Acari on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mites are small
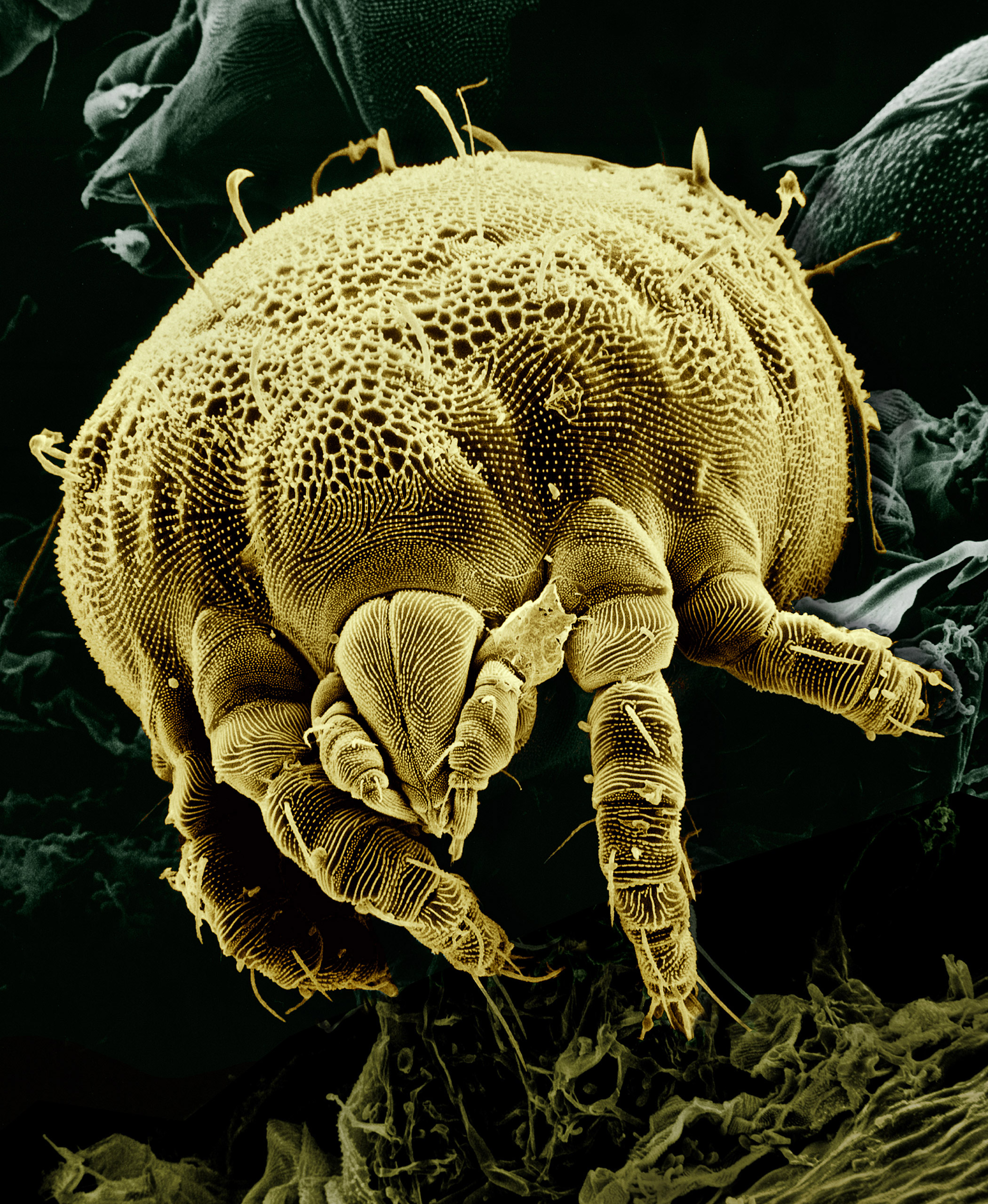 The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachnids, the
The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachnids, the
 The mite fossil record is sparse, due to their small size and low preservation potential. The oldest fossils of acariform mites are from the
The mite fossil record is sparse, due to their small size and low preservation potential. The oldest fossils of acariform mites are from the
 At the front of the body is the
At the front of the body is the
 The sexes are separate in mites; males have a pair of
The sexes are separate in mites; males have a pair of
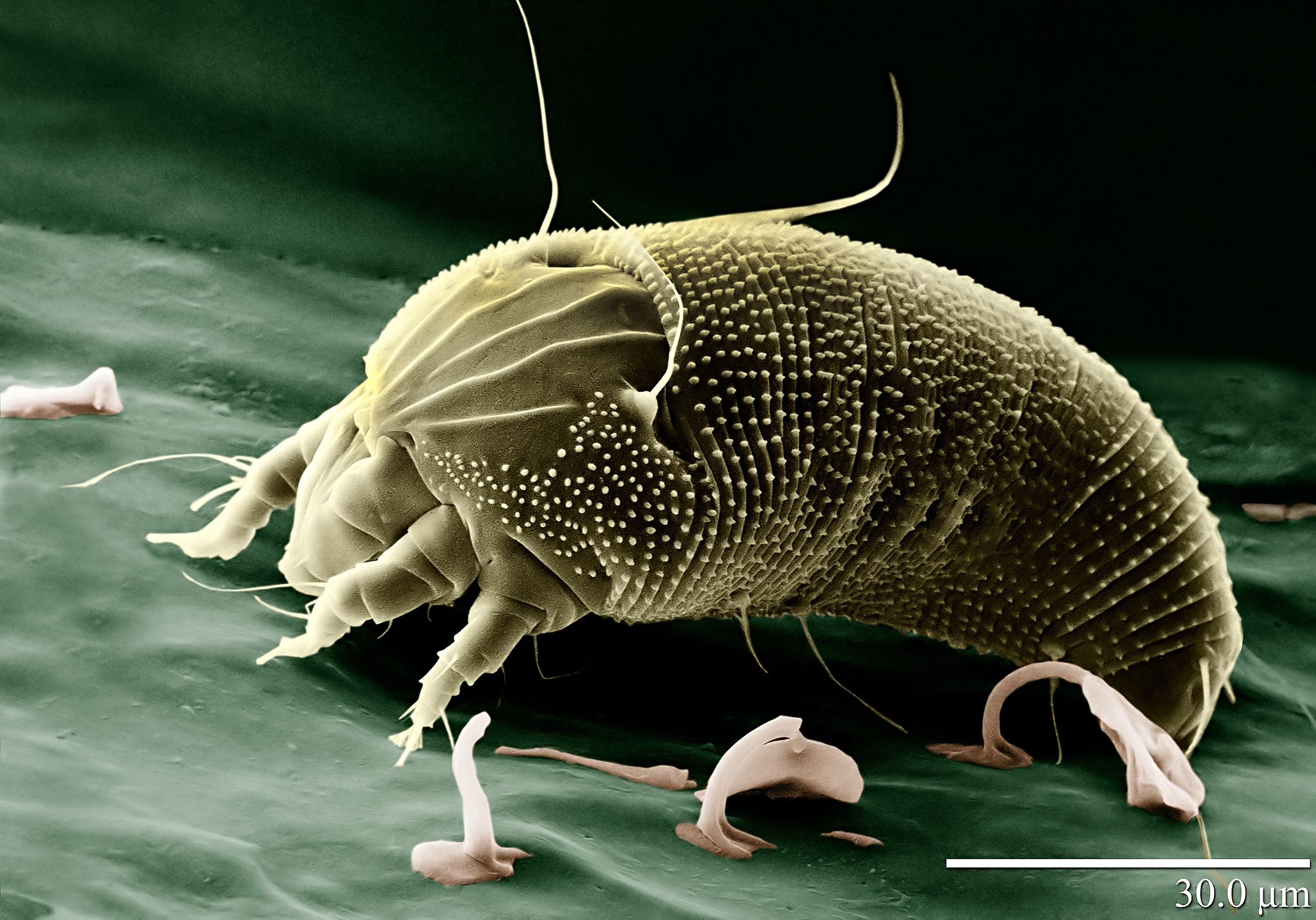 Mites occupy a wide range of
Mites occupy a wide range of
 Plant pests include the so-called
Plant pests include the so-called
 Mites are tiny and apart from those that are of economic concern to humans, little studied. The majority are beneficial, living in the soil or aqueous environments and assisting in the decomposition of decaying organic material, as part of the
Mites are tiny and apart from those that are of economic concern to humans, little studied. The majority are beneficial, living in the soil or aqueous environments and assisting in the decomposition of decaying organic material, as part of the
 Chiggers are known primarily for their itchy bite, but they can also spread disease in some limited circumstances, such as scrub typhus. The house-mouse mite is the only known vector of the disease
Chiggers are known primarily for their itchy bite, but they can also spread disease in some limited circumstances, such as scrub typhus. The house-mouse mite is the only known vector of the disease
Bitingmites.org: What's biting you?
chapter in
arachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegar ...
s (eight-legged arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s). Mites span two large orders of arachnids, the Acariformes
The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the most diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed specie ...
and the Parasitiformes
Parasitiformes are a superorder of Arachnids, constituting one of the two major groups of mites, alongside Acariformes. Parasitiformes has, at times, been classified at the rank of order or suborder.
It is uncertain whether Parasitiformes and Ac ...
, which were historically grouped together in the subclass Acari, but genetic analysis does not show clear evidence of a close relationship.
Most mites are tiny, less than in length, and have a simple, unsegmented body plan. The small size of most species makes them easily overlooked; some species live in water, many live in soil as decomposers, others live on plants, sometimes creating gall
Galls (from the Latin , 'oak-apple') or ''cecidia'' (from the Greek , anything gushing out) are a kind of swelling growth on the external tissues of plants, fungi, or animals. Plant galls are abnormal outgrowths of plant tissues, similar to be ...
s, while others again are predators or parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
. This last type includes the commercially destructive ''Varroa
''Varroa'' is a genus of parasitic mesostigmatan mites associated with honey bees, placed in its own family, Varroidae. The genus was named for Marcus Terentius Varro, a Roman scholar and beekeeper. The condition of a honeybee colony being infe ...
'' parasite of honey bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosm ...
s, as well as scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the ski ...
mites of humans. Most species are harmless to humans, but a few are associated with allergies or may transmit diseases.
The scientific discipline devoted to the study of mites is called acarology
Acarology (from Ancient Greek /, , a type of mite; and , ) is the study of mites and ticks, the animals in the order Acarina. It is a subfield of arachnology, a subdiscipline of the field of zoology. A zoologist specializing in acarology is call ...
.
Evolution and taxonomy
 The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachnids, the
The mites are not a defined taxon, but is used for two distinct groups of arachnids, the Acariformes
The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the most diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed specie ...
and the Parasitiformes
Parasitiformes are a superorder of Arachnids, constituting one of the two major groups of mites, alongside Acariformes. Parasitiformes has, at times, been classified at the rank of order or suborder.
It is uncertain whether Parasitiformes and Ac ...
. The phylogeny
A phylogenetic tree (also phylogeny or evolutionary tree Felsenstein J. (2004). ''Inferring Phylogenies'' Sinauer Associates: Sunderland, MA.) is a branching diagram or a tree showing the evolutionary relationships among various biological s ...
of the Acari has been relatively little studied, but molecular information from ribosomal DNA
Ribosomal DNA (rDNA) is a DNA sequence that codes for ribosomal RNA. These sequences regulate transcription initiation and amplification, and contain both transcribed and non-transcribed spacer segments.
In the human genome there are 5 chro ...
is being extensively used to understand relationships between groups. The 18 S rRNA gene provides information on relationships among phyla Phyla, the plural of ''phylum'', may refer to:
* Phylum, a biological taxon between Kingdom and Class
* by analogy, in linguistics, a large division of possibly related languages, or a major language family which is not subordinate to another
Phy ...
and superphyla, while the ITS2
Internal transcribed spacer (ITS) is the spacer DNA situated between the small-subunit ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and large-subunit rRNA genes in the chromosome or the corresponding transcribed region in the polycistronic rRNA precursor transcript.
...
, and the 18S ribosomal RNA
18S ribosomal RNA (abbreviated 18S rRNA) is a part of the ribosomal RNA. The S in 18S represents Svedberg units. 18S rRNA is an SSU rRNA, a component of the eukaryotic ribosomal small subunit ( 40S). 18S rRNA is the structural RNA for the small ...
and 28S ribosomal RNA
28S ribosomal RNA is the structural ribosomal RNA (rRNA) for the large subunit (LSU) of eukaryotic cytoplasmic ribosomes, and thus one of the basic components of all eukaryotic cells. It has a size of 25S in plants and 28S in mammals, hence th ...
genes, provide clues at deeper levels.
Taxonomy
* SuperorderParasitiformes
Parasitiformes are a superorder of Arachnids, constituting one of the two major groups of mites, alongside Acariformes. Parasitiformes has, at times, been classified at the rank of order or suborder.
It is uncertain whether Parasitiformes and Ac ...
– ticks and a variety of mites
** Opilioacarida
Opilioacaridae is the sole family of mites in the order Opilioacarida, made up of about 13 genera. The mites of this family are rare, large (1.5 to 2.5 mm) mites, and are widely considered primitive, as they retain six pairs of eyes, and a ...
– a small order of large mites that superficially resemble harvestmen
The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an order of arachnids colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs. , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, although the total number of extan ...
(Opiliones
The Opiliones (formerly Phalangida) are an order of arachnids colloquially known as harvestmen, harvesters, harvest spiders, or daddy longlegs. , over 6,650 species of harvestmen have been discovered worldwide, although the total number of ext ...
), hence their name
** Holothyrida
The Holothyrida are a small order of mites in the superorder Parasitiformes. No fossils are known. With body lengths of more than they are relatively large mites, with a heavily sclerotized body. It is divided into three families, Allothyridae, ...
- small group of predatory mites native to former Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final sta ...
landmasses
** Ixodida
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
– ticks
** Mesostigmata
Mesostigmata is an order of mites belonging to the Parasitiformes. They are by far the largest group of Parasitiformes, with over 8,000 species in 130 families. Mesostigmata includes parasitic as well as free-living and predatory forms. They can ...
– a large order of predatory and parasitic mites
*** Trigynaspida
Trigynaspida is a suborder of mites in the order Mesostigmata. There are more than 25 families and at least 90 described species in Trigynaspida.
Families
These 27 families belong to the suborder Trigynaspida:
* Aenictequidae Kethley, 1977
* An ...
- large, diverse order
*** Monogynaspida
Mesostigmata is an order of mites belonging to the Parasitiformes. They are by far the largest group of Parasitiformes, with over 8,000 species in 130 families. Mesostigmata includes parasitic as well as free-living and predatory forms. They can ...
- diverse order of parasitic and predatory mites
* Superorder Acariformes
The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the most diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed specie ...
– the most diverse group of mites
** Endeostigmata
Endeostigmata is a suborder of acariform mites. There are about ten families in Endeostigmata. The grouping is strongly suspected to be paraphyletic, containing unrelated early diverging lineages of mites.
Taxonomy
* Suborder Endeostigmata Reut ...
(probably paraphyletic
In taxonomy, a group is paraphyletic if it consists of the group's last common ancestor and most of its descendants, excluding a few monophyletic subgroups. The group is said to be paraphyletic ''with respect to'' the excluded subgroups. In ...
)
** Eriophyoidea
Eriophyoidea are a superfamily of herbivorous mites. All post-embryonic instars lack the third and fourth pairs of legs. The respiratory system is also absent.
The taxonomy of this group has always been confused. There were families created for ...
– gall mites and relatives
** Trombidiformes
The Trombidiformes are a large, diverse order of mites.
Taxonomy
In 1998, Trombidiformes was divided into the Sphaerolichida and the Prostigmata. The group has few synapomorphies by which it can be defined, unlike the other major group of ac ...
– plant parasitic mites (spider mites, peacock mites, red-legged earth mites, etc.), snout mites, chiggers, hair follicle mites, velvet mites, water mites, etc.
*** Sphaerolichida - small order of mites containing two families
*** Prostigmata - large order of sucking mites
** Sarcoptiformes
The Sarcoptiformes are an order of Acari comprising over 15,000 described species in around 230 families. Previously it was divided into two suborders, Oribatida and Astigmatina, but Oribatida has been promoted to an order, and Astigmatina is ...
*** Oribatida – oribatid mites, beetle mites, armored mites (also cryptostigmata)
*** Astigmatina
Astigmatina is a clade of mites in the superorder Acariformes. Astigmata has been ranked as an order or suborder in the past, but was lowered to the unranked clade Astigmatina of the clade Desmonomatides (synonym Desmonomata) in the order Sarc ...
– stored product, fur, feather, dust, and human itch mites, etc.Fossil record
 The mite fossil record is sparse, due to their small size and low preservation potential. The oldest fossils of acariform mites are from the
The mite fossil record is sparse, due to their small size and low preservation potential. The oldest fossils of acariform mites are from the Rhynie Chert
The Rhynie chert is a Lower Devonian sedimentary deposit exhibiting extraordinary fossil detail or completeness (a Lagerstätte). It is exposed near the village of Rhynie, Aberdeenshire, Scotland; a second unit, the Windyfield chert, is located ...
, Scotland, which dates to the early Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, wh ...
, around 410 million years ago while the earliest fossils of Parasitiformes are known from amber
Amber is fossilized tree resin that has been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since Neolithic times. Much valued from antiquity to the present as a gemstone, amber is made into a variety of decorative objects."Amber" (2004). In M ...
specimens dating to the mid-Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 145 to 66 million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era, as well as the longest. At around 79 million years, it is the longest geological period of ...
, around 100 million years ago. Most fossil acarids are no older than the Tertiary
Tertiary ( ) is a widely used but obsolete term for the geologic period from 66 million to 2.6 million years ago.
The period began with the demise of the non-avian dinosaurs in the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, at the start ...
(up to 65 mya).
Phylogeny
Members of the superorders Opilioacariformes andAcariformes
The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the most diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed specie ...
(sometimes known as Actinotrichida) are mites, as well as some of the Parasitiformes
Parasitiformes are a superorder of Arachnids, constituting one of the two major groups of mites, alongside Acariformes. Parasitiformes has, at times, been classified at the rank of order or suborder.
It is uncertain whether Parasitiformes and Ac ...
(sometimes known as Anactinotrichida). Recent genetic research has caused a change in the naming scheme, however, and recent publications have changed the superorder Parasitiformes to an order. Other recent research has suggested that Acari is polyphyletic
A polyphyletic group is an assemblage of organisms or other evolving elements that is of mixed evolutionary origin. The term is often applied to groups that share similar features known as homoplasies, which are explained as a result of conver ...
(of multiple origins), with ticks and spiders more closely related than ticks and mites. The cladogram is based on Dabert et al. 2010, which used molecular data. It shows the Acariformes sister
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a family, familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to r ...
to the Solifugae
Solifugae is an order of animals in the class Arachnida known variously as camel spiders, wind scorpions, sun spiders, or solifuges. The order includes more than 1,000 described species in about 147 genera. Despite the common names, they are ne ...
(camel spiders), while the Parasitiformes are sister to the Pseudoscorpionida
Pseudoscorpions, also known as false scorpions or book scorpions, are small, scorpion-like arachnids belonging to the order Pseudoscorpiones, also known as Pseudoscorpionida or Chelonethida.
Pseudoscorpions are generally beneficial to humans sin ...
.
Anatomy
External
Mites are tiny members of the classArachnid
Arachnida () is a class of joint-legged invertebrate animals (arthropods), in the subphylum Chelicerata. Arachnida includes, among others, spiders, scorpions, ticks, mites, pseudoscorpions, harvestmen, camel spiders, whip spiders and vinegar ...
a; most are in the size range but some are larger and some are no bigger than as adults. The body plan has two regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
, a cephalothorax
The cephalothorax, also called prosoma in some groups, is a tagma of various arthropods, comprising the head and the thorax fused together, as distinct from the abdomen behind. (The terms ''prosoma'' and ''opisthosoma'' are equivalent to ''cepha ...
(with no separate head) or prosoma, and an opisthosoma
The opisthosoma is the posterior part of the body in some arthropods, behind the prosoma (cephalothorax). It is a distinctive feature of the subphylum Chelicerata (arachnids, horseshoe crabs and others). Although it is similar in most respects to ...
or abdomen. Segmentation has almost entirely been lost and the prosoma and opisthosoma are fused, only the positioning of the limbs indicating the location of the segments.
 At the front of the body is the
At the front of the body is the gnathosoma
The gnathosoma (from Greek , ' = "jaw" and , ' = "body") is the part of the body of the Acari ( mites and ticks) comprising the mouth and feeding parts. These are the hypostome, the chelicerae and the pedipalps. It is also called the capitulum (h ...
or capitulum. This is not a head and does not contain the eyes or the brain, but is a retractable feeding apparatus consisting of the chelicerae
The chelicerae () are the mouthparts of the subphylum Chelicerata, an arthropod group that includes arachnids, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. Commonly referred to as " jaws", chelicerae may be shaped as either articulated fangs, or similarl ...
, the pedipalp
Pedipalps (commonly shortened to palps or palpi) are the second pair of appendages of chelicerates – a group of arthropods including spiders, scorpions, horseshoe crabs, and sea spiders. The pedipalps are lateral to the chelicerae ("jaws") an ...
s and the oral cavity. It is covered above by an extension of the body carapace
A carapace is a dorsal (upper) section of the exoskeleton or shell in a number of animal groups, including arthropods, such as crustaceans and arachnids, as well as vertebrates, such as turtles and tortoises. In turtles and tortoises, the unde ...
and is connected to the body by a flexible section of cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non- homologous, differing in their origin, structu ...
.
Two-segmented chelicerae is the ancestral condition in Acariformes, but in more derived groups they are single-segmented. And three-segmented chelicerae is the ancestral condition in Parasitiformes, but has been reduced to just two segments in more derived groups. The pedipalps differ between taxa depending on diet; in some species the appendages resemble legs while in others they are modified into chelicerae-like structures. The oral cavity connects posteriorly to the mouth and pharynx.
Most mites have four pairs of legs, each with six segments, which may be modified for swimming or other purposes. The dorsal surface of the body is clad in hardened tergites
A ''tergum'' (Latin for "the back"; plural ''terga'', associated adjective tergal) is the dorsal ('upper') portion of an arthropod segment other than the head. The anterior edge is called the 'base' and posterior edge is called the 'apex' or 'mar ...
and the ventral surface by hardened sclerite
A sclerite (Greek , ', meaning " hard") is a hardened body part. In various branches of biology the term is applied to various structures, but not as a rule to vertebrate anatomical features such as bones and teeth. Instead it refers most commonly ...
s; sometimes these form transverse ridges. The gonopore
A gonopore, sometimes called a gonadopore, is a genital pore in many invertebrates. Hexapods, including insects have a single common gonopore, except mayflies, which have a pair of gonopores. More specifically, in the unmodified female it is t ...
(genital opening) is located on the ventral surface between the fourth pair of legs. Some species have one to five median or lateral eyes but many species are blind, and slit and pit sense organs are common. Both body and limbs bear seta
In biology, setae (singular seta ; from the Latin word for "bristle") are any of a number of different bristle- or hair-like structures on living organisms.
Animal setae
Protostomes
Annelid setae are stiff bristles present on the body. ...
e (bristles) which may be simple, flattened, club-shaped or sensory. Mites are usually some shade of brown, but some species are red, orange, black or green, or some combination of these colours.
Internal
Mite digestive systems have salivary glands that open into the preoral space rather than the foregut. Most species carry two to six pairs of salivary glands that empty at various points into the subcheliceral space. A few mite species lack an anus: they do not defecate during their short lives. The circulatory system consists of a network of sinuses and most mites lacks a heart, movement of fluid being driven by the contraction of body muscles. But ticks, and some of the larger species of mites, have a dorsal, longitudinal heart. Gas exchange is carried out across the body surface, but many species additionally have between one and four pairs oftrachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
e, the spiracles being located in the front half of the body. The excretory system includes a nephridium
The nephridium (plural ''nephridia'') is an invertebrate organ, found in pairs and performing a function similar to the vertebrate kidneys (which originated from the chordate nephridia). Nephridia remove metabolic wastes from an animal's body. Neph ...
and one or two pairs of Malpighian tubules. Several families of mites, such as Tetranychidae, Eriophyidae, Camerobiidae, Cunaxidae, Trombidiidae, Trombiculidae, Erythraeidae and Bdellidae have silk glands used to produce silk for various purposes. Also water mites (Hydrachnidia) produce long thin threads that may be silk.
Reproduction and life cycle
testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
in the mid-region of the body, each connected to the gonopore by a vas deferens
The vas deferens or ductus deferens is part of the male reproductive system of many vertebrates. The ducts transport sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts in anticipation of ejaculation. The vas deferens is a partially coiled tube ...
, and in some species there is a chitinous penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
; females have a single ovary
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. ...
connected to the gonopore by an oviduct
The oviduct in mammals, is the passageway from an ovary. In human females this is more usually known as the Fallopian tube or uterine tube. The eggs travel along the oviduct. These eggs will either be fertilized by spermatozoa to become a zygote, o ...
, as well as a seminal receptacle
Female sperm storage is a biological process and often a type of sexual selection in which sperm cells transferred to a female during mating are temporarily retained within a specific part of the reproductive tract before the oocyte, or egg, is f ...
for the storage of sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
. In most mites, sperm is transferred to the female indirectly; the male either deposits a spermatophore
A spermatophore or sperm ampulla is a capsule or mass containing spermatozoa created by males of various animal species, especially salamanders and arthropods, and transferred in entirety to the female's ovipore during reproduction. Spermatophore ...
on a surface from which it is picked up by the female, or he uses his chelicerae or third pair of legs to insert it into the female's gonopore. In some of the Acariformes
The Acariformes, also known as the Actinotrichida, are the most diverse of the two superorders of mites. Over 32,000 described species are found in 351 families, with an estimated total of 440,000 to 929,000 species, including undescribed specie ...
, insemination is direct using the male's penis. The spermatophora in all mites are aflagellate.
The eggs are laid in the substrate, or wherever the mite happens to live. They take up to six weeks to hatch, according to species, and the first stage larvae have six legs. After three moults, the larvae become nymphs, with eight legs, and after a further three moults, they become adults. Longevity varies between species, but the lifespan of mites is short as compared to many other arachnids.
Ecology
Niches
 Mites occupy a wide range of
Mites occupy a wide range of ecological niches
In ecology, a niche is the match of a species to a specific environmental condition.
Three variants of ecological niche are described by
It describes how an organism or population responds to the distribution of resources and competitors (for ...
. For example, Oribatida mites are important decomposers in many habitats. They eat a wide variety of material including living and dead plant and fungal material, lichens and carrion; some are predatory, though no oribatid mites are parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
. Mites are among the most diverse and successful of all invertebrate
Invertebrates are a paraphyletic group of animals that neither possess nor develop a vertebral column (commonly known as a ''backbone'' or ''spine''), derived from the notochord. This is a grouping including all animals apart from the chorda ...
groups. They have exploited a wide array of habitat
In ecology, the term habitat summarises the array of resources, physical and biotic factors that are present in an area, such as to support the survival and reproduction of a particular species. A species habitat can be seen as the physical ...
s, and because of their small size go largely unnoticed. They are found in fresh and salt water, in the soil, in forests, pastures, agricultural crops, ornamental plants, thermal springs and caves. They inhabit organic debris of all kinds and are extremely numerous in leaf litter. They feed on animals, plants and fungi and some are parasites
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
of plants and animals. Some 48,200 species of mites have been described, but there may be a million or more species as yet undescribed. The tropical species '' Archegozetes longisetosus'' is one of the strongest animals in the world, relative to its mass (100 μg): It lifts up to 1,182 times its own weight, over five times more than would be expected of such a minute animal. A mite also holds a speed record: for its length, ''Paratarsotomus macropalpis
''Paratarsotomus macropalpis'' is a species of mite belonging to the family Anystidae. The mite is endemic to Southern California and is usually observed darting amongst sidewalks and in rocky areas. Earlier classified as belonging to genus '' T ...
'' is the fastest animal on Earth.
*
Parasitism
Many mites areparasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
on plants and animals. One family of mites, Pyroglyphidae, or nest mites, live primarily in the nests of birds and other animals. These mites are largely parasitic
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson ha ...
and consume blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
, skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation.
Other animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different ...
and keratin
Keratin () is one of a family of structural fibrous proteins also known as ''scleroproteins''. Alpha-keratin (α-keratin) is a type of keratin found in vertebrates. It is the key structural material making up Scale (anatomy), scales, hair, Nail ...
. Dust mites
House dust mites (HDM, or simply dust mites) are various species of acariform mites belonging to the family Pyroglyphidae that are found in association with dust in dwellings. They are known for causing allergies.
Biology
Species
The curren ...
, which feed mostly on dead skin and hair shed from humans instead of consuming them from the organism directly, evolved from these parasitic ancestors.
* Ticks
Ticks (order Ixodida) are parasitic arachnids that are part of the mite superorder Parasitiformes. Adult ticks are approximately 3 to 5 mm in length depending on age, sex, species, and "fullness". Ticks are external parasites, living by ...
are a prominent group of mites that are parasitic on vertebrates, mostly mammal and birds, feeding on blood with specialised mouthparts.
Parasitic mites sometimes infest insects. ''Varroa destructor
''Varroa destructor'', the ''Varroa'' mite is an external parasitic mite that attacks and feeds on the honey bees '' Apis cerana'' and ''Apis mellifera''. The disease caused by the mites is called varroosis.
The ''Varroa'' mite can reproduce o ...
'' attaches to the body of honey bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosm ...
s, and ''Acarapis woodi
''Acarapis woodi'' is an internal parasite affecting honey bees, the symptoms of infestation was originally observed on the Isle of Wight in 1904, but was not described until 1921. ''Acarapis woodi'' mites live and reproduce in the tracheae o ...
'' (family Tarsonemidae) lives in their trachea
The trachea, also known as the windpipe, is a cartilaginous tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi of the lungs, allowing the passage of air, and so is present in almost all air- breathing animals with lungs. The trachea extends from t ...
e. Hundreds of species are associated with other bees, mostly poorly described. They attach to bees in a variety of ways. For example, ''Trigona corvina
''Trigona corvina'' ( Cockerell, 1913) is a species of stingless bee that lives primarily in Central and South America. In Panama, they are sometimes known as zagañas. They live in protective nests high in the trees, but they can be extremely a ...
'' workers have been found with mites attached to the outer face of their hind tibiae. Some are thought to be parasites, while others are beneficial symbionts
Symbiosis (from Greek , , "living together", from , , "together", and , bíōsis, "living") is any type of a close and long-term biological interaction between two different biological organisms, be it mutualistic, commensalistic, or parasit ...
. Mites also parasitize some ant species, such as ''Eciton burchellii
''Eciton burchellii'' is a species of New World army ant in the genus '' Eciton''. This species performs expansive, organized swarm raids that give it the informal name, ''Eciton'' army ant. This species displays a high degree of worker polymor ...
''.
spider mite
Spider mites are members of the Tetranychidae family, which includes about 1,200 species. They are part of the subclass Acari (mites). Spider mites generally live on the undersides of leaves of plants, where they may spin protective silk webs, a ...
s (family Tetranychidae), thread-footed mites (family Tarsonemidae), and the gall mite
Eriophyidae is a family of more than 200 genera of mites, which live as plant parasites, commonly causing galls or other damage to the plant tissues and hence known as gall mites. About 3,600 species have been described, but this is probably ...
s (family Eriophyidae
Eriophyidae is a family of more than 200 genera of mites, which live as plant parasites, commonly causing galls or other damage to the plant tissues and hence known as gall mites. About 3,600 species have been described, but this is probably l ...
). Among the species that attack animals are members of the sarcoptic mange
Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infection ...
mites (family Sarcoptidae), which burrow under the skin. Demodex mite
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: ''Demodex folliculorum'' and ''Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyelash ...
s (family Demodecidae) are parasites that live in or near the hair follicle
The hair follicle is an organ found in mammalian skin. It resides in the dermal layer of the skin and is made up of 20 different cell types, each with distinct functions. The hair follicle regulates hair growth via a complex interaction between ...
s of mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur ...
s, including humans.
Dispersal
Being unable to fly, mites need some other means of dispersal. On a small scale, walking is used to access other suitable locations in the immediate vicinity. Some species mount to a high point and adopt a dispersal posture and get carried away by the wind, while others waft a thread of silk aloft to balloon to a new position. Parasitic mites use their hosts to disperse, and spread from host to host by direct contact. Another strategy isphoresy
Phoresis or phoresy is a non-permanent, commensalistic interaction in which one organism (a phoront or phoretic) attaches itself to another (the host) solely for the purpose of travel. Phoresis has been observed directly in ticks and mites s ...
; the mite, often equipped with suitable claspers or suckers, grips onto an insect or other animal, and gets transported to another place. A phoretic mite is just a hitch-hiker and does not feed during the time it is carried by its temporary host. These travelling mites are mostly species that reproduce rapidly and are quick to colonise new habitats.
Relationship with humans
 Mites are tiny and apart from those that are of economic concern to humans, little studied. The majority are beneficial, living in the soil or aqueous environments and assisting in the decomposition of decaying organic material, as part of the
Mites are tiny and apart from those that are of economic concern to humans, little studied. The majority are beneficial, living in the soil or aqueous environments and assisting in the decomposition of decaying organic material, as part of the carbon cycle
The carbon cycle is the biogeochemical cycle by which carbon is exchanged among the biosphere, pedosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere of the Earth. Carbon is the main component of biological compounds as well as a major compon ...
.
Medical significance
The majority of mite species are harmless to humans anddomestic animal
This page gives a list of domesticated animals, also including a list of domestication of animals, animals which are or may be currently undergoing the process of domestication and animals that have an extensive relationship with humans beyond simp ...
s, but a few species can colonize mammals directly, acting as vector
Vector most often refers to:
*Euclidean vector, a quantity with a magnitude and a direction
*Vector (epidemiology), an agent that carries and transmits an infectious pathogen into another living organism
Vector may also refer to:
Mathematic ...
s for disease transmission, and causing or contributing to allergenic diseases. Mites which colonize human skin are the cause of several types of itchy skin rashes, such as gamasoidosis
Gamasoidosis, or dermanyssosis, is a frequently unrecognized ectoparasitosis and source of growing concern in human medicine, occurring after contact with avian mites which infest canaries, sparrows, starlings, pigeons and poultry and caused ...
, rodent mite dermatitis
Rodent mite dermatitis (also known as rat mite dermatitis) is an often unrecognized ectoparasitosis occurring after human contact with haematophagous mesostigmatid mites that infest rodents, such as house mice, rats and hamsters. The condition ...
, grain itch
Grain itch is a cutaneous condition caused by several types of mites, and characterized by intense pruritus.
See also
* Grocer's itch
* List of cutaneous conditions
* List of mites associated with cutaneous reactions
Many mites can bite huma ...
, grocer's itch
Grocer's itch is a cutaneous condition characterized by a pruritic dermatitis that occurs from coming into contact with mites such as ''Carpoglyphus passularum'' (a fruit mite) or '' Glycyphagus domesticus'' (a common house mite). Contact usually ...
, and scabies
Scabies (; also sometimes known as the seven-year itch) is a contagious skin infestation by the mite ''Sarcoptes scabiei''. The most common symptoms are severe itchiness and a pimple-like rash. Occasionally, tiny burrows may appear on the ski ...
; ''Sarcoptes scabiei
''Sarcoptes scabiei'' or the itch mite is a parasitic mite that burrows into skin and causes scabies. The mite is found in all parts of the world. Humans are not the only mammals that can become infected. Other mammals, such as wild and domes ...
'' is a parasitic mite responsible for scabies, which is one of the three most common skin disorders in children. ''Demodex
''Demodex'' is a genus of tiny mites that live in or near hair follicles of mammals. Around 65 species of ''Demodex'' are known. Two species live on humans: '' Demodex folliculorum'' and '' Demodex brevis'', both frequently referred to as eyela ...
'' mites, which are common cause of mange
Mange is a type of skin disease caused by parasitic mites. Because various species of mites also infect plants, birds and reptiles, the term "mange", or colloquially "the mange", suggesting poor condition of the skin and fur due to the infectio ...
in dogs and other domesticated animals, have also been implicated in the human skin disease rosacea
Rosacea is a long-term skin condition that typically affects the face. It results in redness, pimples, swelling, and small and superficial dilated blood vessels. Often, the nose, cheeks, forehead, and chin are most involved. A red, enlarg ...
, although the mechanism by which ''demodex'' contributes to the disease is unclear. Ticks are well known for carrying diseases, such as Lyme disease
Lyme disease, also known as Lyme borreliosis, is a vector-borne disease caused by the '' Borrelia'' bacterium, which is spread by ticks in the genus '' Ixodes''. The most common sign of infection is an expanding red rash, known as erythema ...
and Rocky Mountain spotted fever
Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) is a bacterial disease spread by ticks. It typically begins with a fever and headache, which is followed a few days later with the development of a rash. The rash is generally made up of small spots of bleedin ...
.
 Chiggers are known primarily for their itchy bite, but they can also spread disease in some limited circumstances, such as scrub typhus. The house-mouse mite is the only known vector of the disease
Chiggers are known primarily for their itchy bite, but they can also spread disease in some limited circumstances, such as scrub typhus. The house-mouse mite is the only known vector of the disease rickettsialpox
Rickettsialpox is a mite-borne infectious illness caused by bacteria of the genus ''Rickettsia'' ('' Rickettsia akari''). Physician Robert Huebner and self-trained entomologist Charles Pomerantz played major roles in identifying the cause of t ...
. House dust mites, found in warm and humid places such as beds, cause several forms of allergic diseases, including hay fever
Allergic rhinitis, of which the seasonal type is called hay fever, is a type of inflammation in the nose that occurs when the immune system overreacts to allergens in the air. Signs and symptoms include a runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, red, i ...
, asthma
Asthma is a long-term inflammatory disease of the airways of the lungs. It is characterized by variable and recurring symptoms, reversible airflow obstruction, and easily triggered bronchospasms. Symptoms include episodes of wheezing, co ...
and eczema
Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, typically characterized by itchiness, redness and a rash. In cases of short duration, there may be small blisters, while in long-term cases the skin may become thickened. The area of skin involved c ...
, and are known to aggravate atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis (AD), also known as atopic eczema, is a long-term type of inflammation of the skin ( dermatitis). It results in itchy, red, swollen, and cracked skin. Clear fluid may come from the affected areas, which often thickens over tim ...
.
Among domestic animals, sheep are affected by the mite ''Psoroptes ovis'' which lives on the skin, causing hypersensitivity and inflammation. Hay mites are a suspected reservoir for scrapie
Scrapie () is a fatal, degenerative disease affecting the nervous systems of sheep and goats. It is one of several transmissible spongiform encephalopathies (TSEs), and as such it is thought to be caused by a prion. Scrapie has been known since ...
, a prion
Prions are misfolded proteins that have the ability to transmit their misfolded shape onto normal variants of the same protein. They characterize several fatal and transmissible neurodegenerative diseases in humans and many other animals. It i ...
disease of sheep.
In beekeeping
The mite ''Varroa destructor'' is a serious pest ofhoney bee
A honey bee (also spelled honeybee) is a eusocial flying insect within the genus ''Apis'' of the bee clade, all native to Afro-Eurasia. After bees spread naturally throughout Africa and Eurasia, humans became responsible for the current cosm ...
s, contributing to colony collapse disorder
Colony collapse disorder (CCD) is an abnormal phenomenon that occurs when the majority of worker bees in a honey bee colony disappear, leaving behind a queen, plenty of food, and a few nurse bees to care for the remaining immature bees. While s ...
in commercial hives. This organism is an obligate external parasite, able to reproduce only in bee colonies. It directly weakens its host by sucking up the bee's fat, and can spread RNA virus
An RNA virus is a virusother than a retrovirusthat has ribonucleic acid ( RNA) as its genetic material. The nucleic acid is usually single-stranded RNA (ssRNA) but it may be double-stranded (dsRNA). Notable human diseases caused by RNA virus ...
es including deformed wing virus
''Deformed wing virus'' (DWV) is an RNA virus, one of 22 known viruses affecting honey bees. While most commonly infecting the honey bee, ''Apis mellifera'', it has also been documented in other bee species, like '' Bombus terrestris'', thus, i ...
. Heavy infestation causes the death of a colony, generally over the winter. Since 2006, over 10 million beehives have been lost.
In culture
Mites were first observed under themicroscope
A microscope () is a laboratory instrument used to examine objects that are too small to be seen by the naked eye. Microscopy is the science of investigating small objects and structures using a microscope. Microscopic means being invisi ...
by the English polymath Robert Hooke
Robert Hooke FRS (; 18 July 16353 March 1703) was an English polymath active as a scientist, natural philosopher and architect, who is credited to be one of two scientists to discover microorganisms in 1665 using a compound microscope that ...
. In his 1665 book ''Micrographia
''Micrographia: or Some Physiological Descriptions of Minute Bodies Made by Magnifying Glasses. With Observations and Inquiries Thereupon.'' is a historically significant book by Robert Hooke about his observations through various lenses. It ...
'', he stated that far from being spontaneously generated from dirt, they were "very prettily shap'd Insects". In 1898, Arthur Conan Doyle
Sir Arthur Ignatius Conan Doyle (22 May 1859 – 7 July 1930) was a British writer and physician. He created the character Sherlock Holmes in 1887 for ''A Study in Scarlet'', the first of four novels and fifty-six short stories about Ho ...
wrote a satirical poem, "A Parable", with the conceit An extended metaphor, also known as a conceit or sustained metaphor, is the use of a single metaphor or analogy at length in a work of literature. It differs from a mere metaphor in its length, and in having more than one single point of contact bet ...
of some cheese mites disputing the origin of the round
Round or rounds may refer to:
Mathematics and science
* The contour of a closed curve or surface with no sharp corners, such as an ellipse, circle, rounded rectangle, cant, or sphere
* Rounding, the shortening of a number to reduce the number ...
cheddar cheese
Cheddar cheese (or simply cheddar) is a natural cheese that is relatively hard, off-white (or orange if colourings such as annatto are added), and sometimes sharp-tasting. Cheddar originates from the English village of Cheddar in Somerset.
Che ...
in which they all lived. The world's first science documentary featured cheese mites, seen under the microscope; the short film was shown in London's Alhambra music hall
Music hall is a type of British theatrical entertainment that was popular from the early Victorian era, beginning around 1850. It faded away after 1918 as the halls rebranded their entertainment as variety. Perceptions of a distinction in Br ...
in 1903, causing a boom in the sales of simple microscopes.
See also
* Chigger bite *Copra itch Copra itch is a skin condition that occurs on persons handling copra who are subject to ''Tyrophagus longior'' mite bites.
See also
* Coolie itch
* Skin lesion
A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition th ...
* Gamasoidosis
Gamasoidosis, or dermanyssosis, is a frequently unrecognized ectoparasitosis and source of growing concern in human medicine, occurring after contact with avian mites which infest canaries, sparrows, starlings, pigeons and poultry and caused ...
* Grain itch
Grain itch is a cutaneous condition caused by several types of mites, and characterized by intense pruritus.
See also
* Grocer's itch
* List of cutaneous conditions
* List of mites associated with cutaneous reactions
Many mites can bite huma ...
* Grocer's itch
Grocer's itch is a cutaneous condition characterized by a pruritic dermatitis that occurs from coming into contact with mites such as ''Carpoglyphus passularum'' (a fruit mite) or '' Glycyphagus domesticus'' (a common house mite). Contact usually ...
* List of mites associated with cutaneous reactions
References
External links
Bitingmites.org: What's biting you?
chapter in
United States Environmental Protection Agency
The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) is an independent executive agency of the United States federal government tasked with environmental protection matters. President Richard Nixon proposed the establishment of EPA on July 9, 1970; it ...
and University of Florida
The University of Florida (Florida or UF) is a public land-grant research university in Gainesville, Florida. It is a senior member of the State University System of Florida, traces its origins to 1853, and has operated continuously on its ...
/Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences
The University of Florida Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences (UF/IFAS) is a teaching, research and Extension scientific organization focused on agriculture and natural resources. It is a partnership of federal, state, and county governmen ...
National Public Health Pesticide Applicator Training Manual
*
{{Taxonbar, from1=Q2441993, from2=Q19137
Acari
Paraphyletic groups
Arthropod common names