Amber Billey on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Amber is
Amber is
Retrieved 6 September 2018.
37.11
. Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the
Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the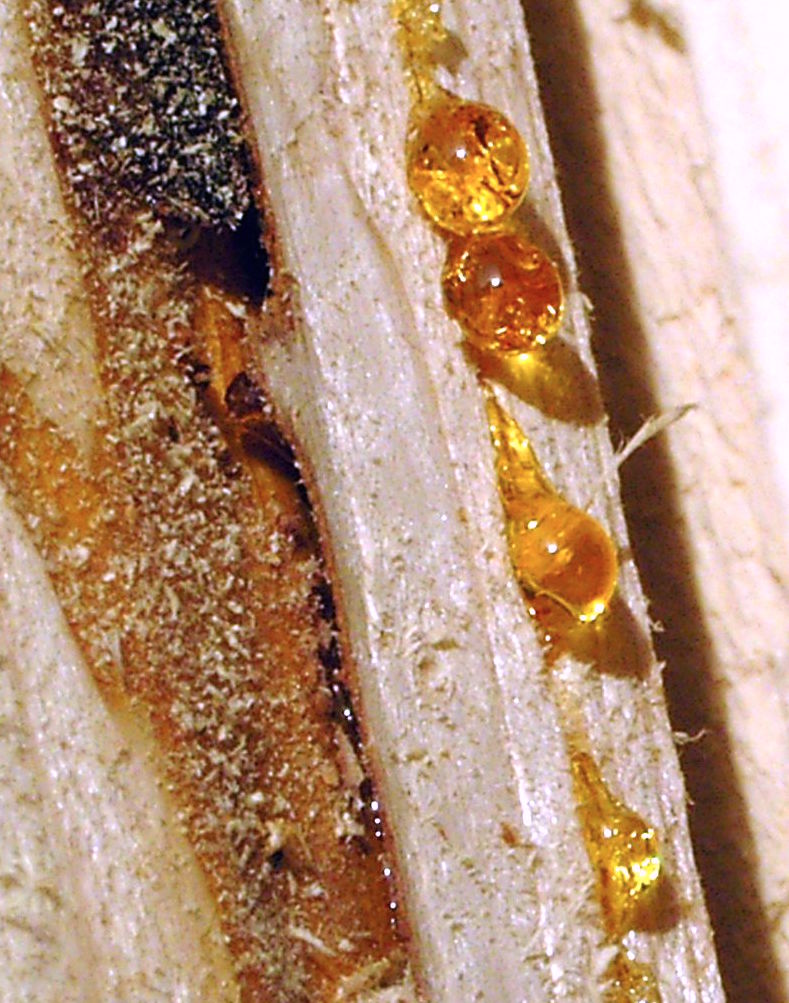  Pliny also cites the opinion of Nicias ( 470–413 BCE), according to whom amber Besides the fanciful explanations according to which amber is "produced by the Sun", Pliny cites opinions that are well aware of its origin in tree resin, citing the native Latin name of ''succinum'' (''sūcinum'', from ''sucus'' "juice"). In Book 37, section XI of ''Natural History'', Pliny wrote:
He also states that amber is also found in Egypt and India, and he even refers to the
Pliny also cites the opinion of Nicias ( 470–413 BCE), according to whom amber Besides the fanciful explanations according to which amber is "produced by the Sun", Pliny cites opinions that are well aware of its origin in tree resin, citing the native Latin name of ''succinum'' (''sūcinum'', from ''sucus'' "juice"). In Book 37, section XI of ''Natural History'', Pliny wrote:
He also states that amber is also found in Egypt and India, and he even refers to the
 The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber.
The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber.
 Amber is globally distributed in or around all continents, mainly in rocks of
Amber is globally distributed in or around all continents, mainly in rocks of
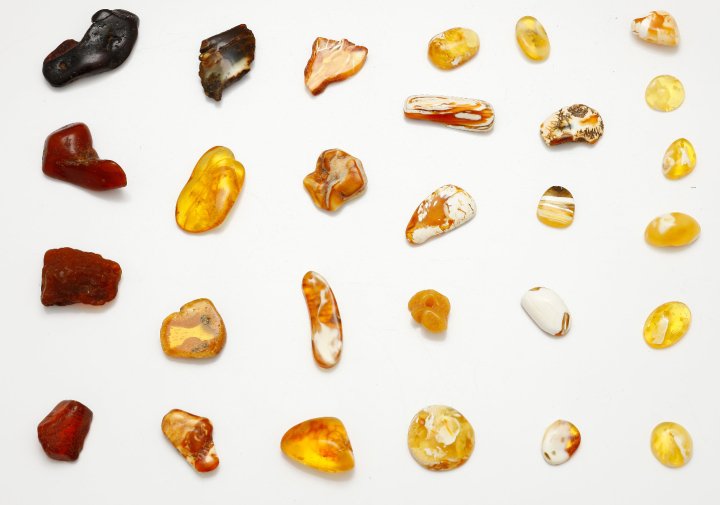 Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even
Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even 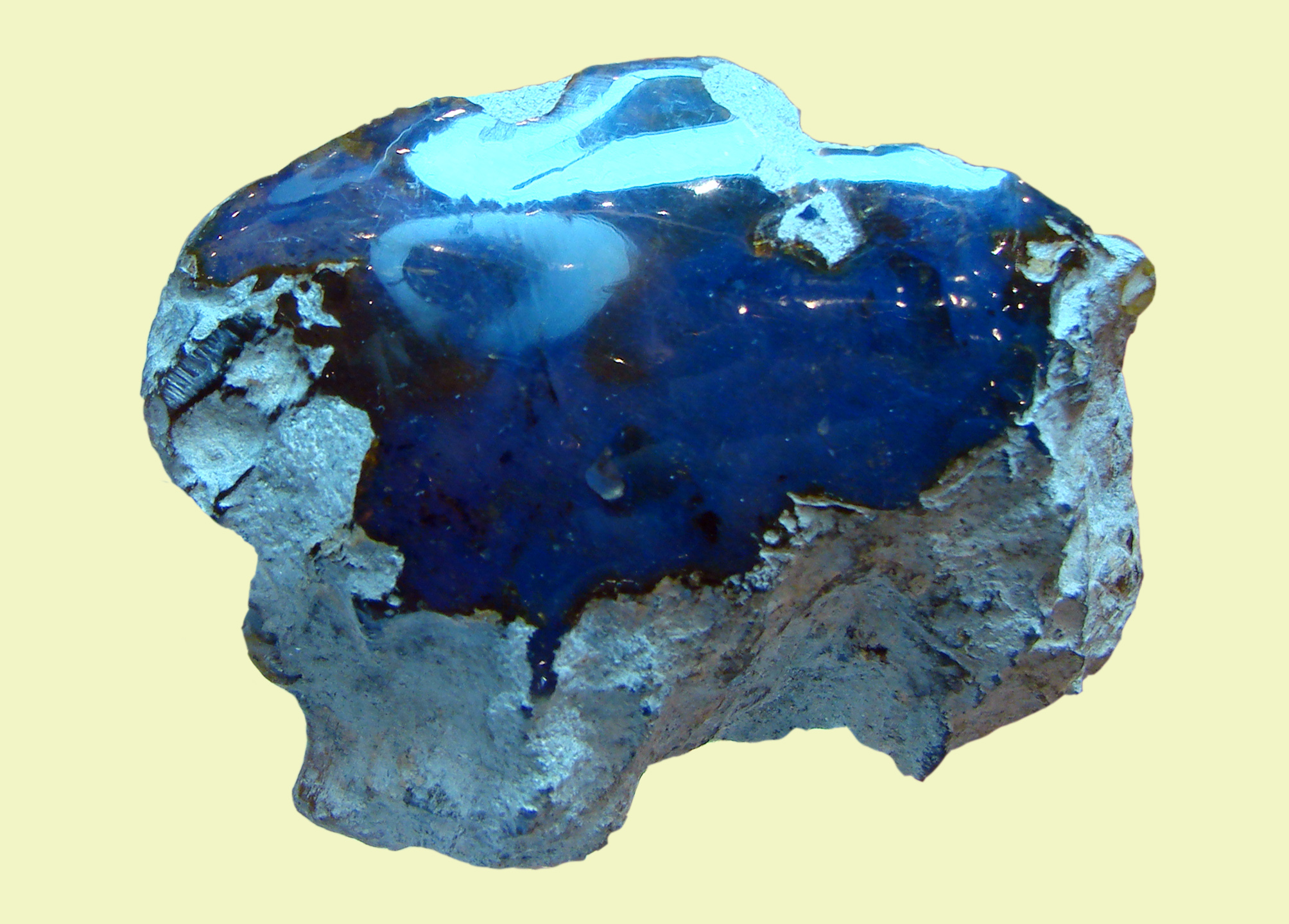 Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
 The oldest amber recovered dates to the Carboniferous, late Carboniferous period (). Its chemical composition makes it difficult to match the amber to its producers – it is most similar to the resins produced by flowering plants; however, the first flowering plants appeared in the Early Cretaceous, about 200 million years after the oldest amber known to date, and they were not common until the Late Cretaceous. Amber becomes abundant long after the Carboniferous, in the Early Cretaceous, when it is found in association with insects. The oldest amber with arthropod inclusions comes from the Late Triassic (late Carnian 230 Ma) of Italy, where four microscopic (0.2–0.1 mm) mites, ''Triasacarus,'' ''Ampezzoa, Minyacarus'' and ''Cheirolepidoptus,'' and a poorly preserved nematoceran fly were found in millimetre-sized droplets of amber. The oldest amber with significant numbers of arthropod inclusions comes from Lebanon. This amber, referred to as Lebanese amber, is roughly 125–135 million years old, is considered of high scientific value, providing evidence of some of the oldest sampled ecosystems.Poinar, P.O., Jr., and R.K. Milki (2001) ''Lebanese Amber: The Oldest Insect Ecosystem in Fossilized Resin.'' Oregon State University Press, Corvallis. .
In Lebanon, more than 450 outcrops of Lower Cretaceous amber were discovered by Dany Azar, a Lebanese paleontologist and entomologist. Among these outcrops, 20 have yielded biological inclusions comprising the oldest representatives of several recent families of terrestrial arthropods. Even older Jurassic amber has been found recently in Lebanon as well. Many remarkable insects and spiders were recently discovered in the amber of Jordan including the oldest zorapterans, Cleridae, clerid beetles, Umenocoleidae, umenocoleid cockroach, roaches, and achiliid planthoppers.
The oldest amber recovered dates to the Carboniferous, late Carboniferous period (). Its chemical composition makes it difficult to match the amber to its producers – it is most similar to the resins produced by flowering plants; however, the first flowering plants appeared in the Early Cretaceous, about 200 million years after the oldest amber known to date, and they were not common until the Late Cretaceous. Amber becomes abundant long after the Carboniferous, in the Early Cretaceous, when it is found in association with insects. The oldest amber with arthropod inclusions comes from the Late Triassic (late Carnian 230 Ma) of Italy, where four microscopic (0.2–0.1 mm) mites, ''Triasacarus,'' ''Ampezzoa, Minyacarus'' and ''Cheirolepidoptus,'' and a poorly preserved nematoceran fly were found in millimetre-sized droplets of amber. The oldest amber with significant numbers of arthropod inclusions comes from Lebanon. This amber, referred to as Lebanese amber, is roughly 125–135 million years old, is considered of high scientific value, providing evidence of some of the oldest sampled ecosystems.Poinar, P.O., Jr., and R.K. Milki (2001) ''Lebanese Amber: The Oldest Insect Ecosystem in Fossilized Resin.'' Oregon State University Press, Corvallis. .
In Lebanon, more than 450 outcrops of Lower Cretaceous amber were discovered by Dany Azar, a Lebanese paleontologist and entomologist. Among these outcrops, 20 have yielded biological inclusions comprising the oldest representatives of several recent families of terrestrial arthropods. Even older Jurassic amber has been found recently in Lebanon as well. Many remarkable insects and spiders were recently discovered in the amber of Jordan including the oldest zorapterans, Cleridae, clerid beetles, Umenocoleidae, umenocoleid cockroach, roaches, and achiliid planthoppers.
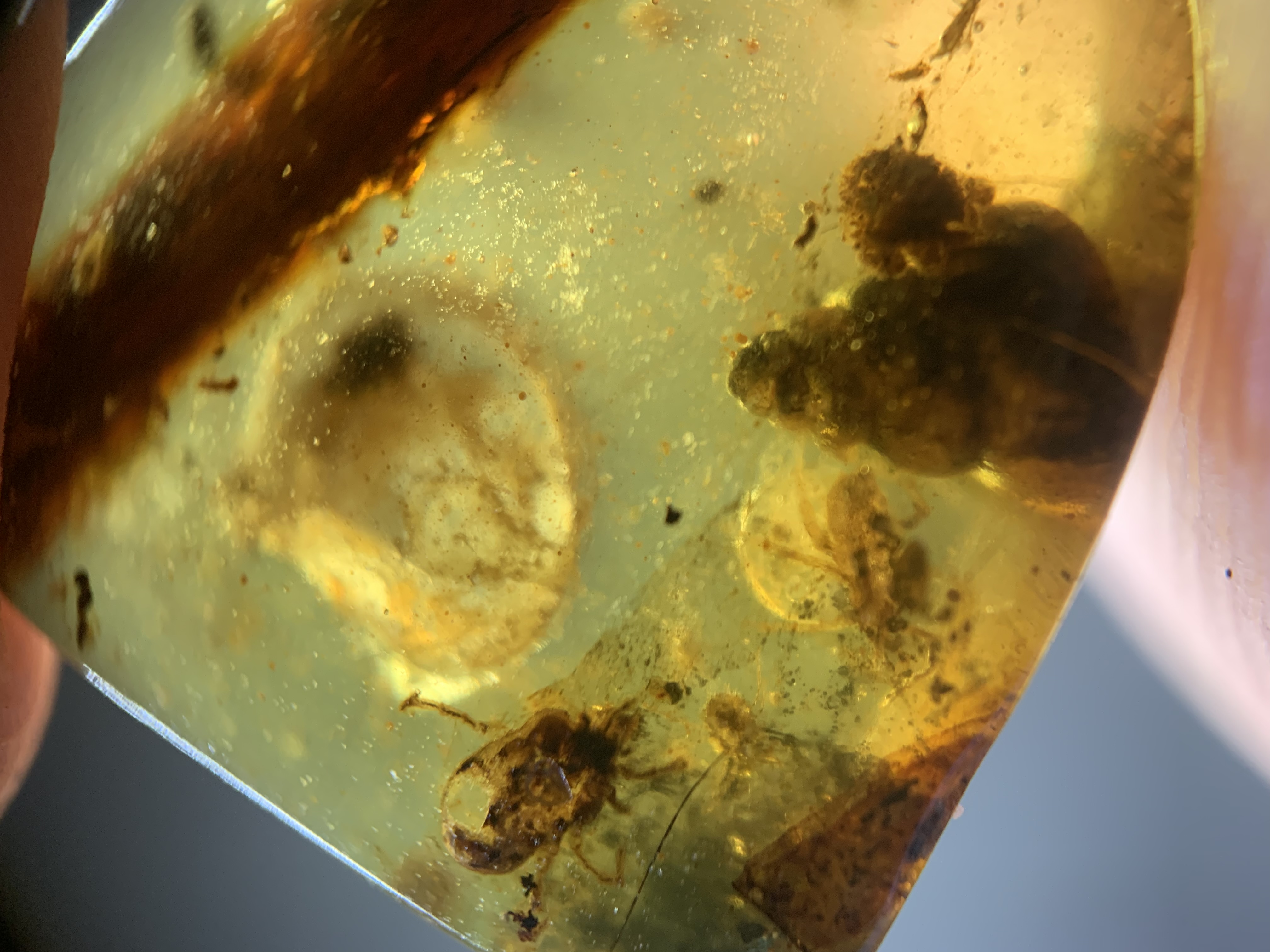 Burmese amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar is the only commercially exploited Cretaceous amber. Uranium–lead dating of zircon crystals associated with the deposit have given an estimated depositional age of approximately 99 million years ago. Over 1,300 species have been described from the amber, with over 300 in 2019 alone.
Baltic amber is found as irregular Nodule (geology), nodules in marine Glauconite, glauconitic sand, known as ''blue earth'', occurring in Upper Eocene strata of Sambia Peninsula, Sambia in Prussia. It appears to have been partly derived from older Eocene deposits and it occurs also as a derivative phase in later formations, such as Drift (geology), glacial drift. Relics of an abundant flora occur as inclusions trapped within the amber while the resin was yet fresh, suggesting relations with the flora of eastern Asia and the southern part of North America. Heinrich Göppert named the common amber-yielding pine of the Baltic forests ''Pinites succiniter'', but as the wood does not seem to differ from that of the existing genus it has been also called ''Pinus succinifera''. It is improbable that the production of amber was limited to a single species; and indeed a large number of conifers belonging to different genera are represented in the amber-flora.
Burmese amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar is the only commercially exploited Cretaceous amber. Uranium–lead dating of zircon crystals associated with the deposit have given an estimated depositional age of approximately 99 million years ago. Over 1,300 species have been described from the amber, with over 300 in 2019 alone.
Baltic amber is found as irregular Nodule (geology), nodules in marine Glauconite, glauconitic sand, known as ''blue earth'', occurring in Upper Eocene strata of Sambia Peninsula, Sambia in Prussia. It appears to have been partly derived from older Eocene deposits and it occurs also as a derivative phase in later formations, such as Drift (geology), glacial drift. Relics of an abundant flora occur as inclusions trapped within the amber while the resin was yet fresh, suggesting relations with the flora of eastern Asia and the southern part of North America. Heinrich Göppert named the common amber-yielding pine of the Baltic forests ''Pinites succiniter'', but as the wood does not seem to differ from that of the existing genus it has been also called ''Pinus succinifera''. It is improbable that the production of amber was limited to a single species; and indeed a large number of conifers belonging to different genera are represented in the amber-flora.
 The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' and the Jurassic Park (film), 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric mosquitoes trapped in amber, from which they genetically clone living dinosaurs. Scientifically this is as yet impossible, since no amber with fossilized mosquitoes has ever yielded preserved blood. Amber is, however, conducive to preserving DNA, since it dehydrates and thus stabilizes organisms trapped inside. One projection in 1999 estimated that DNA trapped in amber could last up to 100 million years, far beyond most estimates of around 1 million years in the most ideal conditions, although a later 2013 study was unable to extract DNA from insects trapped in much more recent Holocene
The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' and the Jurassic Park (film), 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric mosquitoes trapped in amber, from which they genetically clone living dinosaurs. Scientifically this is as yet impossible, since no amber with fossilized mosquitoes has ever yielded preserved blood. Amber is, however, conducive to preserving DNA, since it dehydrates and thus stabilizes organisms trapped inside. One projection in 1999 estimated that DNA trapped in amber could last up to 100 million years, far beyond most estimates of around 1 million years in the most ideal conditions, although a later 2013 study was unable to extract DNA from insects trapped in much more recent Holocene
 Amber has been used since prehistory (Solutrean) in the manufacture of jewelry and ornaments, and also in
Amber has been used since prehistory (Solutrean) in the manufacture of jewelry and ornaments, and also in
Farlang many full text historical references on Amber
IPS Publications on amber inclusions
International Paleoentomological Society: Scientific Articles on amber and its inclusions
Webmineral on Amber
Physical properties and mineralogical information
Image and locality information on amber
40 million year old extinct bee in Dominican amber {{Authority control Amber, Fossil resins Amorphous solids Traditional medicine

 Amber is
Amber is fossil
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserve ...
ized tree resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
. Examples of it have been appreciated for its color and natural beauty since the Neolithic
The Neolithic or New Stone Age (from Ancient Greek, Greek 'new' and 'stone') is an archaeological period, the final division of the Stone Age in Mesopotamia, Asia, Europe and Africa (c. 10,000 BCE to c. 2,000 BCE). It saw the Neolithic Revo ...
times, and worked as a gemstone
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, semiprecious stone, or simply gem) is a piece of mineral crystal which, when cut or polished, is used to make jewellery, jewelry or other adornments. Certain Rock (geology), rocks (such ...
since antiquity."Amber" (2004). In Maxine N. Lurie and Marc Mappen (eds.) ''Encyclopedia of New Jersey'', Rutgers University Press, . Amber is used in jewelry
Jewellery (or jewelry in American English) consists of decorative items worn for personal adornment such as brooches, ring (jewellery), rings, necklaces, earrings, pendants, bracelets, and cufflinks. Jewellery may be attached to the body or the ...
and as a healing agent in folk medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
.
There are five classes of amber, defined on the basis of their chemical constituents. Because it originates as a soft, sticky tree resin, amber sometimes contains animal and plant material as inclusions. Amber occurring in coal seams is also called resinite, and the term ''ambrite'' is applied to that found specifically within New Zealand coal seams.
Etymology
The English word ''amber'' derives fromArabic
Arabic (, , or , ) is a Central Semitic languages, Central Semitic language of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family spoken primarily in the Arab world. The International Organization for Standardization (ISO) assigns lang ...
from Middle Persian 𐭠𐭭𐭡𐭫 (''ʾnbl'' /ambar/, “ambergris”) via Middle Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. It was also the administrative language in the former Roman Provinces of Mauretania, Numidia and Africa Proconsularis under the Vandals ...
''ambar'' and Middle French
Middle French () is a historical division of the French language that covers the period from the mid-14th to the early 17th centuries. It is a period of transition during which:
* the French language became clearly distinguished from the other co ...
''ambre''. The word referred to what is now known as ''ambergris
Ambergris ( or ; ; ), ''ambergrease'', or grey amber is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull grey or blackish colour produced in the digestive system of sperm whales. Freshly produced ambergris has a marine, fecal odor. It acquires a sw ...
'' (''ambre gris'' or "gray amber"), a solid waxy substance derived from the sperm whale
The sperm whale or cachalot (''Physeter macrocephalus'') is the largest of the toothed whales and the largest toothed predator. It is the only living member of the Genus (biology), genus ''Physeter'' and one of three extant species in the s ...
. The word, in its sense of "ambergris," was adopted in Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman Conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English pe ...
in the 14th century.
In the Romance languages
The Romance languages, also known as the Latin or Neo-Latin languages, are the languages that are Language family, directly descended from Vulgar Latin. They are the only extant subgroup of the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-E ...
, the sense of the word was extended to Baltic amber
Baltic amber or succinite is amber from the Baltic region, home of its largest known deposits. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that this forested region provided the re ...
(fossil resin) from as early as the late 13th century. At first called white or yellow amber (''ambre jaune''), this meaning was adopted in English by the early 15th century. As the use of ambergris waned, this became the main sense of the word.
The two substances ("yellow amber" and "gray amber") conceivably became associated or confused because they both were found washed up on beaches. Ambergris is less dense than water and floats, whereas amber is denser and floats only in concentrated saline, or strong salty seawater though less dense than stone.
The classical names for amber, Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek ...
(''ēlektron'') and one of its Latin
Latin ( or ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally spoken by the Latins (Italic tribe), Latins in Latium (now known as Lazio), the lower Tiber area aroun ...
names, ''electrum,'' are connected to a term ἠλέκτωρ (''ēlektōr'') meaning "beaming Sun".
Homeric
Homer (; , ; possibly born ) was an Ancient Greek poet who is credited as the author of the ''Iliad'' and the ''Odyssey'', two epic poems that are foundational works of ancient Greek literature. Despite doubts about his authorship, Homer is ...
(Iliad
The ''Iliad'' (; , ; ) is one of two major Ancient Greek epic poems attributed to Homer. It is one of the oldest extant works of literature still widely read by modern audiences. As with the ''Odyssey'', the poem is divided into 24 books and ...
6.513, 19.398). The feminine being later used as a name of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It Orbit of the Moon, orbits around Earth at Lunar distance, an average distance of (; about 30 times Earth diameter, Earth's diameter). The Moon rotation, rotates, with a rotation period (lunar ...
.
According to myth, when Phaëton, son of Helios
In ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology, Helios (; ; Homeric Greek: ) is the god who personification, personifies the Sun. His name is also Latinized as Helius, and he is often given the epithets Hyperion ("the one above") an ...
(the Sun) was killed, his mourning sisters became poplar trees, and their tears became ''elektron'', amber. The word ''elektron'' gave rise to the words ''electric, electricity'', and their relatives because of amber's ability to bear a charge of static electricity
Static electricity is an imbalance of electric charges within or on the surface of a material. The charge remains until it can move away by an electric current or electrical discharge. The word "static" is used to differentiate it from electric ...
."Electric." ''Online Etymological Dictionary.''Retrieved 6 September 2018.
Varietal names
A number of regional and varietal names have been applied to ambers over the centuries, including allingite, beckerite, gedanite, kochenite, krantzite, and stantienite.History
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the ...
discussed amber in the 4th century BCE, as did Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéās ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greeks, Greek List of Graeco-Roman geographers, geographer, explo ...
(), whose work "On the Ocean" is lost, but was referenced by Pliny, according to whose ''Natural History
Natural history is a domain of inquiry involving organisms, including animals, fungi, and plants, in their natural environment, leaning more towards observational than experimental methods of study. A person who studies natural history is cal ...
'':''Natural History'37.11
.
Pytheas says that the Gutones, a people of Germany, inhabit the shores of an estuary of the Ocean called Mentonomon, their territory extending a distance of six thousand stadia; that, at one day's sail from this territory, is the Isle of Abalus, upon the shores of which, amber is thrown up by the waves in spring, it being an excretion of the sea in a concrete form; as, also, that the inhabitants use this amber by way of fuel, and sell it to their neighbors, theTeutones The Teutons (, ; ) were an ancient northern European tribe mentioned by Roman authors. The Teutons are best known for their participation, together with the Cimbri and other groups, in the Cimbrian War with the Roman Republic in the late secon ....
 Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the
Earlier Pliny says that Pytheas refers to a large island—three days' sail from the Scythia
Scythia (, ) or Scythica (, ) was a geographic region defined in the ancient Graeco-Roman world that encompassed the Pontic steppe. It was inhabited by Scythians, an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people.
Etymology
The names ...
n coast and called Balcia by Xenophon of Lampsacus (author of a fanciful travel book in Greek)—as ''Basilia''—a name generally equated with ''Abalus''. Given the presence of amber, the island could have been Heligoland
Heligoland (; , ; Heligolandic Frisian: , , Mooring Frisian: , ) is a small archipelago in the North Sea. The islands were historically possessions of Denmark, then became possessions of the United Kingdom from 1807 to 1890. Since 1890, the ...
, Zealand
Zealand ( ) is the largest and most populous islands of Denmark, island in Denmark proper (thus excluding Greenland and Disko Island, which are larger in size) at 7,031 km2 (2715 sq. mi.). Zealand had a population of 2,319,705 on 1 Januar ...
, the shores of Gdańsk Bay
Gdańsk Bay or the Gulf of Gdańsk is a southeastern bay of the Baltic Sea. It is named after the adjacent port city of Gdańsk in Poland.
Geography
The western part of Gulf of Gdańsk is formed by the shallow waters of the Bay of Puck. The so ...
, the Sambia Peninsula
Sambia () or Samland () or Kaliningrad Peninsula (official name, , ''Kaliningradsky poluostrov'') is a peninsula in the Kaliningrad Oblast of Russia, on the southeastern shore of the Baltic Sea. The peninsula is bounded by the Curonian Lagoon to ...
or the Curonian Lagoon
The Curonian Lagoon (or Bay, Gulf; Prussian: ''Kursjanmari'', , ) is a freshwater lagoon separated from the Baltic Sea by the Curonian Spit. Its surface area is . The Neman River () supplies about 90% of its inflows; its watershed consists of ...
, which were historically the richest sources of amber in northern Europe. There were well-established trade routes for amber connecting the Baltic with the Mediterranean (known as the "Amber Road
The Amber Road was an ancient trade route for the transfer of amber from coastal areas of the North Sea and the Baltic Sea to the Mediterranean Sea. Prehistoric trade routes between Northern and Southern Europe were defined by the amber trade. ...
"). Pliny states explicitly that the Germans exported amber to Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a Roman province, province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, on the west by Noricum and upper Roman Italy, Italy, and on the southward by Dalmatia (Roman province), Dalmatia and upper Moesia. It ...
, from where the Veneti distributed it onwards.
The ancient Italic peoples of southern Italy used to work amber; the National Archaeological Museum of Siritide (Museo Archeologico Nazionale della Siritide) at Policoro
Policoro ( Lucano: ) is a town and ''comune'' in the province of Matera, in the Southern Italian region of Basilicata. With some 18,000 inhabitants, is bounded by the towns of Rotondella, Scanzano Jonico and Tursi. Situated on the coast, i ...
in the province of Matera
The province of Matera (; Materano: ) is a province in the Basilicata region of Italy. Its capital is the city of Matera. It has an area of and a total population of 201,133; the city of Matera has a population of 61,204. The province contains ...
(Basilicata
Basilicata (, ; ), also known by its ancient name Lucania (, , ), is an administrative region in Southern Italy, bordering on Campania to the west, Apulia to the north and east, and Calabria to the south. It has two coastlines: a 30-kilometr ...
) displays important surviving examples. It has been suggested that amber used in antiquity, as at Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; ; or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines, Greece, Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos, Peloponnese, Argos; and sou ...
and in the prehistory of the Mediterranean, came from deposits in Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
 Pliny also cites the opinion of Nicias ( 470–413 BCE), according to whom amber Besides the fanciful explanations according to which amber is "produced by the Sun", Pliny cites opinions that are well aware of its origin in tree resin, citing the native Latin name of ''succinum'' (''sūcinum'', from ''sucus'' "juice"). In Book 37, section XI of ''Natural History'', Pliny wrote:
He also states that amber is also found in Egypt and India, and he even refers to the
Pliny also cites the opinion of Nicias ( 470–413 BCE), according to whom amber Besides the fanciful explanations according to which amber is "produced by the Sun", Pliny cites opinions that are well aware of its origin in tree resin, citing the native Latin name of ''succinum'' (''sūcinum'', from ''sucus'' "juice"). In Book 37, section XI of ''Natural History'', Pliny wrote:
He also states that amber is also found in Egypt and India, and he even refers to the electrostatic
Electrostatics is a branch of physics that studies slow-moving or stationary electric charges.
Since classical times, it has been known that some materials, such as amber, attract lightweight particles after rubbing. The Greek word (), mean ...
properties of amber, by saying that "in Syria the women make the whorl
A whorl ( or ) is an individual circle, oval, volution or equivalent in a whorled pattern, which consists of a spiral or multiple concentric objects (including circles, ovals and arcs).
In nature
File:Photograph and axial plane floral diagra ...
s of their spindles of this substance, and give it the name of ''harpax'' rom ἁρπάζω, "to drag"from the circumstance that it attracts leaves towards it, chaff, and the light fringe of tissues".
The Romans traded for amber from the shores of the southern Baltic
Baltic may refer to:
Peoples and languages
*Baltic languages, a subfamily of Indo-European languages, including Lithuanian, Latvian and extinct Old Prussian
*Balts (or Baltic peoples), ethnic groups speaking the Baltic languages and/or originatin ...
at least as far back as the time of Nero
Nero Claudius Caesar Augustus Germanicus ( ; born Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus; 15 December AD 37 – 9 June AD 68) was a Roman emperor and the final emperor of the Julio-Claudian dynasty, reigning from AD 54 until his ...
.
Amber has a long history of use in China, with the first written record from 200 BCE. Early in the 19th century, the first reports of amber found in North America came from discoveries in New Jersey
New Jersey is a U.S. state, state located in both the Mid-Atlantic States, Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern United States, Northeastern regions of the United States. Located at the geographic hub of the urban area, heavily urbanized Northeas ...
along Crosswicks Creek near Trenton, at Camden, and near Woodbury.
Composition
Amber isheterogeneous
Homogeneity and heterogeneity are concepts relating to the uniformity of a substance, process or image. A homogeneous feature is uniform in composition or character (i.e., color, shape, size, weight, height, distribution, texture, language, i ...
in composition, but consists of several resin
A resin is a solid or highly viscous liquid that can be converted into a polymer. Resins may be biological or synthetic in origin, but are typically harvested from plants. Resins are mixtures of organic compounds, predominantly terpenes. Commo ...
ous more or less soluble in alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
, ether
In organic chemistry, ethers are a class of compounds that contain an ether group, a single oxygen atom bonded to two separate carbon atoms, each part of an organyl group (e.g., alkyl or aryl). They have the general formula , where R and R� ...
and chloroform
Chloroform, or trichloromethane (often abbreviated as TCM), is an organochloride with the formula and a common solvent. It is a volatile, colorless, sweet-smelling, dense liquid produced on a large scale as a precursor to refrigerants and po ...
, associated with an insoluble bituminous
Bitumen ( , ) is an immensely viscous constituent of petroleum. Depending on its exact composition, it can be a sticky, black liquid or an apparently solid mass that behaves as a liquid over very large time scales. In American English, the m ...
substance. Amber is a macromolecule
A macromolecule is a "molecule of high relative molecular mass, the structure of which essentially comprises the multiple repetition of units derived, actually or conceptually, from molecules of low relative molecular mass." Polymers are physi ...
formed by free radical polymerization of several precursors in the labdane family, for example, communic acid, communol, and biformene. These labdanes are diterpene
Diterpenes are a class of terpenes composed of four isoprene units, often with the molecular formula C20H32. They are biosynthesized by plants, animals and fungi via the HMG-CoA reductase pathway, with geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate being a primary ...
s (C20H32) and triene
In organic chemistry, polyenes are polyunsaturated organic compounds that contain multiple carbon–carbon double bonds (). Some sources consider dienes to be polyenes, whereas others require polyenes to contain at least three carbon–carbon d ...
s, equipping the organic skeleton with three alkene
In organic chemistry, an alkene, or olefin, is a hydrocarbon containing a carbon–carbon double bond. The double bond may be internal or at the terminal position. Terminal alkenes are also known as Alpha-olefin, α-olefins.
The Internationa ...
groups for polymerization
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many fo ...
. As amber matures over the years, more polymerization takes place as well as isomerization
In chemistry, isomerization or isomerisation is the process in which a molecule, polyatomic ion or molecular fragment is transformed into an isomer with a different chemical structure. Enolization is an example of isomerization, as is tautomer ...
reactions, crosslinking and cyclization.
Most amber has a hardness between 2.0 and 2.5 on the Mohs scale
The Mohs scale ( ) of mineral hardness is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by the Ger ...
, a refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
of 1.5–1.6, a specific gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nea ...
between 1.06 and 1.10, and a melting point of 250–300 °C. Heated above , amber decomposes, yielding an oil of amber, and leaves a black residue which is known as "amber colophony", or "amber pitch"; when dissolved in oil of turpentine
Turpentine (which is also called spirit of turpentine, oil of turpentine, terebenthine, terebenthene, terebinthine and, colloquially, turps) is a fluid obtainable by the distillation of resin harvested from living trees, mainly pines. Principall ...
or in linseed oil
Linseed oil, also known as flaxseed oil or flax oil (in its edible form), is a colorless to yellowish oil obtained from the dried, ripened seeds of the flax plant (''Linum usitatissimum''). The oil is obtained by pressing, sometimes followed by ...
this forms "amber varnish" or "amber lac".
Impurities are quite often present, especially when the resin has dropped onto the ground, so the material may be useless except for varnish-making. Such impure amber is called ''firniss''. Such inclusion
Inclusion or Include may refer to:
Sociology
* Social inclusion, action taken to support people of different backgrounds sharing life together.
** Inclusion (disability rights), promotion of people with disabilities sharing various aspects of lif ...
of other substances can cause the amber to have an unexpected color. Pyrite
The mineral pyrite ( ), or iron pyrite, also known as fool's gold, is an iron sulfide with the chemical formula Fe S2 (iron (II) disulfide). Pyrite is the most abundant sulfide mineral.
Pyrite's metallic luster and pale brass-yellow hue ...
s may give a bluish color. ''Bony amber'' owes its cloudy opacity to numerous tiny bubbles inside the resin. However, so-called ''black amber'' is really a kind of jet. In darkly clouded and even opaque amber, inclusions can be imaged using high-energy, high-contrast, high-resolution X-ray
An X-ray (also known in many languages as Röntgen radiation) is a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than those of ultraviolet rays and longer than those of gamma rays. Roughly, X-rays have a wavelength ran ...
s.
Formation
Molecular polymerization, resulting from high pressures and temperatures produced by overlying sediment, transforms the resin first intocopal
Copal is a tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree '' Protium copal'' ( Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includ ...
. Sustained heat and pressure drives off terpene
Terpenes () are a class of natural products consisting of compounds with the formula (C5H8)n for n ≥ 2. Terpenes are major biosynthetic building blocks. Comprising more than 30,000 compounds, these unsaturated hydrocarbons are produced predomi ...
s and results in the formation of amber. For this to happen, the resin must be resistant to decay. Many trees produce resin, but in the majority of cases this deposit is broken down by physical and biological processes. Exposure to sunlight, rain, microorganisms, and extreme temperatures tends to disintegrate the resin. For the resin to survive long enough to become amber, it must be resistant to such forces or be produced under conditions that exclude them. Fossil resins from Europe fall into two categories, the Baltic ambers and another that resembles the ''Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees, native to Australasia and Southeast Asia. It is one of three extant genera in the family Araucariaceae, alongside ''Wollemia'' and ''Araucaria'' (being ...
'' group. Fossil resins from the Americas and Africa are closely related to the modern genus '' Hymenaea'', while Baltic ambers are thought to be fossil resins from plants of the family Sciadopityaceae that once lived in north Europe. The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber.
The abnormal development of resin in living trees (''succinosis'') can result in the formation of amber.
Extraction and processing
Distribution and mining
 Amber is globally distributed in or around all continents, mainly in rocks of
Amber is globally distributed in or around all continents, mainly in rocks of Cretaceous
The Cretaceous ( ) is a geological period that lasted from about 143.1 to 66 mya (unit), million years ago (Mya). It is the third and final period of the Mesozoic Era (geology), Era, as well as the longest. At around 77.1 million years, it is the ...
age or younger. Historically, the coast west of Königsberg
Königsberg (; ; ; ; ; ; , ) is the historic Germany, German and Prussian name of the city now called Kaliningrad, Russia. The city was founded in 1255 on the site of the small Old Prussians, Old Prussian settlement ''Twangste'' by the Teuton ...
in Prussia
Prussia (; ; Old Prussian: ''Prūsija'') was a Germans, German state centred on the North European Plain that originated from the 1525 secularization of the Prussia (region), Prussian part of the State of the Teutonic Order. For centuries, ...
was the world's leading source of amber. The first mentions of amber deposits there date back to the 12th century. Juodkrantė in Lithuania
Lithuania, officially the Republic of Lithuania, is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea, bordered by Latvia to the north, Belarus to the east and south, P ...
was established in the mid-19th century as a mining town of amber. About 90% of the world's extractable amber is still located in that area, which was transferred to the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (Russian SFSR or RSFSR), previously known as the Russian Socialist Federative Soviet Republic and the Russian Soviet Republic, and unofficially as Soviet Russia,Declaration of Rights of the labo ...
of the USSR
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in 1946, becoming the Kaliningrad Oblast
Kaliningrad Oblast () is the westernmost federal subjects of Russia, federal subject of the Russian Federation. It is a Enclave and exclave, semi-exclave on the Baltic Sea within the Baltic region of Prussia (region), Prussia, surrounded by Pola ...
.
Pieces of amber torn from the seafloor are cast up by the waves and collected by hand, dredging, or diving. Elsewhere, amber is mined, both in open works and underground galleries. Then nodules of ''blue earth'' have to be removed and an opaque crust must be cleaned off, which can be done in revolving barrels containing sand and water. Erosion removes this crust from sea-worn amber. Dominican amber
Dominican amber is amber from the Dominican Republic derived from resin of the extinct tree '' Hymenaea protera''.
Dominican amber differentiates itself from Baltic amber by being nearly always transparent, and it has a higher number of fossil in ...
is mined through bell pitting, which is dangerous because of the risk of tunnel collapse.
An important source of amber is Kachin State
Kachin State (; Jingpho language, Kachin: ) is the northernmost administrative divisions of Myanmar, state of Myanmar. It is bordered by China to the north and east (Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet and Yunnan, respectively), Shan State to the sou ...
in northern Myanmar
Myanmar, officially the Republic of the Union of Myanmar; and also referred to as Burma (the official English name until 1989), is a country in northwest Southeast Asia. It is the largest country by area in Mainland Southeast Asia and has ...
, which has been a major source of amber in China for at least 1,800 years. Contemporary mining of this deposit has attracted attention for unsafe working conditions and its role in funding internal conflict in the country. Amber from the Rivne Oblast
Rivne Oblast (), also referred to as Rivnenshchyna (), is an administrative divisions of Ukraine, oblast in western Ukraine. Its administrative center is Rivne. The surface area of the region is . Its population is:
Before its annexation by the ...
of Ukraine, referred to as Rivne amber, is mined illegally by organised crime groups, who deforest the surrounding areas and pump water into the sediments to extract the amber, causing severe environmental deterioration.
Treatment
The Vienna amber factories, which use pale amber to manufacture pipes and other smoking tools, turn it on alathe
A lathe () is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the w ...
and polish it with whitening and water or with rotten stone and oil. The final luster is given by polishing with flannel.
When gradually heated in an oil bath, amber "becomes soft and flexible. Two pieces of amber may be united by smearing the surfaces with linseed oil, heating them, and then pressing them together while hot. Cloudy amber may be clarified in an oil bath, as the oil fills the numerous pores that cause the turbidity. Small fragments, formerly thrown away or used only for varnish are now used on a large scale in the formation of "ambroid" or "pressed amber". The pieces are carefully heated with exclusion of air and then compressed into a uniform mass by intense hydraulic pressure, the softened amber being forced through holes in a metal plate. The product is extensively used for the production of cheap jewelry and articles for smoking. This pressed amber yields brilliant interference colors in polarized light."
Amber has often been imitated by other resins like copal
Copal is a tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree '' Protium copal'' ( Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includ ...
and kauri gum
Kauri gum is resin from kauri trees (''Agathis australis''), which historically had several important industrial uses. It can also be used to make crafts such as jewellery. Kauri forests once covered much of the North Island of New Zealand, bef ...
, as well as by celluloid
Celluloids are a class of materials produced by mixing nitrocellulose and camphor, often with added dyes and other agents. Once much more common for its use as photographic film before the advent of safer methods, celluloid's common present-day ...
and even glass. Baltic amber is sometimes colored artificially but also called "true amber".
Appearance
 Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even
Amber occurs in a range of different colors. As well as the usual yellow-orange-brown that is associated with the color "amber", amber can range from a whitish color through a pale lemon yellow, to brown and almost black. Other uncommon colors include red amber (sometimes known as "cherry amber"), green amber, and even blue amber
Blue amber is a rare variety of amber resin that exhibits a blue coloration. Blue amber has been most commonly found in the Dominican Republic—especially in the amber mines around the city of Santiago and, less commonly, in the eastern half of ...
, which is rare and highly sought after.
Yellow amber is a hard fossil resin from evergreen trees, and despite the name it can be translucent, yellow, orange, or brown colored. Known to the Iranians by the Pahlavi compound word kah-ruba (from ''kah'' "straw" plus ''rubay'' "attract, snatch", referring to its electrical properties), which entered Arabic as kahraba' or kahraba (which later became the Arabic word for electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter possessing an electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described by Maxwel ...
, كهرباء ''kahrabā''), it too was called amber in Europe (Old French and Middle English ambre). Found along the southern shore of the Baltic Sea, yellow amber reached the Middle East and western Europe via trade. Its coastal acquisition may have been one reason yellow amber came to be designated by the same term as ambergris. Moreover, like ambergris, the resin could be burned as an incense. The resin's most popular use was, however, for ornamentation—easily cut and polished, it could be transformed into beautiful jewelry. Much of the most highly prized amber is transparent, in contrast to the very common cloudy amber and opaque amber. Opaque amber contains numerous minute bubbles. This kind of amber is known as "bony amber".
 Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly
Although all Dominican amber is fluorescent, the rarest Dominican amber is blue amber. It turns blue in natural sunlight and any other partially or wholly ultraviolet
Ultraviolet radiation, also known as simply UV, is electromagnetic radiation of wavelengths of 10–400 nanometers, shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation is present in sunlight and constitutes about 10% of ...
light source. In long-wave UV light it has a very strong reflection, almost white. Only about is found per year, which makes it valuable and expensive.
Sometimes amber retains the form of drops and stalactite
A stalactite (, ; , ) is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble and that can be deposited as a colloid, or is in suspension (chemistry ...
s, just as it exuded from the ducts and receptacles of the injured trees. It is thought that, in addition to exuding onto the surface of the tree, amber resin also originally flowed into hollow cavities or cracks within trees, thereby leading to the development of large lumps of amber of irregular form.
Classification
Amber can be classified into several forms. Most fundamentally, there are two types of plant resin with the potential for fossilization.Terpenoid
The terpenoids, also known as isoprenoids, are a class of naturally occurring organic compound, organic chemicals derived from the 5-carbon compound isoprene and its derivatives called terpenes, diterpenes, etc. While sometimes used interchangeabl ...
s, produced by conifer
Conifers () are a group of conifer cone, cone-bearing Spermatophyte, seed plants, a subset of gymnosperms. Scientifically, they make up the phylum, division Pinophyta (), also known as Coniferophyta () or Coniferae. The division contains a sin ...
s and angiosperms
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (). The term angiosperm is derived from the Greek words (; 'container, vessel') and (; 'seed'), meaning that the seeds are enclosed within a fruit. T ...
, consist of ring structures formed of isoprene
Isoprene, or 2-methyl-1,3-butadiene, is a common volatile organic compound with the formula CH2=C(CH3)−CH=CH2. In its pure form it is a colorless volatile liquid. It is produced by many plants and animals (including humans) and its polymers ar ...
(C5H8) units. Phenolic resins are today only produced by angiosperms, and tend to serve functional uses. The extinct medullosans produced a third type of resin, which is often found as amber within their veins. The composition of resins is highly variable; each species produces a unique blend of chemicals which can be identified by the use of pyrolysis
Pyrolysis is a process involving the Bond cleavage, separation of covalent bonds in organic matter by thermal decomposition within an Chemically inert, inert environment without oxygen. Etymology
The word ''pyrolysis'' is coined from the Gree ...
–gas chromatography
Gas chromatography (GC) is a common type of chromatography used in analytical chemistry for Separation process, separating and analyzing compounds that can be vaporized without Chemical decomposition, decomposition. Typical uses of GC include t ...
–mass spectrometry
Mass spectrometry (MS) is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ions. The results are presented as a ''mass spectrum'', a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratio. Mass spectrometry is used ...
. The overall chemical and structural composition is used to divide ambers into five classes. There is also a separate classification of amber gemstones, according to the way of production.
Class I
This class is by far the most abundant. It comprises labdatriene carboxylic acids such as communic or ozic acids. It is further split into three sub-classes. Classes Ia and Ib utilize regular labdanoid diterpenes (e.g. communic acid, communol, biformenes), while Ic uses ''enantio'' labdanoids (ozic acid, ozol, ''enantio'' biformenes). Class Ia includes ''Succinite'' (= 'normal' Baltic amber) and ''Glessite''. They have a communic acid base, and they also include much succinic acid.Baltic amber
Baltic amber or succinite is amber from the Baltic region, home of its largest known deposits. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that this forested region provided the re ...
yields on dry distillation succinic acid, the proportion varying from about 3% to 8%, and being greatest in the pale opaque or ''bony'' varieties. The aromatic and irritating fumes emitted by burning amber are mainly from this acid. Baltic amber is distinguished by its yield of succinic acid
Succinic acid () is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula (CH2)2(CO2H)2. In living organisms, succinic acid takes the form of an anion, succinate, which has multiple biological roles as a metabolic intermediate being converted into fum ...
, hence the name ''succinite''. Succinite has a hardness between 2 and 3, which is greater than many other fossil resins. Its specific gravity varies from 1.05 to 1.10. It can be distinguished from other ambers via infrared spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functio ...
through a specific carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group with the formula , composed of a carbon atom double bond, double-bonded to an oxygen atom, and it is divalent at the C atom. It is common to several classes of organic compounds (such a ...
absorption peak. Infrared spectroscopy can detect the relative age of an amber sample. Succinic acid may not be an original component of amber but rather a degradation product of abietic acid.
Class Ib ambers are based on communic acid; however, they lack succinic acid.
Class Ic is mainly based on ''enantio''-labdatrienonic acids, such as ozic and zanzibaric acids. Its most familiar representative is Dominican amber,. which is mostly transparent and often contains a higher number of fossil inclusions. This has enabled the detailed reconstruction of the ecosystem of a long-vanished tropical forest. Resin from the extinct species ''Hymenaea protera'' is the source of Dominican amber and probably of most amber found in the tropics. It is not "succinite" but "retinite".
Class II
These ambers are formed from resins with a sesquiterpenoid base, such as Cadinenes, cadinene.Class III
These ambers are polystyrenes.Class IV
Class IV is something of a Wastebasket taxon, catch-all: its ambers are not polymerized, but mainly consist of cedrene-based sesquiterpenoids.Class V
Class V resins are considered to be produced by a pine or pine relative. They comprise a mixture of diterpinoid resins and ''n''-alkyl compounds. Their main variety is ''Copaline, Highgate copalite''.Geological record
 Burmese amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar is the only commercially exploited Cretaceous amber. Uranium–lead dating of zircon crystals associated with the deposit have given an estimated depositional age of approximately 99 million years ago. Over 1,300 species have been described from the amber, with over 300 in 2019 alone.
Baltic amber is found as irregular Nodule (geology), nodules in marine Glauconite, glauconitic sand, known as ''blue earth'', occurring in Upper Eocene strata of Sambia Peninsula, Sambia in Prussia. It appears to have been partly derived from older Eocene deposits and it occurs also as a derivative phase in later formations, such as Drift (geology), glacial drift. Relics of an abundant flora occur as inclusions trapped within the amber while the resin was yet fresh, suggesting relations with the flora of eastern Asia and the southern part of North America. Heinrich Göppert named the common amber-yielding pine of the Baltic forests ''Pinites succiniter'', but as the wood does not seem to differ from that of the existing genus it has been also called ''Pinus succinifera''. It is improbable that the production of amber was limited to a single species; and indeed a large number of conifers belonging to different genera are represented in the amber-flora.
Burmese amber from the Hukawng Valley in northern Myanmar is the only commercially exploited Cretaceous amber. Uranium–lead dating of zircon crystals associated with the deposit have given an estimated depositional age of approximately 99 million years ago. Over 1,300 species have been described from the amber, with over 300 in 2019 alone.
Baltic amber is found as irregular Nodule (geology), nodules in marine Glauconite, glauconitic sand, known as ''blue earth'', occurring in Upper Eocene strata of Sambia Peninsula, Sambia in Prussia. It appears to have been partly derived from older Eocene deposits and it occurs also as a derivative phase in later formations, such as Drift (geology), glacial drift. Relics of an abundant flora occur as inclusions trapped within the amber while the resin was yet fresh, suggesting relations with the flora of eastern Asia and the southern part of North America. Heinrich Göppert named the common amber-yielding pine of the Baltic forests ''Pinites succiniter'', but as the wood does not seem to differ from that of the existing genus it has been also called ''Pinus succinifera''. It is improbable that the production of amber was limited to a single species; and indeed a large number of conifers belonging to different genera are represented in the amber-flora.
Paleontological significance
Amber is a unique preservational mode, preserving otherwise unfossilizable parts of organisms; as such it is helpful in the reconstruction of ecosystems as well as organisms; the chemical composition of the resin, however, is of limited utility in reconstructing the phylogenetic affinity of the resin producer. Amber sometimes contains animals or plant matter that became caught in the resin as it was secreted. Insects, spiders and even their webs, annelids, frogs, crustaceans, bacteria and amoebae, marine microfossils, wood, flowers and fruit, hair, feathers and other small organisms have been recovered in Cretaceous ambers (deposited c. ). There is even an ammonite ''Puzosia (Bhimaites)'' and marine gastropods found in Burmese amber. The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' and the Jurassic Park (film), 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric mosquitoes trapped in amber, from which they genetically clone living dinosaurs. Scientifically this is as yet impossible, since no amber with fossilized mosquitoes has ever yielded preserved blood. Amber is, however, conducive to preserving DNA, since it dehydrates and thus stabilizes organisms trapped inside. One projection in 1999 estimated that DNA trapped in amber could last up to 100 million years, far beyond most estimates of around 1 million years in the most ideal conditions, although a later 2013 study was unable to extract DNA from insects trapped in much more recent Holocene
The preservation of prehistoric organisms in amber forms a key plot point in Michael Crichton's 1990 novel ''Jurassic Park (novel), Jurassic Park'' and the Jurassic Park (film), 1993 movie adaptation by Steven Spielberg. In the story, scientists are able to extract the preserved blood of dinosaurs from prehistoric mosquitoes trapped in amber, from which they genetically clone living dinosaurs. Scientifically this is as yet impossible, since no amber with fossilized mosquitoes has ever yielded preserved blood. Amber is, however, conducive to preserving DNA, since it dehydrates and thus stabilizes organisms trapped inside. One projection in 1999 estimated that DNA trapped in amber could last up to 100 million years, far beyond most estimates of around 1 million years in the most ideal conditions, although a later 2013 study was unable to extract DNA from insects trapped in much more recent Holocene copal
Copal is a tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree '' Protium copal'' ( Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includ ...
. In 1938, 12-year-old David Attenborough (brother of Richard Attenborough, Richard who played John Hammond in ''Jurassic Park'') was given a piece of amber containing prehistoric creatures from his adoptive sister; it would be the focus of his 2004 BBC documentary ''The Amber Time Machine.''
Use
 Amber has been used since prehistory (Solutrean) in the manufacture of jewelry and ornaments, and also in
Amber has been used since prehistory (Solutrean) in the manufacture of jewelry and ornaments, and also in folk medicine
Traditional medicine (also known as indigenous medicine or folk medicine) refers to the knowledge, skills, and practices rooted in the cultural beliefs of various societies, especially Indigenous groups, used for maintaining health and treatin ...
.
Jewelry
Amber has been used as jewelry since the Stone Age, from 13,000 years ago. Amber ornaments have been found in Mycenaean tombs and elsewhere across Europe. To this day it is used in the manufacture of smoking and glassblowing mouthpieces. Amber's place in culture and tradition lends it a tourism value; Palanga Amber Museum is dedicated to the fossilized resin.Historical medicinal uses
Amber has long been used in folk medicine for its purported healing properties. Amber and extracts were used from the time of Hippocrates in ancient Greece for a wide variety of treatments through the Middle Ages and up until the early twentieth century. Amber necklaces are a traditional European remedy for Baby colic, colic or Teething, teething pain with purported analgesic properties of succinic acid, although there is no evidence that this is an effective remedy or delivery method. The American Academy of Pediatrics and the Food and Drug Administration, FDA have warned strongly against their use, as they present both a choking and a strangulation hazard.Scent of amber and amber perfumery
In ancient China, it was customary to burn amber during large festivities. If amber is heated under the right conditions, oil of amber is produced, and in past times this was combined carefully with nitric acid to create "artificial musk" – a resin with a peculiar musky odor.. Although when burned, amber does give off a characteristic "pinewood" fragrance, modern products, such as perfume, do not normally use actual amber because fossilized amber produces very little scent. In perfumery, scents referred to as "amber" are often created and patented to emulate the opulent golden warmth of the fossil. The scent of amber was originally derived from emulating the scent ofambergris
Ambergris ( or ; ; ), ''ambergrease'', or grey amber is a solid, waxy, flammable substance of a dull grey or blackish colour produced in the digestive system of sperm whales. Freshly produced ambergris has a marine, fecal odor. It acquires a sw ...
and/or the plant resin labdanum, but since sperm whales are endangered, the scent of amber is now largely derived from labdanum. The term "amber" is loosely used to describe a scent that is warm, musky, rich and honey-like, and also somewhat earthy. Benzoin (resin), Benzoin is usually part of the recipe. Vanilla and cloves are sometimes used to enhance the aroma. "Amber" perfumes may be created using combinations of labdanum, benzoin resin, copal (a type of tree resin used in incense manufacture), vanilla, Agathis, Dammara resin and/or synthetic materials.
In Arab Muslim tradition, popular scents include amber, jasmine, musk and oud (agarwood).
Imitation substances
Young resins used as imitations: * Kauri resin from ''Agathis australis'' trees in New Zealand. * Thecopal
Copal is a tree resin, particularly the aromatic resins from the copal tree '' Protium copal'' ( Burseraceae) used by the cultures of pre-Columbian Mesoamerica as ceremonially burned incense and for other purposes. More generally, copal includ ...
s (subfossil resins). The African and American (Colombia) copals from ''Fabaceae, Leguminosae'' trees family (genus '' Hymenaea''). Dominican amber, Amber of the Dominican or Mexican type (#Class I, Class I of fossil resins). Copals from Manilia (Indonesia) and from New Zealand from trees of the genus ''Agathis
''Agathis'', commonly known as kauri or dammara, is a genus of evergreen coniferous trees, native to Australasia and Southeast Asia. It is one of three extant genera in the family Araucariaceae, alongside ''Wollemia'' and ''Araucaria'' (being ...
'' (family Araucariaceae)
* Other fossil resins: burmite in Burma, rumenite in Romania, and simetite in Sicily
Sicily (Italian language, Italian and ), officially the Sicilian Region (), is an island in the central Mediterranean Sea, south of the Italian Peninsula in continental Europe and is one of the 20 regions of Italy, regions of Italy. With 4. ...
.
* Other natural resins — cellulose or chitin, etc.
Plastics used as imitations:
* Stained glass (inorganic material) and other Ceramic, ceramic materials
* Celluloid
* Nitrocellulose, Cellulose nitrate (first obtained in 1833) — a product of treatment of cellulose with nitration mixture.
* Acetylcellulose (not in the use at present)
* Galalith or "artificial horn" (condensation product of casein and formaldehyde), other trade names: Alladinite, Erinoid, Lactoid.
* Casein — a conjugated protein forming from the casein precursor – caseinogen.
* Resolane (phenolic resins or phenoplasts, not in the use at present)
* Bakelite resine (resol, phenolic resins), product from Africa are known under the misleading name "African amber".
* Urea, Carbamide resins — Melamine resin, melamine, formaldehyde and urea-formaldehyde resins.
* Epoxy Phenol formaldehyde resin, novolac (phenolic resins), unofficial name "antique amber", not in the use at present
* Polyesters (Polish amber imitation) with styrene. For example, unsaturated polyester resins (polymals) are produced by Chemical Industrial Works "Organika" in Sarzyna, Poland; estomal are produced by Laminopol firm. Polybern or sticked amber is artificial resins the curled chips are obtained, whereas in the case of amber – small scraps. "African amber" (polyester, synacryl is then probably other name of the same resine) are produced by Reichhold firm; Styresol trade mark or alkid resin (used in Russia, Reichhold, Inc. patent, 1948.
* Polyethylene
* Epoxy resins
* Polystyrene and polystyrene-like polymers (vinyl polymers).
* The Acrylic resin, resins of acrylic type (vinyl polymers), especially Poly(methyl methacrylate), polymethyl methacrylate PMMA (trade mark Plexiglass, metaplex).
See also
* Ammolite * Illyrian amber jewellery * List of types of amber * Petrified wood * Pearl * Poly(methyl methacrylate)#Acrylate resin casting, Poly(methyl methacrylate) * Precious coralNotes
References
*Bibliography
* * *External links
Farlang many full text historical references on Amber
Theophrastus
Theophrastus (; ; c. 371 – c. 287 BC) was an ancient Greek Philosophy, philosopher and Natural history, naturalist. A native of Eresos in Lesbos, he was Aristotle's close colleague and successor as head of the Lyceum (classical), Lyceum, the ...
, George Frederick Kunz, and special on Baltic amber
Baltic amber or succinite is amber from the Baltic region, home of its largest known deposits. It was produced sometime during the Eocene epoch, but exactly when is controversial. It has been estimated that this forested region provided the re ...
.
IPS Publications on amber inclusions
International Paleoentomological Society: Scientific Articles on amber and its inclusions
Webmineral on Amber
Physical properties and mineralogical information
Image and locality information on amber
40 million year old extinct bee in Dominican amber {{Authority control Amber, Fossil resins Amorphous solids Traditional medicine