3D Rendering on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
3D rendering is the
 Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or
Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or
 Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 240 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a fraction of a second (a.k.a. "in one frame": In the case of a 30 frame-per-second animation, a frame encompasses one 30th of a second).
The primary goal is to achieve an as high as possible degree of
Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 240 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a fraction of a second (a.k.a. "in one frame": In the case of a 30 frame-per-second animation, a frame encompasses one 30th of a second).
The primary goal is to achieve an as high as possible degree of
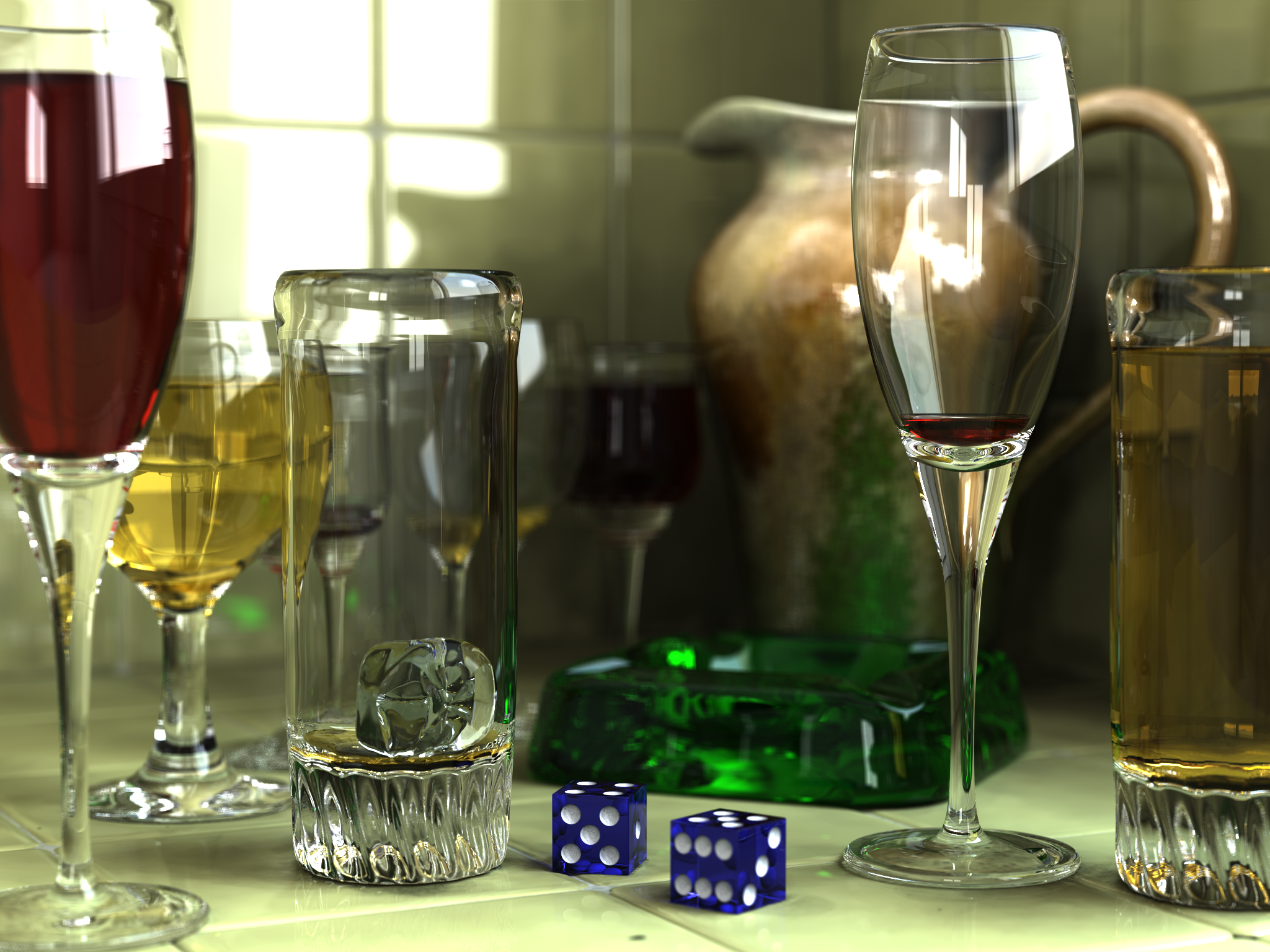 Animations for non-interactive media, such as feature films and video, can take much more time to render. Non-real-time rendering enables the leveraging of limited processing power in order to obtain higher image quality. Rendering times for individual frames may vary from a few seconds to several days for complex scenes. Rendered frames are stored on a
Animations for non-interactive media, such as feature films and video, can take much more time to render. Non-real-time rendering enables the leveraging of limited processing power in order to obtain higher image quality. Rendering times for individual frames may vary from a few seconds to several days for complex scenes. Rendered frames are stored on a
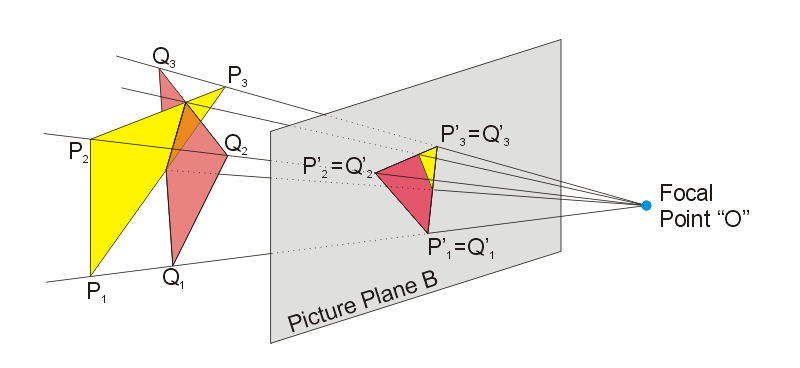 The shaded three-dimensional objects must be flattened so that the display device - namely a monitor - can display it in only two dimensions, this process is called
The shaded three-dimensional objects must be flattened so that the display device - namely a monitor - can display it in only two dimensions, this process is called

How Stuff Works - 3D Graphics
* (
3D computer graphics
3D computer graphics, sometimes called Computer-generated imagery, CGI, 3D-CGI or three-dimensional Computer-generated imagery, computer graphics, are graphics that use a three-dimensional representation of geometric data (often Cartesian coor ...
process of converting 3D models into 2D images on a computer
A computer is a machine that can be Computer programming, programmed to automatically Execution (computing), carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (''computation''). Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic set ...
. 3D renders may include photorealistic effects or non-photorealistic styles.
Rendering methods
 Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or
Rendering is the final process of creating the actual 2D image or animation
Animation is a filmmaking technique whereby still images are manipulated to create moving images. In traditional animation, images are drawn or painted by hand on transparent celluloid sheets to be photographed and exhibited on film. Animati ...
from the prepared scene. This can be compared to taking a photo or filming the scene after the setup is finished in real life. Several different, and often specialized, rendering methods have been developed. These range from the distinctly non-realistic wireframe rendering through polygon-based rendering, to more advanced techniques such as: scanline rendering, ray tracing, or radiosity. Rendering may take from fractions of a second to days for a single image/frame. In general, different methods are better suited for either photorealistic rendering, or real-time rendering.
Real-time
 Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 240 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a fraction of a second (a.k.a. "in one frame": In the case of a 30 frame-per-second animation, a frame encompasses one 30th of a second).
The primary goal is to achieve an as high as possible degree of
Rendering for interactive media, such as games and simulations, is calculated and displayed in real time, at rates of approximately 20 to 240 frames per second. In real-time rendering, the goal is to show as much information as possible as the eye can process in a fraction of a second (a.k.a. "in one frame": In the case of a 30 frame-per-second animation, a frame encompasses one 30th of a second).
The primary goal is to achieve an as high as possible degree of photorealism
Photorealism is a genre of art that encompasses painting, drawing and other graphic media, in which an artist studies a photograph and then attempts to reproduce the image as realistically as possible in another medium. Although the term can b ...
at an acceptable minimum rendering speed (usually 24 frames per second, as that is the minimum the human eye needs to see to successfully create the illusion of movement). In fact, exploitations can be applied in the way the eye 'perceives' the world, and as a result, the final image presented is not necessarily that of the real world, but one close enough for the human eye to tolerate.
Rendering software may simulate such visual effects as lens flares, depth of field or motion blur. These are attempts to simulate visual phenomena resulting from the optical characteristics of cameras and of the human eye. These effects can lend an element of realism to a scene, even if the effect is merely a simulated artifact of a camera. This is the basic method employed in games, interactive worlds and VRML.
The rapid increase in computer processing power has allowed a progressively higher degree of realism even for real-time rendering, including techniques such as HDR rendering. Real-time rendering is often polygonal and aided by the computer's GPU.
Non-real-time
 Animations for non-interactive media, such as feature films and video, can take much more time to render. Non-real-time rendering enables the leveraging of limited processing power in order to obtain higher image quality. Rendering times for individual frames may vary from a few seconds to several days for complex scenes. Rendered frames are stored on a
Animations for non-interactive media, such as feature films and video, can take much more time to render. Non-real-time rendering enables the leveraging of limited processing power in order to obtain higher image quality. Rendering times for individual frames may vary from a few seconds to several days for complex scenes. Rendered frames are stored on a hard disk
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating hard disk drive platter, pla ...
, then transferred to other media such as motion picture film or optical disk. These frames are then displayed sequentially at high frame rates, typically 24, 25, or 30 frames per second (fps), to achieve the illusion of movement.
When the goal is photo-realism, techniques such as ray tracing, path tracing
Path tracing is a rendering algorithm in computer graphics that Simulation, simulates how light interacts with Physical object, objects, voxels, and Volumetric_path_tracing, participating media to generate realistic (''physically plausible'') R ...
, photon mapping or radiosity are employed. This is the basic method employed in digital media and artistic works. Techniques have been developed for the purpose of simulating other naturally occurring effects, such as the interaction of light with various forms of matter. Examples of such techniques include particle systems (which can simulate rain, smoke, or fire), volumetric sampling (to simulate fog, dust and other spatial atmospheric effects), caustics (to simulate light focusing by uneven light-refracting surfaces, such as the light ripples seen on the bottom of a swimming pool), and subsurface scattering (to simulate light reflecting inside the volumes of solid objects, such as human skin
The human skin is the outer covering of the body and is the largest organ of the integumentary system. The skin has up to seven layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue guarding Skeletal muscle, muscles, bones, ligaments and organ (anato ...
).
The rendering process is computationally expensive, given the complex variety of physical processes being simulated. Computer processing power has increased rapidly over the years, allowing for a progressively higher degree of realistic rendering. Film studios that produce computer-generated animations typically make use of a render farm to generate images in a timely manner. However, falling hardware costs mean that it is entirely possible to create small amounts of 3D animation on a home computer system given the costs involved when using render farms. The output of the renderer is often used as only one small part of a completed motion-picture scene. Many layers of material may be rendered separately and integrated into the final shot using compositing software.
Reflection and shading models
Models of reflection/scattering and shading are used to describe the appearance of a surface. Although these issues may seem like problems all on their own, they are studied almost exclusively within the context of rendering. Modern 3D computer graphics rely heavily on a simplified reflection model called the Phong reflection model (not to be confused with Phong ''shading''). In therefraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one transmission medium, medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commo ...
of light, an important concept is the refractive index
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refrac ...
; in most 3D programming implementations, the term for this value is "index of refraction" (usually shortened to IOR).
Shading can be broken down into two different techniques, which are often studied independently:
*Surface shading - how light spreads across a surface (mostly used in scanline rendering for real-time 3D rendering in video games)
*Reflection/scattering - how light interacts with a surface ''at a given point'' (mostly used in ray-traced renders for non-real-time photorealistic and artistic 3D rendering in both CGI still 3D images and CGI non-interactive 3D animations)
Surface shading algorithms
Popular surface shading algorithms in 3D computer graphics include: * Flat shading: a technique that shades each polygon of an object based on the polygon's "normal" and the position and intensity of a light source * Gouraud shading: invented by H. Gouraud in 1971; a fast and resource-conscious vertex shading technique used to simulate smoothly shaded surfaces. * Phong shading: invented by Bui Tuong Phong; used to simulate specular highlights and smooth shaded surfaces.Reflection
Reflection or scattering is the relationship between the incoming and outgoing illumination at a given point. Descriptions of scattering are usually given in terms of a bidirectional scattering distribution function or BSDF.Shading
Shading addresses how different types of scattering are distributed across the surface (i.e., which scattering function applies where). Descriptions of this kind are typically expressed with a program called a shader. A simple example of shading is texture mapping, which uses animage
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be Two-dimensional space, two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be di ...
to specify the diffuse color at each point on a surface, giving it more apparent detail.
Some shading techniques include:
* Bump mapping: Invented by Jim Blinn, a normal-perturbation technique used to simulate wrinkled surfaces.
* Cel shading: A technique used to imitate the look of hand-drawn animation.
Transport
Transport
Transport (in British English) or transportation (in American English) is the intentional Motion, movement of humans, animals, and cargo, goods from one location to another. Mode of transport, Modes of transport include aviation, air, land tr ...
describes how illumination in a scene gets from one place to another. Visibility is a major component of light transport.
Projection
 The shaded three-dimensional objects must be flattened so that the display device - namely a monitor - can display it in only two dimensions, this process is called
The shaded three-dimensional objects must be flattened so that the display device - namely a monitor - can display it in only two dimensions, this process is called 3D projection
A 3D projection (or graphical projection) is a Design, design technique used to display a three-dimensional (3D) object on a two-dimensional (2D) surface. These projections rely on perspective (graphical), visual perspective and aspect analysi ...
. This is done using projection and, for most applications, perspective projection. The basic idea behind perspective projection is that objects that are further away are made smaller in relation to those that are closer to the eye. Perspective projection works by taking the points in camera space and dividing the X and Y coordinates of each point by its Z (depth) coordinate. Orthographic projection
Orthographic projection (also orthogonal projection and analemma) is a means of representing Three-dimensional space, three-dimensional objects in Plane (mathematics), two dimensions. Orthographic projection is a form of parallel projection in ...
is used mainly in CAD or CAM applications where scientific modeling requires precise measurements and preservation of the third dimension.
Rendering engines
Render engines may come together or be integrated with 3D modeling software but there is standalone software as well. Some render engines are compatible with multiple 3D software, while some are exclusive to one. It is the one responsible for the transformation of the prepared 3D scene into a 2D image or animation. 3D render engines can be based on different methods, such as ray-tracing, rasterization, path-tracing, also depending on the speed and the outcome expected, it comes in different types – real-time and non real-time, which was described above
Assets
CAD libraries can have assets such as 3D models, textures, bump maps, HDRIs, and different Computer graphics lighting sources to be rendered.See also
* Architectural rendering * Ambient occlusion *Computer vision
Computer vision tasks include methods for image sensor, acquiring, Image processing, processing, Image analysis, analyzing, and understanding digital images, and extraction of high-dimensional data from the real world in order to produce numerical ...
* Geometry pipeline
* Geometry processing
* Graphics
Graphics () are visual images or designs on some surface, such as a wall, canvas, screen, paper, or stone, to inform, illustrate, or entertain. In contemporary usage, it includes a pictorial representation of the data, as in design and manufa ...
* Graphics processing unit (GPU)
* Graphical output devices
* Image processing
An image or picture is a visual representation. An image can be two-dimensional, such as a drawing, painting, or photograph, or three-dimensional, such as a carving or sculpture. Images may be displayed through other media, including a pr ...
* Industrial CT scanning
* Painter's algorithm
* Parallel rendering
* Reflection (computer graphics)
* SIGGRAPH
* Volume rendering
Notes and references
External links
How Stuff Works - 3D Graphics
* (
Wayback Machine
The Wayback Machine is a digital archive of the World Wide Web founded by Internet Archive, an American nonprofit organization based in San Francisco, California. Launched for public access in 2001, the service allows users to go "back in ...
copy)
{{DEFAULTSORT:3d Rendering