Abu Qir Bay on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Abū Qīr Bay (sometimes transliterated Abukir Bay or Aboukir Bay) (; transliterated: Khalīj Abū Qīr) is a spacious bay on the
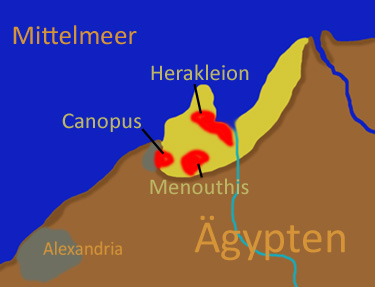 In ancient times Abu Qir Bay was surrounded by marshland and contained several islands. As early as the 7th century BC, port cities were established on the bay. The bay now contains the underwater archaeological sites of three cities from the pre-Hellenistic, Hellenistic and Roman periods. The eastern part of ancient city of
In ancient times Abu Qir Bay was surrounded by marshland and contained several islands. As early as the 7th century BC, port cities were established on the bay. The bay now contains the underwater archaeological sites of three cities from the pre-Hellenistic, Hellenistic and Roman periods. The eastern part of ancient city of
 On August 1, 1798,
On August 1, 1798,
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
near Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, lying between the Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The R ...
mouth of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
and the town of Abu Qir
Abu Qir ( ar, ابو قير, ''Abu Qīr'', or , ), formerly also spelled Abukir or Aboukir, is a town on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt, near the ruins of ancient Canopus and northeast of Alexandria by rail. It is located on Abu Qir Penins ...
. The ancient cities of Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and the second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also designated α Carinae, which is Latinised to Alpha Carinae. With a visual apparent magnitude ...
, Heracleion
Heracleion (Ancient Greek: ), also known by its Egyptian name Thonis ( Ancient Egyptian: ; cop, Ⲧϩⲱⲛⲓ , ; Ancient Greek: ) and sometimes called Thonis-Heracleion, was an ancient Egyptian port city located near the Canopic Mouth o ...
and Menouthis lie submerged beneath the waters of the bay. In 1798 it was the site of the Battle of the Nile
The Battle of the Nile (also known as the Battle of Aboukir Bay; french: Bataille d'Aboukir) was a major naval battle fought between the British Royal Navy and the Navy of the French Republic at Aboukir Bay on the Mediterranean coast off the ...
, a naval battle fought between the British Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
and the navy of the French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
. The bay contains a natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbon d ...
field, discovered in the 1970s.
Geography
Abu Qir Bay lies approximately east of Alexandria, bounded to the southwest by the Abu Qir headland, on which lies the town ofAbu Qir
Abu Qir ( ar, ابو قير, ''Abu Qīr'', or , ), formerly also spelled Abukir or Aboukir, is a town on the Mediterranean coast of Egypt, near the ruins of ancient Canopus and northeast of Alexandria by rail. It is located on Abu Qir Penins ...
, and to the northeast by the Rosetta
Rosetta or Rashid (; ar, رشيد ' ; french: Rosette ; cop, ϯⲣⲁϣⲓⲧ ''ti-Rashit'', Ancient Greek: Βολβιτίνη ''Bolbitinē'') is a port city of the Nile Delta, east of Alexandria, in Egypt's Beheira governorate. The R ...
mouth of the Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest riv ...
. The bay is a highly fertile Egyptian coastal region but suffers from acute eutrophication
Eutrophication is the process by which an entire body of water, or parts of it, becomes progressively enriched with minerals and nutrients, particularly nitrogen and phosphorus. It has also been defined as "nutrient-induced increase in phyt ...
and pollution from untreated industrial and domestic waste. The ABU QIR Fertilizers and Chemicals Industries Company, a large producer of nitrogen fertilizer, is located on the bay.
Land submersion
Classical sources indicate that the Canopic branch of theNile delta
The Nile Delta ( ar, دلتا النيل, or simply , is the delta formed in Lower Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to ...
once entered the sea in the vicinity of Heracleion or the eastern part of Canopus. A combination of Islamic texts and investigation using geoarchaeology
Geoarchaeology is a multi-disciplinary approach which uses the techniques and subject matter of geography, geology, geophysics and other Earth sciences to examine topics which inform archaeological knowledge and thought. Geoarchaeologists study ...
suggest that this branch was still in existence in the eighth century, when a major inundation caused eastern Canopus to sink into the bay. The Canopic branch subsequently declined and eventually became closed.
Land in the area of Canopus was subject to rising sea levels, earthquakes, tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
s, and large parts of it seem to have already succumbed to soil liquefaction
Soil liquefaction occurs when a cohesionless saturated or partially saturated soil substantially loses Shear strength (soil), strength and stiffness in response to an applied Shear stress, stress such as shaking during an earthquake or other ...
sometime at the end of the 2nd century BC, becoming submerged.
Antiquities
 In ancient times Abu Qir Bay was surrounded by marshland and contained several islands. As early as the 7th century BC, port cities were established on the bay. The bay now contains the underwater archaeological sites of three cities from the pre-Hellenistic, Hellenistic and Roman periods. The eastern part of ancient city of
In ancient times Abu Qir Bay was surrounded by marshland and contained several islands. As early as the 7th century BC, port cities were established on the bay. The bay now contains the underwater archaeological sites of three cities from the pre-Hellenistic, Hellenistic and Roman periods. The eastern part of ancient city of Canopus
Canopus is the brightest star in the southern constellation of Carina and the second-brightest star in the night sky. It is also designated α Carinae, which is Latinised to Alpha Carinae. With a visual apparent magnitude ...
is submerged in the bay, along with the remains of Menouthis and its sister-city Herakleion–Thonis which now lies 7 kilometres offshore. They were excavated by French underwater archaeologist Franck Goddio
Franck Goddio (born 1947 in Casablanca, Morocco) is a French underwater archaeologist who, in 2000, discovered the city of Thonis-Heracleion 7 km off the Egyptian shore in Aboukir Bay. He led the excavation of the submerged site of Canopus ...
.
In November 2017, the Egyptian mission in cooperation with the European Institute for Underwater Archaeology announced the discovery of 2.000-year-old three sunken shipwrecks dated back to the Roman Era in Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
's Abu Qir Bay.
The sunken cargo included a royal head of crystal perhaps belong to the commander of the Roman armies of “Antonio”, three gold coins from the era of Emperor Octavius Augustus, large wooden planks and pottery vessels.
In July 2019, a smaller Greek temple and ancient granite columns, treasure-laden ships, along with bronze coins from the reign of Ptolemy II
; egy, Userkanaenre Meryamun Clayton (2006) p. 208
, predecessor = Ptolemy I
, successor = Ptolemy III
, horus = ''ḥwnw-ḳni'Khunuqeni''The brave youth
, nebty = ''wr-pḥtj'Urpekhti''Great of strength
, gold ...
, pottery dating back to the third and fourth centuries BC were found at the sunken city of Heracleion
Heracleion (Ancient Greek: ), also known by its Egyptian name Thonis ( Ancient Egyptian: ; cop, Ⲧϩⲱⲛⲓ , ; Ancient Greek: ) and sometimes called Thonis-Heracleion, was an ancient Egyptian port city located near the Canopic Mouth o ...
, known as Egypt's Atlantis. The investigations were conducted by Egyptian and European divers led by the underwater archaeologist Franck Goddio
Franck Goddio (born 1947 in Casablanca, Morocco) is a French underwater archaeologist who, in 2000, discovered the city of Thonis-Heracleion 7 km off the Egyptian shore in Aboukir Bay. He led the excavation of the submerged site of Canopus ...
. They also uncovered an absolutely devastated historic underwater temple (city's main temple) off Egypt's north coast.
A number of sunken ships have been excavated from the bay, including a ceremonial boat ( Neshmet boat) dedicated to Osiris
Osiris (, from Egyptian ''wsjr'', cop, ⲟⲩⲥⲓⲣⲉ , ; Phoenician: 𐤀𐤎𐤓, romanized: ʾsr) is the god of fertility, agriculture, the afterlife, the dead, resurrection, life, and vegetation in ancient Egyptian religion. He wa ...
and several Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
era ships.
Battle of the Nile
 On August 1, 1798,
On August 1, 1798, Horatio Nelson
Vice-Admiral Horatio Nelson, 1st Viscount Nelson, 1st Duke of Bronte (29 September 1758 – 21 October 1805) was a British flag officer in the Royal Navy. His inspirational leadership, grasp of strategy, and unconventional tactics brought a ...
fought the naval "Battle of the Nile", often referred to as the "Battle of Aboukir Bay". (Not to be confused with the Battle of Abukir (1799)
The Battle of Abukir (or Aboukir or Abu Qir) was a battle in which Napoleon Bonaparte defeated Seid Mustafa Pasha's Ottoman army on 25 July 1799, during the French campaign in Egypt. It is considered the first pitched battle with this name, a ...
and the Battle of Abukir (1801)
The Battle of Abukir of 8 March 1801 was the second pitched battle of the French campaign in Egypt and Syria to be fought at Abu Qir on the Mediterranean coast, near the Nile Delta.
The landing of the British expeditionary force under Sir ...
.)
On 1 March 1801, some 70 British warships, together with transports carrying 16,000 troops, anchored in Aboukir Bay near Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
. The intent was to defeat the French expeditionary force that had remained in Egypt after Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's return to France.
Bad weather delayed disembarkation by a week but, on 8 March, Captain Alexander Cochrane
Admiral of the Blue Sir Alexander Inglis Cochrane (born Alexander Forrester Cochrane; 23 April 1758 – 26 January 1832) was a senior Royal Navy commander during the Napoleonic Wars and achieved the rank of admiral.
He had previously captain ...
of HMS ''Ajax'' deployed 320 boats, in double line abreast, to bring the troops ashore. French shore batteries opposed the landing, but the British were able to drive them back and, by the next day, all of Sir Ralph Abercromby
Lieutenant General Sir Ralph Abercromby (7 October 173428 March 1801) was a British soldier and politician. He rose to the rank of lieutenant-general in the British Army, was appointed Governor of Trinidad, served as Commander-in-Chief, Ir ...
's British army was ashore. The British then defeated the French army at the Battle of Alexandria. The Siege of Alexandria followed, with the city falling on 2 September 1801.
'' L’Orient'', Napoleon's flagship, was destroyed by Nelson's fleet and lies in the bay on the sea bottom. It was carrying five million francs in gold and one million in silver plate taken from the Knights Hospitaller
The Order of Knights of the Hospital of Saint John of Jerusalem ( la, Ordo Fratrum Hospitalis Sancti Ioannis Hierosolymitani), commonly known as the Knights Hospitaller (), was a medieval and early modern Catholic military order. It was headq ...
in Malta
Malta ( , , ), officially the Republic of Malta ( mt, Repubblika ta' Malta ), is an island country in the Mediterranean Sea. It consists of an archipelago, between Italy and Libya, and is often considered a part of Southern Europe. It lies ...
. Between 1998 and 1999, French archaeologist Franck Goddio led an expedition that carried out an underwater archaeological study of the wreck-site.
Nelson's Island
Nelson's Island, also known as Aboukir Island, is a -long island in Abu Qir bay that is used for picnics and recreation. The island has been reduced considerably in size since antiquity as a result of erosion and sandstone quarrying. When it was a part of Ancient Egypt it was probably connected to the mainland at what is now the Aboukir naval base. In Pharaonic times the island lay on a primary commercial route to the Nile River and became a major religious and commercial centre. There is archaeological evidence that a high-status necropolis was sited on the island. During the Ptolemaic Kingdom the island was fortified. Following the Battle of the Nile in 1798, a number of British dead were buried on the island. Their graves were discovered in 2000. As they were in danger of sea erosion, thirty bodies were reburied at ChatbyCommonwealth War Graves
The Commonwealth War Graves Commission (CWGC) is an intergovernmental organisation of six independent member states whose principal function is to mark, record and maintain the graves and places of commemoration of Commonwealth of Nations ...
Cemetery in Alexandria in 2005.
See also
*Lake Burullus
Lake Burullus ( ar, بحيرة البرلس, Buḥayrat al-Burullus; grc-gre, λίμνη Σεβεννυτική, limnē Sebennytikē) is a brackish water lake in the Nile Delta in Egypt, the name coming from Burullus town ( cop, Ϯⲡⲁⲣⲁ� ...
* Lake Mariout
References
{{Authority control Bays of Egypt Bays of the Mediterranean