axial skeleton on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The axial skeleton is the core part of the
The axial skeleton is the core part of the
botany.uwc.ac.za
{{Authority control Human anatomy Skeletal system Axial skeleton
 The axial skeleton is the core part of the
The axial skeleton is the core part of the endoskeleton
An endoskeleton (From Ancient Greek ἔνδον, éndon = "within", "inner" + σκελετός, skeletos = "skeleton") is a structural frame (skeleton) — usually composed of mineralized tissue — on the inside of an animal, overlaid by soft ...
made of the bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s of the head
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple ani ...
and trunk of vertebrate
Vertebrates () are animals with a vertebral column (backbone or spine), and a cranium, or skull. The vertebral column surrounds and protects the spinal cord, while the cranium protects the brain.
The vertebrates make up the subphylum Vertebra ...
s. In the human skeleton
The human skeleton is the internal framework of the human body. It is composed of around 270 bones at birth – this total decreases to around 206 bones by adulthood after some bones get fused together. The bone mass in the skeleton makes up ab ...
, it consists of 80 bones and is composed of the skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
(28 bones, including the cranium, mandible
In jawed vertebrates, the mandible (from the Latin ''mandibula'', 'for chewing'), lower jaw, or jawbone is a bone that makes up the lowerand typically more mobilecomponent of the mouth (the upper jaw being known as the maxilla).
The jawbone i ...
and the middle ear
The middle ear is the portion of the ear medial to the eardrum, and distal to the oval window of the cochlea (of the inner ear).
The mammalian middle ear contains three ossicles (malleus, incus, and stapes), which transfer the vibrations ...
ossicles
The ossicles (also called auditory ossicles) are three irregular bones in the middle ear of humans and other mammals, and are among the smallest bones in the human body. Although the term "ossicle" literally means "tiny bone" (from Latin ''ossi ...
), the vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
(26 bones, including vertebra
Each vertebra (: vertebrae) is an irregular bone with a complex structure composed of bone and some hyaline cartilage, that make up the vertebral column or spine, of vertebrates. The proportions of the vertebrae differ according to their spina ...
e, sacrum and coccyx
The coccyx (: coccyges or coccyxes), commonly referred to as the tailbone, is the final segment of the vertebral column in all apes, and analogous structures in certain other mammals such as horse anatomy, horses. In tailless primates (e.g. hum ...
), the rib cage (25 bones, including ribs and sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
), and the hyoid bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verte ...
. The axial skeleton is joined to the appendicular skeleton (which support the limbs) via the shoulder girdles and the pelvis
The pelvis (: pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of an Anatomy, anatomical Trunk (anatomy), trunk, between the human abdomen, abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also c ...
.
Structure
Flatbone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
s house the brain and other vital organs. This article mainly deals with the axial skeletons of humans; however, it is important to understand its evolutionary lineage. The human axial skeleton consists of 81 different bones forming the medial core of the body and connects the pelvis to the body, where the appendicular skeleton attaches. As the skeleton grows older the bones get weaker with the exception of the skull. The skull remains strong to protect the brain from injury.
In humans, the axial skeleton serves to protect the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs. It also serves as the attachment site for muscles that move the head, neck, and back, and for muscles that act across the shoulder and hip joints to move their corresponding limbs.
Human skull
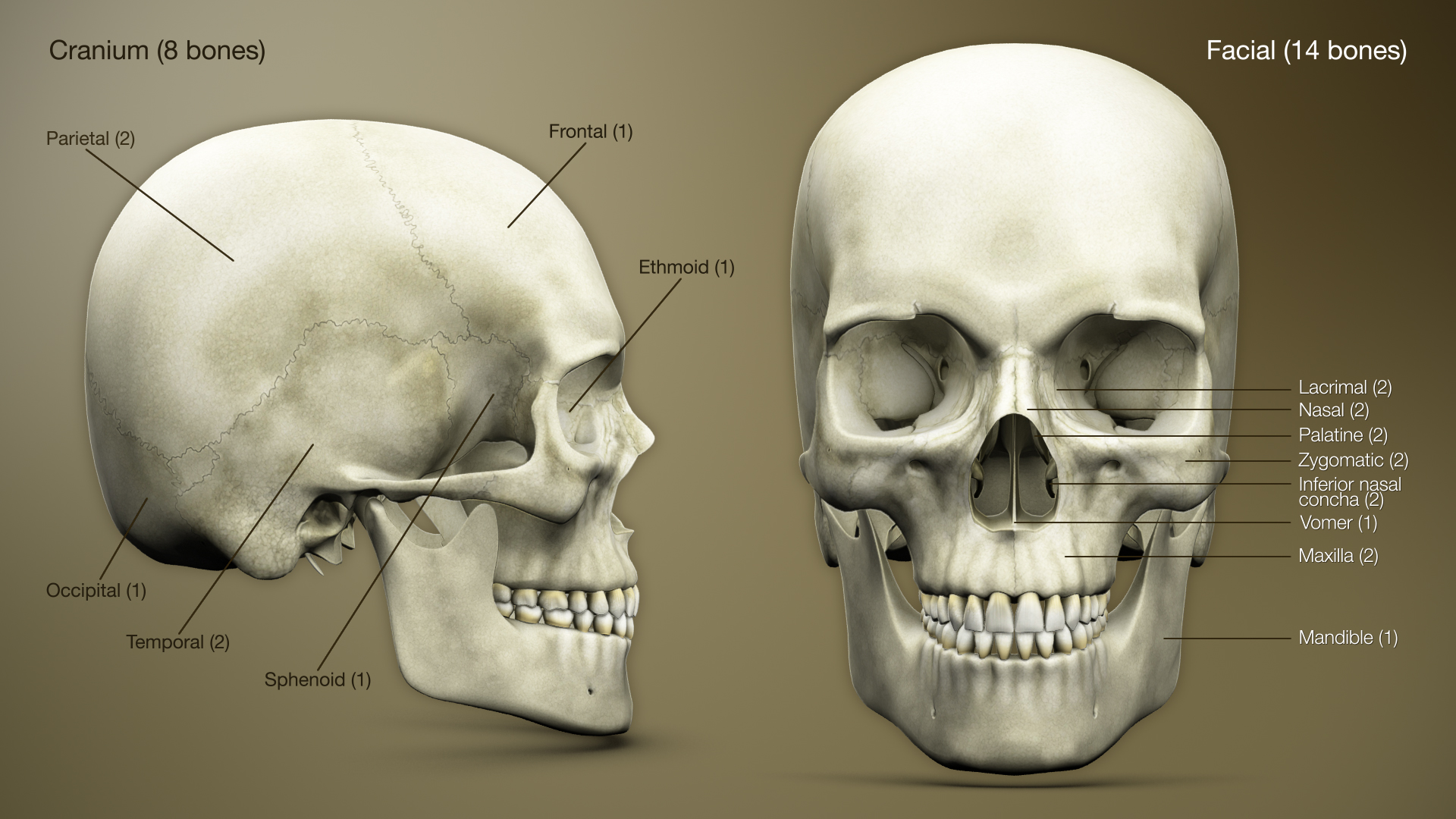
The human skull consists of the cranium and the facial bones. The cranium holds and protects the brain in a large space called the cranial vault. The cranium is formed from eight plate-shaped bones which fit together at meeting points (joints) called sutures. In addition there are 14 facial bones which form the lower front part of the skull. Together the 22 bones that compose the skull form additional, smaller spaces besides the cranial vault, such as the cavities for the eyes, the internal ear, the nose, and the mouth. The most important facial bones include the jaw or mandible, the upper jaw or maxilla, the zygomatic or cheek bone, and the nasal bone. Humans are born with separate plates which later fuse to allow flexibility as the skull passes through the pelvis and birth canal during birth. During development the eight separate plates of the immature bones fuse into one single structure known as the skull. The only bone that remains separate from the rest of the skull is the mandible.Rib cage
The rib cages are composed of 12 pairs of ribs plus the sternum for a total of 25 separate bones. The rib cage functions as protection for the vital organs such as the heart and lungs. The ribs are shaped like crescents, with one end flattened and the other end rounded. The rounded ends are attached at joints to the thoracic vertebrae at the back and the flattened ends come together at the sternum, in the front. The upper seven pairs of ribs attach to the sternum with costal cartilage and are known as "true ribs". The 8th through 10th ribs have non-costal cartilage which connects them to the ribs above, and for this they are known as "false ribs". The last two ribs are called "floating ribs" because they do not attach to the sternum or to other ribs and simply "hang free". The length of each rib increases from number one to seven and then decreases until rib pair number 12. The first rib is the shortest, broadest, flattest, and most curved.Vertebral column
At birth the majority of humans have 33 separate vertebrae. However, during normal development several vertebrae fuse, leaving a total of 24, in most cases. The confusion about whether or not there are 32–34 vertebrae stems from the fact that the two lowest vertebrae, the sacrum and the coccyx, are single bones made up of several smaller bones which have fused together. This is how the vertebrae are counted: 24 separate vertebrae and the sacrum, formed from 5 fused vertebrae, and the coccyx, formed from 3–5 fused vertebrae. If you count the coccyx and sacrum each as one vertebra, then there are 26 vertebrae. If the fused vertebrae are all counted separately, then the total number of vertebrae comes to between 32 and 34 (due to the number making up the coccyx varying between 3 and 5). The vertebral column consists of 5 parts. The most cranial (uppermost) part is made up by thecervical vertebrae
In tetrapods, cervical vertebrae (: vertebra) are the vertebrae of the neck, immediately below the skull. Truncal vertebrae (divided into thoracic and lumbar vertebrae in mammals) lie caudal (toward the tail) of cervical vertebrae. In saurop ...
(7), followed by thoracic vertebrae (12), lumbar (5), sacral (5) and coccygeal vertebrae (3–5).
Cervical vertebrae make up the junction between the vertebral column and the cranium. Sacral and coccygeal vertebrae are fused and thus often called "sacral bone" or "coccygeal bone" as unit. The sacral bone makes up the junction between the vertebral column and the pelvic bones.
Etymology
The word "axial" is taken from the word "axis" and refers to the fact that the bones are located close to or along the central "axis" of the body. The term axis means the central point around which the other structures are distributed.Short summary
The axial skeleton consists of 80 bones: * Theskull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
, which contains 22 bones, from which 8 are cranial and 14 are facial,
* 6 middle ear ossicles (3 in each ear),
* 1 hyoid bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verte ...
in the neck
The neck is the part of the body in many vertebrates that connects the head to the torso. It supports the weight of the head and protects the nerves that transmit sensory and motor information between the brain and the rest of the body. Addition ...
,
* 26 bones of vertebral column
The spinal column, also known as the vertebral column, spine or backbone, is the core part of the axial skeleton in vertebrates. The vertebral column is the defining and eponymous characteristic of the vertebrate. The spinal column is a segmente ...
,
* 1 chest bone (sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
), and
* 24 ribs (12 pairs).
See also
* Appendicular skeleton *Skull
The skull, or cranium, is typically a bony enclosure around the brain of a vertebrate. In some fish, and amphibians, the skull is of cartilage. The skull is at the head end of the vertebrate.
In the human, the skull comprises two prominent ...
*Hyoid bone
The hyoid-bone (lingual-bone or tongue-bone) () is a horseshoe-shaped bone situated in the anterior midline of the neck between the chin and the thyroid-cartilage. At rest, it lies between the base of the mandible and the third cervical verte ...
*Sternum
The sternum (: sternums or sterna) or breastbone is a long flat bone located in the central part of the chest. It connects to the ribs via cartilage and forms the front of the rib cage, thus helping to protect the heart, lungs, and major bl ...
* Ribs
References
External links
botany.uwc.ac.za
{{Authority control Human anatomy Skeletal system Axial skeleton