Axial-flow Pump on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
An axial-flow pump, or AFP, is a common type of
 An axial flow pump has a
An axial flow pump has a
 In an axial flow pump, blades have an airfoil section over which the fluid flows and pressure is developed.
For a constant flow, we have
So, the maximum energy transfer to the fluid per unit weight will be
For constant energy transfer over the entire span of the blade, the above equation should be constant for all values of . But, will increase with an increase in radius , therefore to maintain a constant value an equal increase in must take place. Since, is constant, therefore must increase on increasing . So, the blade is twisted as the radius changes.
In an axial flow pump, blades have an airfoil section over which the fluid flows and pressure is developed.
For a constant flow, we have
So, the maximum energy transfer to the fluid per unit weight will be
For constant energy transfer over the entire span of the blade, the above equation should be constant for all values of . But, will increase with an increase in radius , therefore to maintain a constant value an equal increase in must take place. Since, is constant, therefore must increase on increasing . So, the blade is twisted as the radius changes.
 The characteristics of an axial flow pump are shown in the figure. As shown in the figure, the head at the zero flow rate can be as much as three times the head at the pump's best efficiency point. Also, the power requirement increases as the flow decreases, with the highest power drawn at the zero flow rate. This characteristic is opposite to that of a
The characteristics of an axial flow pump are shown in the figure. As shown in the figure, the head at the zero flow rate can be as much as three times the head at the pump's best efficiency point. Also, the power requirement increases as the flow decreases, with the highest power drawn at the zero flow rate. This characteristic is opposite to that of a
 One of the most common applications of AFPs would be in handling sewage from commercial, municipal and industrial sources.
In sailboats, AFPs are also used in transfer pumps used for sailing ballast. In power plants, they are used for pumping water from a reservoir, river, lake or sea for cooling the main condenser. In the chemical industry, they are used for the circulation of large masses of liquid, such as in
One of the most common applications of AFPs would be in handling sewage from commercial, municipal and industrial sources.
In sailboats, AFPs are also used in transfer pumps used for sailing ballast. In power plants, they are used for pumping water from a reservoir, river, lake or sea for cooling the main condenser. In the chemical industry, they are used for the circulation of large masses of liquid, such as in
pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
that essentially consists of a propeller
A propeller (often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working flu ...
(an axial impeller) in a pipe. The propeller can be driven directly by a sealed motor in the pipe or by electric motor or petrol/diesel engines mounted to the pipe from the outside or by a right-angle drive shaft that pierces the pipe.
Fluid particles, in course of their flow through the pump, do not change their radial locations since the change in radius at the entry (called 'suction') and the exit (called 'discharge') of the pump is very small. Hence the name "axial" pump.
Operation
 An axial flow pump has a
An axial flow pump has a propeller
A propeller (often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working flu ...
-type of impeller running in a casing.
The pressure in an axial flow pump is developed by the flow of liquid over the blades of impeller. The fluid is pushed in a direction parallel to the shaft of the impeller, that is, fluid particles, in course of their flow through the pump, do not change their radial locations. It allows the fluid to enter the impeller axially and discharge the fluid nearly axially. The propeller of an axial flow pump is driven by a motor.
Notes
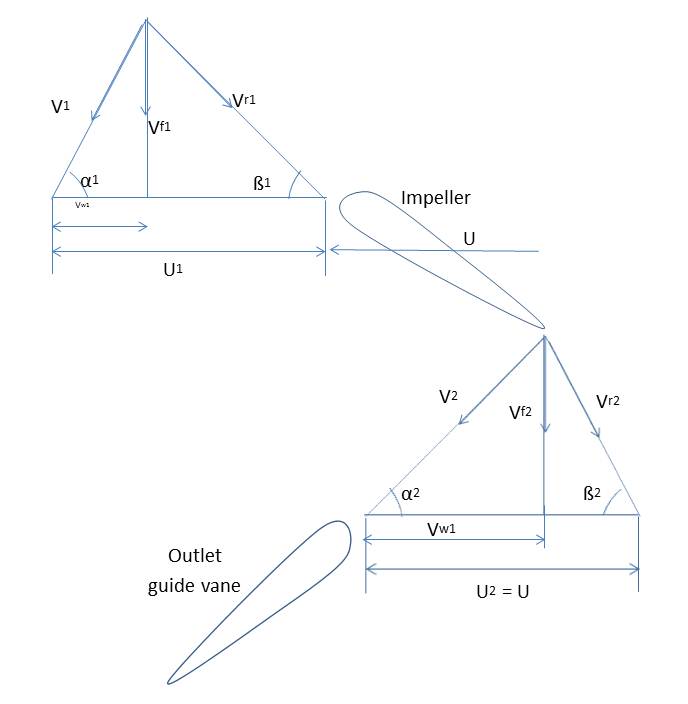
* The fixed diffuser vanes are used to remove the whirl component () of the discharge velocity of the impeller and to convert the energy to pressure. * The impeller vanes may be adjustable. * The machine may be fitted with pre-entry vanes to eliminate pre-rotation and to make the flow purely axial. Work done on the fluid per unit weight = where is the blade velocity. For maximum energy transfer, , that is, Therefore, from outlet velocity triangle, we have Therefore, the maximum energy transfer per unit weight by an axial flow pump =Blade design
 In an axial flow pump, blades have an airfoil section over which the fluid flows and pressure is developed.
For a constant flow, we have
So, the maximum energy transfer to the fluid per unit weight will be
For constant energy transfer over the entire span of the blade, the above equation should be constant for all values of . But, will increase with an increase in radius , therefore to maintain a constant value an equal increase in must take place. Since, is constant, therefore must increase on increasing . So, the blade is twisted as the radius changes.
In an axial flow pump, blades have an airfoil section over which the fluid flows and pressure is developed.
For a constant flow, we have
So, the maximum energy transfer to the fluid per unit weight will be
For constant energy transfer over the entire span of the blade, the above equation should be constant for all values of . But, will increase with an increase in radius , therefore to maintain a constant value an equal increase in must take place. Since, is constant, therefore must increase on increasing . So, the blade is twisted as the radius changes.
Characteristics
 The characteristics of an axial flow pump are shown in the figure. As shown in the figure, the head at the zero flow rate can be as much as three times the head at the pump's best efficiency point. Also, the power requirement increases as the flow decreases, with the highest power drawn at the zero flow rate. This characteristic is opposite to that of a
The characteristics of an axial flow pump are shown in the figure. As shown in the figure, the head at the zero flow rate can be as much as three times the head at the pump's best efficiency point. Also, the power requirement increases as the flow decreases, with the highest power drawn at the zero flow rate. This characteristic is opposite to that of a centrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the Energy transformation, conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are ...
where power requirement increases with an increase in the flow. Also the power requirements and pump head increases with an increase in pitch, thus allowing the pump to adjust according to the system conditions to provide the most efficient operation.
Advantages
The main advantage of an axial flow pump is that it has a relatively high discharge (flow rate) at a relatively low head (vertical distance). For example, it can pump up to 3 times more water and other fluids at lifts of less than 4 meters as compared to the more common radial-flow orcentrifugal pump
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the Energy transformation, conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are ...
. It also can easily be adjusted to run at peak efficiency
Efficiency is the often measurable ability to avoid making mistakes or wasting materials, energy, efforts, money, and time while performing a task. In a more general sense, it is the ability to do things well, successfully, and without waste.
...
at low-flow/high-pressure and high-flow/low-pressure by changing the pitch on the propeller (some models only).
The effect of turning of the fluid is not too severe in an axial pump
and the length of the impeller blades is also short. This leads to lower hydrodynamic losses and higher stage efficiencies. These pumps have the smallest of the dimensions among many of the conventional pumps and are more suited for low heads and higher discharges.
Applications
 One of the most common applications of AFPs would be in handling sewage from commercial, municipal and industrial sources.
In sailboats, AFPs are also used in transfer pumps used for sailing ballast. In power plants, they are used for pumping water from a reservoir, river, lake or sea for cooling the main condenser. In the chemical industry, they are used for the circulation of large masses of liquid, such as in
One of the most common applications of AFPs would be in handling sewage from commercial, municipal and industrial sources.
In sailboats, AFPs are also used in transfer pumps used for sailing ballast. In power plants, they are used for pumping water from a reservoir, river, lake or sea for cooling the main condenser. In the chemical industry, they are used for the circulation of large masses of liquid, such as in evaporator
An evaporator is a type of heat exchanger device that facilitates evaporation by utilizing conductive and convective heat transfer, which provides the necessary thermal energy for phase transition from liquid to vapour. Within evaporators, a ci ...
s and crystallizers. In sewage treatment
Sewage treatment is a type of wastewater treatment which aims to remove contaminants from sewage to produce an effluent that is suitable to discharge to the surrounding environment or an intended reuse application, thereby preventing water p ...
, an AFP is often used for internal mixed liquor recirculation (i.e. transferring nitrified mixed liquor from aeration zone to denitrification zone).
In agriculture and fisheries very large horsepower AFPs are used to lift water for irrigation and drainage. In East Asia, millions of smaller horsepower (6-20 HP) mobile units are powered mostly by single cylinder diesel and petrol engines. They are used by smaller farmers for crop irrigation, drainage and fisheries. Impeller designs have improved as well bringing even more efficiency and reducing energy costs to farming there. Earlier designs were less than two meters long but nowadays they can be up to 6 meters or more to enable them to more safely "reach out" to the water source while allowing the power source (many times two-wheel tractors are used) to be kept in safer, more stable positions, as shown in the adjacent picture.
See also
*Pump
A pump is a device that moves fluids (liquids or gases), or sometimes Slurry, slurries, by mechanical action, typically converted from electrical energy into hydraulic or pneumatic energy.
Mechanical pumps serve in a wide range of application ...
* Specific Speed
*Axial compressor
An axial compressor is a gas compressor that can continuously pressurize gases. It is a rotating, airfoil-based compressor in which the gas or working fluid principally flows parallel to the axis of rotation, or axially. This differs from other ...
* Roots blower
References
Bibliography
*SM Yahya "Turbines Compressors and Fans, 3rd edition", Tata McGraw-Hill Education, 2005 *A Valan Arasu "Turbo Machines, 2nd edition", Vikas Publishing House Pvt. Ltd. {{DEFAULTSORT:Axial Flow Pump Pumps