|
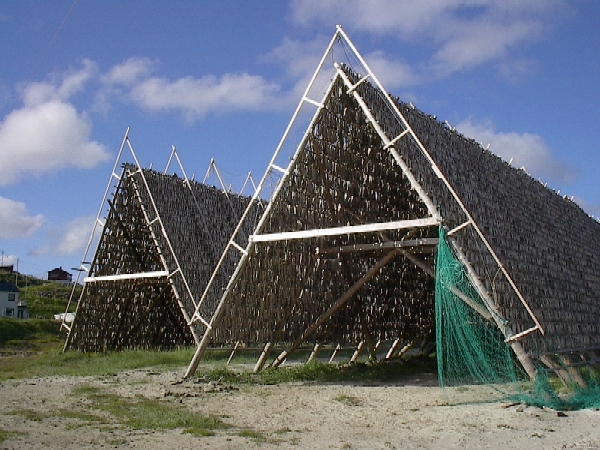
Yukola
Yukola (, Nivkh languages, Nivkh: ма) is dried fish or a dried reindeer meat, a way of food preservation used by the peoples of Eastern Siberia and Russian Far East. Similarly to stockfish, youkola is prepared by drying under sun and wind. Mostly ''Salmonidae'' fish was used for yukola. It was used to feed people and sled dogs. Victor Shnierelman describes fish preservation by Itelmens of Kamchatka as follows. There were two ways: yukola and fermented fish. The latter one was fish seasoned in pits. For yukola, fish was cut into three parts, two of which were edible flesh for humans, while the third one, which consisted of the head and spine, was used as "dog yukola". Dogs were fed with dog yukola while on travel and with soup from fermented fish at home.Victor A. Shnierelman, "''Cherchez le Chien'': Perspectives on the Economy on the Traditional Fishing-Oriented People of Kamchatka", In: ''Key Issues in Hunter-Gatherer Research'', 2020p. 125/ref> References {{reflist Dried ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nivkh Languages
Nivkh ( ; occasionally also Nivkhic; self-designation: Нивхгу диф, ''Nivhgu dif'', ), Gilyak ( ), or Amuric, is a small language family, often portrayed as a language isolate, of two or three mutually unintelligible languages spoken by the Nivkh people in Outer Manchuria, in the basin of the Amgun (a tributary of the Amur), along the lower reaches of the Amur itself, and on the northern half of Sakhalin. "Gilyak" is the Russian rendering of terms derived from the Tungusic "Gileke" and Manchu-Chinese "Gilemi" (Gilimi, Gilyami) for culturally similar peoples of the Amur River region, and was applied principally to the Nivkh in Western literature. The population of ethnic Nivkhs has been reasonably stable over the past century, with 4,549 Nivkhs counted in 1897 and 4,673 in 1989. However, the number of native speakers of the Nivkh language among these dropped from 100% to 23.3% in the same period, so by the 1989 census there were only 1,079 first-language speakers left. Tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dried Fish
Fresh fish rapidly deteriorates unless some way can be found to preserve it. Drying (food), Drying is a method of food preservation that works by removing water from the food, which inhibits the growth of microorganisms. Open air drying using sun and wind has been practiced since ancient times to preserve food."Historical Origins of Food Preservation." Accessed June 2011. Water is usually removed by evaporation (air drying, sun drying, smoking or wind drying) but, in the case of freeze-drying, food is first frozen food, frozen and then the water is removed by sublimation (chemistry), sublimation. Bacteria, yeasts and molds need the water in the food to grow, and drying effectively prevents them from surviving in the food. Fish are Food preservation, preserved through such traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reindeer
The reindeer or caribou (''Rangifer tarandus'') is a species of deer with circumpolar distribution, native to Arctic, subarctic, tundra, taiga, boreal, and mountainous regions of Northern Europe, Siberia, and North America. It is the only representative of the genus ''Rangifer''. More recent studies suggest the splitting of reindeer and caribou into six distinct species over their range. Reindeer occur in both Animal migration, migratory and wiktionary:sedentary#Adjective, sedentary populations, and their herd sizes vary greatly in different regions. The tundra subspecies are adapted for extreme cold, and some are adapted for long-distance migration. Reindeer vary greatly in size and color from the smallest, the Svalbard reindeer (''R.'' (''t.'') ''platyrhynchus''), to the largest, Osborn's caribou (''R. t. osborni''). Although reindeer are quite numerous, some species and subspecies are in decline and considered Vulnerable species, vulnerable. They are unique among deer (Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food Preservation
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the redox, oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhibit visual deterioration, such as the enzymatic browning reaction in apples after they are cut during food preparation. By preserving food, food waste can be reduced, which is an important way to decrease production costs and increase the efficiency of food systems, improve food security and nutrition and contribute towards environmental sustainability. For instance, it can reduce the Environmental impact of agriculture, environmental impact of food production. Many processes designed to preserve food involve more than one food preservation method. Preserving fruit by turning it into jam, for example, involves boiling (to reduce the fruit's moisture content and to kill bacteria, etc.), sugaring (to prevent their re-growth) and sealing wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
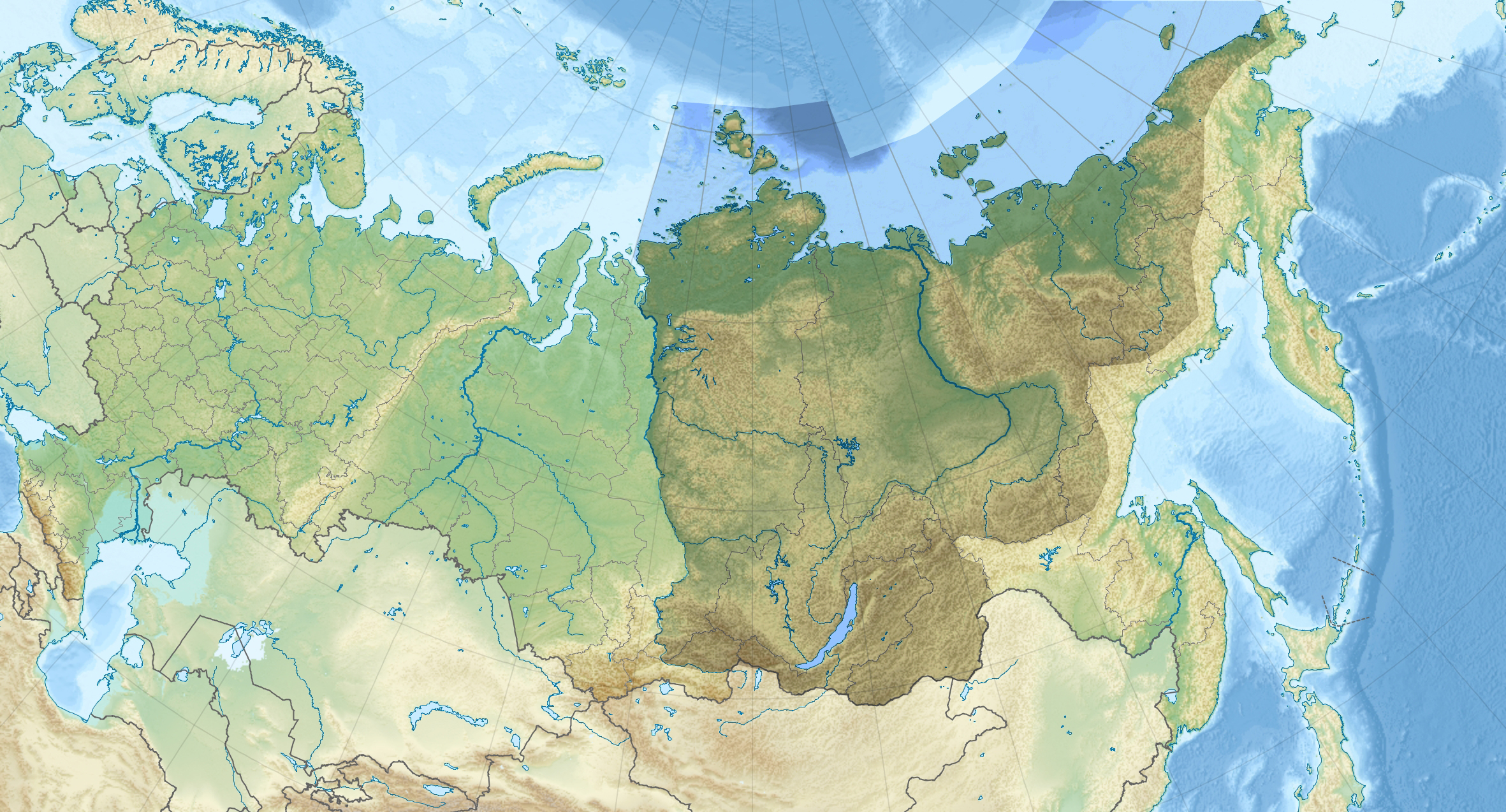
Eastern Siberia
Eastern Siberia is a part of Siberia that incorporates the territory located between the Yenisei River in the west and the Pacific Ocean divides in the east. Its area is equal to 7.2 million sq. km.Galina Samoylova (Г. С. Самойлова)ВОСТО́ЧНАЯ СИБИ́РЬ/ref> Most of Eastern Siberia is occupied by the Central Siberian Plateau, as well as by tundra in the north and mountain ranges in the south. The Eastern Siberian region consists of Yakutia, Buryatia, Tuva, Krasnoyarsk Krai, Irkutsk Oblast and Chita Oblast. The largest cities are Irkutsk and Krasnoyarsk. It considerably overlaps, but not coincides with, the Russian Far East, which stretches from Lake Baikal to the Pacific Ocean The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five Borders of the oceans, oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean, or, depending on the definition, to Antarctica in the south, and is .... References {{reflist Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Far East
The Russian Far East ( rus, Дальний Восток России, p=ˈdalʲnʲɪj vɐˈstok rɐˈsʲiɪ) is a region in North Asia. It is the easternmost part of Russia and the Asia, Asian continent, and is coextensive with the Far Eastern Federal District, which encompasses the area between Lake Baikal and the Pacific Ocean. The area's largest city is Khabarovsk, followed by Vladivostok. The region shares land borders with the countries of Mongolia, China, and North Korea to its south, as well as maritime boundary, maritime boundaries with Japan to its southeast, and with the United States along the Bering Strait to its northeast. Although the Russian Far East is often considered as a part of Siberia abroad, it has been historically categorized separately from Siberia in Russian regional schemes (and previously during the history of the Soviet Union, Soviet era when it was called the Soviet Far East). Terminology In Russia, the region is usually referred to as simply th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stockfish
Stockfish is unsalted fish, especially cod, dried by cold air and wind on wooden racks (which are called "hjell" in Norway) on the foreshore. The drying of food is the world's oldest known preservation method, and dried fish has a storage life of several years. The method is cheap and effective in suitable climates; the work can be done by the fisherman and family, and the resulting product is easily transported to market. Over the centuries, several variants of dried fish have evolved. The ''stockfish'' (fresh dried, not salted) category is often mistaken for the ''klippfisk'', or salted cod, category where the fish is salted before drying. Salting was not economically feasible until the 17th century, when cheap salt from southern Europe became available to the maritime nations of northern Europe. Stockfish is cured in a fermentation process where cold-adapted bacteria matures the fish, similar to the maturing process of cheese. In English legal records of the medieval ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmonidae
Salmonidae (, ) is a family (biology), family of ray-finned fish, the only extant member of the suborder Salmonoidei, consisting of 11 extant genera and over 200 species collectively known as "salmonids" or "salmonoids". The family includes salmon (both Atlantic and Pacific species), trout (both ocean-going and landlocked), Salvelinus, char, Thymallus, graylings, freshwater whitefishes, taimens and lenoks, all coldwater fish, coldwater mid-trophic level, level predatory fish that inhabit the subarctic and cool temperate waters of the Northern Hemisphere. The Atlantic salmon (''Salmo salar''), whose Latin name became that of its genus ''Salmo'', is also the eponym of the family and order names. Salmonids have a relatively primitive appearance among teleost fish, with the pelvic fins being placed far back, and an adipose fin towards the rear of the back. They have slender bodies with rounded fish scale, scales and forked caudal fin, tail fins, and their fish jaw, mouths contain a si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sled Dog
A sled dog is a dog trained and used to pull a land vehicle in Dog harness, harness, most commonly a Dog sled, sled over snow. Sled dogs have been used in the Arctic for at least 8,000 years and, along with watercraft, were the only transportation in Arctic areas until the introduction of semi-trailer trucks, snowmobiles and airplanes in the 20th century, hauling supplies in areas that were inaccessible by other methods. They were used with varying success in the explorations of both Geographical pole, poles, as well as during the Yukon Gold Rush, Alaskan gold rush. Sled dog teams delivered mail to rural communities in Alaska, Yukon, Northwest Territories and Nunavut. Sled dogs today are still used by some rural communities, especially in areas of Russia, Canada, and Alaska as well as much of Greenland. They are used for recreational purposes and dog sled racing, racing events, such as the Iditarod Trail Sled Dog Race, Iditarod Trail and the Yukon Quest. History Sled dogs are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (GSE; , ''BSE'') is one of the largest Russian-language encyclopedias, published in the Soviet Union from 1926 to 1990. After 2002, the encyclopedia's data was partially included into the later ''Great Russian Encyclopedia'' in an updated and revised form. The GSE claimed to be "the first Marxist–Leninist general-purpose encyclopedia". Origins The idea of the ''Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' emerged in 1923 on the initiative of Otto Schmidt, a member of the Russian Academy of Sciences. In early 1924 Schmidt worked with a group which included Mikhail Pokrovsky, (rector of the Institute of Red Professors), Nikolai Meshcheryakov (Former head of the General Directorate for the Protection of State Secrets in the Press, Glavit, the State Administration of Publishing Affairs), Valery Bryusov (poet), Veniamin Kagan (mathematician) and Konstantin Kuzminsky to draw up a proposal which was agreed to in April 1924. Also involved was Anatoly Lunacharsky, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |