking apart in 1961, when a group of army officers seized power and declared Syria independent.
A succession of coups ensued until, in 1963, a secretive military committee (including Alawite officers Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad ', , (, 6 October 1930 – 10 June 2000) was a Syrian statesman and military officer who served as President of Syria from taking power in 1971 until his death in 2000. He was also Prime Minister of Syria from 1970 to 1 ...
and Salah Jadid) helped the Ba'ath Party seize power. In 1966, Alawite-affiliated military officers successfully rebelled and expelled the Ba’ath Party old guard followers of Greek Orthodox
The term Greek Orthodox Church ( Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also cal ...
Christian Michel Aflaq
Michel Aflaq ( ar, ميشيل عفلق, Mīšīl ʿAflaq, , 9 January 1910 – 23 June 1989) was a Syrian philosopher, sociologist and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and its politica ...
and Sunni Muslim Salah ad-Din al-Bitar
Salah al-Din al-Bitar ( ar, صلاح الدين البيطار, Ṣalāḥ ad-Dīn al-Biṭār; 1 January 1912 – 21 July 1980) was a Syrian politician who co-founded the Arab Ba'ath Party with Michel Aflaq in the early 1940s. As student ...
, calling Zaki al-Arsuzi
Zaki al-Arsuzi ( ar, زكي الأرسوزي, Zakī al-Arsūzī; June 18992 July 1968) was a Syrian philosopher, philologist, sociologist, historian, and Arab nationalist. His ideas played a significant role in the development of Ba'athism and i ...
the "Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no t ...
" of the reconstituted Ba'ath Party.
In 1970, Air Force
An air force – in the broadest sense – is the national military branch that primarily conducts aerial warfare. More specifically, it is the branch of a nation's armed services that is responsible for aerial warfare as distinct from an ...
General Hafez al-Assad, an Alawite, took power and instigated a "Corrective Movement" in the Ba'ath Party. The coup of 1970 ended the political instability which had existed since independence. Robert D. Kaplan compared Hafez al-Assad's coming to power to "an untouchable
Untouchable or The Untouchable may refer to:
People
* Untouchability, the practice of socially ostracizing a minority group of very low social status
** A word for the Dalits or Scheduled Caste of India, a group that experiences untouchability
* ...
becoming maharaja
Mahārāja (; also spelled Maharajah, Maharaj) is a Sanskrit title for a "great ruler", "great king" or " high king".
A few ruled states informally called empires, including ruler raja Sri Gupta, founder of the ancient Indian Gupta Empire, a ...
h in India or a Jew becoming tsar in Russia—an unprecedented development shocking to the Sunni majority population which had monopolized power for so many centuries". In 1971, al-Assad declared himself president of Syria, a position the constitution at the time permitted only for Sunni Muslims. In 1973, a new constitution was adopted, replacing Islam as the state religion with a mandate that the president's religion be Islam, and protests erupted. In 1974, to satisfy this constitutional requirement, Musa as-Sadr
Musa Sadr al-Din al-Sadr ( ar, موسى صدر الدين الصدر; 4 June 1928 – disappeared 31 August 1978) was an Iranian-born Lebanese scholar and political leader who founded the Amal Movement.
Born in the Chaharmardan neighborhood o ...
(a leader of the Twelvers of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
and founder of the Amal Movement, who had unsuccessfully sought to unite Lebanese Alawites and Shiites under the Supreme Islamic Shiite Council)Riad Yazbeck.Return of the Pink Panthers?
" ''Mideast Monitor''. Vol. 3, No. 2, August 2008. issued a
fatwa
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist ...
that Alawites were a community of Twelver Shiite Muslims.''The New Encyclopedia of Islam'' by Cyril Glasse, Altamira, 2001, p.36–7 Under the authoritarian, secular, Assad government, religious minorities were tolerated more than before, but political dissidents were not. In 1982, when the Muslim Brotherhood mounted an anti-government Islamist insurgency
An insurgency is a violent, armed rebellion against authority waged by small, lightly armed bands who practice guerrilla warfare from primarily rural base areas. The key descriptive feature of insurgency is its asymmetric nature: small irr ...
, Hafez Assad staged a military offensive against them known as the Hama massacre.
Syrian Civil War
During the Syrian Civil War, many pro-opposition pundits believe the Alawites have suffered as a result of their support for the Assad government against the mainly Sunni opposition, with one journalist claiming up to a third of young Alawite men killed in the increasingly sectarian conflict. Some have claimed many Alawites fear a negative outcome for the government in the conflict would result in an existential threat to their community. In May 2013, pro opposition SOHR stated that out of 94,000 Syrian regime soldiers killed during the war, at least 41,000 were Alawites. In April 2017, a pro-opposition source claimed 150,000 young Alawites had died. However, these claims by pro-opposition pundits and sources have been considered highly exaggerated, unsubstantiated (statistically or scientifically), among neutral observers across the globe. The Alawites faced significant danger during the Syrian Civil War; particularly from Islamic groups who were a part of the opposition, though often denied by secular oppositionists. In 2022, a professor in the opposition-founded Idlib University (internationally unrecognized) performed a speech in which he expressed negative views on the ethnoreligious minority saying "the Alawite sect has only been able to produce violent mercenaries", claiming there are no scientists or intellectuals descending from the minority. Notably, Uğur Şahin; descending from an Alawite family from the city of Iskenderun in which the ethnoreligious group has a significant presence, has been internationally accredited for being the developer of the Pfizer vaccine against COVID-19 and the CEO of BioNTech.Beliefs
 Alawites and their beliefs have been described as "secretive""Alawi Islam"
Alawites and their beliefs have been described as "secretive""Alawi Islam"Globalsecurity.org (Yaron Friedman, for example, in his scholarly work on the sect, has written that the Alawi religious material quoted in his book came only from "public libraries and printed books" since the "sacred writings" of the Alawi "are kept secret"); some tenets of the faith are kept secret from most Alawi and known only to a select few, Friedman, ''Nuṣayrī-ʿAlawīs'', 2010: p.xii they have therefore been described as a mystical sect. Alawite beliefs have never been confirmed by their modern religious authorities.'Abd al‑Latif al‑Yunis, Mudhakkirat al‑Duktur 'Abd al‑Latif al‑Yunis, Damascus: Dar al‑'Ilm, 1992, p. 63. Alawites tend to conceal their beliefs ('' taqiyya'') due to historical persecution.
Theology and practices
Alawite doctrine incorporatesIslamic
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ma ...
, Gnostic
Gnosticism (from grc, γνωστικός, gnōstikós, , 'having knowledge') is a collection of religious ideas and systems which coalesced in the late 1st century AD among Jewish and early Christian sects. These various groups emphasized p ...
, neo-Platonic
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some id ...
, Christian (for example, they celebrate Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
including the consecration of bread and wine) and other elements and has, therefore, been described as syncretic.
According to an article that appeared in ''The Telegraph'', the 1995 edition of ''The Oxford Encyclopedia of the Modern Islamic World'' allegedly describes them as "extremist" Shia whose "religious system separates them from Sunni Muslims."
Reincarnation
Alawites hold that they were originally stars or divine lights that were cast out of heaven through disobedience and must undergo repeatedreincarnation
Reincarnation, also known as rebirth or transmigration, is the philosophical or religious concept that the non-physical essence of a living being begins a new life in a different physical form or body after biological death. Resurrectio ...
(or metempsychosis) before returning to heaven. In addition, according to the Israeli Begin–Sadat Center for Strategic Studies
The Begin–Sadat Center for Strategic Studies (BESA Center) is an Israeli think tank affiliated with Bar-Ilan University and supported by the NATO ''Mediterranean Initiative'', conducting policy-relevant research on Middle Eastern and global st ...
, they believe that God might have incarnated twice; the first incarnation was Joshua
Joshua () or Yehoshua ( ''Yəhōšuaʿ'', Tiberian: ''Yŏhōšuaʿ,'' lit. 'Yahweh is salvation') ''Yēšūaʿ''; syr, ܝܫܘܥ ܒܪ ܢܘܢ ''Yəšūʿ bar Nōn''; el, Ἰησοῦς, ar , يُوشَعُ ٱبْنُ نُونٍ '' Yūšaʿ ...
who conquered Canaan
Canaan (; Phoenician: 𐤊𐤍𐤏𐤍 – ; he, כְּנַעַן – , in pausa – ; grc-bib, Χανααν – ;The current scholarly edition of the Greek Old Testament spells the word without any accents, cf. Septuaginta : id est Vetus T ...
, and the second was the fourth Caliph, Ali.
Other beliefs
 Other beliefs and practices include: the consecration of wine in a secret form of
Other beliefs and practices include: the consecration of wine in a secret form of Mass
Mass is an intrinsic property of a body. It was traditionally believed to be related to the quantity of matter in a physical body, until the discovery of the atom and particle physics. It was found that different atoms and different ele ...
performed only by males; frequently being given Christian name
A Christian name, sometimes referred to as a baptismal name, is a religious personal name given on the occasion of a Christian baptism, though now most often assigned by parents at birth. In English-speaking cultures, a person's Christian nam ...
s; entombing the dead in sarcophagi above ground; observing Epiphany, Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a religious and cultural celebration among billions of people around the world. A feast central to the Christian liturgical year ...
and the feast days of John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his preaching and public speaking, his denunciation of ...
and Mary Magdalene; the only religious structures they have are the shrines of tombs; the book ''Kitab al-Majmu
Kitab al-Majmu‘ ( ar, كتاب المجموع "The Book of the Collection") is a book which is claimed by some Sunni Muslims and former Alawites to be the main source of teaching of the ‘Alawi sect of Islam.Glassé, Cyril. 2008. The New Encyc ...
'', which is allegedly a central source of Alawite doctrine, where they have their own trinity, comprising Mohammed, Ali, and Salman the Persian.
In addition, they celebrate different holidays such as Old New Year
The Old New Year or the Orthodox New Year is an informal traditional holiday, celebrated as the start of the New Year by the Julian calendar. In the 20th and 21st centuries, the Old New Year falls on January 14 in the Gregorian calendar.
This tra ...
, Akitu
Akitu or Akitum is a spring festival held on the first day of Nisan in ancient Mesopotamia, to celebrate the sowing of barley. The Assyrian and Babylonian Akitu festival has played a pivotal role in the development of theories of religion, myth ...
, Eid al-Ghadir, Mid-Sha'ban and Eid il-Burbara
Eid il-Burbara or Saint Barbara's Day ( ar, عيد البربارة), and also called the Feast of Saint Barbara, is a holiday annually celebrated on 17 December (Gregorian calendar) or 4 December (Julian calendar) amongst Middle Eastern Christ ...
. They also believe in intercession
Intercession or intercessory prayer is the act of praying to a deity on behalf of others, or asking a saint in heaven to pray on behalf of oneself or for others.
The Apostle Paul's exhortation to Timothy specified that intercession prayers sh ...
of certain legendary saints such as Khidr (Saint George
Saint George ( Greek: Γεώργιος (Geórgios), Latin: Georgius, Arabic: القديس جرجس; died 23 April 303), also George of Lydda, was a Christian who is venerated as a saint in Christianity. According to tradition he was a soldie ...
) and Simeon Stylites.
Evolution
Yaron Friedman and many researchers of Alawi doctrine write that the founder of the religion, Ibn Nusayr, did not necessarily believe he was representative of a splinter, rebel group of the Shias, but rather believed he held the true doctrine of the Shias, and most of the aspects that are similar toChristianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
are considered more a coincidence and not a direct influence from it, as well as other external doctrines that were actually popular among Shia esoteric groups in Basra in the 8th century. According to Friedman and other scholars, the Alawi movement started as many other mystical ghulat sects with an explicit concentration on an allegorical and esoteric meaning of the Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , ...
and other mystical practices, and not as a pure syncretic sect, though later, they embraced some other practices as they believed all religions had the same ''Batin'' core.
Journalist Robert F. Worth
Robert Forsyth Worth (born September 29, 1965) is an American journalist and former chief of ''The New York Times'' Beirut bureau. He is the author of ''Rage for Order''.
Life
Born and raised in Manhattan, Worth has an M.A. and a Ph.D. (in Engli ...
argues that the idea that the Alawi religion as a branch of Islam is a rewriting of history made necessary by the French colonialists' abandonment of the Alawi and departure from Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
. Worth describes the "first ... authentic source for outsiders about the religion" (written by Soleyman of Adana – a 19th-century Alawi convert to Christianity who broke his oath of secrecy on the religion) explaining that the Alawi (according to Soleyman) deified Ali, venerated Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label= Hebrew/ Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and relig ...
, Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mon ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no t ...
, and Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of ...
, and held themselves apart from Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
, whom they considered heretics. Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.82
According to a disputed letter, in 1936, six Alawi notables petitioned the French colonialists not to merge their Alawi enclave with the rest of Syria, insisting that "the spirit of hatred and fanaticism embedded in the hearts of the Arab Muslims against everything that is non-Muslim has been perpetually nurtured by the Islamic religion". Worth, ''A Rage for Order'', 2016: p.85 However, according to associate professor Stefan Winter, this letter is a forgery. According to Worth, later ''fatwa
A fatwā ( ; ar, فتوى; plural ''fatāwā'' ) is a legal ruling on a point of Islamic law (''sharia'') given by a qualified '' Faqih'' (Islamic jurist) in response to a question posed by a private individual, judge or government. A jurist ...
s'' declaring Alawi to be part of the Shia community were by Shia clerics "eager for Syrian patronage" from Syria's Alawi president Hafez al-Assad
Hafez al-Assad ', , (, 6 October 1930 – 10 June 2000) was a Syrian statesman and military officer who served as President of Syria from taking power in 1971 until his death in 2000. He was also Prime Minister of Syria from 1970 to 1 ...
, who was eager for Islamic legitimacy in the face of the hostility of Syria's Muslim majority.
Yaron Friedman does not suggest that Alawi did not consider themselves Muslims, but does state that:
According to Peter Theo Curtis, the Alawi religion underwent a process of "Sunnification" during the years under Hafez Al Assad's rule, so that Alawites became not Shia, but effectively Sunni. Public manifestation or "even mentioning of any Alawite religious activities" was banned, as were any Alawite religious organizations or "any formation of a unified religious council" or a higher Alawite religious authority. "Sunni-style" mosques were built in every Alawite village, and Alawi were encouraged to perform Hajj
The Hajj (; ar, حَجّ '; sometimes also spelled Hadj, Hadji or Haj in English) is an annual Islamic pilgrimage to Mecca, Saudi Arabia, the holiest city for Muslims. Hajj is a mandatory religious duty for Muslims that must be carried o ...
.
Opinions on position within Islam
The Sunni Grand Mufti of Jerusalem, Haj Amin al-Husseini, issued a ''fatwa'' recognizing them as part of the Muslim community in the interest ofArab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language ...
. However, other Sunni scholars such as the Syrian historian Ibn Kathir have categorised Alawites as non-Muslim and mushrikeen ( polytheists), in their writings;Abd-Allah, Umar F., ''Islamic Struggle in Syria'', Berkeley : Mizan Press, c1983, pp. 43–48 with Ibn Taymiyya
Ibn Taymiyyah (January 22, 1263 – September 26, 1328; ar, ابن تيمية), birth name Taqī ad-Dīn ʾAḥmad ibn ʿAbd al-Ḥalīm ibn ʿAbd al-Salām al-Numayrī al-Ḥarrānī ( ar, تقي الدين أحمد بن عبد الحليم � ...
arguably being the most virulent anti-Alawite in his fatwas, accusing them of aiding the Crusader and Mongol enemies of the Muslims. Other Sunni scholars, such as Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111; ), full name (), and known in Persian-speaking countries as Imam Muhammad-i Ghazali (Persian: امام محمد غزالی) or in Medieval Europe by the Latinized as Algazelus or Algazel, was a Persian poly ...
, also considered them as non-Muslims. Benjamin Disraeli, in his novel ''Tancred
Tancred or Tankred is a masculine given name of Germanic origin that comes from ''thank-'' (thought) and ''-rath'' (counsel), meaning "well-thought advice". It was used in the High Middle Ages mainly by the Normans (see French Tancrède) and espe ...
'', also expressed the view that Alawites are not Shia Muslims.
Historically, Twelver Shia scholars (such as Shaykh Tusi
Shaykh Tusi ( fa, شیخ طوسی), full name ''Abu Jafar Muhammad Ibn Hassan Tusi'' ( ar, ابو جعفر محمد بن حسن طوسی), known as Shaykh al-Taʾifah ( ar, links=no, شيخ الطائفة) was a prominent Persian scholar of th ...
) did not consider Alawites as Shia Muslims while condemning their heretical beliefs. Ibn Taymiyyah also said that Alawites are not Muslims.
In 2016, according to several international media reports, an unspecified number of Alawite community leaders released a "Declaration of an Alawite Identity Reform" (of the Alawite community). The manifesto presents Alawism a current "within Islam" and rejects attempts to incorporate the Alawite community into Twelver Shiism. The document was interpreted as an attempt by representatives of the Alawite community to overcome the sectarian polarisation and to distance themselves from the growing Sunni-Shia divide in the Middle East.
According to Matti Moosa,
The Christian elements in the Nusayri religion are unmistakable. They include the concept of trinity; the celebration of Christmas, the consecration of the Qurbana, that is, the sacrament of the flesh and blood which Christ offered to his disciples, and, most important, the celebration of the Quddas (a lengthy prayer proclaiming the divine attributes of Ali and the personification of all the biblical patriarchs fromAdam Adam; el, Ἀδάμ, Adám; la, Adam is the name given in Genesis 1-5 to the first human. Beyond its use as the name of the first man, ''adam'' is also used in the Bible as a pronoun, individually as "a human" and in a collective sense as " ...to Simon Peter, founder of the Church, who is seen, paradoxically, as the embodiment of true Islam).
Barry Rubin
Barry M. Rubin (28 January 1950 – February 3, 2014) was an American-born Israeli writer and academic on terrorism and Middle Eastern affairs.
Career
Rubin was the director of the Global Research in International Affairs (GLORIA) Center, editor ...
has suggested that Syrian leader Hafez al-Assad and his son and successor Bashar al-Assad
Bashar Hafez al-Assad, ', Levantine pronunciation: ; (, born 11 September 1965) is a Syrian politician who is the 19th president of Syria, since 17 July 2000. In addition, he is the commander-in-chief of the Syrian Armed Forces and the ...
pressed their fellow Alawites "to behave like 'regular Muslims', shedding (or at least concealing) their distinctive aspects". During the early 1970s, a booklet, ''al-'Alawiyyun Shi'atu Ahl al-Bait'' ("The Alawites are Followers of the Household of the Prophet") was published, which was "signed by numerous 'Alawi' men of religion", described the doctrines of the Imami Shia as Alawite. Additionally, there has been a recent movement to unite Alawism and the other branches of Twelver Islam through educational exchange programs in Syria and Qom
Qom (also spelled as "Ghom", "Ghum", or "Qum") ( fa, قم ) is the seventh largest metropolis and also the seventh largest city in Iran. Qom is the capital of Qom Province. It is located to the south of Tehran. At the 2016 census, its pop ...
.
 Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime. Joshua Landis, director of the Center for Middle East Studies, writes that Hafiz al-Assad "tried to turn Alawites into 'good' (read Sunnified) Muslims in exchange for preserving a modicum of secularism and tolerance in society". On the other hand, Al-Assad "declared the Alawites to be nothing but Twelver Shiites".Syrian comment. Asad's Alawi dilemma
Some sources have discussed the "Sunnification" of Alawites under the al-Assad regime. Joshua Landis, director of the Center for Middle East Studies, writes that Hafiz al-Assad "tried to turn Alawites into 'good' (read Sunnified) Muslims in exchange for preserving a modicum of secularism and tolerance in society". On the other hand, Al-Assad "declared the Alawites to be nothing but Twelver Shiites".Syrian comment. Asad's Alawi dilemma8 October 2004 In a paper, "Islamic Education in Syria", Landis wrote that "no mention" is made in Syrian textbooks (controlled by the Al-Assad regime) of Alawites, Druze, Ismailis or Shia Islam; Islam was presented as a monolithic religion. Ali Sulayman al-Ahmad, chief judge of the Baathist Syrian state, has said:
Population

Syria
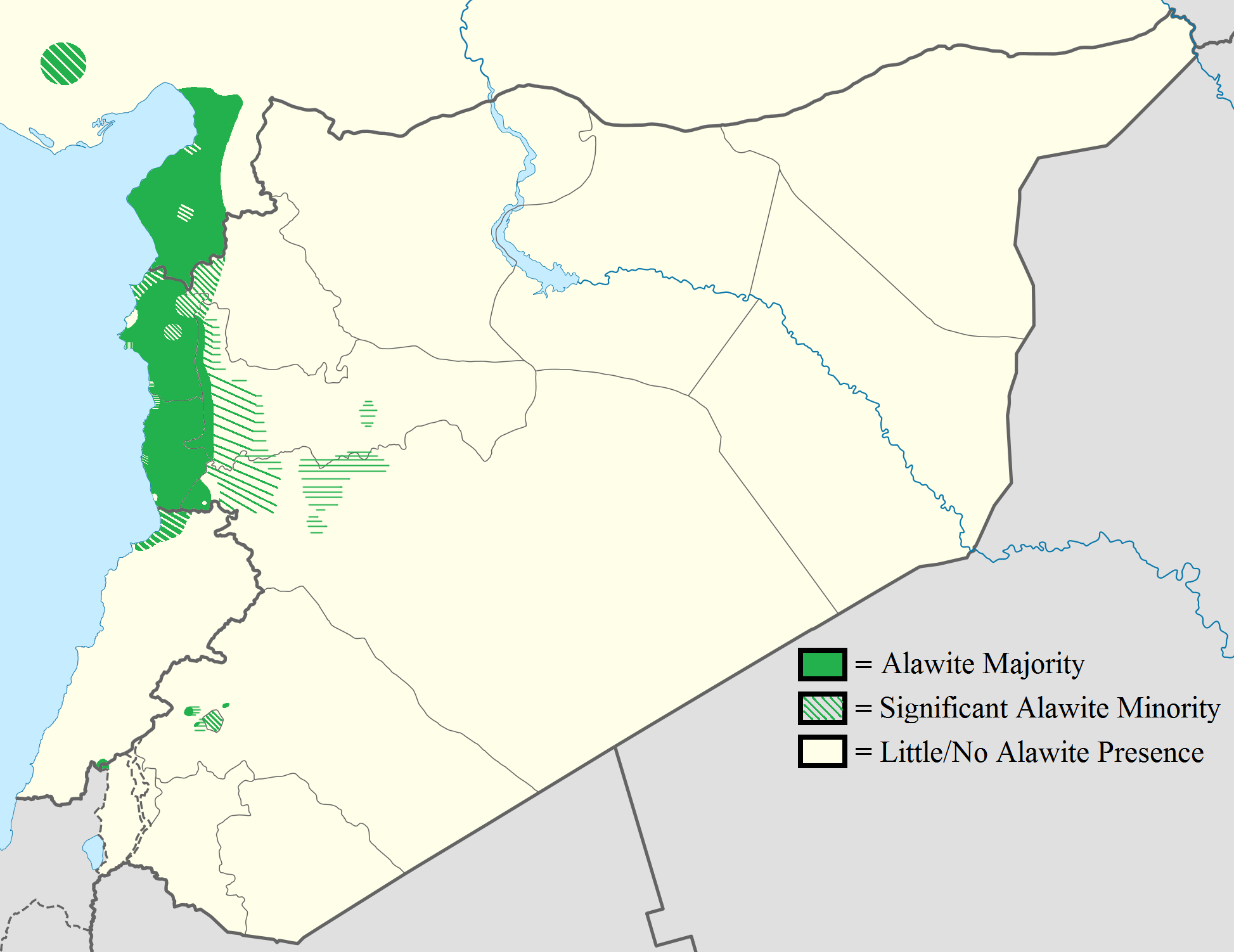
Alawites have traditionally lived in the Coastal Mountain Range, along the Mediterranean coast of Syria. Latakia andTartus
)
, settlement_type = City
, image_skyline =
, imagesize =
, image_caption = Tartus corniche Port of Tartus • Tartus beach and boulevard Cathedral of Our Lady of Tortosa • Al-Assad Stadium&n ...
are the region's principal cities. They are also concentrated in the plains around Hama
Hama ( ar, حَمَاة ', ; syr, ܚܡܬ, ħ(ə)mɑθ, lit=fortress; Biblical Hebrew: ''Ḥamāṯ'') is a city on the banks of the Orontes River in west-central Syria. It is located north of Damascus and north of Homs. It is the provincial ...
and Homs
ar, حمصي, Himsi
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_t ...
. Alawites also live in Syria's major cities, and are estimated at 11 percent of the country's population
There are four Alawite confederations — Kalbiyya, Khaiyatin, Haddadin, and Matawirah – each divided into tribes based on their geographical origins or their main religious leader, such as Ḥaidarīya of Alī Ḥaidar, and Kalāziyya of Sheikh Muḥammad ibn Yūnus from the village Kalāzū near Antakya
Antakya (), historically known as Antioch ( el, Ἀντιόχεια; hy, Անտիոք, Andiok), is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes River, ...
. Those Alawites are concentrated in the Latakia region of Syria, extending north to Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
(Antakya
Antakya (), historically known as Antioch ( el, Ἀντιόχεια; hy, Անտիոք, Andiok), is the capital of Hatay Province, the southernmost province of Turkey. The city is located in a well-watered and fertile valley on the Orontes River, ...
), Turkey, and in and around Homs and Hama.
Before 1953, Alawites held specifically reserved seats in the Syrian Parliament, in common with all other religious communities. After that (including the 1960 census), there were only general Muslim and Christian categories, without mention of subgroups, to reduce sectarianism (''taifiyya'').
Turkey
 To avoid confusion with the ethnic-Turkish and Kurdish
To avoid confusion with the ethnic-Turkish and Kurdish Alevis
Alevism or Anatolian Alevism (; tr, Alevilik, ''Anadolu Aleviliği'' or ''Kızılbaşlık''; ; az, Ələvilik) is a local Islamic tradition, whose adherents follow the mystical Alevi Islamic ( ''bāṭenī'') teachings of Haji Bektash Veli, ...
, the Alawites call themselves ''Arap Alevileri'' ("Arab Alevis") in Turkish. The term ''Nusayrī'', previously used in theological texts, has been revived in recent studies. In Çukurova, Alawites are known as '' Fellah'' and ''Arabuşağı'' (although the latter is considered offensive) by the Sunni population. A quasi-official name used during the 1930s by Turkish authorities was ''Eti Türkleri'' ("Hittite Turks"), to conceal their Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
origins. Although this term is obsolete, it is still used by some older people as a euphemism
A euphemism () is an innocuous word or expression used in place of one that is deemed offensive or suggests something unpleasant. Some euphemisms are intended to amuse, while others use bland, inoffensive terms for concepts that the user wishes ...
.
In 1939, the Alawites accounted for some 40 percent of the population of the province of Iskenderun. According to French geographer Fabrice Balanche, relations between the Alawites of Turkey and the Alawites of Syria are limited. Community ties were broken by the Turkification policy and the decades-long closure of the Syria-Turkey border.
The exact number of Alawites in Turkey is unknown; there were 185,000 in 1970. As Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
s, they are not recorded separately from Sunnis. In the 1965 census (the last Turkish census where informants were asked their mother tongue), 185,000 people in the three provinces declared their mother tongue as Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
; however, Arabic-speaking Sunnis and Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ� ...
were also included in this figure. Turkish Alawites traditionally speak the same dialect of Levantine Arabic as Syrian Alawites. Arabic is preserved in rural communities and in Samandağ
Samandağ ( ar, السويدية, ''as-Sūwaydīyah''), formerly known as Süveydiye, is a town and district in Hatay Province of southern Turkey, at the mouth of the Asi River on the Mediterranean coast, near Turkey's border with Syria, from the ...
. Younger people in the cities of Çukurova and İskenderun tend to speak Turkish. The Turkish spoken by Alawites is distinguished by its accents and vocabulary
A vocabulary is a set of familiar words within a person's language. A vocabulary, usually developed with age, serves as a useful and fundamental tool for communication and acquiring knowledge. Acquiring an extensive vocabulary is one of the ...
. Knowledge of the Arabic alphabet is confined to religious leaders and men who have worked or studied in Arab countries.
Alawites demonstrate considerable social mobility
Social mobility is the movement of individuals, families, households or other categories of people within or between social strata in a society. It is a change in social status relative to one's current social location within a given society ...
. Until the 1960s, they were bound to Sunni ''aghas'' (landholders) around Antakya and were poor. Alawites are prominent in the sectors of transportation and commerce and a large, professional middle class has emerged. Male exogamy has increased, particularly by those who attend universities or live in other parts of Turkey. These marriages are tolerated; however, female exogamy (as in other patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritan ...
groups) is discouraged.
Alawites, like Alevis, have strong leftist political beliefs. However, some people in rural areas (usually members of notable Alawite families) may support secular, conservative parties such as the Democratic Party. Most Alawites feel oppressed by the policies of the Presidency of Religious Affairs in Turkey (''Diyanet İşleri Başkanlığı'').
Lebanon
There are an estimated 40,000 Alawites in Lebanon, where they have lived since at least the 16th century. They are one of the 18 official Lebanese sects; due to the efforts of their leader, Ali Eid, the Taif Agreement of 1989 gave them two reserved seats in Parliament. Lebanese Alawites live primarily in the Jabal Mohsen neighbourhood of Tripoli and in 10 villages in the Akkar District, and are represented by the Arab Democratic Party. Their Mufti is Sheikh Assad Assi. TheBab al-Tabbaneh–Jabal Mohsen conflict
The Bab al-Tabbaneh–Jabal Mohsen conflict was a recurring conflict between the Sunni Muslim residents of the Bab-al-Tabbaneh neighbourhood and the Alawite residents of the Jabal Mohsen neighbourhood of Tripoli, Lebanon from 1976 through 2 ...
between pro-Syrian Alawites and anti-Syrian Sunnis has affected Tripoli for decades.
Golan Heights
There are also about 3,900 Alawites living in the village of Ghajar, which is located on the border between Lebanon and the Israeli-occupiedGolan Heights
The Golan Heights ( ar, هَضْبَةُ الْجَوْلَانِ, Haḍbatu l-Jawlān or ; he, רמת הגולן, ), or simply the Golan, is a region in the Levant spanning about . The region defined as the Golan Heights differs between di ...
. In 1932, the residents of Ghajar were given the option of choosing their nationality, and overwhelmingly chose to be a part of Syria, which has a sizable Alawite minority. Before the 1967 Arab-Israeli War
The Six-Day War (, ; ar, النكسة, , or ) or June War, also known as the 1967 Arab–Israeli War or Third Arab–Israeli War, was fought between Israel and a coalition of Arab states (primarily Egypt, Syria, and Jordan) from 5 to 10 Jun ...
, the residents of Ghajar were counted in the 1960 Syrian census. According to Joshua Project
The Joshua Project is a Christian organization based in Colorado Springs, United States, which seeks to coordinate the work of missionary organizations to track the ethnic groups of the world with the fewest followers of evangelical Christianity ...
, after Israel captured the Golan Heights from Syria, and after implementing Israeli civil law in 1981, the Alawite community chose to become Israeli citizens. However, according to Al-Marsad, Alawites were forced to undergo a process of naturalisation.
Language
Alawites in Syria speak a special dialect (part of Levantine Arabic) famous for the usage of letter ( qāf), but this feature is also shared with neighboring non-Alawites villages such as Idlib. Due to foreign occupation of Syria, the same dialect is characterized by multiple borrowings, mainly from Turkish and then French, especially terms used for imported inventions such as television, radio, elevator (ascenseur), etc.See also
* List of AlawitesNotes
References
Further reading
* * Kazimi, Nibras. ''Syria Through Jihadist Eyes: A Perfect Enemy'', Hoover Institution Press, 2010. . * * * RFWRfO2016 * * *External links
{{Authority control Arab groups Esoteric schools of thought Ethnoreligious groups in Asia Islam in Syria Islamic mysticism Shia communities Shia Islamic branches Ghulat sects