alcohol level on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as alc/vol or ABV) is a common measure of the amount of
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as alc/vol or ABV) is a common measure of the amount of
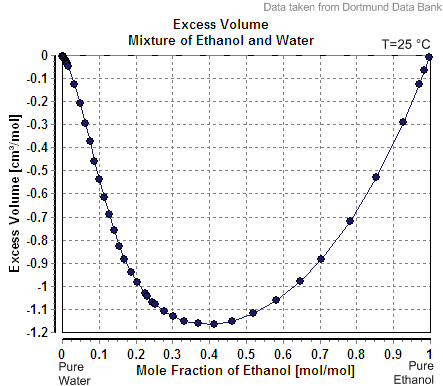 Mixing two solutions of alcohol of different strengths usually causes a change in volume. Mixing pure water with a solution less than 24% by mass causes a slight increase in total volume, whereas the mixing of two solutions above 24% causes a decrease in volume. The phenomenon of volume changes due to mixing dissimilar solutions is called "
Mixing two solutions of alcohol of different strengths usually causes a change in volume. Mixing pure water with a solution less than 24% by mass causes a slight increase in total volume, whereas the mixing of two solutions above 24% causes a decrease in volume. The phenomenon of volume changes due to mixing dissimilar solutions is called "
 Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as alc/vol or ABV) is a common measure of the amount of
Alcohol by volume (abbreviated as alc/vol or ABV) is a common measure of the amount of alcohol
Alcohol may refer to:
Common uses
* Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds
* Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life
** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages
** Alcoholic beverage, an alco ...
contained in a given alcoholic beverage
Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ...
. It is defined as the volume the ethanol in the liquid would take if separated from the rest of the solution, divided by the volume of the solution, both at . Pure ethanol is lighter than water, with a density of . The alc/vol standard is used worldwide. The International Organization of Legal Metrology
The International Organization of Legal Metrology ( - OIML), is an intergovernmental organisation that was created in 1955 to promote the global harmonisation of the legal metrology procedures that underpin and facilitate international trade.
Such ...
has tables of density of water–ethanol mixtures at different concentrations and temperatures.
In some countries, e.g. France
France, officially the French Republic, is a country located primarily in Western Europe. Overseas France, Its overseas regions and territories include French Guiana in South America, Saint Pierre and Miquelon in the Atlantic Ocean#North Atlan ...
, alcohol by volume is often referred to as degrees Gay-Lussac (after the French chemist Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac
Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac ( , ; ; 6 December 1778 – 9 May 1850) was a French chemist and physicist. He is known mostly for his discovery that water is made of two parts hydrogen and one part oxygen by volume (with Alexander von Humboldt), f ...
), although there is a slight difference since the Gay-Lussac convention uses the International Standard Atmosphere
The International Standard Atmosphere (ISA) is a static atmospheric model of how the pressure, temperature, density, and viscosity of the Earth's atmosphere change over a wide range of altitudes or elevations. It has been established to provide ...
value for temperature, .
Volume change
 Mixing two solutions of alcohol of different strengths usually causes a change in volume. Mixing pure water with a solution less than 24% by mass causes a slight increase in total volume, whereas the mixing of two solutions above 24% causes a decrease in volume. The phenomenon of volume changes due to mixing dissimilar solutions is called "
Mixing two solutions of alcohol of different strengths usually causes a change in volume. Mixing pure water with a solution less than 24% by mass causes a slight increase in total volume, whereas the mixing of two solutions above 24% causes a decrease in volume. The phenomenon of volume changes due to mixing dissimilar solutions is called "partial molar volume
In thermodynamics, a partial molar property is a quantity which describes the variation of an extensive property of a solution or mixture with changes in the molar composition of the mixture at constant temperature and pressure. It is the par ...
". Water and ethanol are both polar solvents. When water is added to ethanol, the smaller water molecules are attracted to the ethanol's hydroxyl group, and each molecule alters the polarity field of the other. The attraction allows closer spacing between molecules than is usually found in non-polar mixtures.
Thus, alc/vol is not the same as volume fraction
In chemistry and fluid mechanics, the volume fraction \varphi_i is defined as the volume of a constituent ''V'i'' divided by the volume of all constituents of the mixture ''V'' prior to mixing:
:\varphi_i = \frac .
Being dimensionless quantit ...
expressed as a percentage. Volume fraction, which is widely used in chemistry (commonly denoted as v/v), is defined as the volume of a particular component divided by the sum of all components in the mixture when they are measured separately. For example, to make 100 mL of 50% alc/vol ethanol solution, water would be added to 50 mL of ethanol to make up exactly 100 mL. Whereas to make a 50% v/v ethanol solution, 50 mL of ethanol and 50 mL of water could be mixed but the resulting volume of solution will measure less than 100 mL due to the change of volume on mixing, and will contain a higher concentration of ethanol. The difference is not large, with the maximum difference being less than 2.5%, and less than 0.5% difference for concentrations under 20%.
Threshold levels
Legal thresholds
Some drinks have requirements of alcoholic content in order to be certified as a certain alcohol brand or label. For example, in theUnited Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, making it the world's List of coun ...
and European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are Geography of the European Union, located primarily in Europe. The u ...
whisky
Whisky or whiskey is a type of liquor made from Fermentation in food processing, fermented grain mashing, mash. Various grains (which may be Malting, malted) are used for different varieties, including barley, Maize, corn, rye, and wheat. Whisky ...
is legally required to be no less than 40% ABV bottled.
Low-alcohol beers (<0.5) are considered in some countries such as Iran as permitted (or "halal" under Muslim vocabulary) despite alcohol being banned. However, the level of alcohol-free beers is typically the lowest commercially sold 0.05.
Biological thresholds
It is near impossible for a healthy person to become intoxicated drinking low-alcohol drinks. The low concentration severely limits the rate of intake, which is easily dispatched by human metabolism. Quickly drinking 1.5 L of 0.4% alc/vol beer in an hour resulted in a maximum of 0.0056% BAC in a study of German volunteers. Healthy human kidneys can only excrete 0.8–1.0 L of water per hour, makingwater intoxication
Water intoxication, also known as water poisoning, hyperhydration, overhydration, or water toxemia, is a potentially fatal disturbance in brain functions that can result when the normal balance of electrolytes in the body is pushed outside safe ...
likely to set in before any alcoholic intoxication.
The process of ethanol fermentation will slow down and eventually come to a halt as the alcohol produced becomes too concentrated for the yeast to tolerate, defining an upper limit of alc/vol for non-distilled alcoholic drinks. The typical tolerance for beer yeasts is at 8–12%, while wine yeasts typically range from 14–18%, with speciality ones reaching 20% alc/vol. Any higher would require distillation, producing liquor
Liquor ( , sometimes hard liquor), spirits, distilled spirits, or spiritous liquor are alcoholic drinks produced by the distillation of grains, fruits, vegetables, or sugar that have already gone through ethanol fermentation, alcoholic ferm ...
.
Typical levels
Details about typical amounts of alcohol contained in various beverages can be found in the articles about them.Practical estimation of alcohol content
During the production of wine and beer,yeast
Yeasts are eukaryotic, single-celled microorganisms classified as members of the fungus kingdom (biology), kingdom. The first yeast originated hundreds of millions of years ago, and at least 1,500 species are currently recognized. They are est ...
is added to a sugary solution. During fermentation, the yeasts consume the sugars and produce alcohol. The density of sugar in water is greater than the density of alcohol in water. A hydrometer
A hydrometer or lactometer is an instrument used for measuring density or relative density of liquids based on the concept of buoyancy. They are typically Calibration, calibrated and Graduation (instrument), graduated with one or more scales suc ...
is used to measure the change in specific gravity
Relative density, also called specific gravity, is a dimensionless quantity defined as the ratio of the density (mass of a unit volume) of a substance to the density of a given reference material. Specific gravity for solids and liquids is nea ...
(SG) of the solution before and after fermentation. The volume of alcohol in the solution can then be estimated. There are a number of empirical formulae which brewers and winemakers use to estimate the alcohol content of the liquor made.
Specific gravity is the density of a liquid relative to that of water, i.e., if the density of the liquid is 1.05 times that of water, it has a specific gravity of 1.05. In UK brewing usage, it is customary to regard the reference value for water to be 1000, so the specific gravity of the same example beer would be quoted as 1050. The formulas here assume that the former definition is used for specific gravity.
General
During ethanol fermentation the yeast converts one mole of sugar into two moles of alcohol. A general formula for calculating the resulting alcohol concentration by volume can be written: : where SBV fermented is sugar by volume (g/dL) converted to alcohol during fermentation and GECF is the glucose-ethanol conversion factor: : where 46.069 is themolar mass
In chemistry, the molar mass () (sometimes called molecular weight or formula weight, but see related quantities for usage) of a chemical substance ( element or compound) is defined as the ratio between the mass () and the amount of substance ...
of ethanol
Ethanol (also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound with the chemical formula . It is an Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol, with its formula also written as , or EtOH, where Et is the ps ...
and 180.156 is the molar mass of glucose
Glucose is a sugar with the Chemical formula#Molecular formula, molecular formula , which is often abbreviated as Glc. It is overall the most abundant monosaccharide, a subcategory of carbohydrates. It is mainly made by plants and most algae d ...
and fructose
Fructose (), or fruit sugar, is a Ketose, ketonic monosaccharide, simple sugar found in many plants, where it is often bonded to glucose to form the disaccharide sucrose. It is one of the three dietary monosaccharides, along with glucose and gal ...
.
:
:
Sugar by volume can be calculated from Brix
Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, based on its specific gravity, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of a solution. One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose solute dissolved in 100 grams ...
(sugar by weight) and SG (relative density):
:
SG can be measured using an hydrometer
A hydrometer or lactometer is an instrument used for measuring density or relative density of liquids based on the concept of buoyancy. They are typically Calibration, calibrated and Graduation (instrument), graduated with one or more scales suc ...
and Brix can be calculated from SG. A simple formula for calculating Brix
Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, based on its specific gravity, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of a solution. One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose solute dissolved in 100 grams ...
from SG is (SG 1.000 - 1.179):
:
By substituting Brix in the SBV formula above, we get a formula for calculating SBV from SG only:
:
By further substitution, we get a formula for calculating ABV from SG only:
:
:
:
The factor 135 is most accurate in the center of the SG drop range of 0.000 to 0.179. Since the correlation of SG and Brix is non-linear it is common to divide the range to increase accuracy when using the simple ABV formula:
:
Advanced
Advanced formula derived from Carl Balling empirical formulas. The formula compensates for changes in SG with changes in alcohol concentration and for the fact that not all sugar is converted into alcohol. All values are measured at 20 degree C. where SG final is the specific gravity when fermentation ends, Plato start is the sugar by weight when fermentation begins, Plato final is the sugar by weight when fermentation ends.Brix
Degrees Brix (symbol °Bx) is a measure of the dissolved solids in a liquid, based on its specific gravity, and is commonly used to measure dissolved sugar content of a solution. One degree Brix is 1 gram of sucrose solute dissolved in 100 grams ...
can be used instead of Plato as they are nearly identical.
Wine
The simplest method for wine has been described by English author Cyril Berry:Beer
One calculation for beer is: For higher ABV above 6% many brewers use this formula:Other methods of specifying alcohol content
Alcohol proof
Another way of specifying the amount of alcohol content is alcohol ''proof'', which in theUnited States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
is twice the alcohol-by-volume (alc/vol) number. This may lead to confusion over similar products bought in varying regions that have different names on country-specific labels. For example, Stroh
Stroh Austria GmbH () is an Austrian manufacturer of liquors, especially spiced rums and high-proof rum-like drinks used in warm drinks and cooking. The Stroh brand is one of the best-known spirits from Austria.
The (technically incorrect) ter ...
rum that is 80% ABV is advertised and labeled as ''Stroh 80'' when sold in Europe, but is named ''Stroh 160'' when sold in the United States.
In the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Northwestern Europe, off the coast of European mainland, the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, proof is 1.75 times the number (expressed as a percentage). For example, 40% alc/vol is 80 proof in the US and 70 proof in the UK. However, since 1980, alcohol proof in the UK has been replaced by alc/vol as a measure of alcohol content, avoiding confusion between the UK and US proof standards.
Alcohol by weight
In the United States,Arkansas
Arkansas ( ) is a landlocked state in the West South Central region of the Southern United States. It borders Missouri to the north, Tennessee and Mississippi to the east, Louisiana to the south, Texas to the southwest, and Oklahoma ...
, Kansas
Kansas ( ) is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. It borders Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the west. Kansas is named a ...
, Mississippi
Mississippi ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern and Deep South regions of the United States. It borders Tennessee to the north, Alabama to the east, the Gulf of Mexico to the south, Louisiana to the s ...
, South Carolina
South Carolina ( ) is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders North Carolina to the north and northeast, the Atlantic Ocean to the southeast, and Georgia (U.S. state), Georg ...
, and Tennessee
Tennessee (, ), officially the State of Tennessee, is a landlocked U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. It borders Kentucky to the north, Virginia to the northeast, North Carolina t ...
regulate and tax alcoholic beverages according to alcohol by weight (ABW), expressed as a percentage of total mass. The alc/vol value of a beverage is always higher than the ABW.
Because ABW measures the proportion of the drink's mass which is alcohol, while alc/vol is the proportion of the drink's volume which is alcohol, the two values are in the same proportion as the drink's density is with the density of alcohol. Therefore, one can use the following equation to convert between ABV and ABW:
At relatively low alc/vol, the alcohol percentage by weight is about 4/5 of the alc/vol (e.g., 3.2% ABW is about 4% alc/vol).
However, because of the miscibility
Miscibility () is the property of two substances to mix in all proportions (that is, to fully dissolve in each other at any concentration), forming a homogeneous mixture (a solution). Such substances are said to be miscible (etymologically ...
of alcohol and water, the conversion factor is not constant but rather depends upon the concentration of alcohol.
See also
*Apparent molar property
In thermodynamics, an apparent molar property of a solution component in a mixture or solution is a quantity defined with the purpose of isolating the contribution of each component to the non-ideality of the mixture. It shows the change in the ...
*Excess molar quantity
In chemical thermodynamics, excess properties are properties of mixtures which quantify the non- ideal behavior of real mixtures. They are defined as the difference between the value of the property in a real mixture and the value that would exist ...
* Standard drink
* Unit of alcohol
*Volume fraction
In chemistry and fluid mechanics, the volume fraction \varphi_i is defined as the volume of a constituent ''V'i'' divided by the volume of all constituents of the mixture ''V'' prior to mixing:
:\varphi_i = \frac .
Being dimensionless quantit ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
* * {{Authority control volume by