Abdominal muscles on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Abdominal muscles cover the anterior and lateral abdominal region and meet at the anterior midline. These muscles of the anterolateral abdominal wall can be divided into four groups: the
 There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transversus abdominis, is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to the front of a belt on a pair of pants. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.
There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transversus abdominis, is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to the front of a belt on a pair of pants. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.
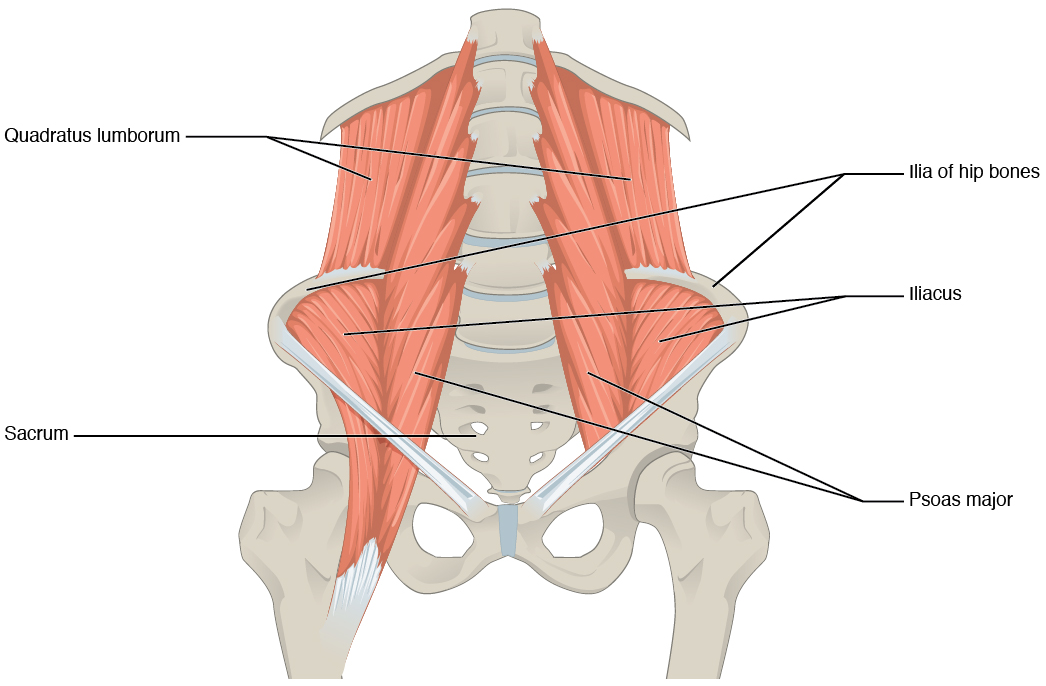 The posterior abdominal wall is formed by the
The posterior abdominal wall is formed by the
external obliques
The abdominal external oblique muscle (also external oblique muscle or exterior oblique) is the largest and outermost of the three flat Abdomen#Muscles, abdominal muscles of the lateral anterior abdomen.
Structure
The external oblique is situat ...
, the internal obliques, the transversus abdominis, and the rectus abdominis
The rectus abdominis muscle, () also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply better known as the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person, person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline b ...
.
Anterior abdominal wall
 There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transversus abdominis, is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to the front of a belt on a pair of pants. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.
There are three flat skeletal muscles in the antero-lateral wall of the abdomen. The external oblique, closest to the surface, extend inferiorly and medially, in the direction of sliding one’s four fingers into pants pockets. Perpendicular to it is the intermediate internal oblique, extending superiorly and medially, the direction the thumbs usually go when the other fingers are in the pants pocket. The deep muscle, the transversus abdominis, is arranged transversely around the abdomen, similar to the front of a belt on a pair of pants. This arrangement of three bands of muscles in different orientations allows various movements and rotations of the trunk. The three layers of muscle also help to protect the internal abdominal organs in an area where there is no bone.
Linea alba
The linea alba is a white, fibrous band that is made of the bilateral rectus sheaths that join at the anterior midline of the body. These enclose therectus abdominis
The rectus abdominis muscle, () also known as the "abdominal muscle" or simply better known as the "abs", is a pair of segmented skeletal muscle on the ventral aspect of a person, person's abdomen. The paired muscle is separated at the midline b ...
muscles (a pair of long, linear muscles, commonly called the “sit-up” muscles) that originate at the pubic crest
Medial to the pubic tubercle is the pubic crest, which extends from this process to the medial end of the pubis (bone), pubic bone.
It gives attachment to the conjoint tendon, the rectus abdominis, the abdominal external oblique muscle, and the ...
and pubic symphysis
The pubic symphysis (: symphyses) is a secondary cartilaginous joint between the left and right superior rami of the pubis of the hip bones. It is in front of and below the urinary bladder. In males, the suspensory ligament of the penis attache ...
, and extend the length of the body’s trunk. Each muscle is segmented by three transverse bands of collagen fibers called the tendinous intersections. This results in the look of “six-pack abs,” as each segment hypertrophies on individuals at the gym who do many sit-ups.
Posterior abdominal wall
 The posterior abdominal wall is formed by the
The posterior abdominal wall is formed by the lumbar vertebrae
The lumbar vertebrae are located between the thoracic vertebrae and pelvis. They form the lower part of the back in humans, and the tail end of the back in quadrupeds. In humans, there are five lumbar vertebrae. The term is used to describe t ...
, parts of the ilia of the hip bones, psoas major
The psoas major ( or ; from ) is a long fusiform muscle located in the lateral lumbar region between the vertebral column and the brim of the lesser pelvis. It joins the iliacus muscle to form the iliopsoas. In other animals, this muscle is e ...
and iliacus muscles, and quadratus lumborum muscle. This part of the core plays a key role in stabilizing the rest of the body and maintaining posture.
Functions
Source text
{{Authority control Muscles of the torso