7400 series on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) are a popular logic family of
The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) are a popular logic family of

 Although the 7400 series was the first ''de facto'' industry standard TTL logic family (i.e. second-sourced by several semiconductor companies), there were earlier TTL logic families such as:
* Sylvania Universal High-level Logic in 1963
* Motorola MC4000 MTTL
* National Semiconductor DM8000
* Fairchild 9300 series
* Signetics 8200 and 8T00
The 7400 quad NAND gate was the first product in the series, introduced by Texas Instruments in a military grade metal flat package (5400W) in October 1964. The pin assignment of this early series differed from the de facto standard set by the later series in DIP packages (in particular, ground was connected to pin 11 and the power supply to pin 4, compared to pins 7 and 14 for DIP packages). The extremely popular commercial grade plastic DIP (7400N) followed in the third quarter of 1966.
The 5400 and 7400 series were used in many popular minicomputers in the 1970s and early 1980s. Some models of the DEC PDP-series 'minis' used the
Although the 7400 series was the first ''de facto'' industry standard TTL logic family (i.e. second-sourced by several semiconductor companies), there were earlier TTL logic families such as:
* Sylvania Universal High-level Logic in 1963
* Motorola MC4000 MTTL
* National Semiconductor DM8000
* Fairchild 9300 series
* Signetics 8200 and 8T00
The 7400 quad NAND gate was the first product in the series, introduced by Texas Instruments in a military grade metal flat package (5400W) in October 1964. The pin assignment of this early series differed from the de facto standard set by the later series in DIP packages (in particular, ground was connected to pin 11 and the power supply to pin 4, compared to pins 7 and 14 for DIP packages). The extremely popular commercial grade plastic DIP (7400N) followed in the third quarter of 1966.
The 5400 and 7400 series were used in many popular minicomputers in the 1970s and early 1980s. Some models of the DEC PDP-series 'minis' used the
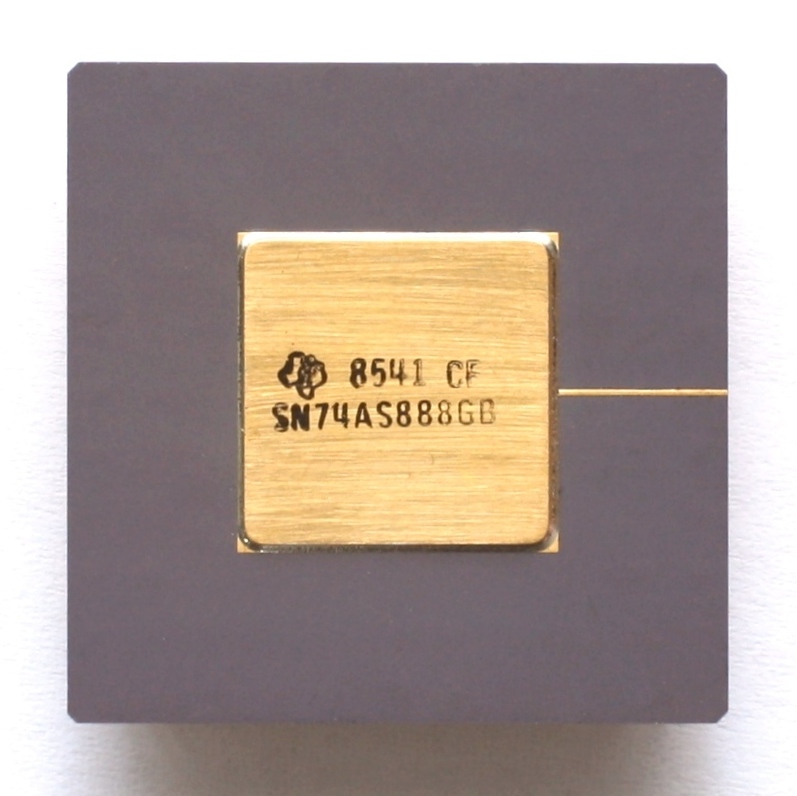

 7400 series parts were constructed using
7400 series parts were constructed using
/ref> The 74S family, using Schottky circuitry, uses more power than the 74, but is faster. The 74LS family of ICs is a lower-power version of the 74S family, with slightly higher speed but lower power dissipation than the original 74 family; it became the most popular variant once it was widely available. Many 74LS ICs can be found in microcomputers and digital consumer electronics manufactured in the 1980s and early 1990s. The 74F family was introduced by Fairchild Semiconductor and adopted by other manufacturers; it is faster than the 74, 74LS and 74S families. Through the late 1980s and 1990s newer versions of this family were introduced to support the lower operating voltages used in newer
 Part number schemes varied by manufacturer. The part numbers for 7400-series logic devices often use the following designators:
* Often first, a two or three letter prefix, denoting the manufacturer and flow class of the device (e.g. SN for Texas Instruments using a commercial processing, SNV for Texas Instruments using military processing, M for
Part number schemes varied by manufacturer. The part numbers for 7400-series logic devices often use the following designators:
* Often first, a two or three letter prefix, denoting the manufacturer and flow class of the device (e.g. SN for Texas Instruments using a commercial processing, SNV for Texas Instruments using military processing, M for


 Some manufacturers, such as Mullard and Siemens, had
Some manufacturers, such as Mullard and Siemens, had
. A number of different technologies were available from the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia, Poland, and East Germany. The 8400 series in the table below indicates an industrial temperature range from −25 °C to +85 °C (as opposed to −40 °C to +85 °C for the 6400 series). Around 1990 the production of standard logic ceased in all Eastern European countries except the Soviet Union and later
''(archive)''
/small> * ''TTL Cookbook''; 1st Ed; Don Lancaster; Sams Publishing; 412 pages; 1974; .''(archive)''
/small> * ''Designing with TTL Integrated Circuits''; 1st Ed; Robert Morris, John Miller; Texas Instruments and McGraw-Hill; 322 pages; 1971; .''(archive)''
/small> ;App Notes
''Understanding and Interpreting Standard-Logic Data Sheets''
Stephen Nolan, Jose Soltero, Shreyas Rao; Texas Instruments; 60 pages; 2016.
''Comparison of 74HC / 74S / 74LS / 74ALS Logic''
Fairchild; 6 pages, 1983.
''Interfacing to 74HC Logic''
Fairchild; 10 pages; 1998.
''74AHC / 74AHCT Designer’s Guide''
TI; 53pages; 1998. Compares 74HC / 74AHC / 74AC (CMOS I/O) and 74HCT / 74AHCT / 74ACT (TTL I/O). ;Fairchild Semiconductor / ON Semiconductor * Historical Data Books
''TTL'' (1978, 752 pages)''FAST'' (1981, 349 pages)
''Logic Selection Guide'' (2008, 12 pages)
;Nexperia / NXP Semiconductor
''Logic Selection Guide'' (2020, 234 pages)
;Texas Instruments / National Semiconductor * Historical Catalog
(1967, 375 pages)
* Historical Databooks
''TTL Vol1'' (1984, 339 pages)''TTL Vol2'' (1985, 1402 pages)''TTL Vol3'' (1984, 793 pages)''TTL Vol4'' (1986, 445 pages)
''Digital Logic Pocket Data Book'' (2007, 794 pages)''Logic Reference Guide'' (2004, 8 pages)''Logic Selection Guide'' (1998, 215 pages)
''Little Logic Guide'' (2018, 25 pages)''Little Logic Selection Guide'' (2004, 24 pages)
;Toshiba
''General-Purpose Logic ICs'' (2012, 55 pages)
Understanding 7400-series digital logic ICs
- Nuts and Volts magazine
- Electronics Club {{Authority control Integrated circuits Digital electronics 1964 introductions
 The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) are a popular logic family of
The 7400 series of integrated circuits (ICs) are a popular logic family of transistor–transistor logic Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor"), as opp ...
(TTL) logic chips.
In 1964, Texas Instruments introduced the SN5400 series of logic chips, in a ceramic semiconductor package. A low-cost plastic package SN7400 series was introduced in 1966 which quickly gained over 50% of the logic chip market, and eventually becoming ''de facto'' standardized electronic components. Over the decades, many generations of pin-compatible
In electronics, pin-compatible devices are electronic components, generally integrated circuits or expansion cards, sharing a common footprint and with the same functions assigned or usable on the same pins. Pin compatibility is a property ...
descendant families evolved to include support for low power CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
technology, lower supply voltages, and surface mount packages.
Overview
The 7400 series contains hundreds of devices that provide everything from basiclogic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate ...
s, flip-flops, and counters, to special purpose bus transceivers and arithmetic logic unit
In computing, an arithmetic logic unit (ALU) is a combinational digital circuit that performs arithmetic and bitwise operations on integer binary numbers. This is in contrast to a floating-point unit (FPU), which operates on floating point nu ...
s (ALU). Specific functions are described in a list of 7400 series integrated circuits
The following is a list of 7400-series digital logic integrated circuits. In the mid-1960s, the original 7400-series integrated circuits were introduced by Texas Instruments with the prefix "SN" to create the name SN74xx. Due to the popularity o ...
. Some TTL logic parts were made with an extended military-specification temperature range. These parts are prefixed with 54 instead of 74 in the part number. A short-lived 64 prefix on Texas Instruments parts indicated an industrial temperature range; this prefix had been dropped from the TI literature by 1973. Since the 1970s, new product families have been released to replace the original 7400 series. More recent TTL logic families were manufactured using CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
or BiCMOS technology rather than TTL.
Today, surface-mount
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referre ...
ed CMOS versions of the 7400 series are used in various applications in electronics and for glue logic in computers and industrial electronics. The original through-hole
In electronics, through-hole technology (also spelled "thru-hole") is a manufacturing scheme in which leads on the components are inserted through holes drilled in printed circuit boards (PCB) and soldered to pads on the opposite side, either ...
devices in dual in-line package
In microelectronics, a dual in-line package (DIP or DIL), is an electronic component package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board (P ...
s (DIP/DIL) were the mainstay of the industry for many decades. They are useful for rapid breadboard
A breadboard, solderless breadboard, or protoboard is a construction base used to build semi-permanent prototypes of electronic circuits. Unlike a perfboard or stripboard, breadboards do not require soldering or destruction of tracks and are h ...
-prototyping and for education and remain available from most manufacturers. The fastest types and very low voltage versions are typically surface-mount
Surface-mount technology (SMT), originally called planar mounting, is a method in which the electrical components are mounted directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). An electrical component mounted in this manner is referre ...
only, however.
The first part number in the series, the 7400, is a 14-pin IC containing four two-input NAND gates. Each gate uses two input pins and one output pin, with the remaining two pins being power (+5 V) and ground. This part was made in various through-hole and surface-mount packages, including flat pack and plastic/ceramic dual in-line. Additional characters in a part number identify the package and other variations.
Unlike the older resistor-transistor logic integrated circuits, bipolar TTL gates were unsuitable to be used as analog devices, providing low gain, poor stability, and low input impedance. Special-purpose TTL devices were used to provide interface functions such as Schmitt trigger
In electronics, a Schmitt trigger is a comparator circuit with hysteresis implemented by applying positive feedback to the noninverting input of a comparator or differential amplifier. It is an active circuit which converts an analog input s ...
s or monostable multivibrator
A multivibrator is an electronic circuit used to implement a variety of simple two-state devices such as relaxation oscillators, timers, and flip-flops. The first multivibrator circuit, the astable multivibrator oscillator, was invented by Henri ...
timing circuits. Inverting gates could be cascaded as a ring oscillator
A ring oscillator is a device composed of an odd number of NOT gates in a ring, whose output oscillates between two voltage levels, representing ''true'' and ''false''. The NOT gates, or inverters, are attached in a chain and the output of the ...
, useful for purposes where high stability was not required.
History

 Although the 7400 series was the first ''de facto'' industry standard TTL logic family (i.e. second-sourced by several semiconductor companies), there were earlier TTL logic families such as:
* Sylvania Universal High-level Logic in 1963
* Motorola MC4000 MTTL
* National Semiconductor DM8000
* Fairchild 9300 series
* Signetics 8200 and 8T00
The 7400 quad NAND gate was the first product in the series, introduced by Texas Instruments in a military grade metal flat package (5400W) in October 1964. The pin assignment of this early series differed from the de facto standard set by the later series in DIP packages (in particular, ground was connected to pin 11 and the power supply to pin 4, compared to pins 7 and 14 for DIP packages). The extremely popular commercial grade plastic DIP (7400N) followed in the third quarter of 1966.
The 5400 and 7400 series were used in many popular minicomputers in the 1970s and early 1980s. Some models of the DEC PDP-series 'minis' used the
Although the 7400 series was the first ''de facto'' industry standard TTL logic family (i.e. second-sourced by several semiconductor companies), there were earlier TTL logic families such as:
* Sylvania Universal High-level Logic in 1963
* Motorola MC4000 MTTL
* National Semiconductor DM8000
* Fairchild 9300 series
* Signetics 8200 and 8T00
The 7400 quad NAND gate was the first product in the series, introduced by Texas Instruments in a military grade metal flat package (5400W) in October 1964. The pin assignment of this early series differed from the de facto standard set by the later series in DIP packages (in particular, ground was connected to pin 11 and the power supply to pin 4, compared to pins 7 and 14 for DIP packages). The extremely popular commercial grade plastic DIP (7400N) followed in the third quarter of 1966.
The 5400 and 7400 series were used in many popular minicomputers in the 1970s and early 1980s. Some models of the DEC PDP-series 'minis' used the 74181
The 74181 is a 4-bit slice arithmetic logic unit (ALU), implemented as a 7400 series TTL integrated circuit. The first complete ALU on a single chip, it was used as the arithmetic/logic core in the CPUs of many historically significant minicomp ...
ALU as the main computing element in the CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
. Other examples were the Data General Nova series and Hewlett-Packard 21MX, 1000, and 3000 series.
In 1965, typical quantity-one pricing for the SN5400 (military grade, in ceramic welded flat-pack
Ready-to-assemble furniture (RTA), also known as knock-down furniture (KD), flat pack furniture, or kit furniture, is a form of furniture that requires customer assembly. The separate components are packed for sale in cartons which also contain ...
) was around 22 USD.
As of 2007, individual commercial-grade chips in molded epoxy (plastic) packages can be purchased for approximately US$0.25 each, depending on the particular chip.
Families


 7400 series parts were constructed using
7400 series parts were constructed using bipolar transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar ...
s, forming what is referred to as transistor–transistor logic Transistor–transistor logic (TTL) is a logic family built from bipolar junction transistors. Its name signifies that transistors perform both the logic function (the first "transistor") and the amplifying function (the second "transistor"), as opp ...
or TTL. Newer series, more or less compatible in function and logic level with the original parts, use CMOS
Complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS, pronounced "sea-moss", ) is a type of metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) fabrication process that uses complementary and symmetrical pairs of p-type and n-type MOSF ...
technology or a combination of the two (BiCMOS
Bipolar CMOS (BiCMOS) is a semiconductor technology that integrates two semiconductor technologies, those of the bipolar junction transistor and the CMOS (complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor) logic gate, into a single integrated circuit. In ...
). Originally the bipolar circuits provided higher speed but consumed more power than the competing 4000 series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It had a supply voltage range of 5V to 20V, which is much wider than any contemporary logic family.
Almost all IC manufacturers active during t ...
of CMOS devices. Bipolar devices are also limited to a fixed power supply voltage, typically 5 V, while CMOS parts often support a range of supply voltages.
Milspec
A United States defense standard, often called a military standard, "MIL-STD", "MIL-SPEC", or (informally) "MilSpecs", is used to help achieve standardization objectives by the U.S. Department of Defense.
Standardization is beneficial in achievi ...
-rated devices for use in extended temperature conditions are available as the 5400 series. Texas Instruments also manufactured radiation-hardened devices with the prefix ''RSN'', and the company offered beam-lead
Beam lead technology is a method of fabricating a semiconductor device. Its original application was to high-frequency silicon switching transistors and high-speed integrated circuits. It eliminated the labor-intensive wire-bonding process used f ...
bare dies for integration into hybrid circuits with a ''BL'' prefix designation.
Regular-speed TTL parts were also available for a time in the 6400 series – these had an extended industrial temperature range of −40 °C to +85 °C. While companies such as Mullard listed 6400-series compatible parts in 1970 data sheets, by 1973 there was no mention of the 6400 family in the Texas Instruments ''TTL Data Book''. Some companies have also offered industrial extended temperature range variants using the regular 7400-series part numbers with a prefix or suffix to indicate the temperature grade.
As integrated circuits in the 7400 series were made in different technologies, usually compatibility was retained with the original TTL logic levels and power supply voltages. An integrated circuit made in CMOS is not a TTL chip, since it uses field-effect transistors (FETs) and not bipolar junction transistors, but similar part numbers are retained to identify similar logic functions and electrical (power and I/O voltage) compatibility in the different subfamilies.
Over 40 different logic subfamilies use this standardized part number scheme.
Many parts in the CMOS HC, AC, and FC families are also offered in "T" versions (HCT, ACT, and FCT) which have input thresholds that are compatible with both TTL and 3.3 V CMOS signals. The non-T parts have conventional CMOS input thresholds, which are more restrictive than TTL thresholds. Typically, CMOS input thresholds require high-level signals to be at least 70% of Vcc and low-level signals to be at most 30% of Vcc. (TTL has the input high level above 2.0 V and the input low level below 0.8 V, so a TTL high-level signal could be in the forbidden middle range for 5 V CMOS.)
The 74H family is the same basic design as the 7400 family with resistor values reduced. This reduced the typical propagation delay
Propagation delay is the time duration taken for a signal to reach its destination. It can relate to networking, electronics or physics. ''Hold time'' is the minimum interval required for the logic level to remain on the input after triggering e ...
from 9 ns to 6 ns but increased the power consumption. The 74H family provided a number of unique devices for CPU designs in the 1970s. Many designers of military and aerospace equipment used this family over a long period and as they need exact replacements, this family is still produced by Lansdale Semiconductor.Lansdale Semiconductor home page/ref> The 74S family, using Schottky circuitry, uses more power than the 74, but is faster. The 74LS family of ICs is a lower-power version of the 74S family, with slightly higher speed but lower power dissipation than the original 74 family; it became the most popular variant once it was widely available. Many 74LS ICs can be found in microcomputers and digital consumer electronics manufactured in the 1980s and early 1990s. The 74F family was introduced by Fairchild Semiconductor and adopted by other manufacturers; it is faster than the 74, 74LS and 74S families. Through the late 1980s and 1990s newer versions of this family were introduced to support the lower operating voltages used in newer
CPU
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU performs basic arithmetic, logic, controlling, a ...
devices.
Part numbering
 Part number schemes varied by manufacturer. The part numbers for 7400-series logic devices often use the following designators:
* Often first, a two or three letter prefix, denoting the manufacturer and flow class of the device (e.g. SN for Texas Instruments using a commercial processing, SNV for Texas Instruments using military processing, M for
Part number schemes varied by manufacturer. The part numbers for 7400-series logic devices often use the following designators:
* Often first, a two or three letter prefix, denoting the manufacturer and flow class of the device (e.g. SN for Texas Instruments using a commercial processing, SNV for Texas Instruments using military processing, M for ST Microelectronics
STMicroelectronics N.V. commonly referred as ST or STMicro is a Dutch multinational corporation and technology company of French-Italian origin headquartered in Plan-les-Ouates near Geneva, Switzerland and listed on the French stock market. ST ...
, DM for National Semiconductor, UT for Cobham PLC, SG for Sylvania). These codes are no longer closely associated with a single manufacturer, for example, Fairchild Semiconductor manufactures parts with MM and DM prefixes, and no prefixes.
* Two digits, where "74" denotes a commercial temperature range device and "54" denotes a military temperature range. Historically, "64" denoted a short-lived series with an intermediate "industrial" temperature range.
* No, or up to four letters denoting the logic subfamily (such as "LS", "HCT" or nothing for basic bipolar TTL).
* Two or more arbitrarily assigned digits that identify the function of the device. There are hundreds of different devices in each family.
* Additional suffix letters and numbers may be appended to denote the package type, quality grade, or other information, but this varies widely by manufacturer.
For example, "SN5400N" signifies that the part is a 7400-series IC probably manufactured by Texas Instruments ("SN" originally meaning "Semiconductor Network") using commercial processing, is of the military temperature rating ("54"), and is of the TTL family (absence of a family designator), its function being the ''quad 2-input NAND gate'' ("00") implemented in a plastic through-hole DIP package ("N").
Many logic families
In computer engineering, a logic family is one of two related concepts:
* A logic family of monolithic digital integrated circuit devices is a group of electronic logic gates constructed using one of several different designs, usually with compati ...
maintain a consistent use of the device numbers as an aid to designers. Often a part from a different 74x00 subfamily could be substituted ("drop-in replacement {{unreferenced, date=April 2016
Drop-in replacement is a term used in computer science and other fields. It refers to the ability
to replace one hardware (or software) component with another one without any other code or configuration
changes being ...
") in a circuit, with the same function and pin-out yet more appropriate characteristics for an application (perhaps speed or power consumption), which was a large part of the appeal of the 74C00 series over the competing CD4000B series, for example. But there are a few exceptions where incompatibilities (mainly in pin-out) across the subfamilies occurred, such as:
* some flat-pack devices (e.g. 7400W) and surface-mount devices,
* some of the faster CMOS series (for example 74AC),
* a few low-power TTL devices (e.g. 74L86, 74L9 and 74L95) have a different pin-out than the regular (or even 74LS) series part.
* five versions of the 74x54 (4-wide AND-OR-INVERT gates IC), namely 7454(N), 7454W, 74H54, 74L54W and 74L54N/74LS54, are different from each other in pin-out and/or function,
Second sources from Europe and Eastern Bloc



 Some manufacturers, such as Mullard and Siemens, had
Some manufacturers, such as Mullard and Siemens, had pin-compatible
In electronics, pin-compatible devices are electronic components, generally integrated circuits or expansion cards, sharing a common footprint and with the same functions assigned or usable on the same pins. Pin compatibility is a property ...
TTL parts, but with a completely different numbering scheme; however, data sheets identified the ''7400-compatible'' number as an aid to recognition.
At the time the 7400 series was being made, some European manufacturers (that traditionally followed the Pro Electron Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components (such as semiconductors, liquid crystal displays, sensor devices, electronic tubes and cathode ray tubes).
Pro Electron was set up in 1966 in Br ...
naming convention), such as Philips/ Mullard, produced a series of TTL integrated circuits with part names beginning with FJ. Some examples of FJ series are:
* FJH101 (=7430) single 8-input NAND gate,
* FJH131 (=7400) quadruple 2-input NAND gate,
* FJH181 (=7454N or J) 2+2+2+2 input AND-OR-NOT gate.
The Soviet Union started manufacturing TTL ICs with 7400-series pinout in the late 1960s and early 1970s, such as the K155ЛA3, which was pin-compatible with the 7400 part available in the United States, except for using a metric spacing of 2.5 mm between pins instead of the pin-to-pin spacing used in the west.
Another peculiarity of the Soviet-made 7400 series was the packaging material used in the 1970s–1980s. Instead of the ubiquitous black resin, they had a brownish-green body colour with subtle swirl marks created during the moulding process. It was jokingly referred to in the Eastern Bloc electronics industry as the "elephant-dung packaging", due to its appearance.
The Soviet integrated circuit designation
Soviet integrated circuit designation is an industrial specification for encoding of names of integrated circuits manufactured in the Soviet Union and Post-Soviet Union countries. 25 years after the dissolution of the Soviet Union, a number of m ...
is different from the Western series:
* the technology modifications were considered different series and were identified by different numbered prefixes – К155 series is equivalent to plain 74, К555 series is 74LS, К1533 is 74ALS, etc.;
* the function of the unit is described with a two-letter code followed by a number:
** the first letter represents the functional group – logical, triggers, counters, multiplexers, etc.;
** the second letter shows the functional subgroup, making the distinction between logical NAND and NOR, D- and JK-triggers, decimal and binary counters, etc.;
** the number distinguishes variants with different number of inputs or different number of elements within a die – ЛА1/ЛА2/ЛА3 (LA1/LA2/LA3) are 2 four-input / 1 eight-input / 4 two-input NAND elements respectively (equivalent to 7420/7430/7400).
Before July 1974 the two letters from the functional description were inserted after the first digit of the series. Examples: К1ЛБ551 and К155ЛА1 (7420), К1ТМ552 and К155ТМ2 (7474) are the same ICs made at different times.
Clones of the 7400 series were also made in other Eastern Bloc countries:
* Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, България, Bǎlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Maced ...
(Mikroelektronika Botevgrad
Botevgrad ( bg, Ботевград ) is a town in western Bulgaria. It is located in Sofia Province and is close to Pravets. Botevgrad lies 47 km from Sofia.
History and name
The village was called Samundzhievo (Самунджиево) unt ...
) used a designation somewhat similar to that of the Soviet Union, e.g. ''1ЛБ00ШМ'' (1LB00ShM) for a 74LS00. Some of the two-letter functional groups were borrowed from the Soviet designation, while others differed. Unlike the Soviet scheme, the two or three digit number after the functional group matched the western counterpart. The series followed at the end (i.e. ''ШМ'' for LS). Only the LS series is known to have been manufactured in Bulgaria.
* Czechoslovakia ( TESLA) used the 7400 numbering scheme with manufacturer prefix MH. Example: MH7400. Tesla also produced industrial grade (8400, −25 ° to 85 °C) and military grade (5400, −55 ° to 125 °C) ones.
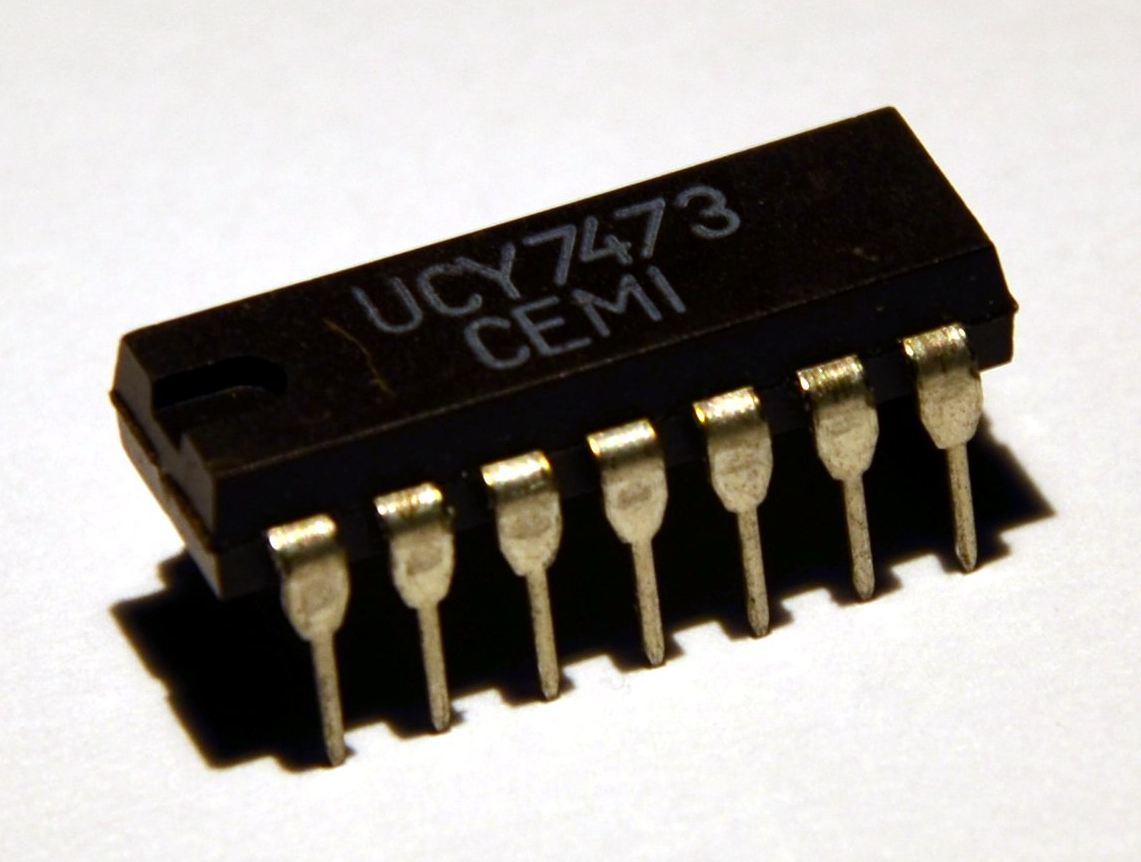
* Poland ( Unitra CEMI) used the 7400 numbering scheme with manufacturer prefixes UCA for the 5400 and 6400 series, as well as UCY for the 7400 series. Examples: UCA6400, UCY7400. Note that ICs with the prefix MCY74 correspond to the 4000 series
The 4000 series is a CMOS logic family of integrated circuits (ICs) first introduced in 1968 by RCA. It had a supply voltage range of 5V to 20V, which is much wider than any contemporary logic family.
Almost all IC manufacturers active during t ...
(e.g. MCY74002 corresponds to 4002 and not to 7402).
* Hungary (Tungsram
Tungsram was a manufacturing company located in Hungary and known for their light bulbs and electronics. Established in Újpest (today part of Budapest, Hungary) in 1896, it initially produced telephones, wires and switchboards. The name "Tungsra ...
, later Mikroelektronikai Vállalat / MEV) also used the 7400 numbering scheme, but with manufacturer suffix – 7400 is marked as 7400APC.
* Romania (I.P.R.S.) used a trimmed 7400 numbering with the manufacturer prefix CDB (example: CDB4123E corresponds to 74123) for the 74 and 74H series, where the suffix ''H'' indicated the 74H series. For the later 74LS series, the standard numbering was used.
* East Germany ( HFO) also used trimmed 7400 numbering without manufacturer prefix or suffix. The prefix D (or E) designates digital IC, and not the manufacturer. Example: D174 is 7474. 74LS clones were designated by the prefix DL; e.g. DL000 = 74LS00. In later years East German made clones were also available with standard 74* numbers, usually for export. GDR semiconductor datasheet comparison. A number of different technologies were available from the Soviet Union, Czechoslovakia, Poland, and East Germany. The 8400 series in the table below indicates an industrial temperature range from −25 °C to +85 °C (as opposed to −40 °C to +85 °C for the 6400 series). Around 1990 the production of standard logic ceased in all Eastern European countries except the Soviet Union and later
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eight ...
and Belarus. As of 2016, the series 133, К155, 1533, КР1533, 1554, 1594, and 5584 were in production at "Integral" in Belarus,
as well as the series 130 and 530 at "NZPP-KBR",
134 and 5574 at "VZPP",
533 at "Svetlana",
1564, К1564, КР1564 at "NZPP",
1564, К1564 at "Voshod",
1564 at "Exiton",
and 133, 530, 533, 1533 at "Mikron" in Russia.
The Russian company Angstrem manufactures 54HC circuits as the 5514БЦ1 series, 54AC as the 5514БЦ2 series, and 54LVC as the 5524БЦ2 series.
See also
* List of 7400-series integrated circuits * 4000-series integrated circuits * List of 4000-series integrated circuits * Push–pull output * Open-collector/drain output * Three-state output * Schmitt trigger input *Logic gate
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate ...
* Logic family
* Programmable logic device
A programmable logic device (PLD) is an electronic component used to build reconfigurable digital circuits. Unlike digital logic constructed using discrete logic gates with fixed functions, a PLD has an undefined function at the time of manu ...
* Pin compatibility
In electronics, pin-compatible devices are electronic components, generally integrated circuits or expansion cards, sharing a common footprint and with the same functions assigned or usable on the same pins. Pin compatibility is a property desir ...
References
Further reading
;Books * ''50 Circuits Using 7400 Series IC's''; 1st Ed; R.N. Soar; Bernard Babani Publishing; 76 pages; 1979; ./small> * ''TTL Cookbook''; 1st Ed; Don Lancaster; Sams Publishing; 412 pages; 1974; .
/small> * ''Designing with TTL Integrated Circuits''; 1st Ed; Robert Morris, John Miller; Texas Instruments and McGraw-Hill; 322 pages; 1971; .
/small> ;App Notes
''Understanding and Interpreting Standard-Logic Data Sheets''
Stephen Nolan, Jose Soltero, Shreyas Rao; Texas Instruments; 60 pages; 2016.
''Comparison of 74HC / 74S / 74LS / 74ALS Logic''
Fairchild; 6 pages, 1983.
''Interfacing to 74HC Logic''
Fairchild; 10 pages; 1998.
''74AHC / 74AHCT Designer’s Guide''
TI; 53pages; 1998. Compares 74HC / 74AHC / 74AC (CMOS I/O) and 74HCT / 74AHCT / 74ACT (TTL I/O). ;Fairchild Semiconductor / ON Semiconductor * Historical Data Books
''TTL'' (1978, 752 pages)
''Logic Selection Guide'' (2008, 12 pages)
;Nexperia / NXP Semiconductor
''Logic Selection Guide'' (2020, 234 pages)
;Texas Instruments / National Semiconductor * Historical Catalog
(1967, 375 pages)
* Historical Databooks
''TTL Vol1'' (1984, 339 pages)
''Digital Logic Pocket Data Book'' (2007, 794 pages)
''Little Logic Guide'' (2018, 25 pages)
;Toshiba
''General-Purpose Logic ICs'' (2012, 55 pages)
External links
Understanding 7400-series digital logic ICs
- Nuts and Volts magazine
- Electronics Club {{Authority control Integrated circuits Digital electronics 1964 introductions