Aleppo Plateau on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Aleppo plateau ( ) is a low, gently undulating
The Aleppo plateau ( ) is a low, gently undulating
 The average elevation of the plateau is 400 m. The surface gradually slopes down in north-south and west-east directions. The surface undulates gently with an amplitude of 10–30 m for each wave. The lowlands are covered with combined
The average elevation of the plateau is 400 m. The surface gradually slopes down in north-south and west-east directions. The surface undulates gently with an amplitude of 10–30 m for each wave. The lowlands are covered with combined
 The Aleppo plateau ( ) is a low, gently undulating
The Aleppo plateau ( ) is a low, gently undulating plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; : plateaus or plateaux), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. ...
of northern Syria
Syria, officially the Syrian Arab Republic, is a country in West Asia located in the Eastern Mediterranean and the Levant. It borders the Mediterranean Sea to the west, Turkey to Syria–Turkey border, the north, Iraq to Iraq–Syria border, t ...
. It lies at the northern end of the junction between the Arabian Plate and the African Plate at the Dead Sea Rift. The plateau lies mostly in the Aleppo Governorate
Aleppo Governorate ( / ALA-LC: ''Muḥāfaẓat Ḥalab'' ) is one of the fourteen Governorates of Syria, governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000 (2011 Est.), almost 23% of the t ...
and Idlib Governorate
Idlib Governorate ( / ALA-LC: ''Muḥāfaẓat Idlib'') is one of the 14 governorates of Syria. It is situated in northwestern Syria, bordering Turkey's Hatay province to the north, Aleppo Governorate to the east, Hama Governorate to the sou ...
. Aleppo
Aleppo is a city in Syria, which serves as the capital of the Aleppo Governorate, the most populous Governorates of Syria, governorate of Syria. With an estimated population of 2,098,000 residents it is Syria's largest city by urban area, and ...
is located in the north-center of the plateau.
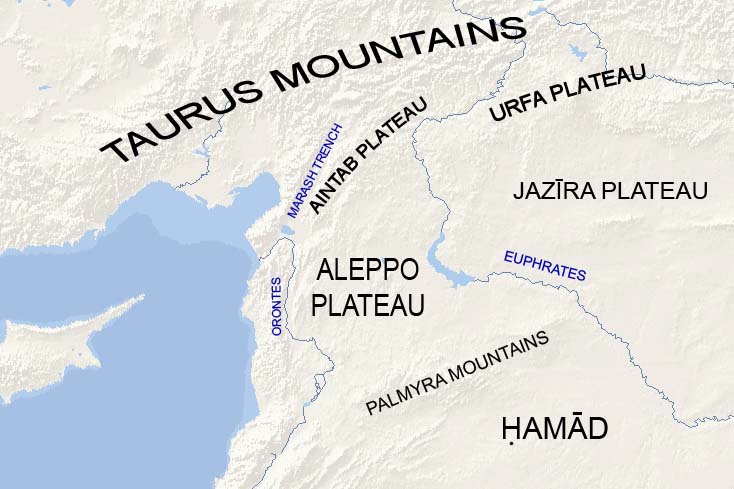
Boundaries
The Aleppo plateau lies immediately north of the Palmyra mountain belt. To the east it is bounded by theEuphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see #Etymology, below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Tigris–Euphrates river system, Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originati ...
river valley, which separates it from the Jazirah plateau. To the west it is bounded by the northern half of the Dead Sea Rift, namely the Orontes river valley. The Aintab plateau forms a northern continuation of the plateau that leads to the Taurus Mountains
The Taurus Mountains (Turkish language, Turkish: ''Toros Dağları'' or ''Toroslar,'' Greek language, Greek'':'' Ταύρος) are a mountain range, mountain complex in southern Turkey, separating the Mediterranean Sea, Mediterranean coastal reg ...
.
Description
 The average elevation of the plateau is 400 m. The surface gradually slopes down in north-south and west-east directions. The surface undulates gently with an amplitude of 10–30 m for each wave. The lowlands are covered with combined
The average elevation of the plateau is 400 m. The surface gradually slopes down in north-south and west-east directions. The surface undulates gently with an amplitude of 10–30 m for each wave. The lowlands are covered with combined Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma a ...
and Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era is the Era (geology), era of Earth's Geologic time scale, geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceous Period (geology), Periods. It is characterized by the dominance of archosaurian r ...
sediments that average 4–5 km in thickness over the whole surface.
Starting from the valley of the Euphrates, the terrain rises forming the Manbij plain and then sinks again at the Dhahab river valley in the east of Aleppo Governorate
Aleppo Governorate ( / ALA-LC: ''Muḥāfaẓat Ḥalab'' ) is one of the fourteen Governorates of Syria, governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000 (2011 Est.), almost 23% of the t ...
. The Dhahab drains the highlands north of Bāb and runs in a north-south direction for about 50 km until it drains into Lake Jabboul. West of the Dhahab valley the terrain rises again forming Mount ʻAqīl (Mount Taymar) (534 m) west of Bāb and Mount Ḥaṣṣ (550 m) west of Lake Jabboul. The terrain sinks again forming the valley of River Quwēq. The endpoint of Quwēq, the Maṭkh swamp (249 m), is the lowest point in Aleppo Governorate. West of the Quwēq is Mount Simeon. South of Mount Simeon are the plains of Idlib
Idlib (, ; also spelt Idleb or Edlib) is a city in northwestern Syria, and is the capital of the Idlib Governorate. It has an elevation of nearly above sea level, and is southwest of Aleppo. It is located near the border with Turkey.
History
...
. River ʻIfrīn runs west of Mount Simeon. To the west of River ʻIfrīn the land rises again forming Mount Kurd. River ʻIfrīn runs from north to south between Mount Simeon and Mount Kurd and then turns west to the Orontes valley, thus separating Mount Kurd from Mount Ḥārim to the south. Mount Ḥārim is separated from Mount Zāwiya to the south by the Rouj plain, which leads to the Ghab plain in the Orontes valley. The highlands of the western Aleppo plateau are collectively known as the Limestone Massif.
The southeastern portion of the plateau is an arid steppe that forms the northern tip of the Syrian Desert
The Syrian Desert ( ''Bādiyat Ash-Shām''), also known as the North Arabian Desert, the Jordanian steppe, or the Badiya, is a region of desert, semi-desert, and steppe, covering about of West Asia, including parts of northern Saudi Arabia, ea ...
. The rest of the plateau is generally fertile, especially the northwest. The plateau is generally deforested except for a dispersed forest of about 50 km2 on the eastern slope of Mount Kurd where it faces the plain of Aʻzāz. The main trees in the region are Aleppo Pine
''Pinus halepensis'', commonly known as the Aleppo pine, also known as the Jerusalem pine, is a pine native to the Mediterranean region. It was officially named by the botanist Philip Miller in his 1768 book ''The Gardener's Dictionary''; he pro ...
and oak.
Geology
Theisotope
Isotopes are distinct nuclear species (or ''nuclides'') of the same chemical element. They have the same atomic number (number of protons in their Atomic nucleus, nuclei) and position in the periodic table (and hence belong to the same chemica ...
composition of the region indicate that there were similarities between the deeper Upper Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the more recent of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''cret ...
aquifer
An aquifer is an underground layer of water-bearing material, consisting of permeability (Earth sciences), permeable or fractured rock, or of unconsolidated materials (gravel, sand, or silt). Aquifers vary greatly in their characteristics. The s ...
s in both the Aleppo plateau and the Palmyrean mountain zone, but differences with the shallow Paleogene
The Paleogene Period ( ; also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene) is a geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period Ma (million years ago) to the beginning of the Neogene Period Ma. It is the fir ...
aquifer.
Early–Middle Miocene
The Miocene ( ) is the first epoch (geology), geological epoch of the Neogene Period and extends from about (Ma). The Miocene was named by Scottish geologist Charles Lyell; the name comes from the Greek words (', "less") and (', "new") and mea ...
intraplate basalts obtained from the Aleppo plateau contained low abundances of platinum-group elements compared to alkali basalts from Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; ) is an island U.S. state, state of the United States, in the Pacific Ocean about southwest of the U.S. mainland. One of the two Non-contiguous United States, non-contiguous U.S. states (along with Alaska), it is the only sta ...
, and mid-ocean ridge
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a undersea mountain range, seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading ...
basalts. However, the Aleppo Plateau and vicinity had two discrete Miocene volcanic phases, ~ 19–18 Ma and ~ 13.5–12 Ma.
References
Bibliography
*See also
*Aleppo Governorate
Aleppo Governorate ( / ALA-LC: ''Muḥāfaẓat Ḥalab'' ) is one of the fourteen Governorates of Syria, governorates of Syria. It is the most populous governorate in Syria with a population of more than 4,867,000 (2011 Est.), almost 23% of the t ...
{{coord, 36, 11, 12, N, 37, 8, 48, E, display=title
Plains of Syria
Aleppo
Geography of Aleppo Governorate
Physiographic provinces