AW101 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The AgustaWestland AW101 is a medium-lift
"AgustaWestland pursues new AW101 sales avenues"
. ''
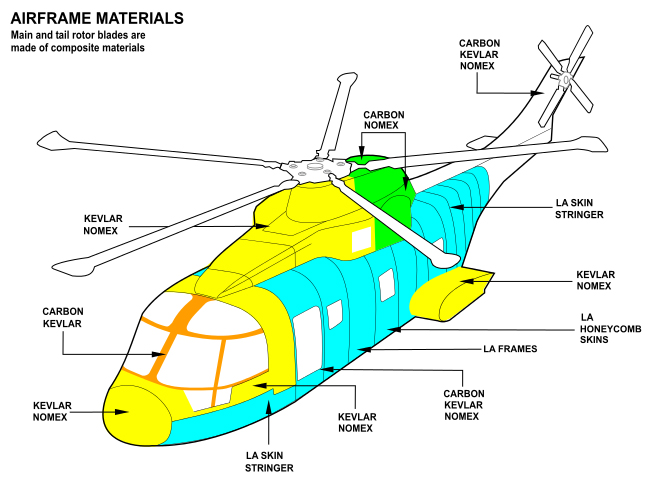 The AW101 follows a conventional design layout, but makes use of advanced technologies, such as the design of the rotor blades, avionics systems, and extensive use of composite materials. The fuselage structure is modular and comprises an aluminium–lithium alloy, designed to be both light and damage-resistant. The AW101 is designed for operating in extreme weather conditions; it is fitted with a de-icing system and rated to operate in temperatures ranging between −45 and +50 °C.Crawford 2003, p. 27. The aircraft's control systems allow the AW101 to maintain a stable hover in crosswinds.
An active vibration control system, known as the ''active control of structural response system'', reduces airframe vibration by up to 80%, increasing crew comfort and minimising buildup of stress on the airframe. The cockpit is fitted with armoured seats for the crew, and can withstand an impact velocity of over 10 m/s. Dual flight controls are provided, though the AW101 can be flown by a single person. The pilots' instrument displays include six full-colour high-definition screens and an optional mission display; a digital map or forward looking infrared (FLIR) display can also be installed.
The AW101 follows a conventional design layout, but makes use of advanced technologies, such as the design of the rotor blades, avionics systems, and extensive use of composite materials. The fuselage structure is modular and comprises an aluminium–lithium alloy, designed to be both light and damage-resistant. The AW101 is designed for operating in extreme weather conditions; it is fitted with a de-icing system and rated to operate in temperatures ranging between −45 and +50 °C.Crawford 2003, p. 27. The aircraft's control systems allow the AW101 to maintain a stable hover in crosswinds.
An active vibration control system, known as the ''active control of structural response system'', reduces airframe vibration by up to 80%, increasing crew comfort and minimising buildup of stress on the airframe. The cockpit is fitted with armoured seats for the crew, and can withstand an impact velocity of over 10 m/s. Dual flight controls are provided, though the AW101 can be flown by a single person. The pilots' instrument displays include six full-colour high-definition screens and an optional mission display; a digital map or forward looking infrared (FLIR) display can also be installed.
 The AW101 is powered by three
The AW101 is powered by three
Rolls-Royce plc. Retrieved 21 April 2012. The engines power an diameter five-bladed main rotor. The rotor blades are constructed from carbon/glass with nomex honeycomb and rohacell foam, edged with titanium alloy in a sandwich construction. The shaping of the main rotor blades is derived from the BERP rotor blades first used on the
 Most variants of the AW101 are equipped with self-defence systems, such as chaff and flare dispensers, directed infrared countermeasures (infrared jammers), ESM (electronic support measures in the form of RF heads), and a laser detection and warning system. British Merlins have been outfitted with protective armour against small-arms fire. A side-mounted forward looking infrared (FLIR) imaging sensor has been fitted to some variants.
Two hardpoints are present in the underside of the airframe on which the HM1 model can carry four Sting Ray torpedoes or Mk 11 Mod 3 depth charges. Some customers have chosen to deploy the Marte anti-ship missile on the AW101; as of 2011, the Royal Navy is considering equipping their Merlin fleet with an anti-surface missile. The Mk1, Mk3 and Mk3A variants can mount general purpose machine guns in up to five locations in the main cabin, aimed out of both door and window apertures. AgustaWestland has examined the integration of
Most variants of the AW101 are equipped with self-defence systems, such as chaff and flare dispensers, directed infrared countermeasures (infrared jammers), ESM (electronic support measures in the form of RF heads), and a laser detection and warning system. British Merlins have been outfitted with protective armour against small-arms fire. A side-mounted forward looking infrared (FLIR) imaging sensor has been fitted to some variants.
Two hardpoints are present in the underside of the airframe on which the HM1 model can carry four Sting Ray torpedoes or Mk 11 Mod 3 depth charges. Some customers have chosen to deploy the Marte anti-ship missile on the AW101; as of 2011, the Royal Navy is considering equipping their Merlin fleet with an anti-surface missile. The Mk1, Mk3 and Mk3A variants can mount general purpose machine guns in up to five locations in the main cabin, aimed out of both door and window apertures. AgustaWestland has examined the integration of
 The AW101 is typically operated by a crew of three: a pilot, an observer, and a crewman/operator. The pilot is able to fly for the majority of a mission in a hands-off mode, enabled by the sophisticated autopilot. All crew members have individual access to management computers and tactical information.Evans 2004, p. 23.
The fuselage has a volume of and the cargo compartment is in length, wide and high. The military version of the AW101 can accommodate up to 24 seated or 45 standing combat troops and their equipment. Alternative loads include a medical team and 16 stretchers, and cargo pallets.
The ramp, , can take a load, allowing it to carry vehicles such as Land Rovers. The ramp and cabin floor are fitted with flush tie-down points. A cargo hook under the fuselage can carry external loads of via the use of a semi-automatic cargo release unit (SACRU). A rescue hoist and a hover trim controller are fitted at the cargo door. An optional cargo winch can be installed near to the rear ramp.
The AW101 is typically operated by a crew of three: a pilot, an observer, and a crewman/operator. The pilot is able to fly for the majority of a mission in a hands-off mode, enabled by the sophisticated autopilot. All crew members have individual access to management computers and tactical information.Evans 2004, p. 23.
The fuselage has a volume of and the cargo compartment is in length, wide and high. The military version of the AW101 can accommodate up to 24 seated or 45 standing combat troops and their equipment. Alternative loads include a medical team and 16 stretchers, and cargo pallets.
The ramp, , can take a load, allowing it to carry vehicles such as Land Rovers. The ramp and cabin floor are fitted with flush tie-down points. A cargo hook under the fuselage can carry external loads of via the use of a semi-automatic cargo release unit (SACRU). A rescue hoist and a hover trim controller are fitted at the cargo door. An optional cargo winch can be installed near to the rear ramp.

 The British Royal Navy's final order was for 44 ASW aircraft, originally designated ''Merlin HAS.1'' (Helicopter, Anti-Submarine Mark 1) but soon changed to ''Merlin HM1'' (Helicopter, Maritime Mark 1). The first fully operational Merlin was delivered on 17 May 1997, entering service on 2 June 2000. All aircraft were delivered by the end of 2002, and are operated by 3
The British Royal Navy's final order was for 44 ASW aircraft, originally designated ''Merlin HAS.1'' (Helicopter, Anti-Submarine Mark 1) but soon changed to ''Merlin HM1'' (Helicopter, Maritime Mark 1). The first fully operational Merlin was delivered on 17 May 1997, entering service on 2 June 2000. All aircraft were delivered by the end of 2002, and are operated by 3
 The RAF ordered 22 Merlin HC3 for transport missions, the first of which entered service in January 2001 with No. 28 Squadron RAF based at RAF Benson. The type is equipped with extended-range fuel tanks and is capable of air-to-air refuelling. The Merlin is frequently utilised for troop transport duties and for the transport of bulky objects, either internally or underslung, including vehicles and artillery. The Merlin Depth Maintenance Facility at RNAS Culdrose performed most tasks upon the Merlin HC3.
The Merlin's first operational deployment was to the
The RAF ordered 22 Merlin HC3 for transport missions, the first of which entered service in January 2001 with No. 28 Squadron RAF based at RAF Benson. The type is equipped with extended-range fuel tanks and is capable of air-to-air refuelling. The Merlin is frequently utilised for troop transport duties and for the transport of bulky objects, either internally or underslung, including vehicles and artillery. The Merlin Depth Maintenance Facility at RNAS Culdrose performed most tasks upon the Merlin HC3.
The Merlin's first operational deployment was to the
 In 1997, the Italian government ordered 16 AW101 helicopters for the
In 1997, the Italian government ordered 16 AW101 helicopters for the
 Danish AW101s have a higher gross weight capacity of 15,600 kg and were, as delivered, coated in a paint designed to reduce the aircraft's infrared signature. In the SAR role, RDAF AW101s have a crew of six and were initially painted yellow to distinguish themselves from AW101 allocated to military duties, but were later painted green, and all 14 AW101s are used for SAR and troop transport.EH-101 Merlin
Danish AW101s have a higher gross weight capacity of 15,600 kg and were, as delivered, coated in a paint designed to reduce the aircraft's infrared signature. In the SAR role, RDAF AW101s have a crew of six and were initially painted yellow to distinguish themselves from AW101 allocated to military duties, but were later painted green, and all 14 AW101s are used for SAR and troop transport.EH-101 Merlin
" '' Royal Danish Air Force''. Accessed: 19 December 2013. On 28 January 2008, the drive shaft of a Danish AW101 broke, leading to an emergency landing at Billund Airport. Following the incident, the Danish fleet was grounded as a precaution and the AW101's future was publicly debated. In the first six months of 2008, the RDAF reported an operational availability of roughly 50%, well below the target of 80%, partly due to an inadequate maintenance organisation and staff shortages. In January 2011, the Danish Ministry of Defence reportedly could not afford the retrofitting of the AW101 fleet for Afghanistan operations, against earlier reports of a deployment in 2012. In February 2013, ''Aviation Week'' reported that earlier reliability problems had been resolved and that a full upgrade package would be applied to Danish AW101s; these included the addition of electronic warfare pods and a new electro-optical system, in advance of a deployment in Afghanistan in 2014. In September 2013, Danish AW101s were to receive L-3 Wescam MX-15 electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) sensors; SAR aircraft already carry the FLIR Systems Star Safire II EO/IR sensor.
 The Portuguese Air Force had purchased 12 Merlins under a €446 million contract, the first of which was delivered on 22 December 2004. The type has been used to conduct transport, search and rescue, and maritime surveillance missions, progressively replacing the Aérospatiale Puma previously tasked with these missions. The main role of Portuguese AW101s is to perform search and rescue missions within Portugal's maritime zone. They are operated by 751 Squadron and are kept on constant alert at three bases: Montijo near
The Portuguese Air Force had purchased 12 Merlins under a €446 million contract, the first of which was delivered on 22 December 2004. The type has been used to conduct transport, search and rescue, and maritime surveillance missions, progressively replacing the Aérospatiale Puma previously tasked with these missions. The main role of Portuguese AW101s is to perform search and rescue missions within Portugal's maritime zone. They are operated by 751 Squadron and are kept on constant alert at three bases: Montijo near
''Flight International'', 2 June 2009. After the cancellation, the delivered helicopters were sold to Canada for $164 million, where they were used as source of spare parts for its fleet of AgustaWestland CH-149 Cormorant search-and-rescue helicopters. Separately, the Marine Corps had also conducted studies into the adoption of the EH101 as a fall-back option to the Bell-Boeing V-22 Osprey tiltrotor during the 1990s. In April 2009, India ordered 12 AW101 to serve as executive transport helicopters for the Indian president and prime minister. The selection followed field trial assessments between the AW101 and the Sikorsky S-92 held in 2008. However, the procurement was put on hold and subsequently cancelled due to the 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal, in which Finmeccanica, AgustaWestland's parent company, was accused of using bribery to win the contract. The three helicopters delivered as part of the contract may be returned to the manufacturer as part of the arbitration process.
 ;Model 111
: Royal Navy ASW/ASuW variant, designated Merlin HM1 by customer. Powered by RTM322 engines and fitted with Blue Kestrel radar, Thomson Marconi FLASH dipping sonar and Orange Reaper ESM. 44 built.Lake 2007, p. 124.
;Model 112
: Italian Navy early warning variant with same airframe as Model 110 but with Eliradar HEW-784 radar in large underfuselage radome. Four built.Lake 2007, p. 125.
;Series 200
: Proposed military utility version with no rear-loading ramp.
;Series 300 Heliliner
: Proposed civil transport with no ramp.Lake 2007, pp. 125–126. In 2000, British International Helicopters conducted service trials using ''PP8''; these did not lead to a commercial service.
;Series 310
: Proposed version of Heliliner with full airline avionics for operation from oil platforms. No production.Lake 2007, p. 126.
;Model 410
: Italian Navy transport variant with folding rotors and tail boom. Four built.
;Model 411
: Royal Air Force transport variant, designated Merlin HC3 by customer, 22 built.Lake 2007, pp. 126–127.
;Model 413
: Italian Navy special forces and amphibious assault transport with more advanced avionics.Lake 2007, p. 128.
;Model 500
: Proposed civil utility variant with rear-ramp.
;Model 510
: Civil utility variant with rear ramp, two built. One used for Tokyo Metropolitan Police Agency and one used to support US101 bid.
;Model 511
: Canadian Armed Forces search and rescue variant, designated CH-149 Cormorant.Lake 2007, pp. 128–129.
;Model 512
: Merlin Joint Supporter for Royal Danish Air Force. Eight acquired for search and rescue (''512 SAR'') and six for tactical troop transport (''512 TTT''). The six transports were sold to RAF (as Merlin HC3As) and replaced by six new-build Merlins.Lake 2007, pp. 129–131.
;Model 514
: Portuguese Air Force search and rescue variant, six built.
;Model 515
: Portuguese Air Force fisheries protection variant, two built.
;Model 516
: Portuguese Air Force combat search and rescue variant, four built.
;Model 518
: Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force mine countermeasures and transport variant, two built.
;Model 519
:Presidential Transport variant for the United States Marine Corps as the VH-71 Kestrel, four test vehicles and five pilot production aircraft built. Canceled and aircraft sold to Royal Canadian Air Force as spares for CH-149 Cormorant fleet.
;Model 610
: Algerian Naval variant. 6 delivered.
;Model 611
: Italian Air Force Combat Search and Rescue variant, powered by CT7-8E engines. 15 on order.
;Model 612 (SAR Queen)
: Norwegian search and rescue variant, operated by the Air Force. 16 ordered with option for 6 more.
;Model 614
: Polish ASW/ CSAR "convertible" variant, operated by the Polish Navy, 4 delivered.
;Model 615
: Canadian military search and rescue variant, upgraded -511 variant, again designated the CH-149 Cormorant. 16 to be delivered.
;Model 640
: Saudi Arabian VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Model 641
: Indian VVIP variant. (See 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal). Latterly delivered to Nigerian and Azerbaijani Air Forces.
;Model 642
: Algerian VVIP variant, 2 delivered.
;Model 643
: Turkmenistani VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Merlin HM1
: Royal Navy designation for the Model 111.
;Merlin HM2
: Avionics retrofit of 30 HM1s for the Royal Navy.
;Model 111
: Royal Navy ASW/ASuW variant, designated Merlin HM1 by customer. Powered by RTM322 engines and fitted with Blue Kestrel radar, Thomson Marconi FLASH dipping sonar and Orange Reaper ESM. 44 built.Lake 2007, p. 124.
;Model 112
: Italian Navy early warning variant with same airframe as Model 110 but with Eliradar HEW-784 radar in large underfuselage radome. Four built.Lake 2007, p. 125.
;Series 200
: Proposed military utility version with no rear-loading ramp.
;Series 300 Heliliner
: Proposed civil transport with no ramp.Lake 2007, pp. 125–126. In 2000, British International Helicopters conducted service trials using ''PP8''; these did not lead to a commercial service.
;Series 310
: Proposed version of Heliliner with full airline avionics for operation from oil platforms. No production.Lake 2007, p. 126.
;Model 410
: Italian Navy transport variant with folding rotors and tail boom. Four built.
;Model 411
: Royal Air Force transport variant, designated Merlin HC3 by customer, 22 built.Lake 2007, pp. 126–127.
;Model 413
: Italian Navy special forces and amphibious assault transport with more advanced avionics.Lake 2007, p. 128.
;Model 500
: Proposed civil utility variant with rear-ramp.
;Model 510
: Civil utility variant with rear ramp, two built. One used for Tokyo Metropolitan Police Agency and one used to support US101 bid.
;Model 511
: Canadian Armed Forces search and rescue variant, designated CH-149 Cormorant.Lake 2007, pp. 128–129.
;Model 512
: Merlin Joint Supporter for Royal Danish Air Force. Eight acquired for search and rescue (''512 SAR'') and six for tactical troop transport (''512 TTT''). The six transports were sold to RAF (as Merlin HC3As) and replaced by six new-build Merlins.Lake 2007, pp. 129–131.
;Model 514
: Portuguese Air Force search and rescue variant, six built.
;Model 515
: Portuguese Air Force fisheries protection variant, two built.
;Model 516
: Portuguese Air Force combat search and rescue variant, four built.
;Model 518
: Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force mine countermeasures and transport variant, two built.
;Model 519
:Presidential Transport variant for the United States Marine Corps as the VH-71 Kestrel, four test vehicles and five pilot production aircraft built. Canceled and aircraft sold to Royal Canadian Air Force as spares for CH-149 Cormorant fleet.
;Model 610
: Algerian Naval variant. 6 delivered.
;Model 611
: Italian Air Force Combat Search and Rescue variant, powered by CT7-8E engines. 15 on order.
;Model 612 (SAR Queen)
: Norwegian search and rescue variant, operated by the Air Force. 16 ordered with option for 6 more.
;Model 614
: Polish ASW/ CSAR "convertible" variant, operated by the Polish Navy, 4 delivered.
;Model 615
: Canadian military search and rescue variant, upgraded -511 variant, again designated the CH-149 Cormorant. 16 to be delivered.
;Model 640
: Saudi Arabian VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Model 641
: Indian VVIP variant. (See 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal). Latterly delivered to Nigerian and Azerbaijani Air Forces.
;Model 642
: Algerian VVIP variant, 2 delivered.
;Model 643
: Turkmenistani VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Merlin HM1
: Royal Navy designation for the Model 111.
;Merlin HM2
: Avionics retrofit of 30 HM1s for the Royal Navy.
 ;Merlin HC3
: Royal Air Force designation for the Model 411.
;Merlin HC3A
: Royal Air Force designation for six former Royal Danish Air Force Model 512s modified to UK standards.
;Merlin HC3i
: Royal Navy will fit seven HC3 with folding rotor heads as an interim (3i) measure until the full HC4 upgrade is available.
;Merlin HC4/4A
: The conversion of 25 RAF HC3/3A (19 HC3 and 6 HC3A) for RN use in hand with the first flight taking place in November 2016. HM2 cockpit, folding tail/blades and other adaptations for naval use.
;CH-148 Petrel
: Ship-based anti-submarine helicopter for Canada. 35 originally ordered by the
;Merlin HC3
: Royal Air Force designation for the Model 411.
;Merlin HC3A
: Royal Air Force designation for six former Royal Danish Air Force Model 512s modified to UK standards.
;Merlin HC3i
: Royal Navy will fit seven HC3 with folding rotor heads as an interim (3i) measure until the full HC4 upgrade is available.
;Merlin HC4/4A
: The conversion of 25 RAF HC3/3A (19 HC3 and 6 HC3A) for RN use in hand with the first flight taking place in November 2016. HM2 cockpit, folding tail/blades and other adaptations for naval use.
;CH-148 Petrel
: Ship-based anti-submarine helicopter for Canada. 35 originally ordered by the  ;EH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the AEW variant.
;MH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the Amphibious Support Helicopter (ASH) variant.
;HH-101A
:Italian Air Force designation for the CSAR variant.
; Kawasaki Heavy Industries MCH-101
:Japan Defense Agency designation of Model 518
;EH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the AEW variant.
;MH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the Amphibious Support Helicopter (ASH) variant.
;HH-101A
:Italian Air Force designation for the CSAR variant.
; Kawasaki Heavy Industries MCH-101
:Japan Defense Agency designation of Model 518
 ;
* Algerian Air Force
* Algerian Navy
;
* Royal Canadian Air Force (see CH-149 Cormorant)
;
* Royal Danish Air Force
;
*
;
* Algerian Air Force
* Algerian Navy
;
* Royal Canadian Air Force (see CH-149 Cormorant)
;
* Royal Danish Air Force
;
*
Japan Ministry of Defence ; * Nigerian Air Force ; * Royal Norwegian Air Force ; * Polish Navy (4 delivered) ; * Portuguese Air Force ; * Royal Saudi Air Force
;
* Turkmen Air Force
;
*
* Royal Saudi Air Force
;
* Turkmen Air Force
;
*


''AW101 Utility''.
AgustaWestland, June 2008. * Cooper, Neil. ''The business of death: Britain's arms trade at home and abroad''. I.B.Tauris, 1997. . * Crawford, Stephen. ''Twenty-first century military helicopters: today's fighting gunships''. Zenith Imprint, 2003. . * Dobbin, Murray. ''The politics of Kim Campbell: from school trustee to Prime Minister''. James Lorimer & Company, 1993. . * Donald, David, ed. ''The Complete Encyclopedia of World Aircraft''. New York: Barnes & Noble Books, 1997. . * Eden, Paul, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Modern Military Aircraft''. London: Amber Books, 2004. . * Evans, Nicholas D. ''Military gadgets: how advanced technology is transforming today's battlefield-- and tomorrow's''. FT Press, 2004. . * Frawley, Gerald. ''The International Directory of Military Aircraft, 2002/2003''. Fyshwick, Australian Capital Territory">Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 2002. . * Friedman, Norman. ''The Naval Institute guide to world naval weapons systems, 1997–1998''. Annapolis, Maryland, USA: Naval Institute Press, 1997. . * Gunston, Bill and Mike Spick. ''Modern fighting helicopters''. Random House Value Publishing, 1986. . * Harding, Ian. "Long distance wizard". ''Air International'', Vol. 79, No. 1, July 2010. pp. 70–75. . * Jackson, Paul. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2003–2004''. 2003, Jane's Information Group. Coulsdon, UK. * Jackson, Paul; Munson, Kenneth; Peacock, Lindsay. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2009–2010''. 2009, Jane's Information Group. Coulsdon, UK. * Lake, Jon. "Variant File: AgustaWestland EH101/AW101". ''International Air Power Review''. Volume 22. Westport, Connecticut, USA: AIRtime Publishing, 2007. pp. 116–135. . . * Lavington, Simon. ''Moving Targets: Elliott-Automation and the Dawn of the Computer Age in Britain, 1947–67''. Springer 2011, . * Martin, Stephen. ''The economics of offsets: defence procurement and countertrade''. Routledge, 1996. . * Matthews, Ron. ''European armaments collaboration: policy, problems and prospects''. Routledge, 1992. . * Moir, Ian and Allan G. Seabridge. ''Aircraft systems: mechanical, electrical, and avionics subsystems integration''. John Wiley and Sons, 2008. . * Plamondon, Aaron. ''The politics of procurement: military acquisition in Canada and the Sea King helicopter''. UBC Press, 2009. .
Royal Navy Merlin website
EH-101 Merlin page (in English) on Portuguese Air Force site
{{Italian military aircraft AW101 Aircraft first flown in 1987 Anti-submarine helicopters 1980s international anti-submarine aircraft 1980s international civil utility aircraft 1980s international military transport aircraft Italy–United Kingdom relations Kawasaki Aerospace Company 1980s international helicopters Military transport helicopters Three-turbine helicopters Single-rotor helicopters Aircraft with retractable tricycle landing gear
helicopter
A helicopter is a type of rotorcraft in which Lift (force), lift and thrust are supplied by horizontally spinning Helicopter rotor, rotors. This allows the helicopter to VTOL, take off and land vertically, to hover (helicopter), hover, and ...
in military and civil use. First flown in 1987, it was developed by a joint venture between Westland Helicopters in the United Kingdom and Agusta
Agusta was an Italian helicopter manufacturer. It was based in Samarate, Northern Italy. The company was founded by Count Giovanni Agusta in 1923, who flew his first aeroplane in 1907. The MV Agusta motorcycle manufacturer began as an offshoot ...
in Italy in response to national requirements for a modern naval utility helicopter. Several operators, including the armed forces of Britain, Denmark, and Portugal, use the name Merlin for their AW101 aircraft. It is manufactured at factories in Yeovil
Yeovil () is a town and civil parishes in England, civil parish in Somerset, England. It is close to Somerset's southern border with Dorset, west of London, south of Bristol, west of Sherborne and east of Taunton. The population of the bui ...
, England, and Vergiate, Italy. Licensed assembly work has also taken place in Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea ...
and the United States
The United States of America (USA), also known as the United States (U.S.) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It is a federal republic of 50 U.S. state, states and a federal capital district, Washington, D.C. The 48 ...
.
Prior to 2007, the aircraft had been marketed under the designation EH101. The original designation was EHI 01, from the name given to the Anglo-Italian joint venture—European Helicopter Industries—but a transcription error changed this to EH101. In 2000, Westland Helicopters and Agusta merged to form AgustaWestland, leading to the type's current designation.
The AW101 entered into service in 1999 and has since replaced several older helicopter types, such as the Sikorsky SH-3 Sea King
The Sikorsky SH-3 Sea King (company designation S-61) is an American twin-engine anti-submarine warfare (ASW) helicopter designed and built by Sikorsky Aircraft. A landmark design, it was one of the first ASW rotorcraft to use turboshaft engine ...
, performing roles such as medium-sized transport, anti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in the older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations ar ...
, search and rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
, and ship-based utility operations. The Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) operates the CH-149 Cormorant variant for air-sea rescue
Air-sea rescue (ASR or A/SR, also known as sea-air rescue), and aeronautical and maritime search and rescue (AMSAR) by the ICAO and International Maritime Organization, IMO, is the coordinated search and rescue (SAR) of the survivors of emergenc ...
. Another variant, the Lockheed Martin VH-71 Kestrel, was produced to serve in the United States presidential transport fleet before the program was cancelled and the aircraft sold off to Canada for parts. Civil operators use the AW101 for passenger and VIP transportation. The type has been deployed to active combat theatres, such as in support of coalition forces during the Iraq War
The Iraq War (), also referred to as the Second Gulf War, was a prolonged conflict in Iraq lasting from 2003 to 2011. It began with 2003 invasion of Iraq, the invasion by a Multi-National Force – Iraq, United States-led coalition, which ...
and the war in Afghanistan.
Development
Origins
In 1977, the UK Ministry of Defence issued a requirement for ananti-submarine warfare
Anti-submarine warfare (ASW, or in the older form A/S) is a branch of underwater warfare that uses surface warships, aircraft, submarines, or other platforms, to find, track, and deter, damage, or destroy enemy submarines. Such operations ar ...
(ASW) helicopter to replace the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
's Westland Sea Kings, which were becoming inadequate in the face of advances in Soviet submarine technology. Westland Helicopters put together a proposal, designated WG.34, for a three-engined helicopter of similar dimensions to the Sea King; the WG.34 was to feature more autonomy and a greater range than its predecessor. At the same time, the Italian Navy
The Italian Navy (; abbreviated as MM) is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) after World War II. , the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active per ...
(''Marina Militare'') was also considering the replacement of its fleet of Sea Kings, which had been built by the Italian company Agusta
Agusta was an Italian helicopter manufacturer. It was based in Samarate, Northern Italy. The company was founded by Count Giovanni Agusta in 1923, who flew his first aeroplane in 1907. The MV Agusta motorcycle manufacturer began as an offshoot ...
; Westland and Agusta soon began talks regarding the joint development of a successor helicopter.
Agusta and Westland finalised an agreement to work on the project together, and formed a jointly owned new company, EH Industries Limited (EHI), to pursue the development and marketing of the new helicopter to potential operators. On 12 June 1981, the UK government confirmed its participation in the project, allocated an initial budget of £20 million to develop nine pre-series examples. A major agreement, which secured funding for the majority of the EH101's development program, was signed by both the British and Italian governments in 1984. At the 1985 Paris Air Show, Agusta showed a mock-up of a utility version of the new helicopter, leading to a more generalised design that could be customised to meet the needs of various civilian or military customers. The first prototype flew on 9 October 1987.
In 1987, Canada selected the EH101 to replace its Sea Kings in the anti-submarine warfare and search and rescue
Search and rescue (SAR) is the search for and provision of aid to people who are in distress or imminent danger. The general field of search and rescue includes many specialty sub-fields, typically determined by the type of terrain the search ...
roles. The EH101's third engine and increased range compared favourably with rival aircraft, such as the Sikorsky Seahawk. The range and de-icing capability were also seen as vital for North Atlantic operations. The fledgling EH101, of which up to 50 were on order to replace the Canadian Armed Forces
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; , FAC) are the unified Military, military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air commands referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Under the ''National Defenc ...
's (CAF) Sea Kings, found itself subject to a wider political battle between the country's Conservative
Conservatism is a cultural, social, and political philosophy and ideology that seeks to promote and preserve traditional institutions, customs, and values. The central tenets of conservatism may vary in relation to the culture and civiliza ...
and Liberal parties, the latter viewing the aircraft as too costly. Critics attacked the EH101 purchase as excessive and unnecessary after the Cold War
The Cold War was a period of global Geopolitics, geopolitical rivalry between the United States (US) and the Soviet Union (USSR) and their respective allies, the capitalist Western Bloc and communist Eastern Bloc, which lasted from 1947 unt ...
's end in the early 1990s. Wide-ranging cost estimates were presented by both proponents and opponents of the EH101 procurement, with opponents backing life extensions of Sikorsky CH-124 Sea King and Boeing Vertol CH-113 Labrador helicopter fleets. The EH101 controversy was seen as a factor in the 1993 Canadian federal election. The order was cancelled by the new Liberal government in 1993 resulting in a $470 million cancellation fee.
Into production
Several pre-production aircraft were assembled during the late 1980s and early 1990s. The first pre-production aircraft had its first flight powered by General Electric CT7-2A engines on 9 October 1987. Flight tests were suspended for six months following the crash of the second pre-production aircraft on 21 January 1993. On 6 June 1993, the first EH101 took its maiden flight with the Rolls-Royce Turbomeca RTM322turboshaft
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaft horsepower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the ex ...
engine. Nine prototypes were built to explore military and civil applications, including a "heliliner" configuration. In February 1995, Britain formally placed its first order for a total of 22 EH101s; this was quickly followed by Italy's order for 16 EH101s in October 1995. The EH101 order was not without controversy, the RAF had declared its preference for an all- Chinook fleet; also, Boeing
The Boeing Company, or simply Boeing (), is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product support s ...
allegedly offered cheaper terms for the Chinook. RAF deliveries began in 1997; RN deliveries started the following year.
Following the merger of Westland and Agusta to form AgustaWestland in 2000, there was no need for the separate EHI entity; the EH101 was formally re-branded as the AW101 in 2007. By April 2009, more than 180 AW101s had been sold worldwide; the combined operational fleet had also accumulated a total of 170,000 flying hours.
Further developments
In November 2007, Algeria signed a contract for six AW101 helicopters. In August 2012, it was reported thatAlgeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
had signed an agreement with AgustaWestland for the provision of up to 80 helicopters, 42 of which were to be AW101s. Under the terms of this arrangement, early aircraft were to be manufactured by AgustaWestland, while Algeria was to commence the assembly of some AW101s later on.
By September 2013 AgustaWestland was in the process of acquiring civil certification for the AW101; prospective customers include offshore oil platform operators and VIP clients.Perry, Dominic"AgustaWestland pursues new AW101 sales avenues"
. ''
Flight International
''Flight International'', formerly ''Flight'', is a monthly magazine focused on aerospace. Published in the United Kingdom and founded in 1909 as "A Journal devoted to the Interests, Practice, and Progress of Aerial Locomotion and Transport", i ...
'', 17 September 2013. Accessed: 17 September 2013. As of February 2014, AgustaWestland was considering adapting the AW101 as a heavyweight unmanned aerial vehicle
An unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) or unmanned aircraft system (UAS), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft with no human pilot, crew, or passengers onboard, but rather is controlled remotely or is autonomous.De Gruyter Handbook of Dron ...
, it is proposed that in this configuration an AW101 could be optionally crewed.
On 7 June 2010, it was announced that Boeing had acquired a manufacturing licence and the rights from AgustaWestland for US production of a localised AW101 variant, designated as the Boeing 101. In October 2012, the aircraft was submitted in a U.S. Air Force competition to replace the HH-60 Pave Hawk; however, the bid was dropped three months later.
Design
Overview
 The AW101 follows a conventional design layout, but makes use of advanced technologies, such as the design of the rotor blades, avionics systems, and extensive use of composite materials. The fuselage structure is modular and comprises an aluminium–lithium alloy, designed to be both light and damage-resistant. The AW101 is designed for operating in extreme weather conditions; it is fitted with a de-icing system and rated to operate in temperatures ranging between −45 and +50 °C.Crawford 2003, p. 27. The aircraft's control systems allow the AW101 to maintain a stable hover in crosswinds.
An active vibration control system, known as the ''active control of structural response system'', reduces airframe vibration by up to 80%, increasing crew comfort and minimising buildup of stress on the airframe. The cockpit is fitted with armoured seats for the crew, and can withstand an impact velocity of over 10 m/s. Dual flight controls are provided, though the AW101 can be flown by a single person. The pilots' instrument displays include six full-colour high-definition screens and an optional mission display; a digital map or forward looking infrared (FLIR) display can also be installed.
The AW101 follows a conventional design layout, but makes use of advanced technologies, such as the design of the rotor blades, avionics systems, and extensive use of composite materials. The fuselage structure is modular and comprises an aluminium–lithium alloy, designed to be both light and damage-resistant. The AW101 is designed for operating in extreme weather conditions; it is fitted with a de-icing system and rated to operate in temperatures ranging between −45 and +50 °C.Crawford 2003, p. 27. The aircraft's control systems allow the AW101 to maintain a stable hover in crosswinds.
An active vibration control system, known as the ''active control of structural response system'', reduces airframe vibration by up to 80%, increasing crew comfort and minimising buildup of stress on the airframe. The cockpit is fitted with armoured seats for the crew, and can withstand an impact velocity of over 10 m/s. Dual flight controls are provided, though the AW101 can be flown by a single person. The pilots' instrument displays include six full-colour high-definition screens and an optional mission display; a digital map or forward looking infrared (FLIR) display can also be installed.
Powerplant
 The AW101 is powered by three
The AW101 is powered by three turboshaft
A turboshaft engine is a form of gas turbine that is optimized to produce shaft horsepower rather than jet thrust. In concept, turboshaft engines are very similar to turbojets, with additional turbine expansion to extract heat energy from the ex ...
engines. Initially the Rolls-Royce Turbomeca RTM322 producing and the General Electric CT7 producing were the two available engine types, but by 2020 new aircraft were only being sold with the CT7-8E. The RTM322 powerplant was specifically developed for the AW101; it was subsequently adopted on the AgustaWestland WAH-64 Apache and the NHIndustries NH90 helicopters. According to Rolls-Royce, about 80% of AW101s use the RTM322"RTM322 turboshaft"Rolls-Royce plc. Retrieved 21 April 2012. The engines power an diameter five-bladed main rotor. The rotor blades are constructed from carbon/glass with nomex honeycomb and rohacell foam, edged with titanium alloy in a sandwich construction. The shaping of the main rotor blades is derived from the BERP rotor blades first used on the
Westland Lynx
The Westland Lynx is a British multi-purpose twin-engined military helicopter designed and built by Westland Helicopters at its factory in Yeovil. Originally intended as a utility craft for both civil and naval usage, military interest led to t ...
. This blade design improves aerodynamic efficiency at the blade tip and reduces the acoustic signature. Improved BERP IV rotors have since been developed; when installed this increases the AW101's maximum take-off weight.
Each engine is supplied by a separate fuel tank using dual booster pumps. Optional fourth and fifth tanks can be added to act as a reservoir supply, topping up the main tanks during flight, increasing range or endurance.Jackson 2003, p. 236. The AW101 can also be fitted with a probe for aerial refuelling. Self-sealing fuel tanks are an optional item to be selected by the customer.AgustaWestland 2008, p. 4. An inlet particle separator system can be installed, protecting the engine when operating in sandy environments.AgustaWestland 2008, p. 12.
Armament and defensive systems
 Most variants of the AW101 are equipped with self-defence systems, such as chaff and flare dispensers, directed infrared countermeasures (infrared jammers), ESM (electronic support measures in the form of RF heads), and a laser detection and warning system. British Merlins have been outfitted with protective armour against small-arms fire. A side-mounted forward looking infrared (FLIR) imaging sensor has been fitted to some variants.
Two hardpoints are present in the underside of the airframe on which the HM1 model can carry four Sting Ray torpedoes or Mk 11 Mod 3 depth charges. Some customers have chosen to deploy the Marte anti-ship missile on the AW101; as of 2011, the Royal Navy is considering equipping their Merlin fleet with an anti-surface missile. The Mk1, Mk3 and Mk3A variants can mount general purpose machine guns in up to five locations in the main cabin, aimed out of both door and window apertures. AgustaWestland has examined the integration of
Most variants of the AW101 are equipped with self-defence systems, such as chaff and flare dispensers, directed infrared countermeasures (infrared jammers), ESM (electronic support measures in the form of RF heads), and a laser detection and warning system. British Merlins have been outfitted with protective armour against small-arms fire. A side-mounted forward looking infrared (FLIR) imaging sensor has been fitted to some variants.
Two hardpoints are present in the underside of the airframe on which the HM1 model can carry four Sting Ray torpedoes or Mk 11 Mod 3 depth charges. Some customers have chosen to deploy the Marte anti-ship missile on the AW101; as of 2011, the Royal Navy is considering equipping their Merlin fleet with an anti-surface missile. The Mk1, Mk3 and Mk3A variants can mount general purpose machine guns in up to five locations in the main cabin, aimed out of both door and window apertures. AgustaWestland has examined the integration of rocket
A rocket (from , and so named for its shape) is a vehicle that uses jet propulsion to accelerate without using any surrounding air. A rocket engine produces thrust by reaction to exhaust expelled at high speed. Rocket engines work entirely ...
s and additional ground-attack weapons.
Avionics
Westland andIBM
International Business Machines Corporation (using the trademark IBM), nicknamed Big Blue, is an American Multinational corporation, multinational technology company headquartered in Armonk, New York, and present in over 175 countries. It is ...
formed a consortium in 1991 to perform the helicopter's complex systems integration. The AW101 features a network of helicopter management and mission systems designed to reduce pilot workload and enable the helicopter to undertake a wide variety of missions. A digital automatic flight control system (AFCS) is employed by the AW101. The AFCS allows the operation of a four-axis ( pitch, roll, yaw and collective
A collective is a group of entities that share or are motivated by at least one common issue or interest or work together to achieve a common objective. Collectives can differ from cooperatives in that they are not necessarily focused upon an e ...
) autopilot
An autopilot is a system used to control the path of a vehicle without requiring constant manual control by a human operator. Autopilots do not replace human operators. Instead, the autopilot assists the operator's control of the vehicle, allow ...
and the automatic stabilisation system, and is linked in with the aircraft's flight management systems. The AFCS, manufactured by Smiths Aerospace, is a dual-duplex system using two flight computers to provide redundancy and fault-tolerance.
The AW101's navigation system includes a GPS receiver and inertial navigation system
An inertial navigation system (INS; also inertial guidance system, inertial instrument) is a navigation device that uses motion sensors (accelerometers), rotation sensors (gyroscopes) and a computer to continuously calculate by dead reckoning th ...
, VHF omnidirectional radio range (VOR), instrument landing system (ILS), TACAN, and automatic direction finding. The Mk1 and Mk3 are equipped with a Doppler velocity system (DVS) which provides relative ground velocities; the DVS is also linked into the AFCS as part of the autostabilisation system. For safety, the aircraft is equipped with obstacle and terrain avoidance warning systems, traffic collision avoidance system (TCAS), and both voice
The human voice consists of sound made by a human being using the vocal tract, including talking, singing, laughing, crying, screaming, shouting, humming or yelling. The human voice frequency is specifically a part of human sound produ ...
and flight data recorders.
The AW101 was initially equipped with the Ferranti Blue Kestrel search and detection radar which is capable of 360 degree scanning and can detect small targets as far as 25 nautical mile
A nautical mile is a unit of length used in air, marine, and space navigation, and for the definition of territorial waters. Historically, it was defined as the meridian arc length corresponding to one minute ( of a degree) of latitude at t ...
s away. As part of the Royal Navy's Merlin HM2 upgrade program, Lockheed Martin implemented a series of improvements to the radar, notably allowing it to track 40 times the number of targets previously capable. Danish EH101s are fitted with the RDR-1600 search and weather radar
A weather radar, also called weather surveillance radar (WSR) and Doppler weather radar, is a type of radar used to locate precipitation (meteorology), precipitation, calculate its motion, and estimate its type (rain, snow, hail etc.). Modern w ...
. Mk 2 Royal Navy Merlins are equipped with the AQS903 anti-submarine system for processing sonographic data from sonobuoys to detect and target submerged submarines. The AQS903 was derived from the AQS901 system on the earlier Hawker Siddeley Nimrod maritime patrol aircraft.
Crew and cargo
 The AW101 is typically operated by a crew of three: a pilot, an observer, and a crewman/operator. The pilot is able to fly for the majority of a mission in a hands-off mode, enabled by the sophisticated autopilot. All crew members have individual access to management computers and tactical information.Evans 2004, p. 23.
The fuselage has a volume of and the cargo compartment is in length, wide and high. The military version of the AW101 can accommodate up to 24 seated or 45 standing combat troops and their equipment. Alternative loads include a medical team and 16 stretchers, and cargo pallets.
The ramp, , can take a load, allowing it to carry vehicles such as Land Rovers. The ramp and cabin floor are fitted with flush tie-down points. A cargo hook under the fuselage can carry external loads of via the use of a semi-automatic cargo release unit (SACRU). A rescue hoist and a hover trim controller are fitted at the cargo door. An optional cargo winch can be installed near to the rear ramp.
The AW101 is typically operated by a crew of three: a pilot, an observer, and a crewman/operator. The pilot is able to fly for the majority of a mission in a hands-off mode, enabled by the sophisticated autopilot. All crew members have individual access to management computers and tactical information.Evans 2004, p. 23.
The fuselage has a volume of and the cargo compartment is in length, wide and high. The military version of the AW101 can accommodate up to 24 seated or 45 standing combat troops and their equipment. Alternative loads include a medical team and 16 stretchers, and cargo pallets.
The ramp, , can take a load, allowing it to carry vehicles such as Land Rovers. The ramp and cabin floor are fitted with flush tie-down points. A cargo hook under the fuselage can carry external loads of via the use of a semi-automatic cargo release unit (SACRU). A rescue hoist and a hover trim controller are fitted at the cargo door. An optional cargo winch can be installed near to the rear ramp.
Operational history
Royal Navy

 The British Royal Navy's final order was for 44 ASW aircraft, originally designated ''Merlin HAS.1'' (Helicopter, Anti-Submarine Mark 1) but soon changed to ''Merlin HM1'' (Helicopter, Maritime Mark 1). The first fully operational Merlin was delivered on 17 May 1997, entering service on 2 June 2000. All aircraft were delivered by the end of 2002, and are operated by 3
The British Royal Navy's final order was for 44 ASW aircraft, originally designated ''Merlin HAS.1'' (Helicopter, Anti-Submarine Mark 1) but soon changed to ''Merlin HM1'' (Helicopter, Maritime Mark 1). The first fully operational Merlin was delivered on 17 May 1997, entering service on 2 June 2000. All aircraft were delivered by the end of 2002, and are operated by 3 Fleet Air Arm
The Fleet Air Arm (FAA) is the naval aviation component of the United Kingdom's Royal Navy (RN). The FAA is one of five :Fighting Arms of the Royal Navy, RN fighting arms. it is a primarily helicopter force, though also operating the Lockhee ...
squadrons: 814 NAS, 820 NAS, 824 NAS and 829 NAS (now disbanded and merged with 814 NAS), all based at RNAS Culdrose in Cornwall. 700 NAS was the Merlin Operational Evaluation Unit from 2000 to 2008. In March 2004, Navy Merlins were temporarily grounded following an incident at RNAS Culdrose in which a tail rotor failed due to a manufacturing defect. An improved tail rotor was designed and adopted on most AW101s which significantly reduced associated maintenance.
In 1995, it was announced that the Navy's Westland Lynx
The Westland Lynx is a British multi-purpose twin-engined military helicopter designed and built by Westland Helicopters at its factory in Yeovil. Originally intended as a utility craft for both civil and naval usage, military interest led to t ...
helicopters would be retired in favour of an all-Merlin fleet. However, the subsequent Strategic Defence and Security Review 2010 stated that the future naval helicopters would be the Merlin and the Wildcat, a derivative of the Lynx. Royal Navy Merlins have seen action in the Caribbean, on counter-narcotics and hurricane support duties, as well as maritime security duties in the Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf, sometimes called the Arabian Gulf, is a Mediterranean seas, mediterranean sea in West Asia. The body of water is an extension of the Arabian Sea and the larger Indian Ocean located between Iran and the Arabian Peninsula.Un ...
. Merlins have also seen active duty in Iraq, providing support to British and coalition forces based in the region.
The Merlin HM1 has been cleared to operate from the Royal Navy's aircraft carrier
An aircraft carrier is a warship that serves as a seagoing airbase, equipped with a full-length flight deck and hangar facilities for supporting, arming, deploying and recovering carrier-based aircraft, shipborne aircraft. Typically it is the ...
s, amphibious assault ship
An amphibious assault ship is a type of warship employed to land and support ground forces on enemy territory during an armed conflict. The design evolved from aircraft carriers converted for use as helicopter carriers (which, as a result, ar ...
s, Type 23 frigates, Type 45 destroyer and several Royal Fleet Auxiliary (RFA) vessels including the . 30 aircraft have been upgraded to ''Merlin HM2'' standard under the £750m Merlin Capability Sustainment Programme; Lockheed Martin UK delivered the final HM2 on 11 July 2016. The HM2 has a new mission system, digital cockpit, electro-optical camera and multi-static sonar processing. The HM2 achieved IOC on 30 June 2014 after flying 480 hours from ''Illustrious'' during Exercise Deep Blue earlier that month. It was also reported that some of the eight airframes not scheduled to be upgraded for financial reasons may be updated.Jane's Defence Weekly, 8 July 2009. p. 14. Five HM2s are in maintenance at a time, leaving 25 available, of which 14 were theoretically to be assigned to the . However, in practice with just 30 Merlin HM2s in service, it may be impossible to deploy 14 aircraft on a single operational carrier on a full time basis. During the 2021 carrier strike group deployment to the Pacific, for instance, seven Merlins were embarked with the task group.
In addition to its ASW role, the HM2 will be able to carry an airborne early warning (AEW) pod known as the Crowsnest, replacing the Sea King ASaC7. In September 2011, Thales UK proposed re-using Sea King ASaC7 equipment, such as the Searchwater 2000, on the Merlin; Lockheed Martin has proposed developing a new multi-functional sensor for both the AW101 and other aircraft. Lockheed originally planned to use a derivative of the F-35's APG-81 radar; however, a rival Elta system and the Thales system both commenced flight trials in 2014. On 22 May 2015, the MOD and prime contractor Lockheed Martin UK selected Thales to provide the radar and mission system for the Crowsnest. Initial operating capability of the system was significantly delayed. While Crowsnest was deployed with the U.K. carrier strike group in 2021, it experienced operating challenges and revised plans meant that Crowsnest achieved initial operating capability in July 2023. Full operating capability had been expected in 2024/25. It was reported that initially only five Merlins will be equipped with Crowsnest, three of these being normally assigned to the "high readiness" aircraft carrier. In 2025, nine Merlin HM2s from 820 Naval Air Squadron were specifically assigned to embark on HMS Prince of Wales as part of the Royal Navy's carrier strike group deployment to the Indo-Pacific region. Six of the Merlins were in the ASW role and three in the AEW role, with the Crowsnest system having formally reached full operating capability.
Problems with Merlin/Crowsnest have caused the Royal Navy to look for a replacement. As of 2023 the system had a planned retirement date of 2029. In 2021, the UK's Defence and Security Accelerator (DASA) announced that options would be examined and might draw on the already existing Project Vixen, researching the utility of a naval unmanned system that could encompass strike, AEW, and air-to-air refuelling components. If implemented, the replacement of Merlin/Crowsnest by another system would permit all Merlin helicopters to focus on ASW operations for the remainder of their service lives.
On 15 December 2009, plans were announced to transfer RAF Merlin HC3s and HC3As to the Royal Navy's Commando Helicopter Force to replace retiring Sea King HC4 helicopters. The Sea King was set to retire in 2016, leaving the Navy operating a combination of the Wildcat and Merlin. 846 NAS reformed with ex-RAF Merlin HC3s on 30 September 2014; 845 NAS followed on 9 July 2015. On 25 May 2018, the first of 25 converted Royal Marines Commando Merlin Mk4/4A were delivered to Royal Naval Air Station (RNAS) Yeovilton. In July 2020, the Merlin HM2 and HC4/4A helicopters were planned to be in service until 2029 and 2030, respectively. On 11 June 2021, it was confirmed that their Out of Service Date (OSD) had been moved to 2040.
By the end of 2022, all HC helicopters were upgraded to the HC4/4A Commando Merlin standard.
Royal Air Force
 The RAF ordered 22 Merlin HC3 for transport missions, the first of which entered service in January 2001 with No. 28 Squadron RAF based at RAF Benson. The type is equipped with extended-range fuel tanks and is capable of air-to-air refuelling. The Merlin is frequently utilised for troop transport duties and for the transport of bulky objects, either internally or underslung, including vehicles and artillery. The Merlin Depth Maintenance Facility at RNAS Culdrose performed most tasks upon the Merlin HC3.
The Merlin's first operational deployment was to the
The RAF ordered 22 Merlin HC3 for transport missions, the first of which entered service in January 2001 with No. 28 Squadron RAF based at RAF Benson. The type is equipped with extended-range fuel tanks and is capable of air-to-air refuelling. The Merlin is frequently utilised for troop transport duties and for the transport of bulky objects, either internally or underslung, including vehicles and artillery. The Merlin Depth Maintenance Facility at RNAS Culdrose performed most tasks upon the Merlin HC3.
The Merlin's first operational deployment was to the Balkans
The Balkans ( , ), corresponding partially with the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throug ...
region in 2003. RAF Merlins were first deployed to Iraq as part of Operation Telic in 2004, supporting coalition forces and were operated as the main medevac asset in southern Iraq; both Flight Lieutenant Kev Harris and Flight Lieutenant Michelle Goodman were awarded the DFC during this period. Merlins routinely operated around Basra
Basra () is a port city in Iraq, southern Iraq. It is the capital of the eponymous Basra Governorate, as well as the List of largest cities of Iraq, third largest city in Iraq overall, behind Baghdad and Mosul. Located near the Iran–Iraq bor ...
until Britain's withdrawal in June 2009.
In 2002, Westland made an unsuccessful unsolicited offer to the British Ministry of Defence, proposing an enhanced Merlin variant intended to satisfy the demand for additional lift capacity. An alternative measure was the acquisition of six AW101s from Denmark in 2007; designated ''Merlin HC3A'', these were assigned to the RAF, allowing Merlins to be deployed in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. It is bordered by Pakistan to the Durand Line, east and south, Iran to the Afghanistan–Iran borde ...
. The HC3A is used for training and not for frontline operations due to various configuration differences. In December 2007, a second Merlin squadron, No. 78 Squadron was formed at RAF Benson.
In 2009, five Merlin Mk3s were operating in Afghanistan, transporting troops and supplies. The deployment to Afghanistan was criticised as the aircraft reportedly lacked protective Kevlar armour. By July 2010, the Merlin fleet was fully fitted with ballistic armour. The deployment of Merlins to Afghanistan allowed the detachment of Sea Kings to be withdrawn from the region in October 2011. As part of the UK drawdown in Afghanistan, Merlins were withdrawn from theatre in June 2013.
In 2012, the RAF's Merlin HC3/3A fleet began to be transferred to the Royal Navy for use by the Commando Helicopter Force. Royal Navy personnel worked alongside RAF crew at Benson to build experience during the transition. The £454m Merlin Life Sustainment Programme resulted in 25 HC3/3A airframes being fitted with the cockpit electronics of the HM2, folding tails and main rotor heads, strengthened landing gear, deck lashing mounting points, obsolescence updates, fast-roping points and a common emergency egress system. The first HC4 began flight trials in September 2017, with an IOC in mid-2018; an interim folding main rotor head will be fitted to some HC3 for shipborne operations prior to the HC4 upgrade.
Command of the UK Merlin HC3/3A fleet was formally transferred from the RAF to the Royal Navy during a ceremony at RAF Benson on 30 September 2014. As part of the same ceremony, the RAF's 78 Sqn was disbanded and the Royal Navy's 846 Naval Air Squadron stood-up with the Merlin. The RAF's 28(AC) continued to operate as part of the Commando Helicopter Force until July 2015, when 28(AC) Sqn stood down and 845 Naval Air Squadron stood-up. 846 NAS relocated from RAF Benson to RNAS Yeovilton in March 2015, with 845 NAS following in June 2016.
Italian Navy
 In 1997, the Italian government ordered 16 AW101 helicopters for the
In 1997, the Italian government ordered 16 AW101 helicopters for the Italian Navy
The Italian Navy (; abbreviated as MM) is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) after World War II. , the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active per ...
, with options for four more. These AW101 included eight of the anti-surface/submarine (ASuW/ASW) version, four airborne early warning (AEW), four amphibious support helicopters (ASH). The government then exercised its option for four additional ASH helicopters, which were delivered by 2006. The same year the government ordered two more AW101 ASH helicopters in a slightly modified version.
The first Italian Navy production helicopter (''MM81480'') flew on 4 October 1999 and was officially presented to the press on 6 December 1999. Italy accepted delivery of the 21st AW101, configured for anti-submarine warfare, on 4 August 2009. In total 22 AW101 helicopters have been delivered to the Italian Navy.
Italian AW101s have operated from a variety of ships and have seen service overseas; in 2009 the Italian Navy used its AW101 fleet as executive transports for visiting heads of state and officials during the 35th G8 summit. In 2010, the Italian Navy deployed three AW101s to Afghanistan, where they were flown in both the transport and utility roles. In 2011, it was reported that the Italian contingent in Afghanistan, consisting of AW101s, had been providing coverage of a wide area of the country.
Italian Air Force
In June 2011 the AW101 was chosen by the Italian Air Force to replace its ageing Sea King HH-3F helicopters in the combat search and rescue role. A total of 15 helicopters in the HH-101A variant were ordered and delivered between 2016 and 2020.Royal Canadian Air Force
In 1997, in light of the declining condition of its helicopter fleet, Canada launched the Canadian Search and Rescue Helicopter competition. It was won by the EH101, which was designated ''CH-149 Cormorant'' in Canadian service.Plamondon 2009, pp. 151–152. In 2004, the EH101 was entered into a Canadian competition to replace the shipboard Sea King fleet, but the Sikorsky CH-148 Cyclone was selected. In 2013, following difficulties with the CH-148 procurement, the Royal Canadian Air Force (RCAF) was reported to be seriously considering cancelling the contract with Sikorsky and was investigating the possibility of procuring the AW101 instead. However, an initial batch of six Cyclones was delivered to the RCAF in June 2015. In December 2022, Canada's Department of National Defence announced a C$1.24-billion contract for procurement of three additional aircraft and upgrades to the existing fleet to current configuration of the helicopter; this will increase the fleet to 16 aircraft. The RCAF also acquired its own advanced training simulator configured to the new modernized cockpit.Royal Danish Air Force
In 2001, the Royal Danish Air Force (RDAF) announced the purchase of eight EH101s for SAR duties and six tactical troop transports for 722 Squadron. The last of the 14 AW101s was delivered in March 2007 and the first SAR AW101s became operational out of Karup Airport in April 2007. In 2007, the six troop transport AW101s were transferred to the British MOD; in exchange, the British government ordered six new-build AW101s as replacements for the RDAF. Danish AW101s have a higher gross weight capacity of 15,600 kg and were, as delivered, coated in a paint designed to reduce the aircraft's infrared signature. In the SAR role, RDAF AW101s have a crew of six and were initially painted yellow to distinguish themselves from AW101 allocated to military duties, but were later painted green, and all 14 AW101s are used for SAR and troop transport.EH-101 Merlin
Danish AW101s have a higher gross weight capacity of 15,600 kg and were, as delivered, coated in a paint designed to reduce the aircraft's infrared signature. In the SAR role, RDAF AW101s have a crew of six and were initially painted yellow to distinguish themselves from AW101 allocated to military duties, but were later painted green, and all 14 AW101s are used for SAR and troop transport.EH-101 Merlin" '' Royal Danish Air Force''. Accessed: 19 December 2013. On 28 January 2008, the drive shaft of a Danish AW101 broke, leading to an emergency landing at Billund Airport. Following the incident, the Danish fleet was grounded as a precaution and the AW101's future was publicly debated. In the first six months of 2008, the RDAF reported an operational availability of roughly 50%, well below the target of 80%, partly due to an inadequate maintenance organisation and staff shortages. In January 2011, the Danish Ministry of Defence reportedly could not afford the retrofitting of the AW101 fleet for Afghanistan operations, against earlier reports of a deployment in 2012. In February 2013, ''Aviation Week'' reported that earlier reliability problems had been resolved and that a full upgrade package would be applied to Danish AW101s; these included the addition of electronic warfare pods and a new electro-optical system, in advance of a deployment in Afghanistan in 2014. In September 2013, Danish AW101s were to receive L-3 Wescam MX-15 electro-optical/infrared (EO/IR) sensors; SAR aircraft already carry the FLIR Systems Star Safire II EO/IR sensor.
Royal Norwegian Air Force
On 25 October 2007, a project started that had the intent to replace all Westland Sea King search and rescue helicopters with new rescue helicopters by 2020. On 19 December 2013, a contract was signed between AgustaWestland and the government, for the purchase of 16 AW101 helicopters. The agreement came about after fierce competition between different manufacturers to satisfy the Norwegian requirements. Participants were AgustaWestland,Eurocopter
Airbus Helicopters SAS (formerly Eurocopter S.A., trade name, trading as Eurocopter Group) is the helicopter manufacturer, helicopter manufacturing division of Airbus. It is the largest in the industry in terms of revenues and turbine helicopte ...
, NHIndustries, Sikorsky Aircraft Corporation and Boeing. The government considered that AgustaWestland AW101 met the requirements and specifications in the best possible way.
On 12 June 2017, Per-Willy Amundsen, Minister of Justice and Public Security, announced the opening of Leonardo's AW101 Norway Training Centre at Stavanger
Stavanger, officially the Stavanger Municipality, is a city and municipalities of Norway, municipality in Norway. It is the third largest city and third largest metropolitan area in Norway (through conurbation with neighboring Sandnes) and the ...
Sola Air Station. The training centre includes an AW101 Full Flight Simulator (FFS), jointly developed by Leonardo and CAE to Level D, which is a CAE Series 3000 device, along with an AW101 SAR console training system linked to the FFS to provide rear crew training. The first training course at the centre started prior to delivery of the first rotorcraft. The training centre will be used by both Norwegian and foreign AW101 customers.
The first AW101 was delivered in November 2017. The Norwegian AW101s officially started operating in the rescue role on 1 September 2020. The Sea King was phased out in December 2023, after 47 years of service as rescue helicopter in the Royal Norwegian Air force, and replaced with the AW101. The AW101 is named ''SAR Queen'' in Norwegian service.
Portuguese Air Force
 The Portuguese Air Force had purchased 12 Merlins under a €446 million contract, the first of which was delivered on 22 December 2004. The type has been used to conduct transport, search and rescue, and maritime surveillance missions, progressively replacing the Aérospatiale Puma previously tasked with these missions. The main role of Portuguese AW101s is to perform search and rescue missions within Portugal's maritime zone. They are operated by 751 Squadron and are kept on constant alert at three bases: Montijo near
The Portuguese Air Force had purchased 12 Merlins under a €446 million contract, the first of which was delivered on 22 December 2004. The type has been used to conduct transport, search and rescue, and maritime surveillance missions, progressively replacing the Aérospatiale Puma previously tasked with these missions. The main role of Portuguese AW101s is to perform search and rescue missions within Portugal's maritime zone. They are operated by 751 Squadron and are kept on constant alert at three bases: Montijo near Lisbon
Lisbon ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Portugal, with an estimated population of 567,131, as of 2023, within its administrative limits and 3,028,000 within the Lisbon Metropolitan Area, metropolis, as of 2025. Lisbon is mainlan ...
, Lajes Field on the Azores
The Azores ( , , ; , ), officially the Autonomous Region of the Azores (), is one of the two autonomous regions of Portugal (along with Madeira). It is an archipelago composed of nine volcanic islands in the Macaronesia region of the North Atl ...
, and Porto Santo Island.
Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force
The Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force (JMSDF) ordered 14 aircraft in 2003 to use in both the airborne mine countermeasures (AMCM) and transport roles. The AW101 was modified by Kawasaki Heavy Industries, and the Japan Defense Agency designated the model MCH-101. Special features include the automated folding of the rotor and tail. For the mine-hunting role, the MCH-101 has been outfitted withNorthrop Grumman
Northrop Grumman Corporation is an American multinational Aerospace manufacturer, aerospace and Arms industry, defense company. With 97,000 employees and an annual revenue in excess of $40 billion, it is one of the world's largest Arms industry ...
's AQS-24A airborne mine-hunting system and AN/AES-1 Airborne Laser Mine Detection System (ALMDS) for a complete surface-to-bottom mine detection capability, as well as Mk-104 acoustic mine sweeping gear.
In 2002, AgustaWestland, Kawasaki and Marubeni entered a general agreement for cooperation; Kawasaki began the assembly of both the CH-101 and the MCH-101 in 2003. Kawasaki also began licensed production of the RTM322 engines in 2005. In a separate agreement between Marubeni and AgustaWestland, a supply depot was established in Japan to support the MCH-101 and CH-101 fleets. The first MCH-101 was delivered to the JMSDF on 3 March 2006.
The MCH-101 will replace the MH-53E (S-80-M-1) in the AMCM role. The CH-101 will operate in the transport/support role for Antarctic expeditions, replacing the Sikorsky S-61A, and will be working in coordination with the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology.
After a whistle-blower alleged that the MSDF's preference had been improperly changed an investigation was launched. On 16 December 2016 the Japanese Ministry of Defense (the Defense Agency having been upgraded to a ministry in 2007) stated that it had not confirmed lobbying efforts but the ministry admonished Tomohisa Takei, the JMSDF chief of staff, for mentioning the MCH-101 by name during the procurement process to his subordinates. This had come after MSDF officials had reported that the Mitsubishi-built SH helicopters may be best.
VIP and other usage
AgustaWestland developed a specialised luxury variant, the AW101 VVIP (Very Very Important Person, i.e. a head of state), aimed at business and VIP customers. As of April 2009, 15% of all AW101s sold were for VIP purposes. By September 2013, customers operating the VIP variant includedSaudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in West Asia. Located in the centre of the Middle East, it covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula and has a land area of about , making it the List of Asian countries ...
, Algeria
Algeria, officially the People's Democratic Republic of Algeria, is a country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It is bordered to Algeria–Tunisia border, the northeast by Tunisia; to Algeria–Libya border, the east by Libya; to Alger ...
, Nigeria
Nigeria, officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf of Guinea in the Atlantic Ocean to the south. It covers an area of . With Demographics of Nigeria, ...
and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan is a landlocked country in Central Asia bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the south and southwest and the Caspian Sea to the west. Ash ...
.
The AW101 was being acquired by the United States Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines or simply the Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is responsible for conducting expeditionar ...
under the VXX program as a replacement for the Presidential Marine One helicopters. Designated '' VH-71 Kestrel'', the variant was heavily customised and equipped with various self-defence systems. However the programme encountered significant cost overruns and political opposition, which led to the procurement being scrapped in June 2009."US Navy Terminates VH-71 Presidential Helicopter Contract".''Flight International'', 2 June 2009. After the cancellation, the delivered helicopters were sold to Canada for $164 million, where they were used as source of spare parts for its fleet of AgustaWestland CH-149 Cormorant search-and-rescue helicopters. Separately, the Marine Corps had also conducted studies into the adoption of the EH101 as a fall-back option to the Bell-Boeing V-22 Osprey tiltrotor during the 1990s. In April 2009, India ordered 12 AW101 to serve as executive transport helicopters for the Indian president and prime minister. The selection followed field trial assessments between the AW101 and the Sikorsky S-92 held in 2008. However, the procurement was put on hold and subsequently cancelled due to the 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal, in which Finmeccanica, AgustaWestland's parent company, was accused of using bribery to win the contract. The three helicopters delivered as part of the contract may be returned to the manufacturer as part of the arbitration process.
Potential operators
The Royal Norwegian Air Force is considering ordering the AW101 Merlins for anti-submarine use.Variants
;Pre-production * ''PP1'' – Westland-built basic air vehicle prototype, first flown 9 October 1987.Lake 2007, p. 122. * ''PP2'' – Agusta-built Italian basic air vehicle prototype first flown on 26 November 1987 and used for deck trials but was destroyed on 21 January 1993 following a rotor brake malfunction. * ''PP3'' – Westland-built and the first civil configured ''Heliliner'', used for engine vibration tests and icing trials in Canada. * ''PP4'' – Westland-built British naval prototype, lost in an accident on 7 April 1995 after a drive train control rod failure.Lake 2007, pp. 122–123. * ''PP5'' – Westland-built Merlin development aircraft eventually equipped with Merlin avionics.Lake 2007, p. 123. * ''PP6'' – Agusta-built development aircraft for Italian Navy variant first flown 26 April 1989. * ''PP7'' – Agusta-built military utility aircraft with rear-loading ramp. * ''PP8'' – Westland-built civil prototype. * ''PP9'' – Agusta-built military utility prototype with rear-loading ramp. ;Model 110 : Italian Navy ASW/ASuW variant, eight built. Powered by T-700-GE-T6A1 engines. Fitted with Eliradar APS-784 radar and Honeywell HELRAS dipping sonar. Armed with torpedoes or Marte anti-ship missiles. ;Model 111
: Royal Navy ASW/ASuW variant, designated Merlin HM1 by customer. Powered by RTM322 engines and fitted with Blue Kestrel radar, Thomson Marconi FLASH dipping sonar and Orange Reaper ESM. 44 built.Lake 2007, p. 124.
;Model 112
: Italian Navy early warning variant with same airframe as Model 110 but with Eliradar HEW-784 radar in large underfuselage radome. Four built.Lake 2007, p. 125.
;Series 200
: Proposed military utility version with no rear-loading ramp.
;Series 300 Heliliner
: Proposed civil transport with no ramp.Lake 2007, pp. 125–126. In 2000, British International Helicopters conducted service trials using ''PP8''; these did not lead to a commercial service.
;Series 310
: Proposed version of Heliliner with full airline avionics for operation from oil platforms. No production.Lake 2007, p. 126.
;Model 410
: Italian Navy transport variant with folding rotors and tail boom. Four built.
;Model 411
: Royal Air Force transport variant, designated Merlin HC3 by customer, 22 built.Lake 2007, pp. 126–127.
;Model 413
: Italian Navy special forces and amphibious assault transport with more advanced avionics.Lake 2007, p. 128.
;Model 500
: Proposed civil utility variant with rear-ramp.
;Model 510
: Civil utility variant with rear ramp, two built. One used for Tokyo Metropolitan Police Agency and one used to support US101 bid.
;Model 511
: Canadian Armed Forces search and rescue variant, designated CH-149 Cormorant.Lake 2007, pp. 128–129.
;Model 512
: Merlin Joint Supporter for Royal Danish Air Force. Eight acquired for search and rescue (''512 SAR'') and six for tactical troop transport (''512 TTT''). The six transports were sold to RAF (as Merlin HC3As) and replaced by six new-build Merlins.Lake 2007, pp. 129–131.
;Model 514
: Portuguese Air Force search and rescue variant, six built.
;Model 515
: Portuguese Air Force fisheries protection variant, two built.
;Model 516
: Portuguese Air Force combat search and rescue variant, four built.
;Model 518
: Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force mine countermeasures and transport variant, two built.
;Model 519
:Presidential Transport variant for the United States Marine Corps as the VH-71 Kestrel, four test vehicles and five pilot production aircraft built. Canceled and aircraft sold to Royal Canadian Air Force as spares for CH-149 Cormorant fleet.
;Model 610
: Algerian Naval variant. 6 delivered.
;Model 611
: Italian Air Force Combat Search and Rescue variant, powered by CT7-8E engines. 15 on order.
;Model 612 (SAR Queen)
: Norwegian search and rescue variant, operated by the Air Force. 16 ordered with option for 6 more.
;Model 614
: Polish ASW/ CSAR "convertible" variant, operated by the Polish Navy, 4 delivered.
;Model 615
: Canadian military search and rescue variant, upgraded -511 variant, again designated the CH-149 Cormorant. 16 to be delivered.
;Model 640
: Saudi Arabian VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Model 641
: Indian VVIP variant. (See 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal). Latterly delivered to Nigerian and Azerbaijani Air Forces.
;Model 642
: Algerian VVIP variant, 2 delivered.
;Model 643
: Turkmenistani VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Merlin HM1
: Royal Navy designation for the Model 111.
;Merlin HM2
: Avionics retrofit of 30 HM1s for the Royal Navy.
;Model 111
: Royal Navy ASW/ASuW variant, designated Merlin HM1 by customer. Powered by RTM322 engines and fitted with Blue Kestrel radar, Thomson Marconi FLASH dipping sonar and Orange Reaper ESM. 44 built.Lake 2007, p. 124.
;Model 112
: Italian Navy early warning variant with same airframe as Model 110 but with Eliradar HEW-784 radar in large underfuselage radome. Four built.Lake 2007, p. 125.
;Series 200
: Proposed military utility version with no rear-loading ramp.
;Series 300 Heliliner
: Proposed civil transport with no ramp.Lake 2007, pp. 125–126. In 2000, British International Helicopters conducted service trials using ''PP8''; these did not lead to a commercial service.
;Series 310
: Proposed version of Heliliner with full airline avionics for operation from oil platforms. No production.Lake 2007, p. 126.
;Model 410
: Italian Navy transport variant with folding rotors and tail boom. Four built.
;Model 411
: Royal Air Force transport variant, designated Merlin HC3 by customer, 22 built.Lake 2007, pp. 126–127.
;Model 413
: Italian Navy special forces and amphibious assault transport with more advanced avionics.Lake 2007, p. 128.
;Model 500
: Proposed civil utility variant with rear-ramp.
;Model 510
: Civil utility variant with rear ramp, two built. One used for Tokyo Metropolitan Police Agency and one used to support US101 bid.
;Model 511
: Canadian Armed Forces search and rescue variant, designated CH-149 Cormorant.Lake 2007, pp. 128–129.
;Model 512
: Merlin Joint Supporter for Royal Danish Air Force. Eight acquired for search and rescue (''512 SAR'') and six for tactical troop transport (''512 TTT''). The six transports were sold to RAF (as Merlin HC3As) and replaced by six new-build Merlins.Lake 2007, pp. 129–131.
;Model 514
: Portuguese Air Force search and rescue variant, six built.
;Model 515
: Portuguese Air Force fisheries protection variant, two built.
;Model 516
: Portuguese Air Force combat search and rescue variant, four built.
;Model 518
: Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force mine countermeasures and transport variant, two built.
;Model 519
:Presidential Transport variant for the United States Marine Corps as the VH-71 Kestrel, four test vehicles and five pilot production aircraft built. Canceled and aircraft sold to Royal Canadian Air Force as spares for CH-149 Cormorant fleet.
;Model 610
: Algerian Naval variant. 6 delivered.
;Model 611
: Italian Air Force Combat Search and Rescue variant, powered by CT7-8E engines. 15 on order.
;Model 612 (SAR Queen)
: Norwegian search and rescue variant, operated by the Air Force. 16 ordered with option for 6 more.
;Model 614
: Polish ASW/ CSAR "convertible" variant, operated by the Polish Navy, 4 delivered.
;Model 615
: Canadian military search and rescue variant, upgraded -511 variant, again designated the CH-149 Cormorant. 16 to be delivered.
;Model 640
: Saudi Arabian VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Model 641
: Indian VVIP variant. (See 2013 Indian helicopter bribery scandal). Latterly delivered to Nigerian and Azerbaijani Air Forces.
;Model 642
: Algerian VVIP variant, 2 delivered.
;Model 643
: Turkmenistani VVIP variant, operated by the Air Force. 2 delivered.
;Merlin HM1
: Royal Navy designation for the Model 111.
;Merlin HM2
: Avionics retrofit of 30 HM1s for the Royal Navy.
 ;Merlin HC3
: Royal Air Force designation for the Model 411.
;Merlin HC3A
: Royal Air Force designation for six former Royal Danish Air Force Model 512s modified to UK standards.
;Merlin HC3i
: Royal Navy will fit seven HC3 with folding rotor heads as an interim (3i) measure until the full HC4 upgrade is available.
;Merlin HC4/4A
: The conversion of 25 RAF HC3/3A (19 HC3 and 6 HC3A) for RN use in hand with the first flight taking place in November 2016. HM2 cockpit, folding tail/blades and other adaptations for naval use.
;CH-148 Petrel
: Ship-based anti-submarine helicopter for Canada. 35 originally ordered by the
;Merlin HC3
: Royal Air Force designation for the Model 411.
;Merlin HC3A
: Royal Air Force designation for six former Royal Danish Air Force Model 512s modified to UK standards.
;Merlin HC3i
: Royal Navy will fit seven HC3 with folding rotor heads as an interim (3i) measure until the full HC4 upgrade is available.
;Merlin HC4/4A
: The conversion of 25 RAF HC3/3A (19 HC3 and 6 HC3A) for RN use in hand with the first flight taking place in November 2016. HM2 cockpit, folding tail/blades and other adaptations for naval use.
;CH-148 Petrel
: Ship-based anti-submarine helicopter for Canada. 35 originally ordered by the Canadian Forces
The Canadian Armed Forces (CAF; , FAC) are the unified Military, military forces of Canada, including sea, land, and air commands referred to as the Royal Canadian Navy, Canadian Army and the Royal Canadian Air Force. Under the ''National Defenc ...
, reduced to 28 and cancelled in 1993.
;CH-149 Chimo
: Search and rescue helicopter for Canada. 15 ordered by the Canadian forces, but later cancelled.
; CH-149 Cormorant
:Search and rescue helicopter for Canada, 15 ordered and delivered.
; Lockheed Martin VH-71 Kestrel
:Cancelled USMC variant that was intended to serve as the US Presidential helicopter.
;SH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the MP variant.
 ;EH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the AEW variant.
;MH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the Amphibious Support Helicopter (ASH) variant.
;HH-101A
:Italian Air Force designation for the CSAR variant.
; Kawasaki Heavy Industries MCH-101
:Japan Defense Agency designation of Model 518
;EH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the AEW variant.
;MH-101A
:Italian Navy designation for the Amphibious Support Helicopter (ASH) variant.
;HH-101A
:Italian Air Force designation for the CSAR variant.
; Kawasaki Heavy Industries MCH-101
:Japan Defense Agency designation of Model 518
Operators
Indonesian Air Force
The Indonesian Air Force (, sometimes shortened as IDAF / IdAF) is the Air force, aerial branch of the Indonesian National Armed Forces. The Indonesian Air Force is headquartered in Jakarta, Indonesia, and is headed by the Chief of Staff of th ...
;
* Italian Air Force
* Italian Navy
The Italian Navy (; abbreviated as MM) is one of the four branches of Italian Armed Forces and was formed in 1946 from what remained of the ''Regia Marina'' (Royal Navy) after World War II. , the Italian Navy had a strength of 30,923 active per ...
;
* Japan Maritime Self-Defense Force - 10Defence of Japan 2022 (Annual White Paper). p.53.Japan Ministry of Defence ; * Nigerian Air Force ; * Royal Norwegian Air Force ; * Polish Navy (4 delivered) ; * Portuguese Air Force ;
 * Royal Saudi Air Force
;
* Turkmen Air Force
;
*
* Royal Saudi Air Force
;
* Turkmen Air Force
;
* Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
Former
; *Indian Air Force
The Indian Air Force (IAF) (ISO 15919, ISO: ) is the air force, air arm of the Indian Armed Forces. Its primary mission is to secure Indian airspace and to conduct aerial warfare during armed conflicts. It was officially established on 8 Octob ...
;
* Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department
;
* Royal Air Force
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the Air force, air and space force of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. It was formed towards the end of the World War I, First World War on 1 April 1918, on the merger of t ...
Notable accidents
On 4 September 2024, a member ofRoyal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the naval warfare force of the United Kingdom. It is a component of His Majesty's Naval Service, and its officers hold their commissions from the King of the United Kingdom, King. Although warships were used by Kingdom ...
personnel died after a Royal Navy Merlin Mk. 4 helicopter ditched in the English Channel
The English Channel, also known as the Channel, is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that separates Southern England from northern France. It links to the southern part of the North Sea by the Strait of Dover at its northeastern end. It is the busi ...
near Dorset
Dorset ( ; Archaism, archaically: Dorsetshire , ) is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is bordered by Somerset to the north-west, Wiltshire to the north and the north-east, Hampshire to the east, t ...
while conducting night flying exercises with HMS Queen Elizabeth. The two other crew on board were taken to a hospital.
Specifications (Merlin HM1)


Appearances in media
See also
References
Citations
Bibliography
* AgustaWestland''AW101 Utility''.
AgustaWestland, June 2008. * Cooper, Neil. ''The business of death: Britain's arms trade at home and abroad''. I.B.Tauris, 1997. . * Crawford, Stephen. ''Twenty-first century military helicopters: today's fighting gunships''. Zenith Imprint, 2003. . * Dobbin, Murray. ''The politics of Kim Campbell: from school trustee to Prime Minister''. James Lorimer & Company, 1993. . * Donald, David, ed. ''The Complete Encyclopedia of World Aircraft''. New York: Barnes & Noble Books, 1997. . * Eden, Paul, ed. ''Encyclopedia of Modern Military Aircraft''. London: Amber Books, 2004. . * Evans, Nicholas D. ''Military gadgets: how advanced technology is transforming today's battlefield-- and tomorrow's''. FT Press, 2004. . * Frawley, Gerald. ''The International Directory of Military Aircraft, 2002/2003''. Fyshwick, Australian Capital Territory">Fyshwick, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 2002. . * Friedman, Norman. ''The Naval Institute guide to world naval weapons systems, 1997–1998''. Annapolis, Maryland, USA: Naval Institute Press, 1997. . * Gunston, Bill and Mike Spick. ''Modern fighting helicopters''. Random House Value Publishing, 1986. . * Harding, Ian. "Long distance wizard". ''Air International'', Vol. 79, No. 1, July 2010. pp. 70–75. . * Jackson, Paul. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2003–2004''. 2003, Jane's Information Group. Coulsdon, UK. * Jackson, Paul; Munson, Kenneth; Peacock, Lindsay. ''Jane's All The World's Aircraft 2009–2010''. 2009, Jane's Information Group. Coulsdon, UK. * Lake, Jon. "Variant File: AgustaWestland EH101/AW101". ''International Air Power Review''. Volume 22. Westport, Connecticut, USA: AIRtime Publishing, 2007. pp. 116–135. . . * Lavington, Simon. ''Moving Targets: Elliott-Automation and the Dawn of the Computer Age in Britain, 1947–67''. Springer 2011, . * Martin, Stephen. ''The economics of offsets: defence procurement and countertrade''. Routledge, 1996. . * Matthews, Ron. ''European armaments collaboration: policy, problems and prospects''. Routledge, 1992. . * Moir, Ian and Allan G. Seabridge. ''Aircraft systems: mechanical, electrical, and avionics subsystems integration''. John Wiley and Sons, 2008. . * Plamondon, Aaron. ''The politics of procurement: military acquisition in Canada and the Sea King helicopter''. UBC Press, 2009. .
External links
*Royal Navy Merlin website
EH-101 Merlin page (in English) on Portuguese Air Force site
{{Italian military aircraft AW101 Aircraft first flown in 1987 Anti-submarine helicopters 1980s international anti-submarine aircraft 1980s international civil utility aircraft 1980s international military transport aircraft Italy–United Kingdom relations Kawasaki Aerospace Company 1980s international helicopters Military transport helicopters Three-turbine helicopters Single-rotor helicopters Aircraft with retractable tricycle landing gear