Ammonia Production on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ammonia production takes place worldwide, mostly in large-scale manufacturing plants that produce 240 million metric tonnes of ammonia (2023) annually. Based on the annual production in 2023 the major part (~70%) of the production facilities are based in China (29%), India (9.5%), USA (9.5%), Russia (9.5%), Indonesia (4%), Iran (2,9%), Egypt (2,7%), and middle Saudi Arabia (2,7%). 80% or more of

CaO + 3C <=> CaC2 + CO
: CaC2 + N2 <=> CaCN2 + C
: CaCN2 + 3H2O <=> CaCO3 + 2NH3
 Sustainable production is possible by using non-polluting methane pyrolysis or generating hydrogen by water electrolysis with
Sustainable production is possible by using non-polluting methane pyrolysis or generating hydrogen by water electrolysis with 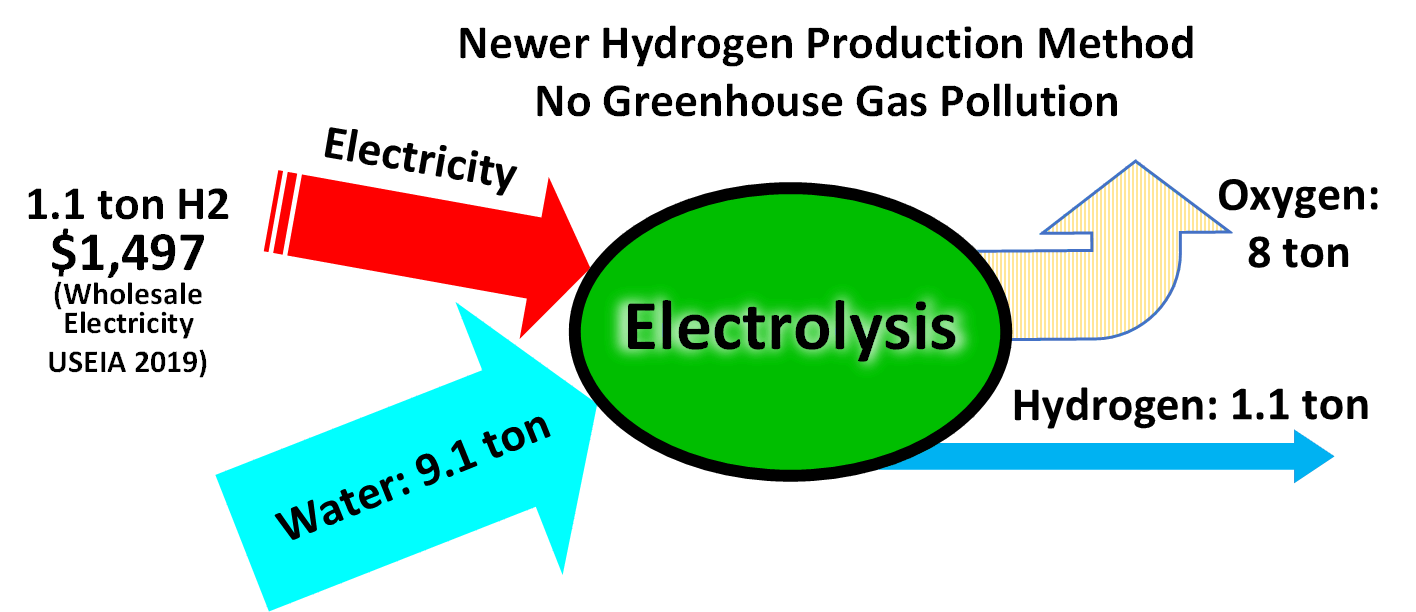 In a
In a
 Making ammonia from coal is mainly practised in China, where it is the main source. Oxygen from the air separation module is fed to the gasifier to convert coal into synthesis gas (, CO, ) and . Most gasifiers are based on fluidized beds that operate above atmospheric pressure and have the ability to utilize different coal feeds.
Making ammonia from coal is mainly practised in China, where it is the main source. Oxygen from the air separation module is fed to the gasifier to convert coal into synthesis gas (, CO, ) and . Most gasifiers are based on fluidized beds that operate above atmospheric pressure and have the ability to utilize different coal feeds.
Today's Hydrogen Production IndustryEnergy Use and Energy Intensity of the U.S. Chemical Industry
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180930081211/https://www.energystar.gov/ia/business/industry/industrial_LBNL-44314.pdf , date=2018-09-30 , Report LBNL-44314,
Ammonia: The Next Step
includes a detailed
Ammonia production process plant flow sheet
in brief with three controls. Ammonia Chemical processes
ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
is used as fertilizer
A fertilizer or fertiliser is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from liming materials or other non-nutrient soil amendments. Man ...
. Ammonia is also used for the production of plastics, fibres, explosives, nitric acid
Nitric acid is an inorganic compound with the formula . It is a highly corrosive mineral acid. The compound is colorless, but samples tend to acquire a yellow cast over time due to decomposition into nitrogen oxide, oxides of nitrogen. Most com ...
(via the Ostwald process), and intermediates for dyes and pharmaceuticals. The industry contributes 1% to 2% of global . Between 18–20 Mt of the gas is transported globally each year.
History
Dry distillation
Before the start ofWorld War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting to ...
, most ammonia was obtained by the dry distillation
Distillation, also classical distillation, is the process of separating the component substances of a liquid mixture of two or more chemically discrete substances; the separation process is realized by way of the selective boiling of the mixt ...
of nitrogenous vegetable and animal products; by the reduction of nitrous acid
Nitrous acid (molecular formula ) is a weak and monoprotic acid known only in solution, in the gas phase, and in the form of nitrite () salts. It was discovered by Carl Wilhelm Scheele, who called it " phlogisticated acid of niter". Nitrous ac ...
and nitrite
The nitrite polyatomic ion, ion has the chemical formula . Nitrite (mostly sodium nitrite) is widely used throughout chemical and pharmaceutical industries. The nitrite anion is a pervasive intermediate in the nitrogen cycle in nature. The name ...
s with hydrogen
Hydrogen is a chemical element; it has chemical symbol, symbol H and atomic number 1. It is the lightest and abundance of the chemical elements, most abundant chemical element in the universe, constituting about 75% of all baryon, normal matter ...
; and also by the decomposition of ammonium salts by alkaline hydroxides or by quicklime
Calcium oxide (formula: Ca O), commonly known as quicklime or burnt lime, is a widely used chemical compound. It is a white, caustic, alkaline, crystalline solid at room temperature. The broadly used term '' lime'' connotes calcium-containin ...
, the salt most generally used being the chloride ( sal-ammoniac).

Frank–Caro process
Adolph Frank and Nikodem Caro found that Nitrogen could be fixed by using the samecalcium carbide
Calcium carbide, also known as calcium acetylide, is a chemical compound with the chemical formula of . Its main use industrially is in the production of acetylene and calcium cyanamide.
The pure material is colorless, while pieces of technica ...
produced to make acetylene
Acetylene (Chemical nomenclature, systematic name: ethyne) is a chemical compound with the formula and structure . It is a hydrocarbon and the simplest alkyne. This colorless gas is widely used as a fuel and a chemical building block. It is u ...
to form calcium-cyanamide, which could then be divided with water to form ammonia.
The method was developed between 1895 and 1899.
: Birkeland–Eyde process
While not strictly speaking a method of producing ammonia, nitrogen can be fixed by passing it (with oxygen) through an electric spark.Nitrides
Heating metals such as magnesium in an atmosphere of pure nitrogen producesnitride
In chemistry, a nitride is a chemical compound of nitrogen. Nitrides can be inorganic or organic, ionic or covalent. The nitride anion, N3−, is very elusive but compounds of nitride are numerous, although rarely naturally occurring. Some nitr ...
, which when combined with water produce metal hydroxide and ammonia.
Haber-Bosch process
Environmental Impacts
Because ammonia production depends on a reliable supply ofenergy
Energy () is the physical quantity, quantitative physical property, property that is transferred to a physical body, body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of Work (thermodynamics), work and in the form of heat and l ...
, fossil fuels are often used, contributing to climate change when they are combusted and create greenhouse gasses. Ammonia production also introduces nitrogen into the Earth's nitrogen cycle, causing imbalances that contribute to environmental issues such as algae blooms. Certain production methods prove to have less of an environmental impact, such as those powered by renewable or nuclear energy.
Sustainable production
 Sustainable production is possible by using non-polluting methane pyrolysis or generating hydrogen by water electrolysis with
Sustainable production is possible by using non-polluting methane pyrolysis or generating hydrogen by water electrolysis with renewable energy
Renewable energy (also called green energy) is energy made from renewable resource, renewable natural resources that are replenished on a human lifetime, human timescale. The most widely used renewable energy types are solar energy, wind pow ...
sources. Thyssenkrupp
ThyssenKrupp AG (, ; stylized as thyssenkrupp) is a German industrial engineering and steel production multinational conglomerate. It resulted from the 1999 merger of Thyssen AG and Krupp and has its operational headquarters in Duisburg and E ...
Uhde Chlorine Engineers expanded its annual production capacity for alkaline water electrolysis to 1 gigawatt of electrolyzer capacity for this purpose.
 In a
In a hydrogen economy
The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not ava ...
some hydrogen production
Hydrogen gas is produced by several industrial methods. Nearly all of the world's current supply of hydrogen is created from fossil fuels. Article in press. Most hydrogen is ''gray hydrogen'' made through steam methane reforming. In this process, ...
could be diverted to feedstock use. For example, in 2002, Iceland produced 2,000 tons of hydrogen gas by electrolysis, using excess power from its hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is Electricity generation, electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies 15% of the world's electricity, almost 4,210 TWh in 2023, which is more than all other Renewable energ ...
plants, primarily for fertilizer.
The Vemork hydroelectric plant in Norway used its surplus electricity output to generate renewable nitric acid from 1911 to 1971,
requiring 15 MWh/ton of nitric acid. The same reaction is carried out by lightning, providing a natural source of soluble nitrates. Natural gas remains the lowest cost method.
Wastewater
Wastewater (or waste water) is water generated after the use of freshwater, raw water, drinking water or saline water in a variety of deliberate applications or processes. Another definition of wastewater is "Used water from any combination of do ...
is often high in ammonia. Because discharging ammonia-laden water into the environment damages marine life, nitrification
''Nitrification'' is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrate via the intermediary nitrite. Nitrification is an important step in the nitrogen cycle in soil. The process of complete nitrification may occur through separate organisms or ent ...
is often necessary to remove the ammonia. This may become a potentially sustainable source of ammonia given its abundance. Alternatively, ammonia from wastewater can be sent into an ammonia electrolyzer (ammonia electrolysis
In chemistry and manufacturing, electrolysis is a technique that uses Direct current, direct electric current (DC) to drive an otherwise non-spontaneous chemical reaction. Electrolysis is commercially important as a stage in the separation of c ...
) operating with renewable energy sources to produce hydrogen and clean water. Ammonia electrolysis may require much less thermodynamic energy than water electrolysis (only 0.06 V in alkaline media).
Another option for recovering ammonia from wastewater is to use the mechanics of the ammonia-water thermal absorption cycle. Ammonia can thus be recovered either as a liquid or as ammonium hydroxide. The advantage of the former is that it is much easier to handle and transport, whereas the latter has commercial value at concentrations of 30 percent in solution.
Coal
 Making ammonia from coal is mainly practised in China, where it is the main source. Oxygen from the air separation module is fed to the gasifier to convert coal into synthesis gas (, CO, ) and . Most gasifiers are based on fluidized beds that operate above atmospheric pressure and have the ability to utilize different coal feeds.
Making ammonia from coal is mainly practised in China, where it is the main source. Oxygen from the air separation module is fed to the gasifier to convert coal into synthesis gas (, CO, ) and . Most gasifiers are based on fluidized beds that operate above atmospheric pressure and have the ability to utilize different coal feeds.
Production plants
The American Oil Co in the mid-1960s positioned a single-converter ammonia plant engineered by M. W. Kellogg at Texas City, Texas, with a capacity of 544 m.t./day. It used a single-train design that received the “Kirkpatrick Chemical Engineering Achievement Award” in 1967. The plant used a four-case centrifugal compressor to compress thesyngas
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide in various ratios. The gas often contains some carbon dioxide and methane. It is principally used for producing ammonia or methanol. Syngas is combustible and can be used as ...
to a pressure of 152 bar Final compression to an operating pressure of 324 bar occurred in a reciprocating compressor. Centrifugal compressors for the synthesis loop and refrigeration services provided significant cost reductions.
Almost every plant built between 1964 and 1992 had large single-train designs with syngas manufacturing at 25–35 bar and ammonia synthesis at 150–200 bar. Braun Purifier process plants utilized a primary or tubular reformer with a low outlet temperature and high methane leakage to reduce the size and cost of the reformer. Air was added to the secondary reformer to reduce the methane content of the primary reformer exit stream to 1–2%. Excess nitrogen and other impurities were erased downstream of the methanator. Because the syngas was essentially free of impurities, two axial-flow ammonia converters were used. In early 2000 Uhde developed a process that enabled plant capacities of 3300 mtpd and more. The key innovation was a single-flow synthesis loop at medium pressure in series with a conventional high-pressure synthesis loop.
Small-scale onsite plants
In April 2017, Japanese company Tsubame BHB implemented a method of ammonia synthesis that could allow economic production at scales 1-2 orders of magnitude below than ordinary plants with utilizing electrochemical catalyst.Green ammonia
In 2024, theBBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) is a British public service broadcaster headquartered at Broadcasting House in London, England. Originally established in 1922 as the British Broadcasting Company, it evolved into its current sta ...
announced numerous companies were attempting to reduce the 2% of global carbon dioxide emissions caused by the use/production of ammonia by producing the product in labs. The industry has become known as ''"''green ammonia''."''
Byproducts and shortages due to shutdowns
One of the main industrial byproducts of ammonia production is CO2. In 2018, high oil prices resulted in an extended summer shutdown of European ammonia factories causing a commercial CO2 shortage, thus limiting production of CO2-based products such as beer and soft drinks. This situation repeated in September 2021 due to a 250-400% increase in the wholesale price of natural gas over the course of the year.See also
*Ammonia
Ammonia is an inorganic chemical compound of nitrogen and hydrogen with the chemical formula, formula . A Binary compounds of hydrogen, stable binary hydride and the simplest pnictogen hydride, ammonia is a colourless gas with a distinctive pu ...
*Amine gas treating
Amine gas treating, also known as amine scrubbing, gas sweetening and acid gas removal, refers to a group of processes that use aqueous solutions of various Amine#Aliphatic amines, alkylamines (commonly referred to simply as amines) to remove hydr ...
*Haber process
The Haber process, also called the Haber–Bosch process, is the main industrial procedure for the ammonia production, production of ammonia. It converts atmospheric nitrogen (N2) to ammonia (NH3) by a reaction with hydrogen (H2) using finely di ...
* Liquid nitrogen wash
*Hydrogen economy
The hydrogen economy is an umbrella term for the roles hydrogen can play alongside low-carbon electricity to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases. The aim is to reduce emissions where cheaper and more energy-efficient clean solutions are not ava ...
* Methane pyrolysis
References
Works cited
*External links
Today's Hydrogen Production Industry
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20180930081211/https://www.energystar.gov/ia/business/industry/industrial_LBNL-44314.pdf , date=2018-09-30 , Report LBNL-44314,
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory (LBNL, Berkeley Lab) is a Federally funded research and development centers, federally funded research and development center in the Berkeley Hills, hills of Berkeley, California, United States. Established i ...
(Scroll down to page 39 of 40 PDF pages for a list of the ammonia plants in the United States)Ammonia: The Next Step
includes a detailed
process flow diagram
A process flow diagram (PFD) is a diagram commonly used in chemical and process engineering to indicate the general flow of plant processes and equipment. The PFD displays the relationship between ''major'' equipment of a plant facility and does ...
.Ammonia production process plant flow sheet
in brief with three controls. Ammonia Chemical processes