1900s (decade) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
File:1900s decademontage2.png, 420px, From left, clockwise: The Wright brothers achieve the first manned flight with a motorized airplane, in Kitty Hawk in 1903; A missionary points to the severed hand of a Congolese villager, symbolic of Belgian atrocities in the Congo Free State; The
The 1900s (pronounced "nineteen-hundreds") was a decade that began on January 1, 1900, and ended on December 31, 1909. The Edwardian era (1901ŌĆō1910) covers a similar span of time. The term "nineteen-hundreds" is sometimes also used to mean the entire century from January 1, 1900 to December 31, 1999 (the years beginning with "19").
The decade saw the widespread application of the internal combustion engine including mass production of the automobile, as well as the introduction of the typewriter. The '' Wright Flyer'' performed the first recorded controlled, powered, sustained heavier than air flight on December 17, 1903. Reginald Fessenden of

 * September 8, 1900 ŌĆō A powerful hurricane
* September 8, 1900 ŌĆō A powerful hurricane
 * March 17, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes his paper "On a heuristic viewpoint concerning the production and transformation of light", in which he explains the photoelectric effect, using the notion of light quanta. For this paper Einstein received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
* May 11, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his doctoral dissertation "On the Motion of Small Particles...", in which he explains Brownian motion.
* June 30, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes the article "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", where he reveals his theory of special relativity.
* September 27, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his paper "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", in which he develops an argument for the famous equation ''E'' = ''mc''2.
* Planck's law of black-body radiation
* Seismographs built in the University of California, Berkeley, in 1900
* Practical
* March 17, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes his paper "On a heuristic viewpoint concerning the production and transformation of light", in which he explains the photoelectric effect, using the notion of light quanta. For this paper Einstein received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
* May 11, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his doctoral dissertation "On the Motion of Small Particles...", in which he explains Brownian motion.
* June 30, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes the article "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", where he reveals his theory of special relativity.
* September 27, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his paper "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", in which he develops an argument for the famous equation ''E'' = ''mc''2.
* Planck's law of black-body radiation
* Seismographs built in the University of California, Berkeley, in 1900
* Practical
 * 1900 ŌĆō The first zeppelin flight occurs over
* 1900 ŌĆō The first zeppelin flight occurs over  * 1901 ŌĆō First electric typewriter is invented by George Canfield Blickensderfer of Erie, Pennsylvania. It was part of a line of Blickensderfer typewriters, known for its portability.
* 1901 ŌĆō Wilhelm Kress of Saint Petersburg, Russia creates his Kress Drachenflieger in Austria-Hungary. Power was provided by a Daimler petrol engine driving two large
* 1901 ŌĆō First electric typewriter is invented by George Canfield Blickensderfer of Erie, Pennsylvania. It was part of a line of Blickensderfer typewriters, known for its portability.
* 1901 ŌĆō Wilhelm Kress of Saint Petersburg, Russia creates his Kress Drachenflieger in Austria-Hungary. Power was provided by a Daimler petrol engine driving two large  * 1902 ŌĆō
* 1902 ŌĆō  * 1903 ŌĆō Ford Motor Company produces its first car ŌĆō the Ford Model A.
* 1903 ŌĆō Ford Motor Company produces its first car ŌĆō the Ford Model A.
 * 1903 ŌĆō Richard Pearse of New Zealand supposedly successfully flew and landed a powered heavier-than-air machine on 31 March 1903 Verifiable eyewitnesses describe Pearse crashing into a hedge on two separate occasions during 1903. His monoplane must have risen to a height of at least three metres on each occasion. Good evidence exists that on 31 March 1903 Pearse achieved a powered, though poorly controlled, flight of several hundred metres. Pearse himself said that he had made a powered takeoff, "but at too low a speed for iscontrols to work". However, he remained airborne until he crashed into the hedge at the end of the field.
* 1903 ŌĆō
* 1903 ŌĆō Richard Pearse of New Zealand supposedly successfully flew and landed a powered heavier-than-air machine on 31 March 1903 Verifiable eyewitnesses describe Pearse crashing into a hedge on two separate occasions during 1903. His monoplane must have risen to a height of at least three metres on each occasion. Good evidence exists that on 31 March 1903 Pearse achieved a powered, though poorly controlled, flight of several hundred metres. Pearse himself said that he had made a powered takeoff, "but at too low a speed for iscontrols to work". However, he remained airborne until he crashed into the hedge at the end of the field.
* 1903 ŌĆō  * 1903 ŌĆō The Wright brothers fly at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their airplane, the '' Wright Flyer'', performed the first recorded controlled, powered, sustained heavier than air flight on December 17, 1903. In the day's fourth flight, Wilbur Wright flew 279 meters (852 ft) in 59 seconds. First three flights were approximately 120, 175, and 200 ft (61 m), respectively. The Wrights laid particular stress on fully and accurately describing all the requirements for controlled, powered flight and put them into use in an aircraft which took off from a level launching rail, with the aid of a headwind to achieve sufficient airspeed before reaching the end of the rail. It is one of the various candidates regarded as the First flying machine.
*1904 ŌĆō SS Haimun sends its first news story on 15 March 1904. Slattery, Peter. "Reporting the Russo-Japanese War,1904ŌĆō5", 2004
* 1903 ŌĆō The Wright brothers fly at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their airplane, the '' Wright Flyer'', performed the first recorded controlled, powered, sustained heavier than air flight on December 17, 1903. In the day's fourth flight, Wilbur Wright flew 279 meters (852 ft) in 59 seconds. First three flights were approximately 120, 175, and 200 ft (61 m), respectively. The Wrights laid particular stress on fully and accurately describing all the requirements for controlled, powered flight and put them into use in an aircraft which took off from a level launching rail, with the aid of a headwind to achieve sufficient airspeed before reaching the end of the rail. It is one of the various candidates regarded as the First flying machine.
*1904 ŌĆō SS Haimun sends its first news story on 15 March 1904. Slattery, Peter. "Reporting the Russo-Japanese War,1904ŌĆō5", 2004
/ref> It was a Chinese Steamboat, steamer ship commanded by war correspondent Lionel James in 1904 during the Russo-Japanese War for The Times. It is the first known instance of a "press boat" dedicated to war correspondence during naval battles. The recent advent of wireless telegraphy meant that reporters were no longer limited to submitting their stories from land-based offices, and The Times spent 74 days outfitting and equipping the ship, installing a De Forest transmitter aboard the ship.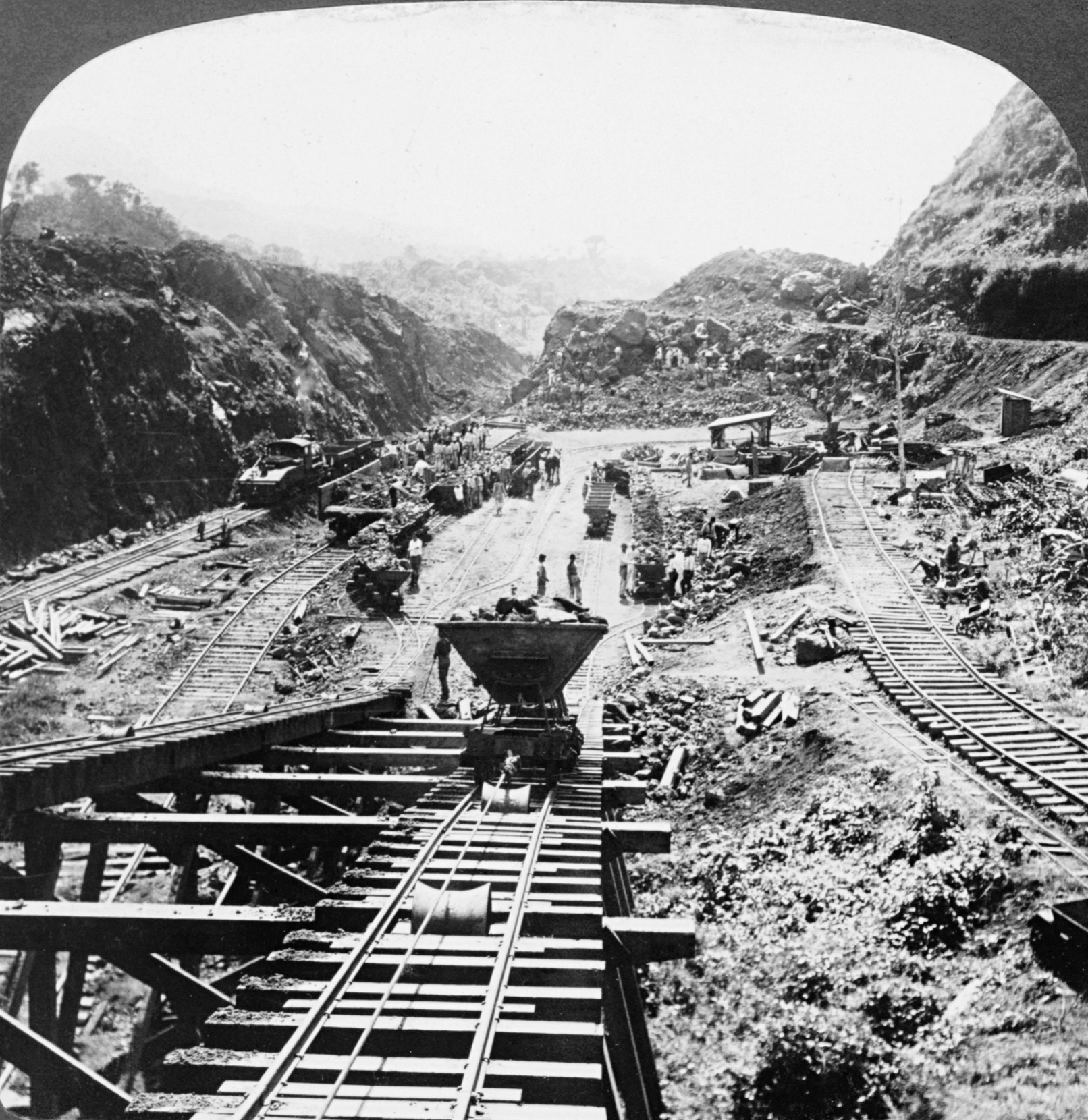 * 1904ŌĆō1914 ŌĆō The Panama Canal constructed by the United States in the territory of Panama, which had just gained independence from
* 1904ŌĆō1914 ŌĆō The Panama Canal constructed by the United States in the territory of Panama, which had just gained independence from  * 1907 ŌĆō The Autochrome Lumi├©re which was patented in 1903 becomes the first commercial color photography process.
* 1907 ŌĆō Thomas Edison invented the "Universal Electric Motor" which made it possible to operate dictation machines, etc. on all lighting circuits.
* 1907 ŌĆō The Photostat machine begins the modern era of document imaging. The Photostat machine was invented in
* 1907 ŌĆō The Autochrome Lumi├©re which was patented in 1903 becomes the first commercial color photography process.
* 1907 ŌĆō Thomas Edison invented the "Universal Electric Motor" which made it possible to operate dictation machines, etc. on all lighting circuits.
* 1907 ŌĆō The Photostat machine begins the modern era of document imaging. The Photostat machine was invented in  * 1908 ŌĆō Henry Ford of the Ford Motor Company introduces the
* 1908 ŌĆō Henry Ford of the Ford Motor Company introduces the
 The best selling books of the decade were ''
The best selling books of the decade were ''
 * Pablo Picasso paints '' Les Demoiselles d'Avignon'', considered by some to be the birth of modern art.
*
* Pablo Picasso paints '' Les Demoiselles d'Avignon'', considered by some to be the birth of modern art.
*
 * April 2, 1902 ŌĆō ''Electric Theatre'', the first
* April 2, 1902 ŌĆō ''Electric Theatre'', the first
1908 Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epicen ...
kills 75,000ŌĆō82,000 people and becomes the most destructive earthquake ever to strike Europe; America gains control over the Philippines in 1902, after the PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War
The PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War or FilipinoŌĆōAmerican War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang PilipinoŌĆōAmerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
; Rock being moved to construct the Panama Canal; Admiral Togo before the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:Õ»Šķ”¼µ▓¢µĄĘµł”, Tsushimaoki''-Kaisen'', russian: ą”čāčüąĖą╝čüą║ąŠąĄ čüčĆą░ąČąĄąĮąĖąĄ, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known as the Battle of Tsushima Strait and the Naval Battle of Sea of Japan (Japanese: µŚź ...
in 1905, part of the Russo-Japanese War, leading to Japanese victory and their establishment as a great power, while Russia's defeat eventually led to the 1905 Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
.
rect 2 2 249 161 Wright Flyer
rect 253 2 497 161 Atrocities in the Congo Free State
rect 250 165 497 334 1908 Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epicen ...
rect 250 338 497 488 PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War
The PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War or FilipinoŌĆōAmerican War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang PilipinoŌĆōAmerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
rect 2 338 246 488 Panama Canal
rect 2 165 123 334 Russo-Japanese War
rect 125 165 246 334 1905 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
East Bolton, Quebec
East Bolton (french: Bolton-Est) is a municipality of about 1,000 people, part of the Memphr├®magog Regional County Municipality in the Estrie region of Quebec, Canada.
It is the birthplace of Reginald Fessenden, radio pioneer who invented amplit ...
, Canada made what appeared to be the first audio radio broadcasts of entertainment and music ever made to a general audience.
First-wave feminism saw progress, with universities being opened for women in Japan, Bulgaria, Cuba, Russia, and Peru. In 1906, Finland granted women the right to vote, the first European country to do so. The foundation of the Women's Social and Political Union by Emmeline Pankhurst
Emmeline Pankhurst ('' n├®e'' Goulden; 15 July 1858 ŌĆō 14 June 1928) was an English political activist who organised the UK suffragette movement and helped women win the right to vote. In 1999, ''Time'' named her as one of the 100 Most Impo ...
in 1903 led to the rise of the Suffragettes
A suffragette was a member of an activist women's organisation in the early 20th century who, under the banner "Votes for Women", fought for the right to vote in public elections in the United Kingdom. The term refers in particular to members ...
in Great Britain and Ireland. Cuba, Bulgaria, and Norway became independent. The First Moroccan and Bosnian crises led to worsened tensions in Europe that would ultimately lead to the First World War in the next decade.
Wars of this decade included the PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War
The PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War or FilipinoŌĆōAmerican War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang PilipinoŌĆōAmerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
, the Second Boer War, the Thousand Days' War, the Anglo-Somali War, the KuwaitiŌĆōRashidi war, the SaudiŌĆōRashidi War, the Russo-Japanese War, and the Honduran-Nicaraguan War. The Scramble for Africa
The Scramble for Africa, also called the Partition of Africa, or Conquest of Africa, was the invasion, annexation, division, and colonisation of Africa, colonization of most of Africa by seven Western Europe, Western European powers during a ...
continued, with the Orange Free State, South African Republic, Ashanti Empire, Aro Confederacy, Sokoto Caliphate
The Sokoto Caliphate (), also known as the Fulani Empire or the Sultanate of Sokoto, was a Sunni Muslim caliphate in West Africa. It was founded by Usman dan Fodio in 1804 during the Fulani jihads after defeating the Hausa Kingdoms in the Ful ...
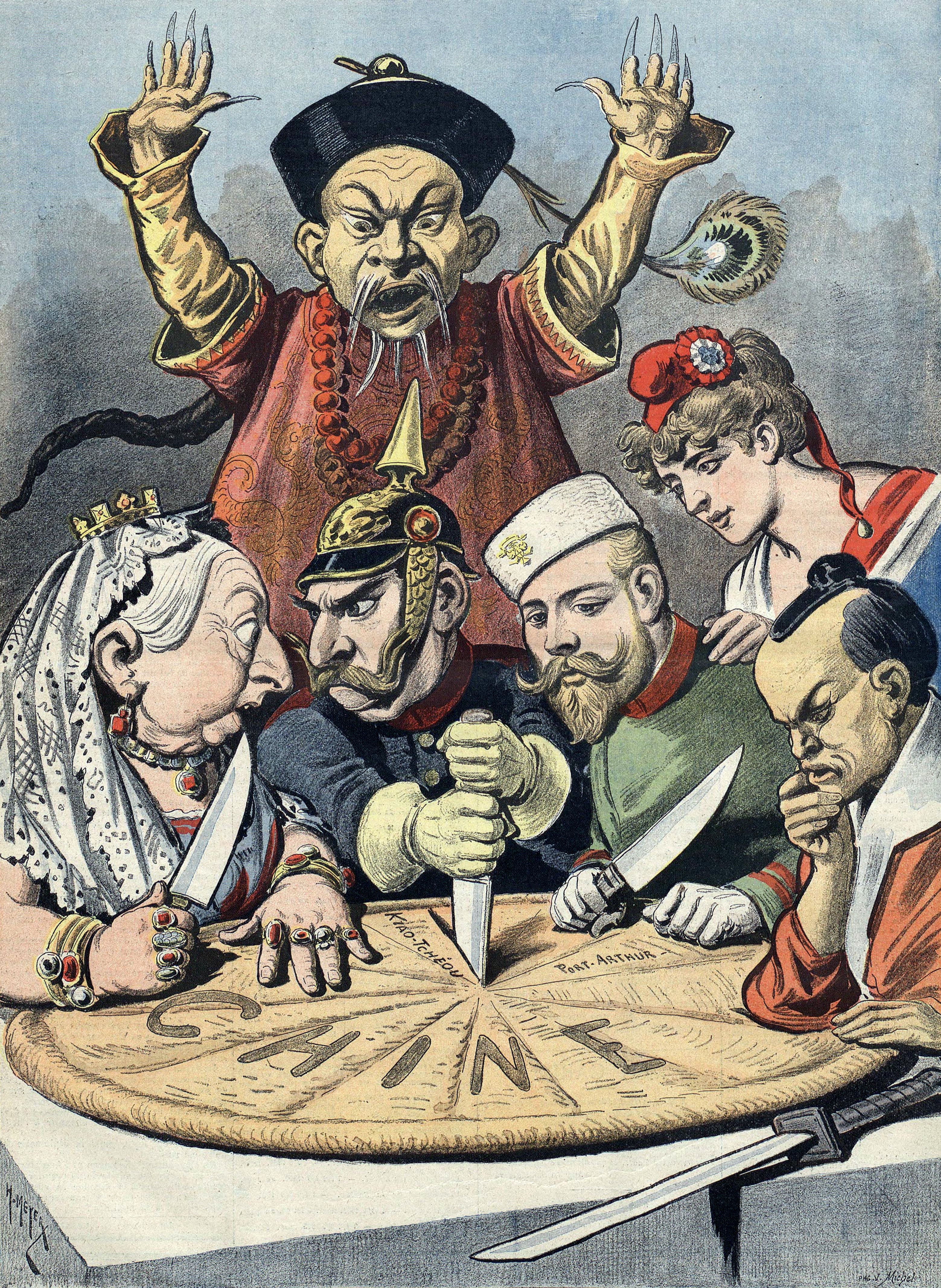
and Kano Emirate being conquered by the British Empire, alongside the French Empire conquering Borno, the German Empire conquering the Adamawa Emirate, and the Portuguese Empire conquering the Ovambo. Atrocities in the Congo Free State were committed by private companies and the '' Force Publique'', with a resultant population decline of 1 to 15 million. The Herero and Namaqua genocide saw 24,000 to 100,000 Hereros and 10,000 Namaqua killed by German colonial forces. The Adana massacre of 1909 saw up to 30,000 mainly Armenian civilians being massacred by local Ottoman Muslims.
Failed uprisings and revolutions that took place included the Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
, the Bailundo revolt, the IlindenŌĆōPreobrazhenie Uprising, the 1904 Sasun uprising
The Sasun uprising or Sasun rebellion of 1904 ( hy, šŹšĪšĮšĖųéšČš½ šźųĆš»ųĆšĖųĆšż šĪš║šĮš┐šĪš┤šóšĖųéš®š½ųéšČš©, ''Sasuni yerkrord apstambut'yun─Ģ'', literally Second Sassoun resistance) was an uprising by Armenian militia against the Ottoman Emp ...
, the Uruguayan Revolution of 1904, an uprising in French Madagascar, the Russian Revolution of 1905, the Argentine Revolution of 1905
The Argentine Revolution of 1905 also known as the Radical Revolution of 1905 was a civil-military uprising organized by the Radical Civic Union and headed by Hip├│lito Yrigoyen against the oligarchic dominance known as the ''Roquismo'' led by J ...
, the Persian Constitutional Revolution
The Persian Constitutional Revolution ( fa, ┘ģž┤ž▒┘łžĘ█īž¬, Mashr┼½tiyyat, or ''Enghel─üb-e Mashr┼½teh''), also known as the Constitutional Revolution of Iran, took place between 1905 and 1911. The revolution led to the establishment of a par ...
, the Maji Maji Rebellion, and the 1907 Romanian Peasants' revolt. A more successful revolution took place in the Ottoman Empire, where the Young Turks movement restored the Ottoman constitution of 1876, establishing the Second Constitutional Era.
Major disasters in this decade included the Chinese famine of 1907
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
, the 1908 Messina earthquake
The 1908 Messina earthquake (also known as the 1908 Messina and Reggio earthquake) occurred on 28 December in Sicily and Calabria, southern Italy with a moment magnitude of 7.1 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The epicen ...
, the San Francisco earthquake and fire and the Great Baltimore Fire. The first huge success of American cinema, as well as the largest experimental achievement to this point, was the 1903 film '' The Great Train Robbery'', directed by Edwin S. Porter, while the world's first feature film, '' The Story of the Kelly Gang'', was released on 26 December 1906 in Melbourne, Australia. Popular books of this decade included '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'' (1902) and ''Anne of Green Gables
''Anne of Green Gables'' is a 1908 novel by Canadian author Lucy Maud Montgomery (published as L. M. Montgomery). Written for all ages, it has been considered a classic children's novel since the mid-20th century. Set in the late 19th century, t ...
'' (1908), which sold 45 million and 50 million copies respectively. Popular songs of this decade include " Lift Every Voice and Sing" and " What Are They Doing in Heaven?", which have been featured in 42 and 16 hymnals respectively.
During the decade, the world population increased from 1.60 to 1.75 billion, with approximately 580 million births and 450 million deaths in total.
Pronunciation varieties
There are several main varieties of how individual years of the decade are pronounced. Using 1906 as an example, they are "nineteen-oh-six", "nineteen-six", and "nineteen-aught-six". Which variety is most prominent depends somewhat on global region and generation. "Nineteen-oh-six" is the most common; "nineteen-six" is less common. InAmerican English
American English, sometimes called United States English or U.S. English, is the set of variety (linguistics), varieties of the English language native to the United States. English is the Languages of the United States, most widely spoken lan ...
, "nineteen-aught-six" is also recognized but not much used.
Demographics
Estimates for the world population by 1900 vary from 1.563 to 1.710 billion.Politics and wars

Major political changes
* New Imperialism * The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland and the French Third Republic sign Entente CordialeWars
* Second Boer War ends. *PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War
The PhilippineŌĆōAmerican War or FilipinoŌĆōAmerican War ( es, Guerra filipina-estadounidense, tl, Digmaang PilipinoŌĆōAmerikano), previously referred to as the Philippine Insurrection or the Tagalog Insurgency by the United States, was an arm ...
takes place (1899ŌĆō1902).
*The KuwaitiŌĆōRashidi war takes place (1900ŌĆō1901).
* Russo-Japanese War establishes the Empire of Japan as a world power.
* Battle of Riyadh
The Battle of Riyadh was a minor battle in Riyadh, then part of the Emirate of Ha'il, fought between the Rashidi dynasty and the House of Saud in January 1902 that resulted in the latter's takeover of walled town by Ibn Saud. The battle is ...
was a minor battle of the Unification of Saudi Arabia.
* Battle of Dilam
Battle of Dilam was a major battle of the Unification War between Rashidi and Saudi rebels. It occurred on 27 January 1903, in the town of Dilam south of Riyadh, the capital of the present day Saudi Arabia.
A year after the Battle of Riyadh, ...
was a major battle of the Unification War
The Austro-Prussian War, also by many variant names such as Seven Weeks' War, German Civil War, Brothers War or Fraternal War, known in Germany as ("German War"), (; "German war of brothers") and by a variety of other names, was fought in 186 ...
between Rashidi and Saudi Saudi may refer to:
* Saudi Arabia
* Saudis, people from Saudi Arabia
* Saudi culture, the culture of Saudi Arabia
* House of Saud
The House of Saud ( ar, žó┘ä ž│┘Åž╣┘Å┘łž», ╩Š─Ćl Su╩┐┼½d ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is c ...
rebels.
* First SaudiŌĆōRashidi War was engaged between the Saudi loyal forces of the newborn Emirate of Riyadh versus the Emirate of Ha'il
The Emirate of Jabal Shammar ( ar, žź┘É┘ģ┘Äž¦ž▒┘Äž® ž¼┘Äž©┘Ä┘ä ž┤┘Ä┘ģ┘Ä┘æž▒), also known as the Emirate of Ha╩Šil () or the Rashidi Emirate (), was a state in the northern part of the Arabian Peninsula, including Najd, existing from the mid-n ...
.
*The Ottomans invade Persia and capture a strip of territory (1906).
Internal conflicts
* TheBoxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an anti-foreign, anti-colonial, and anti-Christian uprising in China between 1899 and 1901, towards the end of the Qing dynasty, by ...
ends.
* The Russian Revolution of 1905.
* The Mesopotamia uprising of 1906.
* Demand for Home Rule for Ireland.
* Herero and Namaqua Genocide in German South-West Africa
South West Africa ( af, Suidwes-Afrika; german: S├╝dwestafrika; nl, Zuidwest-Afrika) was a territory under South African administration from 1915 to 1990, after which it became modern-day Namibia. It bordered Angola (Portuguese colony before 1 ...
(modern Namibia).
* Kurdish uprising in Bitlis against the Ottoman Empire in 1907.
Colonization
* January 1, 1901, British colonies in Australia federate, forming the Commonwealth of Australia.Decolonization
* May 20, 1902 ŌĆō Cuba gains independence from the United States * June 7, 1905 ŌĆō The Norwegian Parliament declares the union with Sweden dissolved, and Norway achieves full independence. * October 5, 1908 ŌĆō Bulgaria declares its independence from the Ottoman Empire.Prominent political events
Disasters
Natural disasters
 * September 8, 1900 ŌĆō A powerful hurricane
* September 8, 1900 ŌĆō A powerful hurricane hits
Hits or H.I.T.S. may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Music
* ''H.I.T.S.'', 1991 album by New Kids on the Block
* ''...Hits'' (Phil Collins album), 1998
* ''Hits'' (compilation series), 1984ŌĆō2006; 2014 - a British compilation album se ...
Galveston, Texas
Galveston ( ) is a coastal resort city and port off the Southeast Texas coast on Galveston Island and Pelican Island in the U.S. state of Texas. The community of , with a population of 47,743 in 2010, is the county seat of surrounding Galvesto ...
, USA killing about 8,000.
* April 19, 1902 ŌĆō A magnitude 7.5 earthquake rocks Guatemala
Guatemala ( ; ), officially the Republic of Guatemala ( es, Rep├║blica de Guatemala, links=no), is a country in Central America. It is bordered to the north and west by Mexico; to the northeast by Belize and the Caribbean; to the east by H ...
, killing 2,000.
* May 8, 1902 ŌĆō In Martinique, Mount Pel├®e erupts, destroying the town of Saint-Pierre and killing over 30,000.
* April 7, 1906 ŌĆō Mount Vesuvius erupts and devastates Naples.
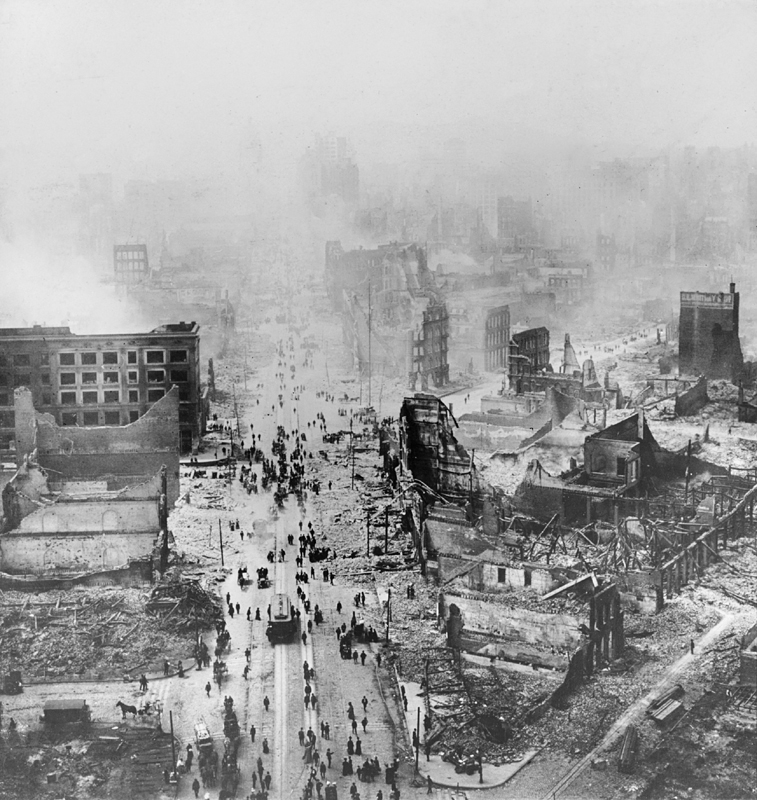
* April 18, 1906 ŌĆō The 1906 San Francisco earthquake
At 05:12 Pacific Standard Time on Wednesday, April 18, 1906, the coast of Northern California was struck by a major earthquake with an estimated moment magnitude of 7.9 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). High-intensity sha ...
(estimated magnitude 7.8) on the San Andreas Fault destroys much of San Francisco, USA, killing at least 3,000, with 225,000ŌĆō300,000 left homeless, and $350 million in damages.
* September 18, 1906 ŌĆō A typhoon and tsunami kill an estimated 10,000 in Hong Kong.
* January 14, 1907 ŌĆō An earthquake in Kingston, Jamaica kills more than 1,000.
* June 30, 1908 ŌĆō The Tunguska event or "Russian explosion" near the Podkamennaya Tunguska River in Krasnoyarsk Krai, Siberia, Russian Empire occuers resulting in the flattening 2,000 km2 (770 sq mi) of forest. It is believed to have been caused by the air burst
An air burst or airburst is the detonation of an explosive device such as an anti-personnel artillery shell or a nuclear weapon in the air instead of on contact with the ground or target. The principal military advantage of an air burst over ...
of a large meteoroid or comet fragment, at an altitude of above the Earth's surface.
* December 28, 1908 ŌĆō An earthquake and tsunami destroys Messina
Messina (, also , ) is a harbour city and the capital of the Italian Metropolitan City of Messina. It is the third largest city on the island of Sicily, and the 13th largest city in Italy, with a population of more than 219,000 inhabitants in ...
, Sicily and Calabria
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 =
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographics1_title1 =
, demographics1_info1 =
, demographics1_title2 ...
, killing over 80,000 people.
Non-natural disasters
* April 26, 1900 ŌĆō The Great Lumber Fire ofOttawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
ŌĆōHull
Hull may refer to:
Structures
* Chassis, of an armored fighting vehicle
* Fuselage, of an aircraft
* Hull (botany), the outer covering of seeds
* Hull (watercraft), the body or frame of a ship
* Submarine hull
Mathematics
* Affine hull, in affi ...
kills 7 and leaves 15,000 homeless.
* May 1, 1900 ŌĆō The Scofield Mine disaster in Scofield, Utah caused by explosion killing at least 200 men.
* June 30, 1900 ŌĆō Hoboken Docks Fire: The German passenger ships ''Saale'', ''Main, Bremen'', and ''Kaiser William der Grosse'', all owned by the North German Lloyd Steamship line, catch fire at the docks in Hoboken, New Jersey, USA . The fire began on a wharf and spread to the adjacent piers, warehouses, and smaller craft, killing 326 people.
* May 3, 1901 ŌĆō The Great Fire of 1901 begins in Jacksonville, FL, USA .
*July 10, 1902 ŌĆō The Rolling Mill Mine disaster in Johnstown, Pennsylvania, USA, kills 112 miners.
* August 10, 1903 ŌĆō Paris M├®tro train fire
The disastrous Paris M├®tro train fire occurred on the evening of 10 August 1903, on what was then Line 2 Nord of the system and is now Paris M├®tro Line 2. There were 84 deaths, most at Couronnes station, so it is also known as the Couronnes D ...
.
* December 30, 1903 ŌĆō A fire at the Iroquois Theater in Chicago, USA kills 600.
* February 7, 1904 ŌĆō The Great Baltimore Fire in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic, and the 30th most populous city in the United States with a population of 585,708 in 2020. Baltimore was d ...
, USA destroys over 1,500 buildings in 30 hours.
* June 15, 1904 ŌĆō A fire aboard the steamboat ''General Slocum
The PS ''General Slocum''"PS" stands for "Paddle Steamer" was a sidewheel passenger steamboat built in Brooklyn, New York, in 1891. During her service history, she was involved in a number of mishaps, including multiple groundings and collision ...
'' in New York City's East River kills 1,021.
* June 28, 1904 ŌĆō The Danish ocean liner runs aground and sinks close to Rockall, killing 635, including 225 Norwegian emigrants.
* January 22, 1906 ŌĆō The strikes a reef off Vancouver Island, Canada, killing over 100 (officially 136) in the ensuing disaster.
Assassinations and attempts
Prominent assassinations, targeted killings, and assassination attempts include: * July 29, 1900 ŌĆō King Umberto I of Italy is assassinated by Italian-born anarchist Gaetano Bresci. * March 6, 1901 ŌĆō InBremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Br├żm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the German state Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consis ...
, an assassin attempts to kill Wilhelm II of Germany.
* September 6, 1901 ŌĆō American anarchist Leon Czolgosz shoots U.S. President William McKinley at the Pan-American Exposition in Buffalo, New York. McKinley dies 8 days later.
* June 16, 1904 ŌĆō Eugen Schauman assassinates Nikolai Bobrikov
Nikolay Ivanovich Bobrikov (russian: ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░╠üą╣ ąśą▓ą░╠üąĮąŠą▓ąĖčć ąæąŠ╠üą▒čĆąĖą║ąŠą▓; in St. Petersburg ŌĆō June 17, 1904 in Helsinki, Grand Duchy of Finland) was a Russian general and politician. He was the Governor-General of Finla ...
, Governor-General of Finland.
* February 1, 1908 ŌĆō Carlos I of Portugal is assassinated in Lisbon, Portugal.
* October 26, 1909 ŌĆō It┼Ź Hirobumi, four time Prime Minister of Japan (the 1st, 5th, 7th and 10th) and Resident-General of Korea, is assassinated by Ahn Jung-geun at the Harbin
Harbin (; mnc, , v=Halbin; ) is a sub-provincial city and the provincial capital and the largest city of Heilongjiang province, People's Republic of China, as well as the second largest city by urban population after Shenyang and largest ...
train station in Manchuria.
Economics
The cost of an American postage stamp was worth 1 cent.Science and technology
Science
 * March 17, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes his paper "On a heuristic viewpoint concerning the production and transformation of light", in which he explains the photoelectric effect, using the notion of light quanta. For this paper Einstein received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
* May 11, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his doctoral dissertation "On the Motion of Small Particles...", in which he explains Brownian motion.
* June 30, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes the article "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", where he reveals his theory of special relativity.
* September 27, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his paper "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", in which he develops an argument for the famous equation ''E'' = ''mc''2.
* Planck's law of black-body radiation
* Seismographs built in the University of California, Berkeley, in 1900
* Practical
* March 17, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes his paper "On a heuristic viewpoint concerning the production and transformation of light", in which he explains the photoelectric effect, using the notion of light quanta. For this paper Einstein received the Nobel Prize for Physics in 1921.
* May 11, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his doctoral dissertation "On the Motion of Small Particles...", in which he explains Brownian motion.
* June 30, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein publishes the article "On the Electrodynamics of Moving Bodies", where he reveals his theory of special relativity.
* September 27, 1905 ŌĆō Annus Mirabilis papers ŌĆō Albert Einstein submits his paper "Does the Inertia of a Body Depend Upon Its Energy Content?", in which he develops an argument for the famous equation ''E'' = ''mc''2.
* Planck's law of black-body radiation
* Seismographs built in the University of California, Berkeley, in 1900
* Practical air conditioner
Air conditioning, often abbreviated as A/C or AC, is the process of removing heat from an enclosed space to achieve a more comfortable interior environment (sometimes referred to as 'comfort cooling') and in some cases also strictly controlling ...
designed by Willis Carrier in 1902
* Geiger counter
A Geiger counter (also known as a GeigerŌĆōM├╝ller counter) is an electronic instrument used for detecting and measuring ionizing radiation. It is widely used in applications such as radiation dosimetry, radiological protection, experimental ph ...
(measures radioactivity) invented by Hans Geiger in 1908
* Pierre
Pierre is a masculine given name. It is a French form of the name Peter. Pierre originally meant "rock" or "stone" in French (derived from the Greek word ŽĆ╬ŁŽäŽü╬┐Žé (''petros'') meaning "stone, rock", via Latin "petra"). It is a translation ...
and Marie Curie discover radium and polonium, they coin the term ' radioactivity'.
* Third law of thermodynamics by Walther Nernst
Walther Hermann Nernst (; 25 June 1864 ŌĆō 18 November 1941) was a German chemist known for his work in thermodynamics, physical chemistry, electrochemistry, and solid state physics. His formulation of the Nernst heat theorem helped pave the wa ...
* Quantum Hypothesis by Max Planck in 1900
* The Bacillus Calmette-Gu├®rin (BCG) immunization for tuberculosis is first developed.
Technology
* Widespread application of the internal combustion engine including mass production of the automobile. Rudolf Diesel demonstrated the diesel engine in the 1900 '' Exposition Universelle'' (World's Fair) in Paris using peanut oil fuel (see biodiesel). The Diesel engine takes the Grand Prix. The exposition was attended by 50 million people. The same year Wilhelm Maybach designed an engine built at Daimler Motoren GesellschaftŌĆöfollowing the specifications of Emil JellinekŌĆöwho required the engine to be named ''Daimler-Mercedes'' after his daughter,Merc├®d├©s Jellinek
Merc├®d├©s Adrienne Ramona Manuela Jellinek (16 September 1889 ŌĆō 23 February 1929) was the daughter of Austrian automobile entrepreneur Emil Jellinek and his first wife Rachel Goggmann Cenrobert. She was born in Vienna. She is best known ...
. In 1902, the Mercedes 35 hp automobiles with that engine were put into production by DMG.
* Wide popularity of home phonograph
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
. "The market for home machines was created through technological innovation and pricing: Phonographs, gramophones, and graphophones were cleverly adapted to run by spring-motors (you wound them up), rather than by messy batteries or treadle mechanisms, while the musical records were adapted to reproduce loudly through a horn attachment. The cheap home machines sold as the $10 Eagle graphophone and the $40 (later $30) Home phonograph in 1896, the $20 Zon-o-phone in 1898, the $3 Victor Toy in 1900, and so on. Records sold because their fidelity improved, mass production processes were soon developed, advertising worked, and prices dropped from one and two dollars to around 35 cents.". In 1907, a Victor Records recording of Enrico Caruso
Enrico Caruso (, , ; 25 February 1873 ŌĆō 2 August 1921) was an Italian operatic first lyrical tenor then dramatic tenor. He sang to great acclaim at the major opera houses of Europe and the Americas, appearing in a wide variety of roles (74) ...
singing Ruggero Leoncavallo's " Vesti la giubba" becomes the first to sell a million copies.
* 1899ŌĆō1900 ŌĆō Thomas Alva Edison of Milan, Ohio, invents the nickel-alkaline storage battery. On May 27, 1901, Edison establishes the Edison Storage Battery Company to develop and manufacture them. "It proved to be Edison's most difficult project, taking ten years to develop a practical alkaline battery. By the time Edison introduced his new alkaline battery, the gasoline powered car had so improved that electric vehicle
An electric vehicle (EV) is a vehicle that uses one or more electric motors for propulsion. It can be powered by a collector system, with electricity from extravehicular sources, or it can be powered autonomously by a battery (sometimes cha ...
s were becoming increasingly less common, being used mainly as delivery vehicles in cities. However, the Edison alkaline battery proved useful for lighting railway cars
A railroad car, railcar (American and Canadian English), railway wagon, railway carriage, railway truck, railwagon, railcarriage or railtruck (British English and UIC), also called a train car, train wagon, train carriage or train truck, is ...
and signals, maritime buoy
A buoy () is a floating device that can have many purposes. It can be anchored (stationary) or allowed to drift with ocean currents.
Types
Navigational buoys
* Race course marker buoys are used for buoy racing, the most prevalent form of yac ...
s, and miners lamps. Unlike iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
mining with the Edison Ore-Milling Company, the heavy investment Edison made over ten years was repaid handsomely, and the storage battery eventually became Edison's most profitable product. Further, Edison's work paved the way for the modern alkaline battery."
* 1900 ŌĆō The Brownie camera is invented; this was the beginning of the Eastman Kodak
The Eastman Kodak Company (referred to simply as Kodak ) is an American public company that produces various products related to its historic basis in analogue photography. The company is headquartered in Rochester, New York, and is incorpor ...
company. The Brownie popularized low-cost photography and introduced the concept of the snapshot. The first Brownie was introduced in February 1900,
 * 1900 ŌĆō The first zeppelin flight occurs over
* 1900 ŌĆō The first zeppelin flight occurs over Lake Constance
Lake Constance (german: Bodensee, ) refers to three Body of water, bodies of water on the Rhine at the northern foot of the Alps: Upper Lake Constance (''Obersee''), Lower Lake Constance (''Untersee''), and a connecting stretch of the Rhine, ca ...
near Friedrichshafen, Germany on July 2, 1900.
 * 1901 ŌĆō First electric typewriter is invented by George Canfield Blickensderfer of Erie, Pennsylvania. It was part of a line of Blickensderfer typewriters, known for its portability.
* 1901 ŌĆō Wilhelm Kress of Saint Petersburg, Russia creates his Kress Drachenflieger in Austria-Hungary. Power was provided by a Daimler petrol engine driving two large
* 1901 ŌĆō First electric typewriter is invented by George Canfield Blickensderfer of Erie, Pennsylvania. It was part of a line of Blickensderfer typewriters, known for its portability.
* 1901 ŌĆō Wilhelm Kress of Saint Petersburg, Russia creates his Kress Drachenflieger in Austria-Hungary. Power was provided by a Daimler petrol engine driving two large auger
Auger may refer to:
Engineering
* Wood auger, a drill for making holes in wood (or in the ground)
** Auger bit, a drill bit
* Auger conveyor, a device for moving material by means of a rotating helical flighting
* Auger (platform), the world's f ...
-style two-bladed propellers, the first attempt to use an internal combustion engine to power a heavier-than-air aircraft.Nicolaou, Stephane (1998). Flying Boats & Seaplanes: A History from 1905. Osceola: Zenith.
, p. 10
* 1901 ŌĆō The first radio receiver (successfully received a radio transmission). This receiver was developed by Guglielmo Marconi
Guglielmo Giovanni Maria Marconi, 1st Marquis of Marconi (; 25 April 187420 July 1937) was an Italians, Italian inventor and electrical engineering, electrical engineer, known for his creation of a practical radio wave-based Wireless telegrap ...
. Marconi established a wireless transmitting station at Marconi House, Rosslare Strand, County Wexford
County Wexford ( ga, Contae Loch Garman) is a county in Ireland. It is in the province of Leinster and is part of the Southern Region. Named after the town of Wexford, it was based on the historic Gaelic territory of Hy Kinsella (''U├Ł Ceinns ...
, Ireland in 1901 to act as a link between Poldhu
Poldhu is a small area in south Cornwall, England, UK, situated on the Lizard Peninsula; it comprises Poldhu Point and Poldhu Cove. Poldhu means "black pool" in Cornish. Poldhu lies on the coast of Mount's Bay and is in the northern part of th ...
in Cornwall and Clifden in County Galway
"Righteousness and Justice"
, anthem = ()
, image_map = Island of Ireland location map Galway.svg
, map_caption = Location in Ireland
, area_footnotes =
, area_total_km2 = ...
. He soon made the announcement that on 12 December 1901, using a kite-supported antenna for reception, the message was received at Signal Hill in St John
Saint John or St. John usually refers to John the Baptist, but also, sometimes, to John the Apostle.
Saint John or St. John may also refer to:
People
* John the Baptist (0s BCŌĆō30s AD), preacher, ascetic, and baptizer of Jesus Christ
* John t ...
's, Newfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
(now part of Canada), signals transmitted by the company's new high-power station at Poldhu, Cornwall. The distance between the two points was about . Heralded as a great scientific advance, there wasŌĆöand continues to beŌĆösome skepticism about this claim, partly because the signals had been heard faintly and sporadically. There was no independent confirmation of the reported reception, and the transmissions, consisting of the Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
letter ''S'' sent repeatedly, were difficult to distinguish from atmospheric noise. (A detailed technical review of Marconi's early transatlantic work appears in John S. Belrose's work of 1995.) The Poldhu transmitter was a two-stage circuit. The first stage operated at a lower voltage and provided the energy for the second stage to spark at a higher voltage.
* 1902 ŌĆō Willis Carrier of Angola, New York, invented the first indoor air conditioning. "He designed his spray driven air conditioning system which controlled both temperature and humidity using a nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, a ...
originally designed to spray insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed to b ...
. He built his "Apparatus for Treating Air" (U.S. Pat. #808897) which was patented in 1906 and using chilled coils which not only controlled heat but could lower the humidity to as low as 55%. The device was even able to adjust the humidity level to the desired setting creating what would become the framework for the modern air conditioner. By adjusting the air movement and temperature level to the refrigeration coils he was able to determine the size and capacity of the unit to match the need of his customers. While Carrier was not the first to design a system like this his was much more stable, successful and safer than other versions and took air conditioning out of the Dark Ages and into the realm of science."
* 1902/1906/1908 ŌĆō Sir James Mackenzie
Sir James Mackenzie (12 April 1853 ŌĆō 26 January 1925) was a Scottish cardiologist who was a pioneer in the study of cardiac arrhythmias. Due to his work in the cardiac field he is known as a research giant in primary care, and was knighted by ...
of Scone, Scotland invented an early lie detector or polygraph. MacKenzie's polygraph "could be used to monitor the cardiovascular responses of his patients by taking their pulse and blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure" r ...
. He had developed an early version of his device in the 1890s, but had Sebastian Shaw, a Lancashire watchmaker, improve it further. "This instrument used a clockwork mechanism for the paper-rolling and time-marker movements and it produced ink recordings of physiological functions that were easier to acquire and to interpret. It has been written that the modern polygraph is really a modification of Dr. Mackenzie's clinical ink polygraph." A more modern and effective polygraph machine would be invented by John Larson in 1921.
* 1902 ŌĆō Georges Claude
Georges Claude (24 September 187023 May 1960) was a French engineer and inventor. He is noted for his early work on the industrial liquefaction of air, for the invention and commercialization of neon lighting, and for a large experiment on genera ...
invented the neon lamp. He applied an electrical discharge to a sealed tube of neon
Neon is a chemical element with the symbol Ne and atomic number 10. It is a noble gas. Neon is a colorless, odorless, inert monatomic gas under standard conditions, with about two-thirds the density of air. It was discovered (along with krypton ...
gas, resulting in a red glow. Claudes started working on neon tubes which could be put to use as ordinary light bulbs. His first public display of a neon lamp took place on December 11, 1910, in Paris. In 1912, Claude's associate began selling neon discharge tubes as advertising signs. They were introduced to U.S. in 1923 when two large neon signs were bought by a Los Angeles Packard
Packard or Packard Motor Car Company was an American luxury automobile company located in Detroit, Michigan. The first Packard automobiles were produced in 1899, and the last Packards were built in South Bend, Indiana in 1958.
One of the "Thr ...
car dealership. The glow and arresting red color made neon advertising completely different from the competition.
* 1902 ŌĆō Teasmade
A teasmade is a machine for making tea automatically, which was once common in the United Kingdom and some Commonwealth countries. Teasmades generally include an analogue alarm clock and are designed to be used at the bedside, to ensure tea is ...
, a device for making tea automatically, is patented on 7 April 1902 by gunsmith
A gunsmith is a person who repairs, modifies, designs, or builds guns. The occupation differs from an armorer, who usually replaces only worn parts in standard firearms. Gunsmiths do modifications and changes to a firearm that may require a very h ...
Frank Clarke of Birmingham, England. He called it "An Apparatus Whereby a Cup of Tea or Coffee is Automatically Made" and it was later marketed as "A Clock That Makes Tea!". However, his original machine and all rights to it had been purchased from its actual inventor Albert E. Richardson Albert Edward Richardson may refer to:
* Albert Richardson (architect) (1880ŌĆō1964), English architect
* Albert E. Richardson (inventor), English inventor who designed the first practical Teasmade See also
* Albert Richardson (disambiguation)
...
, a clockmaker from Ashton-under-Lyne. The device was commercially available by 1904.
 * 1902 ŌĆō
* 1902 ŌĆō Lyman Gilmore
Lyman Wiswell Gilmore, Jr. (June 11, 1874 – February 18, 1951) was an aviation pioneer. In Grass Valley, California, he built a steam-powered airplane and claimed that he flew it on May 15, 1902. Due to the requirement of a heavy boiler and ...
of Washington, United States is awarded a patent for a steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be trans ...
, intended for use in aerial vehicles. At the time he was living in Red Bluff, California. At a later date, Gilmore claimed to have incorporated his engine in "a monoplane with a 32 foot wingspan". Performing his debut flight in May 1902. While occasionally credited with the first powered flight in aviation history, there is no supporting evidence for his account. While Gilmore was probably working on aeronautical experiments since the late 1890s and reportedly had correspondence with Samuel Pierpont Langley, there exists no photo of his creations earlier than 1908.
* 1902 ŌĆō The Wright brothers of Ohio, United States create the 1902 version of the Wright Glider. It was the third free-flight glider built by them and tested at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. This was the first of the brothers' gliders to incorporate yaw control, and its design led directly to the 1903 ''Wright Flyer''. The brothers designed the 1902 glider during the winter of 1901ŌĆō1902 at their home in Dayton, Ohio. They designed the wing based on data from extensive airfoil tests conducted on a homemade wind tunnel. They built many of the components of the glider in Dayton, but they completed assembly at their Kitty Hawk camp in September 1902. They began testing on September 19. Over the next five weeks, they made between 700 and 1000 glide flights (as estimated by the brothers, who did not keep detailed records of these tests). The longest of these was 622.5 ft (189.7 m) in 26 seconds. "In its final form, the 1902 Wright glider was the world's first fully controllable aircraft."
 * 1903 ŌĆō Ford Motor Company produces its first car ŌĆō the Ford Model A.
* 1903 ŌĆō Ford Motor Company produces its first car ŌĆō the Ford Model A.
 * 1903 ŌĆō Richard Pearse of New Zealand supposedly successfully flew and landed a powered heavier-than-air machine on 31 March 1903 Verifiable eyewitnesses describe Pearse crashing into a hedge on two separate occasions during 1903. His monoplane must have risen to a height of at least three metres on each occasion. Good evidence exists that on 31 March 1903 Pearse achieved a powered, though poorly controlled, flight of several hundred metres. Pearse himself said that he had made a powered takeoff, "but at too low a speed for iscontrols to work". However, he remained airborne until he crashed into the hedge at the end of the field.
* 1903 ŌĆō
* 1903 ŌĆō Richard Pearse of New Zealand supposedly successfully flew and landed a powered heavier-than-air machine on 31 March 1903 Verifiable eyewitnesses describe Pearse crashing into a hedge on two separate occasions during 1903. His monoplane must have risen to a height of at least three metres on each occasion. Good evidence exists that on 31 March 1903 Pearse achieved a powered, though poorly controlled, flight of several hundred metres. Pearse himself said that he had made a powered takeoff, "but at too low a speed for iscontrols to work". However, he remained airborne until he crashed into the hedge at the end of the field.
* 1903 ŌĆō Karl Jatho
Karl Jatho ( 3 February 1873 ŌĆō 8 December 1933) was a German inventor and aviation pioneer, performer and public servant of the city of Hanover.
Achievements and claims to precedence over the Wright brothers
From August through November 1903 ...
of Germany performs a series of flights at Vahrenwalder Heide, near Hanover, between August and November, 1903. Using first a pusher triplane, then a biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While ...
. "His longest flight, however, was only 60 meters at 3ŌĆō4 meters altitude." He then quit his efforts, noting his motor was too weak to make longer or higher flights. The plane was equipped with a single-cylinder 10 horsepower (7.5 kW) Buchet engine driving a two-bladed pusher propeller and made hops of up to 200 ft (60 m), flying up to 10 ft (3 m) high. In comparison, Orville Wright's first controlled flight four months later was of 36 m (120 ft) in 12 seconds although Wilbur flew 59 seconds and later that same day. Either way Jatho managed to fly a powered heavier-than-air machine earlier than his American counterparts.
* 1903 ŌĆō Mary Anderson invented windshield wipers. In November 1903 Anderson was granted her first patent for an automatic car window cleaning device controlled inside the car, called the windshield wiper. Her device consisted of a lever and a swinging arm with a rubber blade. The lever could be operated from inside a vehicle to cause the spring-loaded arm to move back and forth across the windshield. Similar devices had been made earlier, but Anderson's was the first to be effective.
 * 1903 ŌĆō The Wright brothers fly at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their airplane, the '' Wright Flyer'', performed the first recorded controlled, powered, sustained heavier than air flight on December 17, 1903. In the day's fourth flight, Wilbur Wright flew 279 meters (852 ft) in 59 seconds. First three flights were approximately 120, 175, and 200 ft (61 m), respectively. The Wrights laid particular stress on fully and accurately describing all the requirements for controlled, powered flight and put them into use in an aircraft which took off from a level launching rail, with the aid of a headwind to achieve sufficient airspeed before reaching the end of the rail. It is one of the various candidates regarded as the First flying machine.
*1904 ŌĆō SS Haimun sends its first news story on 15 March 1904. Slattery, Peter. "Reporting the Russo-Japanese War,1904ŌĆō5", 2004
* 1903 ŌĆō The Wright brothers fly at Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. Their airplane, the '' Wright Flyer'', performed the first recorded controlled, powered, sustained heavier than air flight on December 17, 1903. In the day's fourth flight, Wilbur Wright flew 279 meters (852 ft) in 59 seconds. First three flights were approximately 120, 175, and 200 ft (61 m), respectively. The Wrights laid particular stress on fully and accurately describing all the requirements for controlled, powered flight and put them into use in an aircraft which took off from a level launching rail, with the aid of a headwind to achieve sufficient airspeed before reaching the end of the rail. It is one of the various candidates regarded as the First flying machine.
*1904 ŌĆō SS Haimun sends its first news story on 15 March 1904. Slattery, Peter. "Reporting the Russo-Japanese War,1904ŌĆō5", 2004/ref> It was a Chinese Steamboat, steamer ship commanded by war correspondent Lionel James in 1904 during the Russo-Japanese War for The Times. It is the first known instance of a "press boat" dedicated to war correspondence during naval battles. The recent advent of wireless telegraphy meant that reporters were no longer limited to submitting their stories from land-based offices, and The Times spent 74 days outfitting and equipping the ship, installing a De Forest transmitter aboard the ship.
 * 1904ŌĆō1914 ŌĆō The Panama Canal constructed by the United States in the territory of Panama, which had just gained independence from
* 1904ŌĆō1914 ŌĆō The Panama Canal constructed by the United States in the territory of Panama, which had just gained independence from Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North AmericaŌĆönear Nicaragua's Caribbean coastŌĆöas well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
. The Canal is a ship canal that joins the Atlantic Ocean and the Pacific Ocean and a key conduit for international maritime trade. One of the largest and most difficult engineering projects ever undertaken, the canal had an enormous impact on shipping between the two oceans, replacing the long and treacherous route via the Drake Passage and Cape Horn at the southernmost tip of South America. A ship sailing from New York to San Francisco via the canal travels , well under half the route around Cape Horn. The project starts on May 4, 1904, known as Acquisition Day. The United States government purchased all Canal properties on the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panam├Ī), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
from the New Panama Canal Company, except the Panama Railroad. The project begun under the administration of Theodore Roosevelt, continued in that of William Howard Taft and completed in that of Woodrow Wilson. The Chief engineers were John Frank Stevens and George Washington Goethals
* 1904 ŌĆō The Welte-Mignon reproducing piano is created by Edwin Welte and Karl Bockisch. Both employed by the "Michael Welte und S├Čhne" firm of Freiburg im Breisgau
Freiburg im Breisgau (; abbreviated as Freiburg i. Br. or Freiburg i. B.; Low Alemannic German, Low Alemannic: ''Friburg im Brisgau''), commonly referred to as Freiburg, is an independent city in Baden-W├╝rttemberg, Germany. With a population o ...
, Germany. "It automatically replayed the tempo, phrasing, dynamics and pedalling of a particular performance, and not just the notes of the music, as was the case with other player pianos of the time." In September, 1904, the Mignon was demonstrated in the Leipzig Trade Fair
The Leipzig Trade Fair (german: Leipziger Messe) is a major trade fair, which traces its roots back for nearly a millennium. After the Second World War, Leipzig fell within the territory of East Germany, whereupon the Leipzig Trade Fair became o ...
. In March, 1905 it became better known when showcased "at the showrooms of Hugo Popper, a manufacturer of roll-operated orchestrion
Orchestrion is a generic name for a machine that plays music and is designed to sound like an orchestra or band. Orchestrions may be operated by means of a large pinned cylinder or by a music roll and less commonly book music. The sound is us ...
s". By 1906, the Mignon was also exported to the United States, installed to pianos by the firms Feurich
Feurich (Feurich Pianoforte GmbH) is a piano company founded in 1851 in Leipzig, Germany, by Julius Gustav Feurich, which has been family operated for five generations. The company is renowned for the quality of its pianos.
Since 2011, Feurich ...
and Steinway & Sons
Steinway & Sons, also known as Steinway (), is a German-American piano company, founded in 1853 in Manhattan by German piano builder Henry E. Steinway, Heinrich Engelhard Steinweg (later known as Henry E. Steinway). The company's growth led to ...
.
* 1904 ŌĆō Benjamin Holt of the Holt Manufacturing Company invents one of the first practical continuous track
Continuous track is a system of vehicle propulsion used in tracked vehicles, running on a continuous band of treads or track plates driven by two or more wheels. The large surface area of the tracks distributes the weight of the vehicle b ...
s for use in tractors. While the date of invention was reportedly November 24, 1904, Holt would not receive a patent until December, 1907.
* 1905 ŌĆō John Joseph Montgomery of California, United States designs tandem-wing gliders. His pilot Daniel Maloney performs a number of public exhibitions of high altitude flights in March and April 1905 in the Santa Clara, California, area. These flights received national media attention and demonstrated superior control of the design, with launches as high as 4,000 feet (1,200 m) and landings made at predetermined locations. The gliders were launched from balloons.
* 1905 ŌĆō The Wright Brothers introduce their Wright Flyer III. On October 5, 1905, Wilbur flew in 39 minutes 23 seconds, longer than the total duration of all the flights of 1903
Events January
* January 1 – Edward VII is proclaimed Emperor of India.
* January 19 – The first westŌĆōeast transatlantic radio broadcast is made from the United States to England (the first eastŌĆōwest broadcast having been ...
and 1904
Events
January
* January 7 ŌĆō The distress signal ''CQD'' is established, only to be replaced 2 years later by ''SOS''.
* January 8 ŌĆō The Blackstone Library is dedicated, marking the beginning of the Chicago Public Library system.
* ...
. Ending with a safe landing when the fuel ran out. The flight was seen by a number of people, including several invited friends, their father Milton, and neighboring farmers. Four days later, they wrote to the United States Secretary of War William Howard Taft, offering to sell the world's first practical fixed-wing aircraft.
* 1906 ŌĆō The ''Gabel Automatic Entertainer'', an early jukebox-like machine, is invented by John Gabel. It is the first such device to play a series of gramophone records. "The Automatic Entertainer with 24 selections, was produced and patented by the John Gabel owned company in Chicago. The first model (constructed in 1905) was produced in 1906 with an exposed 40 inch horn (102 cm) on top, and it is today often considered the real father of the modern multi-selection disc-playing phonographs. John Gabel and his company did in fact receive a special prize at the Pan-Pacific Exposition for the Automatic Entertainer."
*1906 ŌĆō The Victor Talking Machine Company releases the Victrola, the most popular gramophone
A phonograph, in its later forms also called a gramophone (as a trademark since 1887, as a generic name in the UK since 1910) or since the 1940s called a record player, or more recently a turntable, is a device for the mechanical and analogu ...
model until the late 1920s. The Victrola is also the first playback
Playback or Play Back may refer to:
Film
* ''Playback'' (1962 film), a British film in the ''Edgar Wallace Mysteries'' series
* ''Playback'', a 1996 film starring Shannon Whirry
* ''Playback'' (2012 film), an American horror film by Michael A. N ...
machine containing an internal horn. Victor also erects the world's largest illuminated billboard at the time, on Broadway in New York City, to advertise the company's records.
* 1906 ŌĆō Traian Vuia of Romania takes off with his "Traian Vuia 1", an early monoplane. His flight was performed in Montesson near Paris and was about 12 meters long.
* 1906 ŌĆō Jacob Ellehammer of Denmark constructs the Ellehammer semi-biplane __NOTOC__
The Ellehammer Semi-biplane was a pioneering aircraft flown in Denmark in 1906. Jacob Ellehammer built the aircraft based on his monoplane design of the previous year. Like that aircraft, it featured a large, triangular wing, with a mo ...
. In this machine, he made a tethered flight on 12 September 1906, becoming the second European to make a powered flight.
* 1906 ŌĆō Alberto Santos-Dumont and his Santos-Dumont 14-bis make the first public flight of an airplane on October 23, 1906, in Paris. The flying machine was the first fixed-wing aircraft officially witnessed to take off, fly, and land. Santos Dumont is considered the "Father of Aviation" in his country of birth, Brazil. His flight is the first to have been certified by the '' A├®ro-Club de France'' and the ''F├®d├®ration A├®ronautique Internationale
The (; FAI; en, World Air Sports Federation) is the world governing body for air sports, and also stewards definitions regarding human spaceflight. It was founded on 14 October 1905, and is headquartered in Lausanne, Switzerland. It maintai ...
(FAI)''. On November 12, 1906, Santos Dumont succeeded in setting the first world record recognized by the Aero-Club De France by flying 220 metres in less than 22 seconds.
* 1906 ŌĆō Sound radio broadcasting was invented by Reginald Fessenden and Lee De Forest
Lee de Forest (August 26, 1873 ŌĆō June 30, 1961) was an American inventor and a fundamentally important early pioneer in electronics. He invented the first electronic device for controlling current flow; the three-element "Audion" triode va ...
. Fessenden and Ernst Alexanderson developed a high-frequency alternator-transmitters, an improvement on an already existing device. The improved model operated at a transmitting frequency of approximately 50 kHz, although with far less power than Fessenden's rotary-spark transmitters. The alternator-transmitter achieved the goal of transmitting quality audio signals, but the lack of any way to amplify the signals meant they were somewhat weak. On December 21, 1906, Fessenden made an extensive demonstration of the new alternator-transmitter at Brant Rock, showing its utility for point-to-point wireless telephony, including interconnecting his stations to the wire telephone network. A detailed review of this demonstration appeared in ''The American Telephone Journal''. Meanwhile, De Forest had developed the Audion tube an electronic amplifier device. He received a patent in January, 1907. "DeForest's audion vacuum tube was the key component of all radio, telephone, radar, television, and computer systems before the invention of the transistor in 1947."
* 1906 ŌĆō Reginald Fessenden of East Bolton, Quebec
East Bolton (french: Bolton-Est) is a municipality of about 1,000 people, part of the Memphr├®magog Regional County Municipality in the Estrie region of Quebec, Canada.
It is the birthplace of Reginald Fessenden, radio pioneer who invented amplit ...
, Canada made what appear to be the first audio radio broadcasts of entertainment and music ever made to a general audience. (Beginning in 1904, the United States Navy had broadcast daily time signals and weather reports, but these employed spark-gap transmitters, transmitting in Morse code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of ...
). On the evening of December 24, 1906 (Christmas Eve
Christmas Eve is the evening or entire day before Christmas Day, the festival commemorating the birth of Jesus. Christmas Day is observed around the world, and Christmas Eve is widely observed as a full or partial holiday in anticipation ...
), Fessenden used the alternator-transmitter to send out a short program from Brant Rock, Plymouth County, Massachusetts. It included a phonograph record of Ombra mai f├╣
"" ("Never was a shadeŌĆ”"), also known as "Largo from ''Xerxes''", is the opening aria from the 1738 opera ''Serse'' by George Frideric Handel.
Context
The opera was a commercial failure, lasting only five performances in London after its prem ...
(Largo) by George Frideric Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 ŌĆō 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque music, Baroque composer well known for his opera#Baroque era, operas, oratorios, anthems, concerto grosso, concerti grossi, ...
, followed by Fessenden himself playing the song '' O Holy Night'' on the violin. Finishing with reading a passage from the Bible: 'Glory to God in the highest and on earth peace to men of good will' ( Gospel of Luke 2:14). On December 31, New Year's Eve
In the Gregorian calendar, New Year's Eve, also known as Old Year's Day or Saint Sylvester's Day in many countries, is the evening or the entire day of the last day of the year, on 31 December. The last day of the year is commonly referred to ...
, a second short program was broadcast. The main audience for both these transmissions was an unknown number of shipboard radio operators along the East Coast of the United States
The East Coast of the United States, also known as the Eastern Seaboard, the Atlantic Coast, and the Atlantic Seaboard, is the coastline along which the Eastern United States meets the North Atlantic Ocean. The eastern seaboard contains the coa ...
. Fessenden claimed that the Christmas Eve broadcast had been heard "as far down" as Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia Be ...
, while the New Year Eve's broadcast had reached places in the Caribbean. Although now seen as a landmark, these two broadcasts were barely noticed at the time and soon forgottenŌĆö the only first-hand account appears to be a letter Fessenden wrote on January 29, 1932, to his former associate, Samuel M. Kinter.
 * 1907 ŌĆō The Autochrome Lumi├©re which was patented in 1903 becomes the first commercial color photography process.
* 1907 ŌĆō Thomas Edison invented the "Universal Electric Motor" which made it possible to operate dictation machines, etc. on all lighting circuits.
* 1907 ŌĆō The Photostat machine begins the modern era of document imaging. The Photostat machine was invented in
* 1907 ŌĆō The Autochrome Lumi├©re which was patented in 1903 becomes the first commercial color photography process.
* 1907 ŌĆō Thomas Edison invented the "Universal Electric Motor" which made it possible to operate dictation machines, etc. on all lighting circuits.
* 1907 ŌĆō The Photostat machine begins the modern era of document imaging. The Photostat machine was invented in Kansas City
The Kansas City metropolitan area is a bi-state metropolitan area anchored by Kansas City, Missouri. Its 14 counties straddle the border between the U.S. states of Missouri (9 counties) and Kansas (5 counties). With and a population of more ...
, Kansas, United States by Oscar Gregory in 1907, and the Photostat Corporation was incorporated in Rhode Island in 1911. "Rectigraph and Photostat machines (Plates 40ŌĆō42) combined a large camera and a developing machine and used sensitized paper furnished in 350-foot rolls. "The prints are made direct on sensitized paper, no negative, plate or film intervening. The usual exposure is ten seconds. After the exposure has been made the paper is cut off and carried underneath the exposure chamber to the developing bath, where it remains for 35 seconds, and is then drawn into a fixing bath. While one print is being developed or fixed, another exposure can be made. When the copies are removed from the fixing bath, they are allowed to dry by exposure to the air, or may be run through a drying machine. The first print taken from the original is a 'black' print; the whites in the original are black and the blacks, white. (Plate 43) A white 'positive' print of the original is made by rephotographing the black print. As many positives as required may be made by continuing to photograph the black print." (The American Digest of Business Machines, 1924.) Du Pont Co. files include black prints of graphs dating from 1909, and the company acquired a Photostat machine in 1912. ... A 1914 Rectigraph ad stated that the U.S. government had been using Rectigraphs for four years and stated that the machines were being used by insurance companies and abstract and title companies. ... In 1911, a Photostat machine was $500."
 * 1908 ŌĆō Henry Ford of the Ford Motor Company introduces the
* 1908 ŌĆō Henry Ford of the Ford Motor Company introduces the Ford Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relati ...
. The first production Model T was built on September 27, 1908, at the Ford Piquette Avenue Plant in Detroit. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, the car that "put America on wheels"; some of this was because of Ford's innovations, including assembly line production instead of individual hand crafting, as well as the concept of paying the workers a wage proportionate to the cost of the car, so that they would provide a ready made market.
*1909 ŌĆō Leo Baekeland of Sint-Martens-Latem, Belgium officially announces his creation of Bakelite
Polyoxybenzylmethylenglycolanhydride, better known as Bakelite ( ), is a thermosetting phenol formaldehyde resin, formed from a condensation reaction of phenol with formaldehyde. The first plastic made from synthetic components, it was developed ...
. The announcement was made at the February 1909 meeting of the New York section of the American Chemical Society. Bakelite is an inexpensive, nonflammable, versatile, and popular plastic.
Popular culture
Literature
 The best selling books of the decade were ''
The best selling books of the decade were ''Anne of Green Gables
''Anne of Green Gables'' is a 1908 novel by Canadian author Lucy Maud Montgomery (published as L. M. Montgomery). Written for all ages, it has been considered a classic children's novel since the mid-20th century. Set in the late 19th century, t ...
'' (1908) and '' The Tale of Peter Rabbit'' (1902), which sold 50 million and 45 million copies respectively. Serbian writers used the Belgrade
Belgrade ( , ;, ; Names of European cities in different languages: B, names in other languages) is the Capital city, capital and List of cities in Serbia, largest city in Serbia. It is located at the confluence of the Sava and Danube rivers a ...
literary style, an Ekavian
Shtokavian or ┼Ātokavian (; sh-Latn, ┼Ītokavski / sh-Cyrl, italics=no, čłč鹊ą║ą░ą▓čüą║ąĖ, ) is the prestige dialect of the pluricentric Serbo-Croatian language and the basis of its Serbian, Croatian, Bosnian and Montenegrin standards. It ...
writing form which set basis for the later standardization of the Serbian language. Theodor Herzl, the founder of political Zionism, published '' The Old New Land'' in 1902, outlining Herzl's vision for a Jewish state in the Land of Israel
The Land of Israel () is the traditional Jewish name for an area of the Southern Levant. Related biblical, religious and historical English terms include the Land of Canaan, the Promised Land, the Holy Land, and Palestine (see also Isra ...
.
Below are the best-selling books in the United States of each year, as determined by '' Publishers Weekly''.
* 1900: '' To Have and to Hold'' by Mary Johnston
* 1901: '' The Crisis'' by Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
* 1902: '' The Virginian'' by Owen Wister
* 1903: '' Lady Rose's Daughter'' by Mary Augusta Ward
* 1904: '' The Crossing'' by Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
* 1905: '' The Marriage of William Ashe'' by Mary Augusta Ward
* 1906: '' Coniston'' by Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
* 1907: '' The Lady of the Decoration'' by Frances Little
Frances Little (November 22, 1863 ŌĆō January 6, 1941) was the pseudonym of American author Fannie Caldwell. Her first and most successful book, ''The Lady of the Decoration'', was based on her experiences in Hiroshima, Japan, from 1902 to 1907. ...
* 1908: ''Mr. Crewe's Career
''Mr. Crewe's Career'' is a 1908 best-selling novel by American writer Winston Churchill.
The novel tells the story of a railroad lobby's attempts to control the New Hampshire state government using all possible tactics. Churchill's prior novel ...
'' by Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 Winston Churchill in the Second World War, dur ...
* 1909: '' The Inner Shrine'' by Anonymous ( Basil King)
Art
 * Pablo Picasso paints '' Les Demoiselles d'Avignon'', considered by some to be the birth of modern art.
*
* Pablo Picasso paints '' Les Demoiselles d'Avignon'', considered by some to be the birth of modern art.
*Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau (; ) is an international style of art, architecture, and applied art, especially the decorative arts. The style is known by different names in different languages: in German, in Italian, in Catalan, and also known as the Modern ...
art movement peaked in popularity at the turn of the 20th century (1890ŌĆō1905).
* Cubism
Cubism is an early-20th-century avant-garde art movement that revolutionized European painting and sculpture, and inspired related movements in music, literature and architecture. In Cubist artwork, objects are analyzed, broken up and reassemble ...
art movement peaked in popularity in France between 1907 and 1911.
* Fauvism
Fauvism /╦łfo╩Ŗv╔¬zm╠®/ is the style of ''les Fauves'' (French language, French for "the wild beasts"), a group of early 20th-century modern artists whose works emphasized painterly qualities and strong colour over the Representation (arts), repr ...
art movement peaked in popularity between 1905 and 1907.
Film
 * April 2, 1902 ŌĆō ''Electric Theatre'', the first
* April 2, 1902 ŌĆō ''Electric Theatre'', the first movie theater
A movie theater (American English), cinema (British English), or cinema hall ( Indian English), also known as a movie house, picture house, the movies, the pictures, picture theater, the silver screen, the big screen, or simply theater is a ...
in the United States, opens in Los Angeles.
* The first huge success of American cinema, as well as the largest experimental achievement to this point, was the 1903 film '' The Great Train Robbery'', directed by Edwin S. Porter.
* The world's first feature film, '' The Story of the Kelly Gang'' is released on 26 December 1906 in Melbourne, Australia.
Music
Popular songs of the 1900s include " Lift Every Voice and Sing" and " What Are They Doing in Heaven?", which have been featured in 42 and 16 hymnals respectively. ** 23rd Jan,1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2 ...
- The Pittsburg Symphony Orchestra makes its Carnegie Hall
Carnegie Hall ( ) is a concert venue in Midtown Manhattan in New York City. It is at 881 Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh Avenue, occupying the east side of Seventh Avenue between West 56th Street (Manhattan), 56th and 57th Street (Manhatta ...
debut with Victor Herbert conducting.
** February 3, 1900 ŌĆō Adonais
''Adonais: An Elegy on the Death of John Keats, Author of Endymion, Hyperion, etc.'' () is a pastoral elegy written by Percy Bysshe Shelley for John Keats in 1821, and widely regarded as one of Shelley's best and best-known works.George Whitefield Chadwick is premiered by the
Prices and Wages by Decade: 1900s
’┐Į’┐ĮResearch guide from the University of Missouri Library shows average wages for various occupations and prices for common items from 1900 to 1909. {{DEFAULTSORT:1900s (Decade) 19th century 20th century 1900s decade overviews
Boston Symphony Orchestra
The Boston Symphony Orchestra (BSO) is an American orchestra based in Boston, Massachusetts. It is the second-oldest of the five major American symphony orchestras commonly referred to as the " Big Five". Founded by Henry Lee Higginson in 1881, ...
.
** December 15, 1900 ŌĆō The second and third movements of Concerto No.2 in C Minor for Piano by Sergej Rachmaninov
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conducting, conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a compo ...
receive their world premiere in Moscow, with Rachmaninov playing the solo part.
** March 29th, 1901
Events
January
* January 1 – The Crown colony, British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria and Western Australia Federation of Australia, federate as the Australia, ...
- Jean de Reszke's final performance of the season with the Metropolitan Opera turns into his farewell performance with that company as he sings the title role in Wagner's
Wilhelm Richard Wagner ( ; ; 22 May 181313 February 1883) was a German composer, theatre director, polemicist, and conductor who is chiefly known for his operas (or, as some of his mature works were later known, "music dramas"). Unlike most op ...
Lohengrin.
** October 27, 1901 ŌĆō Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 ŌĆō 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the ...
's ''Trois Nocturnes'' is given in its first complete performance as Camille Chevillard conducts the Lamoureux Orchestra in Paris.
** November 9
Events Pre-1600
* 694 – At the Seventeenth Council of Toledo, Egica, a king of the Visigoths of Hispania, accuses Jews of aiding Muslims, sentencing all Jews to slavery.
* 1277 – The Treaty of Aberconwy, a humiliating settlement f ...
, 1901
Events
January
* January 1 – The Crown colony, British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria and Western Australia Federation of Australia, federate as the Australia, ...
- First complete performance of Sergei Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one o ...
's Piano Concerto no. 2 in C Minor in Moscow with Rachmaninoff playing the solo part.
** December 16th, 1902
Events
January
* January 1
** The Nurses Registration Act 1901 comes into effect in New Zealand, making it the first country in the world to require state registration of nurses. On January 10, Ellen Dougherty becomes the world's f ...
- Scott Joplin
Scott Joplin ( 1868 ŌĆō April 1, 1917) was an American composer and pianist. Because of the fame achieved for his ragtime compositions, he was dubbed the "King of Ragtime." During his career, he wrote over 40 original ragtime pieces, one ra ...
's signature rag, "The Entertainer An entertainer is a person who entertains (singer, actor, comedian, etc.)
The Entertainer may refer to:
Music Songs
* "The Entertainer" (rag), a 1902 classic piano rag written by Scott Joplin
*"The Entertainer", rearrangement of the Joplin rag by ...
", is released.
** October 18, 1904 ŌĆō Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 ŌĆō 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
's '' Symphony No. 5'' is premiered by the G├╝rzenich Orchestra Cologne
The G├╝rzenich Orchestra Cologne (german: G├╝rzenich-Orchester K├Čln) is a German symphony orchestra based in Cologne. On some recordings, the orchestra goes under the name "G├╝rzenich-Orchester K├Člner Philharmoniker". Its name comes from its ...
with Mahler conducting.
** 1905
As the second year of the massive Russo-Japanese War begins, more than 100,000 die in the largest world battles of that era, and the war chaos leads to the 1905 Russian Revolution against Nicholas II of Russia (Shostakovich's 11th Symphony i ...
- Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 ŌĆō 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the ...
releases his masterpiece and signature song
A signature (; from la, signare, "to sign") is a Handwriting, handwritten (and often Stylization, stylized) depiction of someone's name, nickname, or even a simple "X" or other mark that a person writes on documents as a proof of identity and ...
, " Clair de Lune".
** January 27
Events Pre-1600
* 98 – Trajan succeeds his adoptive father Nerva as Roman emperor; under his rule the Roman Empire will reach its maximum extent.
* 945 – The co-emperors Stephen and Constantine are overthrown and forced to becom ...
, 1907
Events
January
* January 14 – 1907 Kingston earthquake: A 6.5 Mw earthquake in Kingston, Jamaica, kills between 800 and 1,000.
February
* February 11 – The French warship ''Jean Bart'' sinks off the coast of Morocco. ...
ŌĆō Executives of the Metropolitan Opera removes Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 ŌĆō 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wag ...
's Salome
Salome (; he, ū®ų░ū£ūĢų╣ū×ų┤ūÖū¬, Shlomit, related to , "peace"; el, ╬Ż╬▒╬╗ŽÄ╬╝╬Ę), also known as Salome III, was a Jewish princess, the daughter of Herod II, son of Herod the Great, and princess Herodias, granddaughter of Herod the Great, an ...
from the repertoire following protests that the opera was indecent.
** January 26, 1908 ŌĆō Sergei Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one o ...
's Symphony No. 2 receives its premi├©re.
** March 15, 1908 ŌĆō Maurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 ŌĆō 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In ...
's '' Rapsodie espagnole'' receives its premi├©re in Paris.
** April 11, 1908 ŌĆō Spyridon Samaras's opera ''Rhea'' is premiered in Florence (Teatro Verdi)
** September 19, 1908 ŌĆō Premi├©re of Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 ŌĆō 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
's Symphony No. 7 in Prague.
** January 25, 1909 ŌĆō Richard Strauss
Richard Georg Strauss (; 11 June 1864 ŌĆō 8 September 1949) was a German composer, conductor, pianist, and violinist. Considered a leading composer of the late Romantic and early modern eras, he has been described as a successor of Richard Wag ...
's opera Elektra
Electra was a daughter of Agamemnon and Clytemnestra in Greek mythology.
Electra or Elektra may also refer to:
Greek mythology
*Electra (Pleiad), one of the Pleiades
* Electra, one of the Danaids, daughter of Danaus and Polyxo
* Electra (Oc ...
receives its debut performance at the Dresden State Opera
The Semperoper () is the opera house of the S├żchsische Staatsoper Dresden (Saxon State Opera) and the concert hall of the Staatskapelle Dresden (Saxon State Orchestra). It is also home to the Semperoper Ballett. The building is located on the Th ...
** February 19
Events Pre-1600
* 197 – Emperor Septimius Severus defeats usurper Clodius Albinus in the Battle of Lugdunum, the bloodiest battle between Roman armies.
* 356 – The anti-paganism policy of Constantius II forbids the worship of pagan ...
, 1909
Events
January–February
* January 4 ŌĆō Explorer Aeneas Mackintosh of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition escaped death by fleeing across ice floes.
* January 7 – Colombia recognizes the independence of Panama.
* Januar ...
ŌĆō First production Bed┼Öich Smetana's opera '' Prodan├Ī nev─østa'' (The Bartered Bride) in the USA v Metropolitan Opera, conducted by Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 ŌĆō 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
with Ema Destinov├Ī
Emmy Destinn ( (); 26 February 1878 – 28 January 1930) was a Czech operatic soprano with a strong and soaring lyric-dramatic voice. She had a career both in Europe and at the New York Metropolitan Opera.
Biography
Destinn was born Em’┐Į ...
in the titul role.
** February 22, 1909 ŌĆō Thomas Beecham conducts the first concert with his newly established Beecham Symphony Orchestra in the UK.
** November 8, 1909 ŌĆō Boston Opera House in the United States opens with a performance of ''La Gioconda La Gioconda ( , ; "the joyful one" feminine_gender.html" ;"title="'feminine gender">f.'' may refer to:
* ''Mona Lisa'' or ''La Gioconda'', a painting by Leonardo da Vinci
* Lisa del Giocondo, the model depicted in da Vinci's painting
* La Gioconda ...
'' starring Lillian Nordica and Louise Homer.
** November 28, 1909 ŌĆō Sergei Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one o ...
's Piano Concerto No. 3 is premi├©red in New York City.
** December 18, 1909 ŌĆō George Enescu's Octet for Strings and Piano Quartet No. 1 in D Major are premiered together on a program also featuring his ''Sept chansons de Clement Marot'', Op. 15, at the Salle des agriculteurs in Paris, as part of the "Soir├®es d'Art" concert series.
Fashion
Sports
The Tour de France starts for the first time in 1903.Food
* U.S. New Haven, Connecticut Louis Lassen of Louis' Lunch makes the first modern-day hamburger sandwich. According to family legend, one day in 1900 a local businessman dashed into the small New Haven lunch wagon and pleaded for a lunch to go. According to the Lassen family, the customer, Gary Widmore, exclaimed "Louie! I'm in a rush, slap a meatpuck between two planks and step on it!". Louis Lassen, the establishment's owner, placed his own blend of ground steak trimmings between two slices of toast and sent the gentleman on his way, so the story goes, with America's alleged first hamburger being served.People
Modern artists
* Umberto Boccioni *Pierre Bonnard
Pierre Bonnard (; 3 October 186723 January 1947) was a French painter, illustrator and printmaker, known especially for the stylized decorative qualities of his paintings and his bold use of color. A founding member of the Post-Impressionist ...
*Georges Braque
Georges Braque ( , ; 13 May 1882 – 31 August 1963) was a major 20th-century List of French artists, French painter, Collage, collagist, Drawing, draughtsman, printmaker and sculpture, sculptor. His most notable contributions were in his all ...
*Paul C├®zanne
Paul C├®zanne ( , , ; ; 19 January 1839 ŌĆō 22 October 1906) was a French artist and Post-Impressionism, Post-Impressionist painter whose work laid the foundations of the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavour to a ...
*Marc Chagall
Marc Chagall; russian: link=no, ą£ą░čĆą║ ąŚą░čģą░╠üčĆąŠą▓ąĖčć ą©ą░ą│ą░╠üą╗ ; be, ą£ą░čĆą║ ąŚą░čģą░čĆą░ą▓č¢čć ą©ą░ą│ą░ą╗ . (born Moishe Shagal; 28 March 1985) was a Russian-French artist. An early modernism, modernist, he was associated with se ...
*Edgar Degas
Edgar Degas (, ; born Hilaire-Germain-Edgar De Gas, ; 19 July 183427 September 1917) was a French Impressionist artist famous for his pastel drawings and oil paintings.
Degas also produced bronze sculptures, prints and drawings. Degas is es ...
* Andr├® Derain
* Raoul Dufy
* Paul Gauguin
* Juan Gris
* Wassily Kandinsky
*Gustav Klimt
Gustav Klimt (July 14, 1862 ŌĆō February 6, 1918) was an Austrian symbolist painter and one of the most prominent members of the Vienna Secession movement. Klimt is noted for his paintings, murals, sketches, and other objets d'art. Klimt's prim ...
*Fernand L├®ger
Joseph Fernand Henri L├®ger (; February 4, 1881 ŌĆō August 17, 1955) was a French painting, painter, sculpture, sculptor, and film director, filmmaker. In his early works he created a personal form of cubism (known as "tubism") which he gradually ...
*Kazimir Malevich
Kazimir Severinovich Malevich ; german: Kasimir Malewitsch; pl, Kazimierz Malewicz; russian: ąÜą░ąĘąĖą╝ąĖ╠üčĆ ąĪąĄą▓ąĄčĆąĖ╠üąĮąŠą▓ąĖčć ą£ą░ą╗ąĄ╠üą▓ąĖčć ; uk, ąÜą░ąĘąĖą╝ąĖčĆ ąĪąĄą▓ąĄčĆąĖąĮąŠą▓ąĖčć ą£ą░ą╗ąĄą▓ąĖčć, translit=Kazymyr Severynovych ...
* Henri Matisse
*Amedeo Modigliani
Amedeo Clemente Modigliani (, ; 12 July 1884 ŌĆō 24 January 1920) was an Italian painter and sculptor who worked mainly in France. He is known for portraits and nudes in a modern style characterized by a surreal elongation of faces, necks, and ...
* Claude Monet
* Pablo Picasso
*Pierre-Auguste Renoir
Pierre-Auguste Renoir (; 25 February 1841 ŌĆō 3 December 1919) was a French artist who was a leading painter in the development of the Impressionist style. As a celebrator of beauty and especially feminine sensuality, it has been said that "R ...
*Auguste Rodin
Fran├¦ois Auguste Ren├® Rodin (12 November 184017 November 1917) was a French sculptor, generally considered the founder of modern sculpture. He was schooled traditionally and took a craftsman-like approach to his work. Rodin possessed a uniqu ...
* Georges Rouault
* Henri Rousseau
* Albert Pinkham Ryder
*Egon Schiele
Egon Leo Adolf Ludwig Schiele (; 12 June 1890 ŌĆō 31 October 1918) was an Austrian Expressionist painter. His work is noted for its intensity and its raw sexuality, and for the many self-portraits the artist produced, including nude self-portr ...
* Gino Severini
* Paul Signac
* Henri Toulouse-Lautrec
* Suzanne Valadon
* Maurice de Vlaminck
* Gustave Caillebotte
* ├ēdouard Manet
*Camille Pissarro
Jacob Abraham Camille Pissarro ( , ; 10 July 1830 ŌĆō 13 November 1903) was a Danish-French Impressionist and Neo-Impressionist painter born on the island of Saint Thomas, U.S. Virgin Islands, St Thomas (now in the US Virgin Islands, but t ...
* Georges Seurat
* Alfred Sisley
Other notable people
* Eugen d'Albert * Hugo Alfv├®n * Egbert Van Alstyne * Broncho Billy Anderson * Fatty Arbuckle * Louis Daniel Armstrong * Kurt Atterberg *B├®la Bart├│k
B├®la Viktor J├Īnos Bart├│k (; ; 25 March 1881 ŌĆō 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as H ...
*Nora Bayes
Nora Bayes (born Rachel Eleonora "Dora" Goldberg; October 3, 1880March 19, 1928) was an American singer and vaudeville performer who was popular internationally between the 1900s and 1920s. She is credited with co-writing the song "Shine On, Har ...
* Jagdish Chandra Bose
* Irving Berlin
* Francis Boggs
* Frank Bridge
* Alfred Bryan
* Vincent P. Bryan
*Ferruccio Busoni
Ferruccio Busoni (1 April 1866 ŌĆō 27 July 1924) was an Italian composer, pianist, conductor, editor, writer, and teacher. His international career and reputation led him to work closely with many of the leading musicians, artists and literary ...
*Enrico Caruso
Enrico Caruso (, , ; 25 February 1873 ŌĆō 2 August 1921) was an Italian operatic first lyrical tenor then dramatic tenor. He sang to great acclaim at the major opera houses of Europe and the Americas, appearing in a wide variety of roles (74) ...
* Gustave Charpentier
*Thurland Chattaway
Thurland Chattaway (April 8, 1872 – November 12, 1947) was an American composer of popular music, active from approximately 1898 to 1912. He is best known for writing the words to the popular 1907 hit " Red Wing" with Kerry Mills. Other son ...
*Francesco Cilea
Francesco Cilea (; 23 July 1866 ŌĆō 20 November 1950) was an Italian composer. Today he is particularly known for his operas ''L'arlesiana'' and ''Adriana Lecouvreur''.
Biography
Born in Palmi near Reggio di Calabria, Cilea gave early indicatio ...
*Will D. Cobb
William Denight Cobb (July 5, 1876 ŌĆō January 20, 1930) was an American lyricist and composer. He and a partner, Ren Shields, produced several popular musical theater, musicals and musical comedies in the early 20th century. Cobb also had a lon ...
*Bob Cole Robert Cole may refer to:
Entertainment
*Robert William Cole (1869ŌĆō1937), British writer
*Bob Cole (composer) (1868ŌĆō1911), American composer
*Bobby Cole (musician) (1932ŌĆō1996), American musician
Sports
*Bob Cole (cricketer) (born 1938), for ...
* Frederick Converse
* Henry Creamer
* Henry Walford Davies
* Peter Dawson
*Claude Debussy
(Achille) Claude Debussy (; 22 August 1862 ŌĆō 25 March 1918) was a French composer. He is sometimes seen as the first Impressionist composer, although he vigorously rejected the term. He was among the most influential composers of the ...
* Frederick Delius
* Paul Dresser
*Anton├Łn Dvo┼Ö├Īk
Anton├Łn Leopold Dvo┼Ö├Īk ( ; ; 8 September 1841 ŌĆō 1 May 1904) was a Czechs, Czech composer. Dvo┼Ö├Īk frequently employed rhythms and other aspects of the folk music of Moravian traditional music, Moravia and his native Bohemia, following t ...
* Gus Edwards
*Edward Elgar
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, (; 2 June 1857 ŌĆō 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestr ...
*August Enna
August Enna (13 May 1859 ŌĆō 3 August 1939) was a Danish composer, known mainly for his operas.
Enna was born in Nakskov, Lolland, Denmark, but his ethnic origins lay in Sicily. His first major success as a composer was ''The Witch'' (1892), whi ...
* Manuel de Falla
* Geraldine Farrar
* Fred Fisher
* Paul Le Flem
* Sigmund Freud
* Rudolf Friml
* Julius Fu─Ź├Łk
* Amelita Galli-Curci
* Mary Garden
* Edward German
*Alexander Glazunov
Alexander Konstantinovich Glazunov; ger, Glasunow (, 10 August 1865 ŌĆō 21 March 1936) was a Russian composer, music teacher, and conductor of the late Russian Romantic period. He was director of the Saint Petersburg Conservatory between 1905 ...
*Emilio de Gogorza
Emilio Eduardo de Gogorza (May 29, 1872May 10, 1949) was an American baritone of Spanish parentage.
Biography
He was born in Brooklyn, New York, but brought up and trained musically in Spain. He returned to the USA in his early 20s. He sang in m ...
* Percy Grainger
* Enrique Granados
*D. W. Griffith
David Wark Griffith (January 22, 1875 ŌĆō July 23, 1948) was an American film director. Considered one of the most influential figures in the history of the motion picture, he pioneered many aspects of film editing and expanded the art of the na ...
*Guy d'Hardelot
Guy d'Hardelot (August 1858 ŌĆō 7 January 1936) was the pen name of Helen Rhodes (''n├®e'' Helen Guy), a French composer, pianist, and teacher.
Biography
D'Hardelot was born Helen Guy, to an English father and a French mother. She was born a ...
* Hamilton Harty
* The Haydn Quartet
* Anna Held
* Victor Herbert
* Max Hoffmann
* Gustav Holst
* Abe Holzmann
* David Horsley
*Harry Houdini
Harry Houdini (, born Erik Weisz; March 24, 1874 ŌĆō October 31, 1926) was a Hungarian-American escape artist, magic man, and stunt performer, noted for his escape acts. His pseudonym is a reference to his spiritual master, French magician ...
* Mississippi John Hurt
* Jen├Č Huszka
* Mikhail Ippolitov-Ivanov
*Carrie Jacobs-Bond
Carrie Minetta Jacobs-Bond (August 11, 1862 ŌĆō December 28, 1946) was an American singer, pianist, and songwriter who composed some 175 pieces of popular music from the 1890s through the early 1940s.
She is perhaps best remembered for writing t ...
*Alfred Jarry
Alfred Jarry (; 8 September 1873 ŌĆō 1 November 1907) was a French symbolist writer who is best known for his play ''Ubu Roi'' (1896). He also coined the term and philosophical concept of 'pataphysics.
Jarry was born in Laval, Mayenne, France, ...
* William Jerome
* J. Rosamond Johnson
* James Weldon Johnson
*Scott Joplin
Scott Joplin ( 1868 ŌĆō April 1, 1917) was an American composer and pianist. Because of the fame achieved for his ragtime compositions, he was dubbed the "King of Ragtime." During his career, he wrote over 40 original ragtime pieces, one ra ...
* Gus Kahn
* Jerome Kern
* Rudyard Kipling
* Carl Laemmle
* Harry Lauder
*Lead Belly
Huddie William Ledbetter (; January 20, 1888 ŌĆō December 6, 1949), better known by the stage name Lead Belly, was an American folk music, folk and blues singer notable for his strong vocals, Virtuoso, virtuosity on the twelve-string guita ...
* Franz Leh├Īr
* Ruggiero Leoncavallo
* Paul Lincke
*Gustav Mahler
Gustav Mahler (; 7 July 1860 ŌĆō 18 May 1911) was an Austro-Bohemian Romantic composer, and one of the leading conductors of his generation. As a composer he acted as a bridge between the 19th-century Austro-German tradition and the modernism ...
* Arthur Marshall
*Jules Massenet
Jules ├ēmile Fr├®d├®ric Massenet (; 12 May 1842 ŌĆō 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are '' Manon'' (1884) and ''Werther' ...
* Nikolai Karlovich Medtner
* Nellie Melba
*Georges M├®li├©s
Marie-Georges-Jean M├®li├©s (; ; 8 December 1861 ŌĆō 21 January 1938) was a French illusionist, actor, and film director. He led many technical and narrative developments in the earliest days of cinema.
M├®li├©s was well known for the use of ...
* Kerry Mills
* Billy Murray
* Evelyn Nesbit
* Ethelbert Woodbridge Nevin
* Carl Nielsen
* Jack Norworth
*V├Łt─øzslav Nov├Īk
V├Łt─øzslav August├Łn Rudolf Nov├Īk (5 December 1870 ŌĆō 18 July 1949) was a Czech composer and academic teacher at the Prague Conservatory. Stylistically, he was part of the neo-romantic tradition, and his music is considered an important e ...
*Maude Nugent
Maude Nugent (January 12, 1873 or 1874 ŌĆō June 3, 1958) was an American singer and composer.
Biography
Maude Nugent was born in Brooklyn, New York. She became a vaudeville singer, singing at venues like The Abbey and Tony Pastor's.
In 1896, sh ...
* Sidney Olcott
* Charles Path├®
* Edwin S. Porter
* Giacomo Puccini
*Sergei Rachmaninoff
Sergei Vasilyevich Rachmaninoff; in Russian pre-revolutionary script. (28 March 1943) was a Russian composer, virtuoso pianist, and conductor. Rachmaninoff is widely considered one of the finest pianists of his day and, as a composer, one o ...
*Maurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 ŌĆō 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In ...
*Ottorino Respighi
Ottorino Respighi ( , , ; 9 July 187918 April 1936) was an Italian composer, violinist, teacher, and musicologist and one of the leading Italian composers of the early 20th century. List of compositions by Ottorino Respighi, His compositions r ...
*Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░ą╣ ąÉąĮą┤čĆąĄąĄą▓ąĖčćčŖ ąĀąĖą╝čüą║č¢ą╣-ąÜąŠčĆčüą░ą║ąŠą▓čŖ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
* Landon Ronald
* Paul Sarebresole
*Erik Satie
Eric Alfred Leslie Satie (, ; ; 17 May 18661 July 1925), who signed his name Erik Satie after 1884, was a French composer and pianist. He was the son of a French father and a British mother. He studied at the Paris Conservatoire, but was an und ...
*Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Sch├Čnberg (, ; ; 13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian-American composer, music theorist, teacher, writer, and painter. He is widely considered one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was as ...
* Jean Schwartz
*James Scott James Scott may refer to:
Entertainment
* James Scott (composer) (1885ŌĆō1938), African-American ragtime composer
* James Scott (director) (born 1941), British filmmaker
* James Scott (actor) (born 1979), British television actor
* James Scott (Sh ...
*Alexander Scriabin
Alexander Nikolayevich Scriabin (; russian: ąÉą╗ąĄą║čüą░ąĮą┤čĆ ąØąĖą║ąŠą╗ą░ąĄą▓ąĖčć ąĪą║čĆčÅą▒ąĖąĮ ; ŌĆō ) was a Russian composer and virtuoso pianist. Before 1903, Scriabin was greatly influenced by the music of Fr├®d├®ric Chopin and composed ...
* William Selig
* Chris Smith
*Harry B. Smith
Harry Bache Smith (December 28, 1860 ŌĆō January 1, 1936) was a writer, lyricist and composer. The most prolific of all American stage writers, he is said to have written over 300 librettos and more than 6000 lyrics. Some of his best-known works ...
* Ethel Smyth
* John Philip Sousa
* George Kirke Spoor
* Charles Villiers Stanford
*Andrew B. Sterling
Andrew B. Sterling (August 26, 1874 – August 11, 1955) was an American lyricist.
Biography
Born in New York City, after he graduated from high school, he began writing songs and vaudevilles. An important event was his meeting with the compo ...
* Oscar Strauss
* Harry Von Tilzer
* Tom Turpin
*Edgard Var├©se
Edgard Victor Achille Charles Var├©se (; also spelled Edgar; December 22, 1883 ŌĆō November 6, 1965) was a French-born composer who spent the greater part of his career in the United States. Var├©se's music emphasizes timbre and rhythm; he coined ...
*Vesta Victoria
Vesta Victoria (born Victoria Lawrence, 26 November 1873 ŌĆō 7 April 1951) was an English music hall singer and comedian. She was famous for her performances of songs such as " Waiting at the Church" and "Daddy Wouldn't Buy Me a Bow Wow", both ...
* Anton Webern
*Percy Wenrich
Percy Wenrich (January 23, 1880 – March 17, 1952) was an American composer of ragtime and popular music.
Personal life and career
Born in Joplin, Missouri to Daniel Wenrich and Mary Ray, he left for Chicago in 1901 where he attended classe ...
* Bert Williams
* Harry Williams
* Ermanno Wolf-Ferrari
*Amy Woodforde-Finden
Amy Woodforde-Finden (1860 ŌĆō 13 March 1919) was a composer who is best known for writing the music to "Kashmiri Song" from ''Four Indian Love Lyrics'' by Laurence Hope.
Biography
Amy Woodforde-Finden was born Amelia Rowe Ward in 1860 at Valpar ...
* Israel Zangwill
* Ferdinand von Zeppelin
*Charles A. Zimmerman
Charles A. Zimmermann (1861 ŌĆō 16 January 1916) was an American composer of marches and popular music. A graduate of the Peabody Conservatory of Music in Baltimore, he was appointed bandmaster at the United States Naval Academy in 1887 at the ag ...
Sports figures
See also
*1900s in literature
Nineteen or 19 may refer to:
* 19 (number), the natural number following 18 and preceding 20
* one of the years 19 BC, AD 19, 1919, 2019
Films
* ''19'' (film), a 2001 Japanese film
* ''Nineteen'' (film), a 1987 science fiction film
Music ...
Timeline
The following articles contain brief timelines which list the most prominent events of the decade:1900
As of March 1 ( O.S. February 17), when the Julian calendar acknowledged a leap day and the Gregorian calendar did not, the Julian calendar fell one day further behind, bringing the difference to 13 days until February 28 ( O.S. February 15), 2 ...
ŌĆó 1901
Events
January
* January 1 – The Crown colony, British colonies of New South Wales, Queensland, South Australia, Tasmania, Victoria (Australia), Victoria and Western Australia Federation of Australia, federate as the Australia, ...
ŌĆó 1902
Events
January
* January 1
** The Nurses Registration Act 1901 comes into effect in New Zealand, making it the first country in the world to require state registration of nurses. On January 10, Ellen Dougherty becomes the world's f ...
ŌĆó 1903
Events January
* January 1 – Edward VII is proclaimed Emperor of India.
* January 19 – The first westŌĆōeast transatlantic radio broadcast is made from the United States to England (the first eastŌĆōwest broadcast having been ...
ŌĆó 1904
Events
January
* January 7 ŌĆō The distress signal ''CQD'' is established, only to be replaced 2 years later by ''SOS''.
* January 8 ŌĆō The Blackstone Library is dedicated, marking the beginning of the Chicago Public Library system.
* ...
ŌĆó 1905
As the second year of the massive Russo-Japanese War begins, more than 100,000 die in the largest world battles of that era, and the war chaos leads to the 1905 Russian Revolution against Nicholas II of Russia (Shostakovich's 11th Symphony i ...
ŌĆó 1906
Events
JanuaryŌĆōFebruary
* January 12 – Persian Constitutional Revolution: A nationalistic coalition of merchants, religious leaders and intellectuals in Persia forces the shah Mozaffar ad-Din Shah Qajar to grant a constitution, ...
ŌĆó 1907
Events
January
* January 14 – 1907 Kingston earthquake: A 6.5 Mw earthquake in Kingston, Jamaica, kills between 800 and 1,000.
February
* February 11 – The French warship ''Jean Bart'' sinks off the coast of Morocco. ...
ŌĆó 1908
Events
January
* January 1 ŌĆō The British ''Nimrod'' Expedition led by Ernest Shackleton sets sail from New Zealand on the ''Nimrod'' for Antarctica.
* January 3 ŌĆō A total solar eclipse is visible in the Pacific Ocean, and is the 46 ...
ŌĆó 1909
Events
January–February
* January 4 ŌĆō Explorer Aeneas Mackintosh of the Imperial Trans-Antarctic Expedition escaped death by fleeing across ice floes.
* January 7 – Colombia recognizes the independence of Panama.
* Januar ...
Further reading
* * * * * *References
Notes
External links
Prices and Wages by Decade: 1900s
’┐Į’┐ĮResearch guide from the University of Missouri Library shows average wages for various occupations and prices for common items from 1900 to 1909. {{DEFAULTSORT:1900s (Decade) 19th century 20th century 1900s decade overviews