263 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 __NOTOC__
Year 263 ( CCLXIII) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 263 ( CCLXIII) was a
 __NOTOC__
Year 263 ( CCLXIII) was a
__NOTOC__
Year 263 ( CCLXIII) was a common year starting on Thursday
A common year starting on Thursday is any non-leap year (i.e. a year with 365 days) that begins on Thursday, 1 January, and ends on Thursday, 31 December. Its dominical letter hence is D. The most recent year of such kind was 2015, and the next ...
of the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts ...
. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Albinus and Dexter (or, less frequently, year 1016 ''Ab urbe condita
''Ab urbe condita'' (; 'from the founding of Rome, founding of the City'), or (; 'in the year since the city's founding'), abbreviated as AUC or AVC, expresses a date in years since 753 BC, 753 BC, the traditional founding of Rome. It is ...
''). The denomination 263 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini
The terms (AD) and before Christ (BC) are used when designating years in the Gregorian calendar, Gregorian and Julian calendar, Julian calendars. The term is Medieval Latin and means "in the year of the Lord" but is often presented using "o ...
calendar era
A calendar era is the period of time elapsed since one '' epoch'' of a calendar and, if it exists, before the next one. For example, the current year is numbered in the Gregorian calendar, which numbers its years in the Western Christian era ...
became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
Events
By place
Roman Empire
* KingOdenathus
Septimius Odaenathus (Greek: Ὀδαίναθος, Palmyrene Aramaic: 𐡠𐡣𐡩𐡮𐡶 ( 35px), ; ; 220 – 267) was the founder king (malik) of the Palmyrene Kingdom who ruled from Palmyra, Syria. He elevated the status of his kingdom ...
of Palmyra
Palmyra ( ; Palmyrene dialect, Palmyrene: (), romanized: ''Tadmor''; ) is an ancient city in central Syria. It is located in the eastern part of the Levant, and archaeological finds date back to the Neolithic period, and documents first menti ...
declares himself ruler of the area west of the River Euphrates
The Euphrates ( ; see below) is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of West Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia (). Originating in Turkey, the Euphrates flows through Syr ...
and is declared ''Dux Orientalis'' by the Roman emperor Gallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empire. He ...
.
Asia
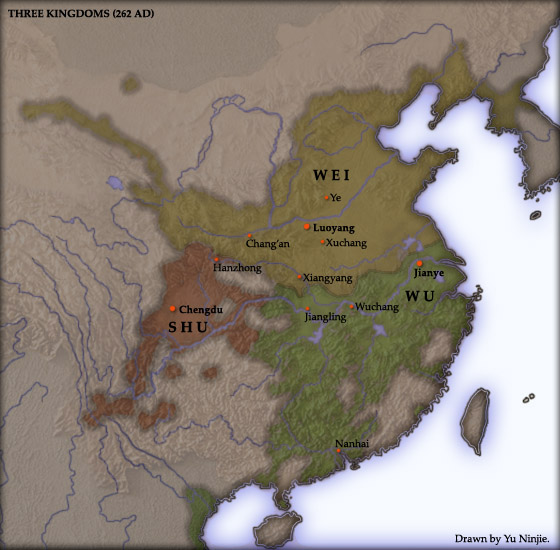
*Conquest of Shu by Wei
The Conquest of Shu by Wei was a military campaign launched by the dynastic state of Cao Wei against its rival Shu Han in late 263 during the Three Kingdoms period of China. The campaign culminated in the fall of Shu Han and the tripartite equil ...
: The Chinese state of Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dy ...
conquers Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu ( zh, t=蜀, p=Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Su'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was a Dynasties in ...
, one of its two rival states.
* Sima Zhao
Sima Zhao () (; 211 – 6 September 265), courtesy name Zishang (子上), was a Chinese military general, politician, and regent of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China.
Sima Zhao capably maintained control of Wei, whi ...
, regent of the Cao Wei
Wei () was one of the major Dynasties in Chinese history, dynastic states in China during the Three Kingdoms period. The state was established in 220 by Cao Pi based upon the foundations laid by his father Cao Cao during the end of the Han dy ...
state, receives and accepts the nine bestowments
The nine bestowments () were awards given by Chinese emperors to officials, ostensibly to reward them for their accomplishments. While the nature of the bestowments was probably established during the Zhou dynasty, there was no record of anyone ...
, state chancellorship, and the title ''Duke of Jin'' from Cao Huan
Cao Huan () (246 – 302/303), courtesy name Jingming, was the fifth and last emperor of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period. On 4 February 266, he abdicated the throne in favour of regent Sima Yan (later Emperor Wu of the J ...
.
By topic
Art and Science
* Chinese mathematicianLiu Hui
Liu Hui () was a Chinese mathematician who published a commentary in 263 CE on ''Jiu Zhang Suan Shu ( The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art).'' He was a descendant of the Marquis of Zixiang of the Eastern Han dynasty and lived in the state ...
writes a commentary on ''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art
''The Nine Chapters on the Mathematical Art'' is a Chinese mathematics book, composed by several generations of scholars from the 10th–2nd century BCE, its latest stage being from the 1st century CE. This book is one of the earliest surviving ...
'', describing what will later be called Gaussian elimination
In mathematics, Gaussian elimination, also known as row reduction, is an algorithm for solving systems of linear equations. It consists of a sequence of row-wise operations performed on the corresponding matrix of coefficients. This method can a ...
, computing pi, etc.
Births
Deaths
*Gao Rou
Gao Rou (174 – October or November 263), courtesy name Wenhui, was a Chinese politician of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was a younger relative of Gao Gan. He previously served under the warlords Yuan Shao ...
(or Wenhui), Chinese politician (b. 174)
* Lady Li (or Lishi), Chinese noblewoman
* Liu Chen, Chinese prince of the Shu Han
Han (; 221–263), known in historiography as Shu Han ( ) or Ji Han ( "Junior Han"), or often shortened to Shu ( zh, t=蜀, p=Shǔ; Sichuanese Pinyin: ''Su'' < Middle Chinese: *''źjowk'' < Eastern Han Chinese: *''dźok''), was a Dynasties in ...
state
* Ruan Ji
Ruan Ji (210–263), courtesy name Sizong, was a Chinese musician, poet, and military officer who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period. He was one of the Seven Sages of the Bamboo Grove. The guqin melody ''Jiukuang'' ( ...
, Chinese poet and musician (b. 210)
* Zhuge Zhan
Zhuge Zhan (227 – November 263), courtesy name Siyuan, was a Chinese military general and politician of the state of Shu Han during the Three Kingdoms period of China. He was a son of Zhuge Liang, the first Imperial Chancellor of Shu.
Earl ...
, Chinese general and politician (b. 227
Year 227 (Roman numerals, CCXXVII) was a common year starting on Monday of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Senecio and Fulvius (or, less frequently, year 980 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination ...
)
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:263