Arlington Line on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
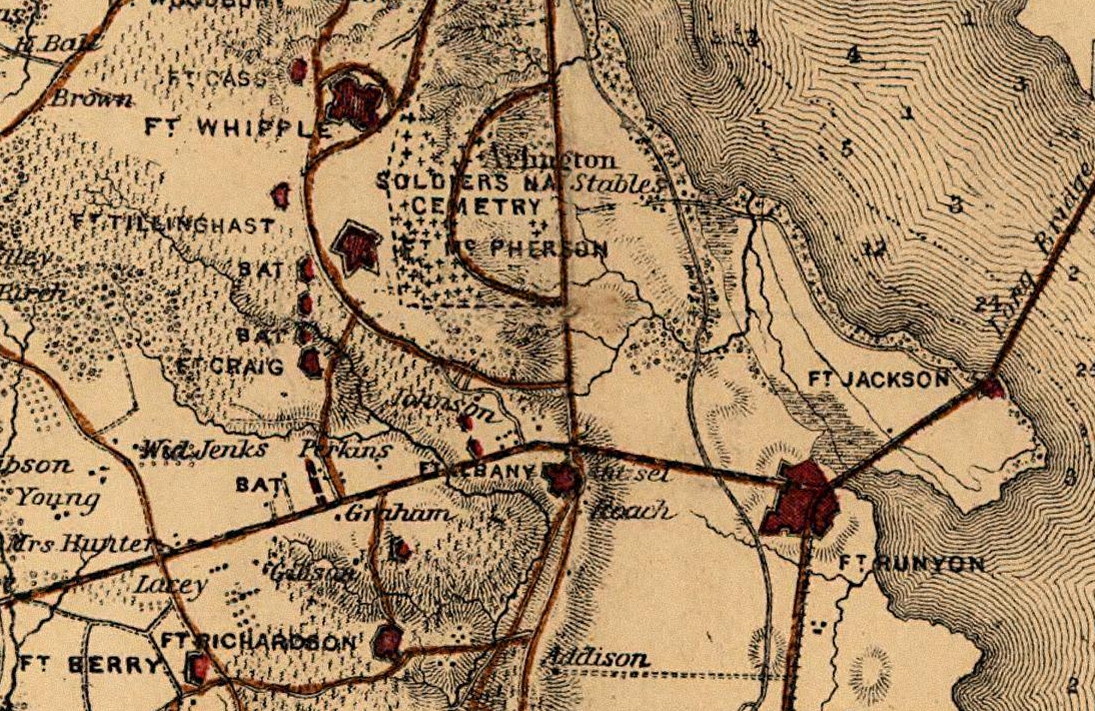 The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications that the
The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications that the
(2)
(3) Just across the
Arlington Historical Society - Military-use structures
{{coord, 38, 53, 22.5, N, 77, 5, 1.5, W, region:US-VA_type:landmark, display=title Virginia in the American Civil War Buildings and structures in Arlington County, Virginia Civil War defenses of Washington, D.C. 1861 establishments in Virginia
 The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications that the
The Arlington Line was a series of fortifications that the Union Army
During the American Civil War, the Union Army, also known as the Federal Army and the Northern Army, referring to the United States Army, was the land force that fought to preserve the Union of the collective states. It proved essential to th ...
erected in Alexandria County (now Arlington County
Arlington County is a county in the Commonwealth of Virginia. The county is situated in Northern Virginia on the southwestern bank of the Potomac River directly across from the District of Columbia, of which it was once a part. The county is ...
), Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
, to protect the City of Washington
The District of Columbia was created in 1801 as the federal district of the United States, with territory previously held by the states of Maryland and Virginia ceded to the federal government of the United States for the purpose of creating its ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
(see Civil War Defenses of Washington and Washington, D.C., in the American Civil War
During the American Civil War (1861–1865), Washington, D.C., the capital city of the United States, was the center of the Union war effort, which rapidly turned it from a small city into a major capital with full civic infrastructure and stron ...
).(1) (2)
(3) Just across the
Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands of West Virginia, Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Datas ...
from the Union capital city, Confederate Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the East Coast of the United States, Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography an ...
was a major Union concern when the war began. In May 1861, federal troops seized much the County and immediately began constructing a group of forts near Washington on the Virginia side of the River to protect the capital city.
After the Confederate Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighti ...
routed the Union Army at the First Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late July 1861, the Union Army began construction on a line of breastworks and lunette
A lunette (French ''lunette'', "little moon") is a half-moon shaped architectural space, variously filled with sculpture, painted, glazed, filled with recessed masonry, or void.
A lunette may also be segmental, and the arch may be an arc taken ...
s to the west of the earlier fortifications. These and larger fortifications later constructed nearby became known as the Arlington Line. They included a lunette ( Fort Cass) and Fort Whipple, which became parts of Fort Myer
Fort Myer is the previous name used for a U.S. Army post next to Arlington National Cemetery in Arlington County, Virginia, and across the Potomac River from Washington, D.C. Founded during the American Civil War as Fort Cass and Fort Whippl ...
, later to be renamed as Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall
Joint Base Myer–Henderson Hall is a Joint Base of the United States military that is located around Arlington, Virginia which is made up of Fort Myer (Arl), Fort McNair (SW DC), and Henderson Hall. It is the local residue of the Base Realign ...
.
The Arlington Line was never attacked, even after the federal defeat at the Second Battle of Bull Run (Manassas) in late August 1863. The Line therefore effectively served its strategic purpose.
Major Daniel Phineas Woodbury was the Union engineer who designed and constructed the Arlington Line. One of its forts, Fort Woodbury
Fort Woodbury was part of the Arlington Line, an extensive network of fortifications erected in present-day Arlington County, Virginia to protect Washington, D.C. from Confederate attack during the American Civil War. Construction began on the ...
(which once stood in what is today Arlington's Courthouse neighborhood), was named for him.
Notes
References/External links
Arlington Historical Society - Military-use structures
{{coord, 38, 53, 22.5, N, 77, 5, 1.5, W, region:US-VA_type:landmark, display=title Virginia in the American Civil War Buildings and structures in Arlington County, Virginia Civil War defenses of Washington, D.C. 1861 establishments in Virginia