Age stratification on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
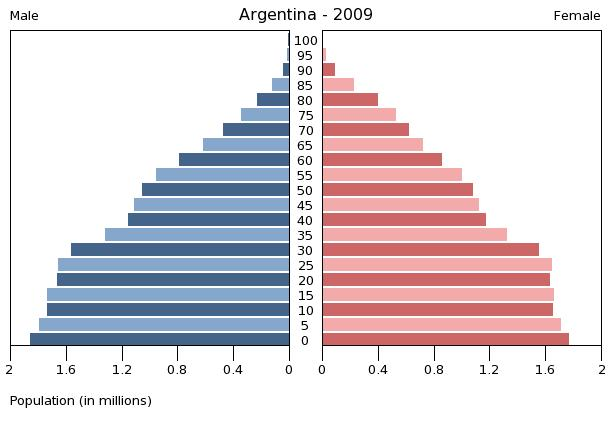 Age stratification is not a fixed phenomenon, but rather varies with the passage of time and between cultures and populations. Shifting age structure of a population changes the age stratification. As
Age stratification is not a fixed phenomenon, but rather varies with the passage of time and between cultures and populations. Shifting age structure of a population changes the age stratification. As
www.uic.edu.
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Age Stratification Actuarial science Population
sociology
Sociology is the scientific study of human society that focuses on society, human social behavior, patterns of Interpersonal ties, social relationships, social interaction, and aspects of culture associated with everyday life. The term sociol ...
, age stratification refers to the hierarchical
A hierarchy (from Greek: , from , 'president of sacred rites') is an arrangement of items (objects, names, values, categories, etc.) that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another. Hierarchy is an importan ...
ranking of people into age group
A demographic profile is a form of demographic analysis in which information is gathered about a group to better understand the group's composition or behaviors for the purpose of providing more relevant services.
In business, a demographic pro ...
s within a society
A society () is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. ...
. Age stratification could also be defined as a system of inequalities linked to age. In Western societies, for example, both the old and the young are perceived and treated as relatively incompetent and excluded from much social life. Age stratification based on an ascribed status
Ascribed status is a term used in sociology that refers to the social status of a person that is assigned at birth or assumed involuntarily later in life. The status is a position that is neither earned by the person nor chosen for them. It is g ...
is a major source inequality, and thus may lead to ageism
Ageism, also called agism in American English, is a type of discrimination based on one's age, generally used to refer to age-based discrimination against Old age, elderly people. The term was coined in 1969 by Robert Neil Butler to describe this ...
. Ageism is a social inequality resulting from age stratification. This is a sociological concept that comes with studying aging population. Age stratification within a population can have major implications, affecting things such as workforce trends, social norms, family structures, government policies, and even health outcomes.
Age structure
 Age stratification is not a fixed phenomenon, but rather varies with the passage of time and between cultures and populations. Shifting age structure of a population changes the age stratification. As
Age stratification is not a fixed phenomenon, but rather varies with the passage of time and between cultures and populations. Shifting age structure of a population changes the age stratification. As life expectancy
Human life expectancy is a statistical measure of the estimate of the average remaining years of life at a given age. The most commonly used measure is ''life expectancy at birth'' (LEB, or in demographic notation ''e''0, where '' ...
has increased dramatically in the last two centuries, the age strata by which people are characterized has changed. With people living longer lives than ever before in more developed areas of the world, there is now a category of "old-old" people which refers to persons ages 85+. Changes in the age structure of populations affects the way in which they distribute resources, along with a shift in expectations from different age strata. For example, as Japan's population has dramatically aged - with individuals aged 65+ accounting for approximately 25% of the population - the country has found itself with an unfavorable dependency ratio
The dependency ratio is an age-population ratio of those typically not in the labor force (the ''dependent'' part ages 0 to 14 and 65+) and those typically in the labor force (the ''productive'' part ages 15 to 64). It is used to measure the press ...
. In an effort to avoid economic downfall, the expectations of young-old and middle-old people have changed. Elderly citizens are encouraged to put off retirement, and the elderly tech market is booming.
Age discrimination
Age is a major component of entry and exit for many parts of life – school, starting a family, retirement, etc. Shifting social status with age can lead toageism
Ageism, also called agism in American English, is a type of discrimination based on one's age, generally used to refer to age-based discrimination against Old age, elderly people. The term was coined in 1969 by Robert Neil Butler to describe this ...
. Discrimination
Discrimination is the process of making unfair or prejudicial distinctions between people based on the groups, classes, or other categories to which they belong or are perceived to belong, such as race, gender, age, class, religion, or sex ...
by a person's age can have profound impacts on the way a society operates – including behavioral expectations, the distribution of resources, and even policies and laws.
Workplace
In the United States, discrimination on the basis of one's age is prohibited in the workplace by the Age Discrimination in Employment Act of 1967. Enforced by theEqual Employment Opportunity Commission
The U.S. Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) is a federal agency that was established via the Civil Rights Act of 1964 to administer and enforce civil rights laws against workplace discrimination. The EEOC investigates discrimination ...
, the act is meant to keep employers unbiased in regards to age when dealing with hiring, promotions, terms, etc. The law also makes it illegal for employees to be harassed due to their age. Emergence of new occupations can lead to a polarization of age cohorts by workforce. As a result, a quick shift of the occupational distribution increases occupational age discrimination.
Health outcomes
The unequal distribution of resources and social support between age strata can lead tohealth disparities
Health equity arises from access to the social determinants of health, specifically from wealth, power and prestige. Individuals who have consistently been deprived of these three determinants are significantly disadvantaged from health inequit ...
in the population. In the U.S., evidence indicates older adults face higher risk of experiencing depression and other mental health issues.
See also
*Gerontology
Gerontology ( ) is the study of the social, culture, cultural, psychology, psychological, cognitive, and biology, biological aspects of aging. The word was coined by Ilya Ilyich Mechnikov in 1903, from the Ancient Greek, Greek ('), meaning "o ...
References
Further reading
* * *External links
www.uic.edu.
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Age Stratification Actuarial science Population