Alain Aspect on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Alain Aspect (; born 15 June 1947) is a French
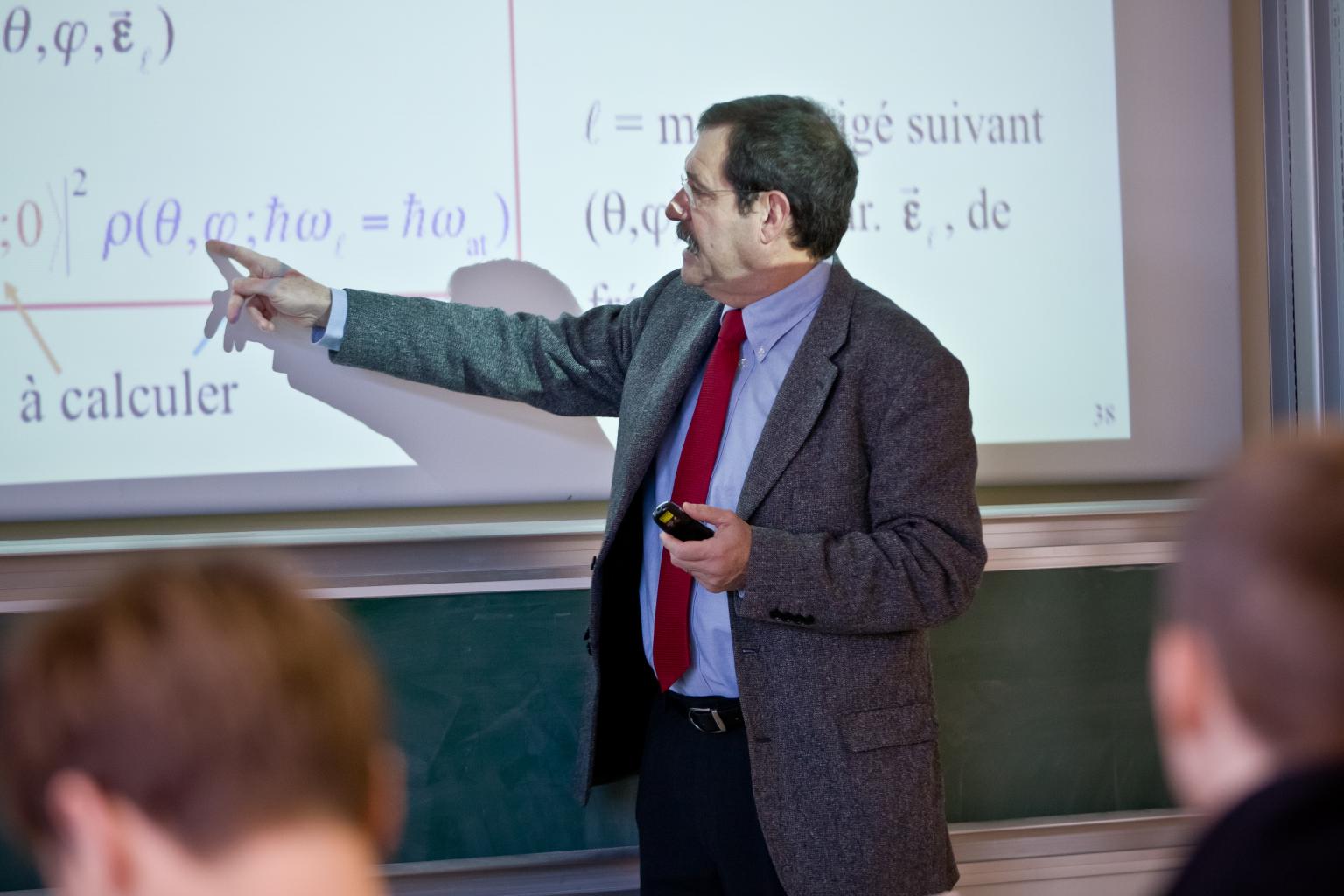 Aspect was deputy director of the French "
Aspect was deputy director of the French "
 * 2022:
* 2022:
Aspect's homepage
at CNRS
Alain Aspect
International Balzan Prize Foundation
Videos of Alain Aspect
in the AV-Portal of the German National Library of Science and Technology * {{DEFAULTSORT:Aspect, Alain 1947 births Living people People from Agen 20th-century French physicists Members of the French Academy of Sciences Wolf Prize in Physics laureates Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences Niels Bohr International Gold Medal recipients UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal recipients Albert Einstein Medal recipients Foreign members of the Royal Society Members of the Royal Academy of Belgium Members of Academia Europaea Fellows of the American Physical Society Members of the Austrian Academy of Sciences École Normale Supérieure alumni Academic staff of École Polytechnique Nobel laureates in Physics French Nobel laureates Research directors of the French National Centre for Scientific Research
physicist
A physicist is a scientist who specializes in the field of physics, which encompasses the interactions of matter and energy at all length and time scales in the physical universe. Physicists generally are interested in the root or ultimate cau ...
noted for his experimental work on quantum entanglement
Quantum entanglement is the phenomenon where the quantum state of each Subatomic particle, particle in a group cannot be described independently of the state of the others, even when the particles are separated by a large distance. The topic o ...
.
Aspect was awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
, jointly with John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger, "for experiments with entangled photons, establishing the violation of Bell inequalities and pioneering quantum information science
Quantum information science is a field that combines the principles of quantum mechanics with information theory to study the processing, analysis, and transmission of information. It covers both theoretical and experimental aspects of quantum phys ...
".
Education
Aspect is a graduate of the École Normale Supérieure de Cachan (ENS Cachan, today part of Paris-Saclay University). He passed the ''agrégation
In France, the () is the most competitive and prestigious examination for civil service in the French public education
A state school, public school, or government school is a primary school, primary or secondary school that educates all stu ...
'' in physics in 1969 and received his PhD degree in 1971 from the École supérieure d'optique (later known as Institut d'Optique Graduate School) of Université d'Orsay (later known as Université Paris-Sud). He then taught for three years in Cameroon
Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and the R ...
as a replacement for then compulsory military service.
In the early 1980s, while working on his doctorat d'État (habilitation thesis), he performed the Bell test experiments that showed that Albert Einstein
Albert Einstein (14 March 187918 April 1955) was a German-born theoretical physicist who is best known for developing the theory of relativity. Einstein also made important contributions to quantum mechanics. His mass–energy equivalence f ...
, Boris Podolsky and Nathan Rosen
Nathan Rosen (; March 22, 1909 – December 18, 1995) was an American and Israeli physicist noted for his study on the structure of the hydrogen molecule and his collaboration with Albert Einstein and Boris Podolsky on entangled wave functions and ...
's putative reductio ad absurdum
In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical argument'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absur ...
of quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics is the fundamental physical Scientific theory, theory that describes the behavior of matter and of light; its unusual characteristics typically occur at and below the scale of atoms. Reprinted, Addison-Wesley, 1989, It is ...
, namely that it implied ' ghostly action at a distance', did in fact appear to be realized when two particle
In the physical sciences, a particle (or corpuscle in older texts) is a small localized object which can be described by several physical or chemical properties, such as volume, density, or mass.
They vary greatly in size or quantity, from s ...
s were separated by an arbitrarily large distance (see EPR paradox
EPR may refer to:
Science and technology
* EPR (nuclear reactor), European Pressurised-Water Reactor
* EPR paradox (Einstein–Podolsky–Rosen paradox), in physics
* Earth potential rise, in electrical engineering
* East Pacific Rise, a mid-ocea ...
and Aspect's experiment). A correlation between the particles' wave function
In quantum physics, a wave function (or wavefunction) is a mathematical description of the quantum state of an isolated quantum system. The most common symbols for a wave function are the Greek letters and (lower-case and capital psi (letter) ...
s remains, as long as they were once part of the same undisturbed wave function before one of the child particles was measured. He defended his doctorat d'État in 1983 at Université Paris-Sud (today part of Paris-Saclay University).
Aspect received an honorary doctorate from Heriot-Watt University
Heriot-Watt University () is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1821 as the School of Arts of Edinburgh, the world's first mechanics' institute, and was subsequently granted university status by roya ...
in 2008.
Research
Aspect's experiments, following the first experiment of Stuart Freedman and John Clauser in 1972, were considered to provide further support to the thesis that Bell's inequalities are violated in its CHSH version, in particular by closing a form of the locality loophole. However, his results were not completely conclusive since there were loopholes that allowed for alternative explanations that comply with local realism. After his work on Bell's inequalities, Aspect turned toward studies oflaser cooling
Laser cooling includes several techniques where atoms, molecules, and small mechanical systems are cooled with laser light. The directed energy of lasers is often associated with heating materials, e.g. laser cutting, so it can be counterintuit ...
of neutral atoms, and Bose–Einstein condensate
In condensed matter physics, a Bose–Einstein condensate (BEC) is a state of matter that is typically formed when a gas of bosons at very low Density, densities is cooled to temperatures very close to absolute zero#Relation with Bose–Einste ...
s at the Kastler-Brossel Laboratory.
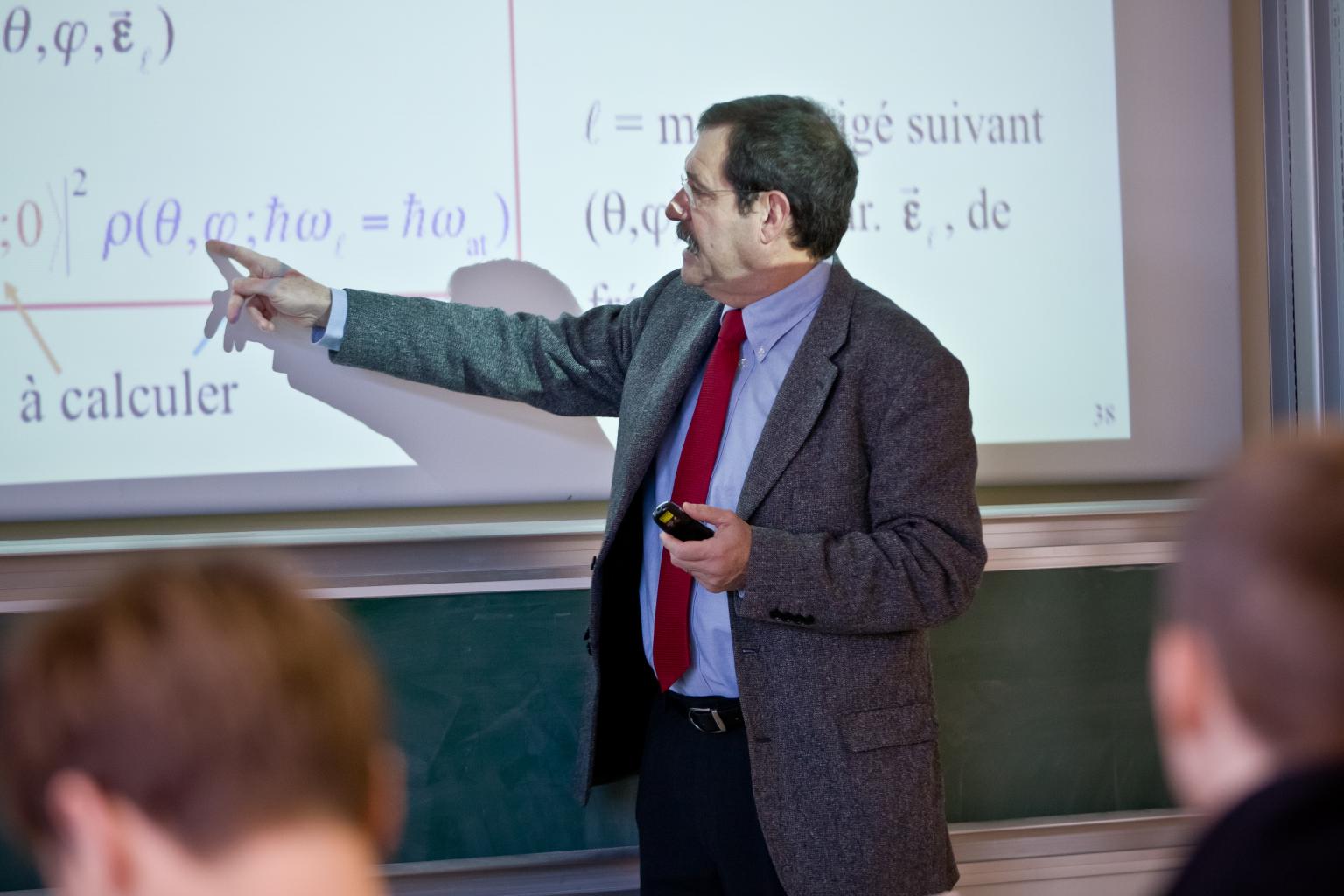 Aspect was deputy director of the French "
Aspect was deputy director of the French "grande Ă©cole
A (; ) is a specialized top-level educational institution in France and some other countries such as Morocco and Tunisia. are part of an alternative educational system that operates alongside the mainstream List of public universities in Franc ...
" École supérieure d'optique until 1994. He is a member of the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefron ...
and French Academy of Technologies
The National Academy of Technologies of France (''Académie des technologies'') is a learned society, founded in 2000, with an emphasis on technology, and the newest of French academies. In 2007 it acquired the status of ''établissement public'', ...
, and a professor at the École Polytechnique
(, ; also known as Polytechnique or l'X ) is a ''grande Ă©cole'' located in Palaiseau, France. It specializes in science and engineering and is a founding member of the Polytechnic Institute of Paris.
The school was founded in 1794 by mat ...
.
Distinctions
Aspect was elected aForeign Member of the Royal Society
Fellowship of the Royal Society (FRS, ForMemRS and HonFRS) is an award granted by the Fellows of the Royal Society of London to individuals who have made a "substantial contribution to the improvement of natural science, natural knowledge, incl ...
(ForMemRS) in 2015. His certificate of election reads
In 2005 he was awarded the gold medal of the Centre national de la recherche scientifique
The French National Centre for Scientific Research (, , CNRS) is the French state research organisation and is the largest fundamental science agency in Europe.
In 2016, it employed 31,637 staff, including 11,137 tenured researchers, 13,415 eng ...
, where he is Research Director. The 2010 Wolf Prize
The Wolf Prize is an international award granted in Israel, that has been presented most years since 1978 to living scientists and artists for "achievements in the interest of mankind and friendly relations among people ... irrespective of natio ...
in physics was awarded to Aspect, Anton Zeilinger and John Clauser. In 2013 Aspect was awarded both the Niels Bohr International Gold Medal
The Niels Bohr International Gold Medal is an international engineering award. It has been awarded since 1955 for "outstanding work by an engineer or physicist for the peaceful utilization of atomic energy". The medal is administered by the Danis ...
and the UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal
The UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal was first minted in 1985 to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the birth of the Danish nuclear physicist Niels Bohr. It is awarded by UNESCO to recognise those who have made outstanding contributions to physics throu ...
. In 2011, he was assigned the Medal of the City of Paris. In 2013, he was also awarded the Balzan Prize for Quantum Information Processing and Communication. In 2014, he was named Officer of the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
.
Asteroid 33163 Alainaspect, discovered by astronomers at Caussols in 1998, was named after him. The official was published by the Minor Planet Center
The Minor Planet Center (MPC) is the official body for observing and reporting on minor planets under the auspices of the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Founded in 1947, it operates at the Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory.
Funct ...
on 8 November 2019 ().
Aspect was awarded the 2022 Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
alongside John F. Clauser and Anton Zeilinger "for experiments with entangled photons
A photon () is an elementary particle that is a quantum of the electromagnetic field, including electromagnetic radiation such as light and radio waves, and the force carrier for the electromagnetic force. Photons are massless particles that ...
, establishing the violation of Bell's inequalities and pioneering quantum information science".
Honours and awards
Accolades received by Aspect include the following:Honours
* 2022 : Commander of theLegion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
.
* 2014 : Officier of the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
.
* 2011 : Officier of the National Order of Merit.
* 2011 : Commander of the Palmes académiques.
* 2011 : Medal of the City of Paris.
* 2005 : Knight of the Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour ( ), formerly the Imperial Order of the Legion of Honour (), is the highest and most prestigious French national order of merit, both military and Civil society, civil. Currently consisting of five cl ...
.
Awards
 * 2022:
* 2022: Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the ...
(with John Clauser and Anton Zeilinger)
* 2022: Honorary Optica Member
* 2013: Balzan Prize
* 2013: Niels Bohr International Gold Medal
The Niels Bohr International Gold Medal is an international engineering award. It has been awarded since 1955 for "outstanding work by an engineer or physicist for the peaceful utilization of atomic energy". The medal is administered by the Danis ...
* 2013: UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal
The UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal was first minted in 1985 to commemorate the 100th anniversary of the birth of the Danish nuclear physicist Niels Bohr. It is awarded by UNESCO to recognise those who have made outstanding contributions to physics throu ...
* 2013: Frederic Ives Medal/Jarus W. Quinn Prize
* 2012: Albert Einstein Medal
* 2012: Herbert Walther Award
* 2010: Wolf Prize
The Wolf Prize is an international award granted in Israel, that has been presented most years since 1978 to living scientists and artists for "achievements in the interest of mankind and friendly relations among people ... irrespective of natio ...
* 2005: CNRS Gold Medal
* 1999: Gay-Lussac–Humboldt Prize
* 1999: Max Born Award
* 1991: Fernand Holweck Medal and Prize
The Fernand Holweck Medal and Prize is a major European prize for Physics awarded jointly every year by the British Institute of Physics (IOP) and the Société Française de Physique (SFP). It is one of the four Grand Prix of the SFP and one of ...
* 1987: International Commission for Optics Award
* 1985: Commonwealth Award for Science and Invention
* 1983: ''Prix Servant''
Acknowledgement
* Member of theAcademia Europaea
The Academia Europaea is a pan-European Academy of humanities, letters, law, and sciences.
The Academia was founded in 1988 as a functioning Europe-wide Academy that encompasses all fields of scholarly inquiry. It acts as co-ordinator of Europe ...
* Member of the French Academy of Sciences
The French Academy of Sciences (, ) is a learned society, founded in 1666 by Louis XIV at the suggestion of Jean-Baptiste Colbert, to encourage and protect the spirit of French Scientific method, scientific research. It was at the forefron ...
* Member of the French Academy of Technologies
The National Academy of Technologies of France (''Académie des technologies'') is a learned society, founded in 2000, with an emphasis on technology, and the newest of French academies. In 2007 it acquired the status of ''établissement public'', ...
* Foreign Member of the Royal Society
The Royal Society, formally The Royal Society of London for Improving Natural Knowledge, is a learned society and the United Kingdom's national academy of sciences. The society fulfils a number of roles: promoting science and its benefits, re ...
* Foreign Associate of the National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences (NAS) is a United States nonprofit, NGO, non-governmental organization. NAS is part of the National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine, along with the National Academy of Engineering (NAE) and the ...
* Associate Member of the Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium
The Royal Academy of Science, Letters and Fine Arts of Belgium ( , sometimes referred to as ' ) is the independent learned society of science and arts of the French Community of Belgium. One of Belgium's numerous academies, it is the French-speak ...
* Corresponding member abroad of the Austrian Academy of Sciences
The Austrian Academy of Sciences (; Ă–AW) is a legal entity under the special protection of the Republic of Austria. According to the statutes of the Academy its mission is to promote the sciences and humanities in every respect and in every fi ...
* Fellow and Honorary Member of Optica
Honorary degrees
* 2006:Université de Montréal
The Université de Montréal (; UdeM; ) is a French-language public research university in Montreal, Quebec, Canada. The university's main campus is located in the Côte-des-Neiges neighborhood of Côte-des-Neiges–Notre-Dame-de-Grâce on M ...
* 2008: Australian National University
The Australian National University (ANU) is a public university, public research university and member of the Group of Eight (Australian universities), Group of Eight, located in Canberra, the capital of Australia. Its main campus in Acton, A ...
* 2008: Heriot-Watt University
Heriot-Watt University () is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. It was established in 1821 as the School of Arts of Edinburgh, the world's first mechanics' institute, and was subsequently granted university status by roya ...
* 2010: University of Glasgow
The University of Glasgow (abbreviated as ''Glas.'' in Post-nominal letters, post-nominals; ) is a Public university, public research university in Glasgow, Scotland. Founded by papal bull in , it is the List of oldest universities in continuous ...
* 2011: University of Haifa
The University of Haifa (, ) is a public research university located on Mount Carmel in Haifa, Israel. Founded in 1963 as a branch of the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, the University of Haifa received full academic accreditation as an inde ...
* 2014: University of Waterloo
The University of Waterloo (UWaterloo, UW, or Waterloo) is a Public university, public research university located in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada. The main campus is on of land adjacent to uptown Waterloo and Waterloo Park. The university also op ...
* 2018: City University of Hong Kong
The City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) is a public research university in Kowloon Tong, Kowloon, Hong Kong. It was founded in 1984 as the City Polytechnic of Hong Kong and formally established as the City University of Hong Kong in 1994 ...
* 2023: Université de Sherbrooke
The Université de Sherbrooke (UdeS; Quebec English, English: ''University of Sherbrooke'') is a French-language Public university, public research university in Sherbrooke, Quebec, Canada, with a second campus in Longueuil, a suburb on the Mont ...
* 2024: University of Minho
The University of Minho (''Universidade do Minho'') is a public university in Minho Province, Portugal. It is divided into the following campuses:
* Largo do Paço (rectorate), in Braga
* Campus of Gualtar, in Braga
* Convento dos Congregados, i ...
References
Publications
* * *External links
Aspect's homepage
at CNRS
Alain Aspect
International Balzan Prize Foundation
Videos of Alain Aspect
in the AV-Portal of the German National Library of Science and Technology * {{DEFAULTSORT:Aspect, Alain 1947 births Living people People from Agen 20th-century French physicists Members of the French Academy of Sciences Wolf Prize in Physics laureates Foreign associates of the National Academy of Sciences Niels Bohr International Gold Medal recipients UNESCO Niels Bohr Medal recipients Albert Einstein Medal recipients Foreign members of the Royal Society Members of the Royal Academy of Belgium Members of Academia Europaea Fellows of the American Physical Society Members of the Austrian Academy of Sciences École Normale Supérieure alumni Academic staff of École Polytechnique Nobel laureates in Physics French Nobel laureates Research directors of the French National Centre for Scientific Research