Auxiliary Cell on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The auxiliary cell is a

 Fungal morphology and anatomy
{{mycology-stub
Fungal morphology and anatomy
{{mycology-stub
spore
In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, ...
-like structure that form within the fungal
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
family
Family (from la, familia) is a group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its members and of society. Idea ...
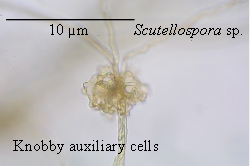
Gigasporaceae (order Gigasporales). Auxiliary cells have thin cell wall
A cell wall is a structural layer surrounding some types of cells, just outside the cell membrane. It can be tough, flexible, and sometimes rigid. It provides the cell with both structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mec ...
s, (spiny), papillate, knobby or sometimes smooth surfaces, and are formed from hyphae
A hypha (; ) is a long, branching, filamentous structure of a fungus, oomycete, or actinobacterium. In most fungi, hyphae are the main mode of vegetative growth, and are collectively called a mycelium.
Structure
A hypha consists of one or ...
after spore germination before the formation of mycorrhizae
A mycorrhiza (from Greek μύκης ', "fungus", and ῥίζα ', "root"; pl. mycorrhizae, mycorrhiza or mycorrhizas) is a symbiotic association between a fungus and a plant. The term mycorrhiza refers to the role of the fungus in the plan ...
, and then on the extraradical hyphae in the soil. They may not be 'cells' in the biological sense of the word, as they are structures found with coenocytic hyphae belonging to members of the phylum (division) Glomeromycota
Glomeromycota (often referred to as glomeromycetes, as they include only one class, Glomeromycetes) are one of eight currently recognized divisions within the kingdom Fungi,
with approximately 230 described species. Members of the Glomeromyco ...
. Mostly they are known from members of the Gigasporaceae. Currently this family contains '' Gigaspora'', '' Scutellospora'' and '' Racocetra'', but there are other generic names that have not been widely accepted (''Dentiscutata'', ''Cetraspora'', ''Fuscutata'' and ''Quatunica'') — all of these form auxiliary cells. Members of the genus ''Pacispora
The Pacisporaceae are a family of fungi in the order Diversisporales
The ''Diversisporales'' are an order of generally hypogeous (underground) arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within the division Glomeromycota. Many have vesicles for energy sto ...
'' (another genus in the Diversisporales
The ''Diversisporales'' are an order of generally hypogeous (underground) arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi within the division Glomeromycota. Many have vesicles for energy storage, or auxiliary cells. Species produce a wide range of spore
...
) are also said to produce a kind of auxiliary cell but this requires further confirmation.
References

 Fungal morphology and anatomy
{{mycology-stub
Fungal morphology and anatomy
{{mycology-stub