Alaska Peninsula on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
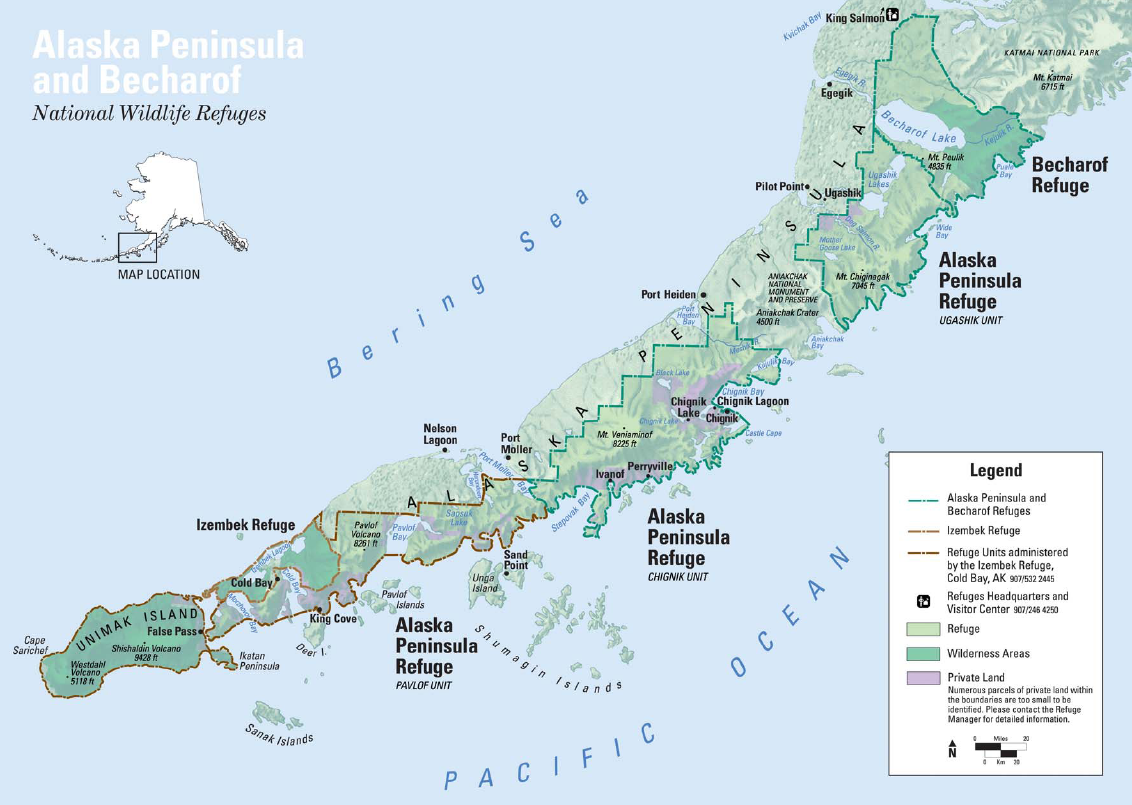

 The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a
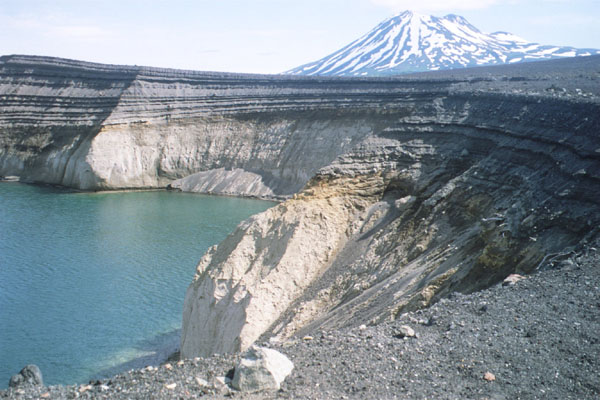


 The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends outward from the end of the
The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends outward from the end of the
 The Alaska Peninsula is home to some of the largest populations of native and undisturbed wildlife in the United States. Besides the famous McNeil River and Katmai Alaskan brown bear populations, large herds of
The Alaska Peninsula is home to some of the largest populations of native and undisturbed wildlife in the United States. Besides the famous McNeil River and Katmai Alaskan brown bear populations, large herds of  Exceptionally large seabird colonies exist along the coast. Additionally, there are large populations of sea mammals in the
Exceptionally large seabird colonies exist along the coast. Additionally, there are large populations of sea mammals in the
Ugashik Area websiteLake & Peninsula BoroughLake and Peninsula School District Trawl survey of shrimp and forage fish in Alaska's Westward region, 2006 / by David R. Jackson.
Hosted b
Alaska State Publications Program
{{Authority control Landforms of Aleutians East Borough, Alaska Landforms of Bristol Bay Borough, Alaska Landforms of Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska Landforms of Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska Landforms of Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska Peninsulas of Alaska Volcanic arcs


 The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a
The Alaska Peninsula (also called Aleut Peninsula or Aleutian Peninsula, ; Sugpiaq: ''Aluuwiq'', ''Al'uwiq'') is a peninsula
A peninsula is a landform that extends from a mainland and is only connected to land on one side. Peninsulas exist on each continent. The largest peninsula in the world is the Arabian Peninsula.
Etymology
The word ''peninsula'' derives , . T ...
extending about to the southwest from the mainland of Alaska
Alaska ( ) is a non-contiguous U.S. state on the northwest extremity of North America. Part of the Western United States region, it is one of the two non-contiguous U.S. states, alongside Hawaii. Alaska is also considered to be the north ...
and ending in the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain ...
. The peninsula separates the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is ...
from Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ...
, an arm of the Bering Sea
The Bering Sea ( , ; rus, Бе́рингово мо́ре, r=Béringovo móre, p=ˈbʲerʲɪnɡəvə ˈmorʲe) is a marginal sea of the Northern Pacific Ocean. It forms, along with the Bering Strait, the divide between the two largest landmasse ...
.
In literature (especially Russian), the term ''Alaska Peninsula'' was used to denote the entire northwestern protrusion of the North American continent
A continent is any of several large geographical regions. Continents are generally identified by convention (norm), convention rather than any strict criteria. A continent could be a single large landmass, a part of a very large landmass, as ...
, or all of what is now the state of Alaska, exclusive of its panhandle and islands
This is a list of the lists of islands in the world grouped by country, by continent, by body of water, and by other classifications. For rank-order lists, see the #Other lists of islands, other lists of islands below.
Lists of islands by count ...
. The Lake and Peninsula borough
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
, the Alaskan equivalent of a county
A county () is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesL. Brookes (ed.) '' Chambers Dictionary''. Edinburgh: Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, 2005. in some nations. The term is derived from the Old French denoti ...
, is named after the peninsula.
The Alaska/Aleutian Peninsula is also grouped into Southwest Alaska
Southwest Alaska is a region of the U.S. state of Alaska. The area is not exactly defined by any governmental administrative region(s); nor does it always have a clear geographic boundary.
Geography
Southwest Alaska includes a huge swath of terr ...
.
The other largest peninsulas in Alaska include the Kenai Peninsula
The Kenai Peninsula ( Dena'ina: ''Yaghenen'') is a large peninsula jutting from the coast of Southcentral Alaska. The name Kenai (, ) is derived from the word "Kenaitze" or "Kenaitze Indian Tribe", the name of the Native Athabascan Alaskan tribe ...
and Seward Peninsula
The Seward Peninsula is a large peninsula on the western coast of the U.S. state of Alaska whose westernmost point is Cape Prince of Wales. The peninsula projects about into the Bering Sea between Norton Sound, the Bering Strait, the Chukchi ...
.
Geography


 The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends outward from the end of the
The base of the Alaska Peninsula extends outward from the end of the Alaska Range
The Alaska Range is a relatively narrow, mountain range in the Southcentral Alaska, southcentral region of the U.S. state of Alaska, from Lake Clark at its southwest endSources differ as to the exact delineation of the Alaska Range. ThBoard on G ...
.
The Aleutian Range
The Aleutian Range is a major mountain range located in southwest Alaska. It extends from Chakachamna Lake (80 miles/130 km southwest of Anchorage) to Unimak Island, which is at the tip of the Alaska Peninsula. It includes all of the mountain ...
is a very active volcanic
A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ...
mountain range
A mountain range or hill range is a series of mountains or hills arranged in a line and connected by high ground. A mountain system or mountain belt is a group of mountain ranges with similarity in form, structure, and alignment that have aris ...
which runs along the entire length of the peninsula. Within it lie Wildlife Refuges, including the Katmai National Park and Preserve
Katmai National Park and Preserve is a List of national parks of the United States, United States national park and National preserve, preserve in southwest Alaska, notable for the Valley of Ten Thousand Smokes and for its Alaska Peninsula brown ...
, the Aniakchak National Monument and Preserve and the Becharof National Wildlife Refuge, the Alaska Peninsula National Wildlife Refuge, and the Izembek National Wildlife Refuge. The most active volcano along the volcanic mountain range is Pavlof Volcano which is more than (see also: Aleutian Arc
The Aleutian Arc is a large volcanic arc of islands extending from the Southwest tip of the U.S. state of Alaska to the Kamchatka Peninsula of the Russian Federation.
It consists of a number of active and dormant volcanoes that have formed as a ...
).
The southern side of the Alaska Peninsula is rugged and mountainous, created by the uplifting tectonic activity of the North Pacific Plate subsiding under a western section of the North American Plate; the northern side is generally flat and marshy, a result of millennia of erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as Surface runoff, water flow or wind) that removes soil, Rock (geology), rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust#Crust, Earth's crust and then sediment transport, tran ...
and general seismic
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes (or generally, quakes) and the generation and propagation of elastic ...
stability. The northern and southern shores are likewise quite different. The northern Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ...
coastal side is generally turbid and muddy, experiences tidal extremes, and is relatively shallow; the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is bounded by the cont ...
side, which is also known as the "ring of fire", has relatively small tidal activity and the water is deep and clear.
Administration
All of the peninsula is organized as a part of four adjacentboroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English language, English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
...
; the Aleutians East Borough, Bristol Bay Borough, Kodiak Island Borough, and Lake and Peninsula Borough. The Lake and Peninsula Borough includes most of the peninsula's territory.
Climate
Average annual precipitation ranges from . Coastal areas are subject to intense storms, wind, and rain. Winter temperatures average between , and in summer between . Frosts can occur any day of the year at higher elevations. The climate can be compared to that of parts ofScotland
Scotland is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It contains nearly one-third of the United Kingdom's land area, consisting of the northern part of the island of Great Britain and more than 790 adjac ...
, the Aleutian Islands
The Aleutian Islands ( ; ; , "land of the Aleuts"; possibly from the Chukchi language, Chukchi ''aliat'', or "island")—also called the Aleut Islands, Aleutic Islands, or, before Alaska Purchase, 1867, the Catherine Archipelago—are a chain ...
, Iceland
Iceland is a Nordic countries, Nordic island country between the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic and Arctic Oceans, on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge between North America and Europe. It is culturally and politically linked with Europe and is the regi ...
, and Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South America, South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan.
The archipelago consists of the main is ...
.
Flora and fauna
 The Alaska Peninsula is home to some of the largest populations of native and undisturbed wildlife in the United States. Besides the famous McNeil River and Katmai Alaskan brown bear populations, large herds of
The Alaska Peninsula is home to some of the largest populations of native and undisturbed wildlife in the United States. Besides the famous McNeil River and Katmai Alaskan brown bear populations, large herds of caribou
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only represe ...
, moose
The moose (: 'moose'; used in North America) or elk (: 'elk' or 'elks'; used in Eurasia) (''Alces alces'') is the world's tallest, largest and heaviest extant species of deer and the only species in the genus ''Alces''. It is also the tal ...
, wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though gr ...
, waterfowl
Anseriformes is an order of birds also known as waterfowl that comprises about 180 living species of birds in three families: Anhimidae (three species of screamers), Anseranatidae (the magpie goose), and Anatidae, the largest family, which i ...
, and willow ptarmigan
The willow ptarmigan ( ); ''Lagopus lagopus'') or willow grouse is a bird in the grouse subfamily Tetraoninae of the pheasant family Phasianidae. It is also known colloquially as awebo bird. The willow ptarmigan breeds in birch and other forests ...
inhabit the area. The bears of the peninsula and Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ...
are so numerous because they feed on the world's largest sockeye salmon
The sockeye salmon (''Oncorhynchus nerka''), also called red salmon, kokanee salmon, blueback salmon, or simply sockeye, is an anadromous species of salmon found in the Northern Pacific Ocean and rivers discharging into it. This species is a ...
(''Oncorhynchus nerka'') runs, which occur here in large part because the many large lakes of the peninsula are an important element in their lifecycle. These salmon, after returning from their brief time at sea, swim into the lakes and their contributing streams to spawn. Their offspring, or ''fry'', overwinter in the deep and food-abundant depths of these lakes until their migration to the sea in one or two years.
 Exceptionally large seabird colonies exist along the coast. Additionally, there are large populations of sea mammals in the
Exceptionally large seabird colonies exist along the coast. Additionally, there are large populations of sea mammals in the North Pacific Ocean
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north'' ...
between the Alaska Peninsula and Kamchatka
The Kamchatka Peninsula (, ) is a peninsula in the Russian Far East, with an area of about . The Pacific Ocean and the Sea of Okhotsk make up the peninsula's eastern and western coastlines, respectively.
Immediately offshore along the Pacific ...
. This includes harbor seals, ringed seals, northern fur seal
The northern fur seal (''Callorhinus ursinus'') is an eared seal found along the north Pacific Ocean, the Bering Sea, and the Sea of Okhotsk. It is the largest member of the fur seal subfamily (Arctocephalinae) and the only living species in the ...
s, whale
Whales are a widely distributed and diverse group of fully Aquatic animal, aquatic placental mammal, placental marine mammals. As an informal and Colloquialism, colloquial grouping, they correspond to large members of the infraorder Cetacea ...
s, porpoise
Porpoises () are small Oceanic dolphin, dolphin-like cetaceans classified under the family Phocoenidae. Although similar in appearance to dolphins, they are more closely related to narwhals and Beluga whale, belugas than to the Oceanic dolphi ...
s, sea otter
The sea otter (''Enhydra lutris'') is a marine mammal native to the coasts of the northern and eastern Pacific Ocean, North Pacific Ocean. Adult sea otters typically weigh between , making them the heaviest members of ...
s and sea lion
Sea lions are pinnipeds characterized by external ear flaps, long foreflippers, the ability to walk on all fours, short and thick hair, and a big chest and belly. Together with the fur seals, they make up the family Otariidae, eared seals. ...
s.
The rugged southern half of the peninsula, and also the Kodiak Archipelago which lie off the south coast of the peninsula and are home to even more bears, constitute the Alaska Peninsula montane taiga ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and c ...
and contain a number of protected areas such as Katmai National Park. Vegetation on the peninsula consists mostly of shrub-lands, grassy meadows, or wet tundra.
Demographics
Besides the communities on the coast (''see:Bristol Bay
Bristol Bay (, ) is the easternmost arm of the Bering Sea, at 57° to 59° North 157° to 162° West in Southwest Alaska. Bristol Bay is 400 km (250 mi) long and 290 km (180 mi) wide at its mouth. A number of rivers flow in ...
''), the Alaska Peninsula also is home to several well-known villages: Cold Bay, King Cove, Perryville, Chignik, Chignik Lake, Chignik Lagoon, and Port Moller. Each is primarily inhabited by Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Native Alaskans, Alaskan Indians, or Indigenous Alaskans) are the Indigenous peoples of Alaska that encompass a diverse arena of cultural and linguistic groups, including the Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tli ...
and each, likewise, is mostly dependent on the fishing industry for sustenance.
References
External links
Ugashik Area website
Hosted b
Alaska State Publications Program
{{Authority control Landforms of Aleutians East Borough, Alaska Landforms of Bristol Bay Borough, Alaska Landforms of Kenai Peninsula Borough, Alaska Landforms of Kodiak Island Borough, Alaska Landforms of Lake and Peninsula Borough, Alaska Peninsulas of Alaska Volcanic arcs