|
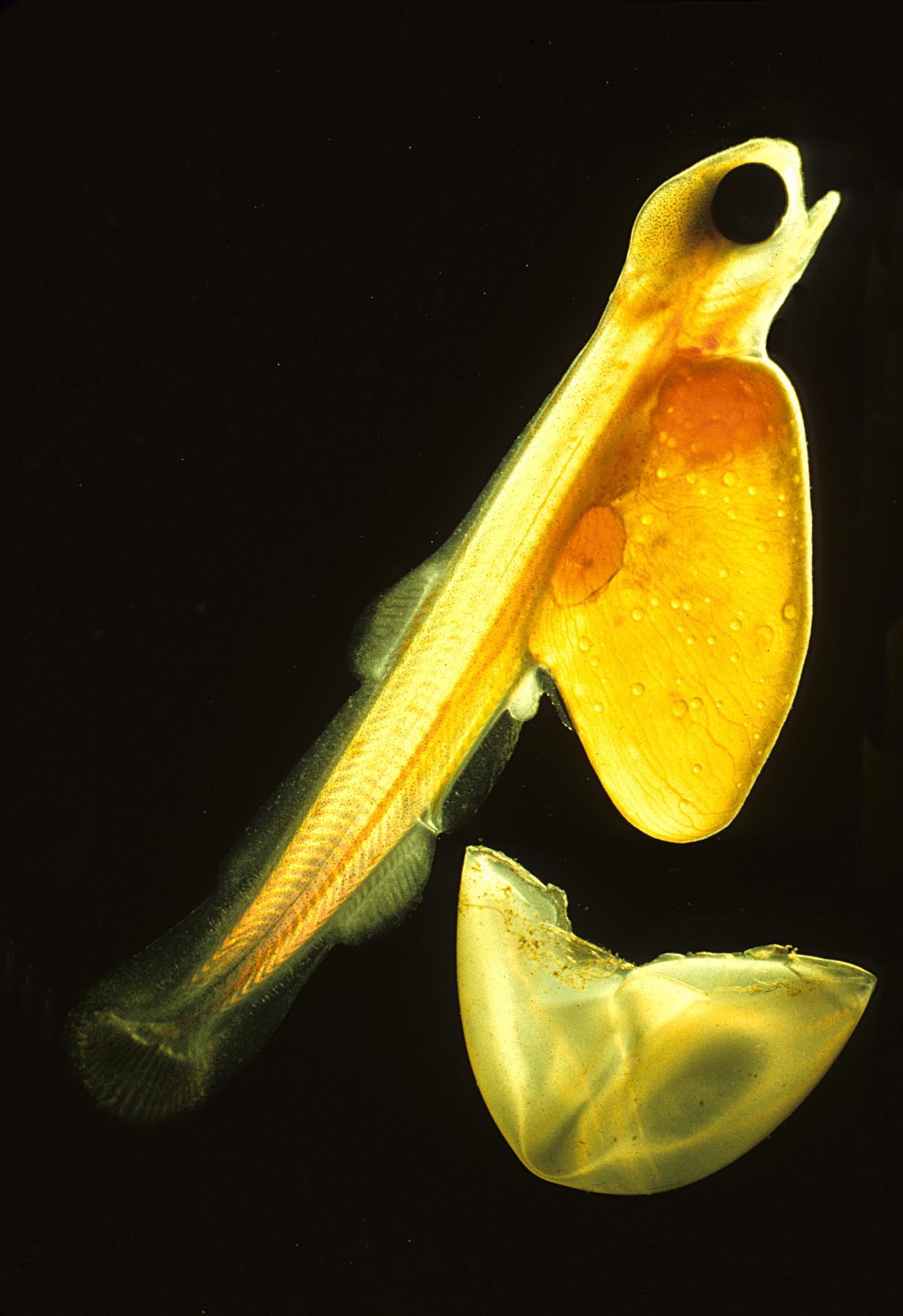
Yellowfin Whiting
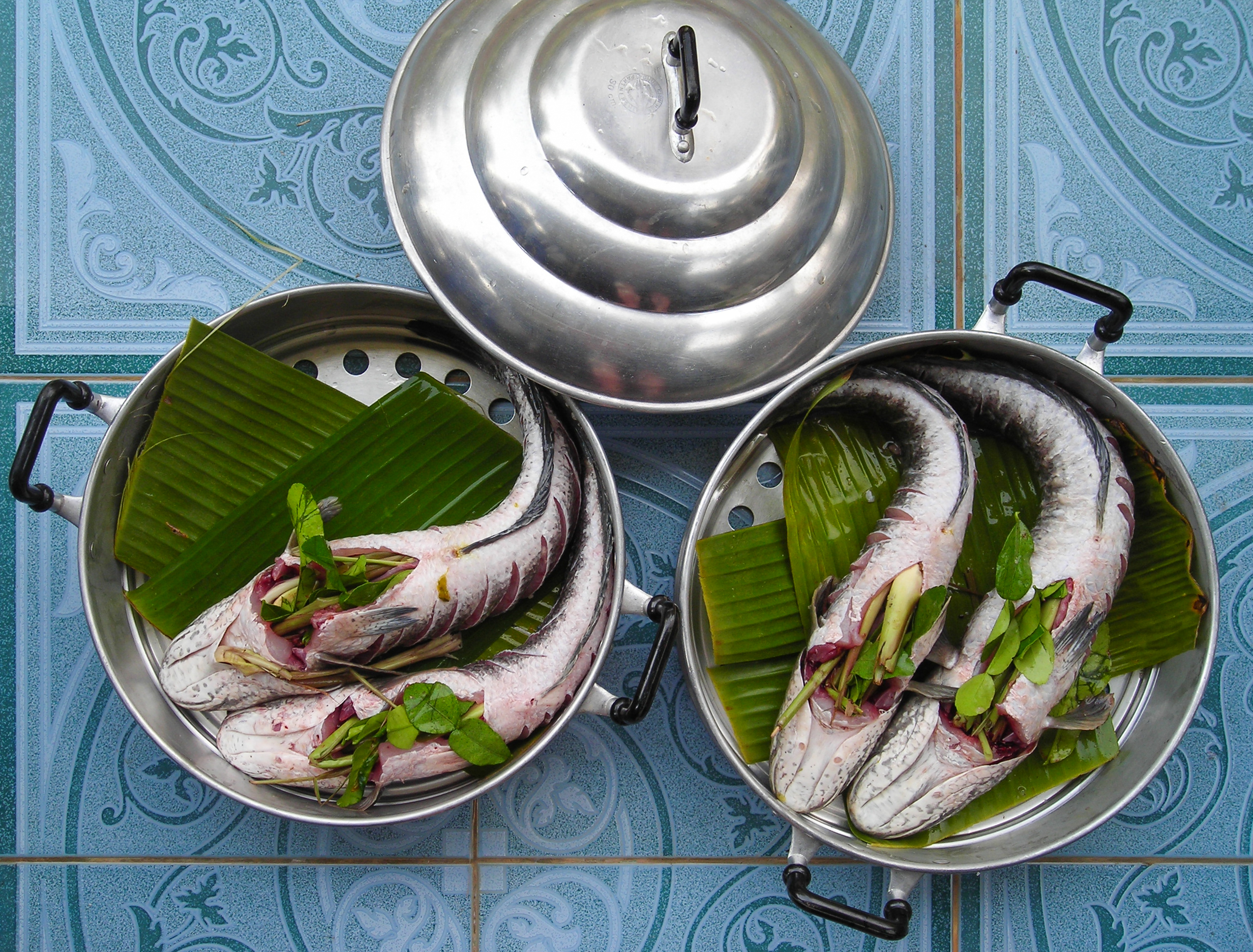
The yellowfin whiting (''Sillago schomburgkii''), also known as the western sand whiting or fine-scaled whiting, is a species of inshore marine fish in the smelt-whiting family Sillaginidae. The species is endemic to the eastern Indian Ocean, ranging from Dampier, Western Australia to Gulf St Vincent in South Australia, with an apparent division in the populations of the two states. Yellowfin whiting inhabit relatively shallow waters for their entire life, often found on tidal flats and creeks, as well as large estuaries. It is one of the largest members of the smelt-whiting family, growing to 42 cm, and can be distinguished by a number of anatomical and colour related features. Yellowfin whiting are benthic carnivores, preying predominantly on polychaete worms, with minor amounts of copepods, amphipods and bivalves also commonly taken. The species shows a change in diet with age, and also dietary differences with other sillaginids presumably to minimize competition. Reproduc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wilhelm Peters
Wilhelm Karl Hartwich (or Hartwig) Peters (22 April 1815 – 20 April 1883) was a German natural history, naturalist and explorer. He was assistant to the anatomist Johannes Peter Müller and later became curator of the Natural History Museum, Berlin, Berlin Zoological Museum. Encouraged by Müller and the explorer Alexander von Humboldt, Peters travelled to Mozambique via Angola in September 1842, exploring the coastal region and the Zambesi River. He returned to Berlin with an enormous collection of natural history specimens, which he then described in ''Naturwissenschaftliche Reise nach Mossambique... in den Jahren 1842 bis 1848 ausgeführt'' (1852–1882). The work was comprehensive in its coverage, dealing with mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, river fish, insects and botany. He replaced Martin Lichtenstein as curator of the museum in 1858, and in the same year he was elected a foreign member of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. In a few years, he greatly increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copepod
Copepods (; meaning 'oar-feet') are a group of small crustaceans found in nearly every freshwater and saltwater habitat (ecology), habitat. Some species are planktonic (living in the water column), some are benthos, benthic (living on the sediments), several species have Parasitism, parasitic phases, and some continental species may live in limnoterrestrial habitats and other wet terrestrial places, such as swamps, under leaf fall in wet forests, bogs, springs, ephemeral ponds, puddles, damp moss, or water-filled recesses of plants (phytotelmata) such as bromeliads and pitcher plants. Many live underground in marine and freshwater caves, sinkholes, or stream beds. Copepods are sometimes used as Ecological indicator, biodiversity indicators. As with other crustaceans, copepods have a larval form. For copepods, the egg hatches into a Crustacean larvae#Nauplius, nauplius form, with a head and a tail but no true thorax or abdomen. The larva molts several times until it resembles the a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perciformes
Perciformes (), also called the Acanthopteri, is an order or superorder of ray-finned fish in the clade Percomorpha. ''Perciformes'' means " perch-like". Among the well-known members of this group are perches and darters ( Percidae), and also sea basses and groupers (Serranidae). This order contains many familiar freshwater temperate and tropical marine fish groups, but also extremophiles that have successfully colonized both the North and South Poles, as well as the deepest depths of the ocean. Taxonomy Formerly, this group was thought to be even more diverse than it is thought to be now, containing about 41% of all bony fish (about 10,000 species) and about 160 families, which is the most of any order within the vertebrates. However, many of these other families have since been reclassified within their own orders within the clade Percomorpha, significantly reducing the size of the group. In contrast to this splitting, other groups formerly considered distinct, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suborder
Order () is one of the eight major hierarchical taxonomic ranks in Linnaean taxonomy. It is classified between family and class. In biological classification, the order is a taxonomic rank used in the classification of organisms and recognized by the nomenclature codes. An immediately higher rank, superorder, is sometimes added directly above order, with suborder directly beneath order. An order can also be defined as a group of related families. What does and does not belong to each order is determined by a taxonomist, as is whether a particular order should be recognized at all. Often there is no exact agreement, with different taxonomists each taking a different position. There are no hard rules that a taxonomist needs to follow in describing or recognizing an order. Some taxa are accepted almost universally, while others are recognized only rarely. The name of an order is usually written with a capital letter. For some groups of organisms, their orders may follow consistent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Percoidea
Percomorpha () is an extremely large and diverse clade of ray-finned fish. With more than 17,000 known species (including tuna, seahorses, gobies, cichlids, flatfish, wrasse, perches, anglerfish, and pufferfish) known from both marine and freshwater ecosystems, it is the most speciose clade of extant vertebrates. Evolution Percomorpha are the most diverse group of teleost fish today. Teleosts, and percomorphs in particular, thrived during the Cenozoic era. Fossil evidence shows that there was a major increase in size and abundance of teleosts immediately after the mass extinction event at the Cretaceous-Paleogene boundary ago. The oldest known percomorph fossils are of the early tetraodontiforms '' Protriacanthus'' and Cretatriacanthidae from the Santonian to Campanian of Italy and Slovenia. A higher diversity of early percomorphs is also known from the Campanian of Nardò, Italy, and these also show some level of diversification into modern orders, with representatives of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sillago
''Sillago'' is a genus of fish in the family (biology), family Sillaginidae and the only non-monotypic genus in the family. Distinguishing the species can be difficult, with many similar in appearance and colour, forcing the use of swim bladder morphology (biology), morphology as a definitive feature. All species are benthic in nature and generally coastal fish, living in shallow, protected waters although there are exceptions. Minor fishery, fisheries exist around various species of ''Sillago'', making them of minor importance in most of their range (biology), range. This genus has the widest Population distribution, distribution of any smelt-whiting genus, spanning much of the Indian Ocean, Indo-Pacific Ocean, Pacific. The genus ranges from the east coast of Africa to Japan in the east and Southern Australia in the south, with most species concentrated around South East Asia, the Indonesian Archipelago and Australia. Many species have overlapping distribution, often making posit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Table Fish
Many species of fish are caught by humans and consumed as food in virtually all regions around the world. Their meat has been an important dietary source of protein and other nutrients in the human diet. The English language does not have a special culinary name for food prepared from fish like with other animals (as with ''pig'' vs. ''pork''), or as in other languages (such as Spanish ''pez'' vs. '' pescado''). In culinary and fishery contexts, ''fish'' may include so-called shellfish such as molluscs, crustaceans, and echinoderms; but, more expansively, ''seafood'' covers both fish and other marine life used as food. Since 1961, the average annual increase in global apparent food fish consumption (3.2 percent) has outpaced population growth (1.6 percent) and exceeded the increase in consumption of meat from all terrestrial animals except poultry (4.9 percent), both combined (2.8 percent) and individually (bovine, ovine, porcine, et cetera). In ''per capita'' terms, food fish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shark Bay, Western Australia
Shark Bay () is a World Heritage Site in the Gascoyne region of Western Australia. The area is located approximately north of Perth, on the westernmost point of the Australian continent. UNESCO's listing of Shark Bay as a World Heritage Site reads: The bay features Australia's most abundant marine ecosystems. It is a popular fishing spot. History The record of Australian Aboriginal occupation of Shark Bay extends to years BP. At that time most of the area was dry land, and rising sea levels flooded Shark Bay between BP and BP. A considerable number of Aboriginal midden sites have been found, especially on Peron Peninsula and Dirk Hartog Island, which provide evidence of some of the foods gathered from the waters and nearby land areas. An expedition led by Dirk Hartog happened upon the area in 1616, becoming the second group of Europeans known to have visited Australia, after the crew of ''Duyfken'' under Willem Janszoon had visited Cape York in 1606. The area was gi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life or, more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a., fishing grounds). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both in freshwater waterbodies (about 10% of all catch) and the oceans (about 90%). About 500 million people worldwide are economically dependent on fisheries. 171 million tonnes of fish were produced in 2016, but overfishing is an increasing problem, causing declines in some populations. Because of their economic and social importance, fisheries are governed by complex fisheries management practices and legal regimes that vary widely across countries. Historically, fisheries were treated with a "first-come, first-served" approach, but recent threats from human overfishing and environmental issues have required increased regulation of fisheries to prevent conflict and increase profitable economic activity on the fishery. Modern jurisd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
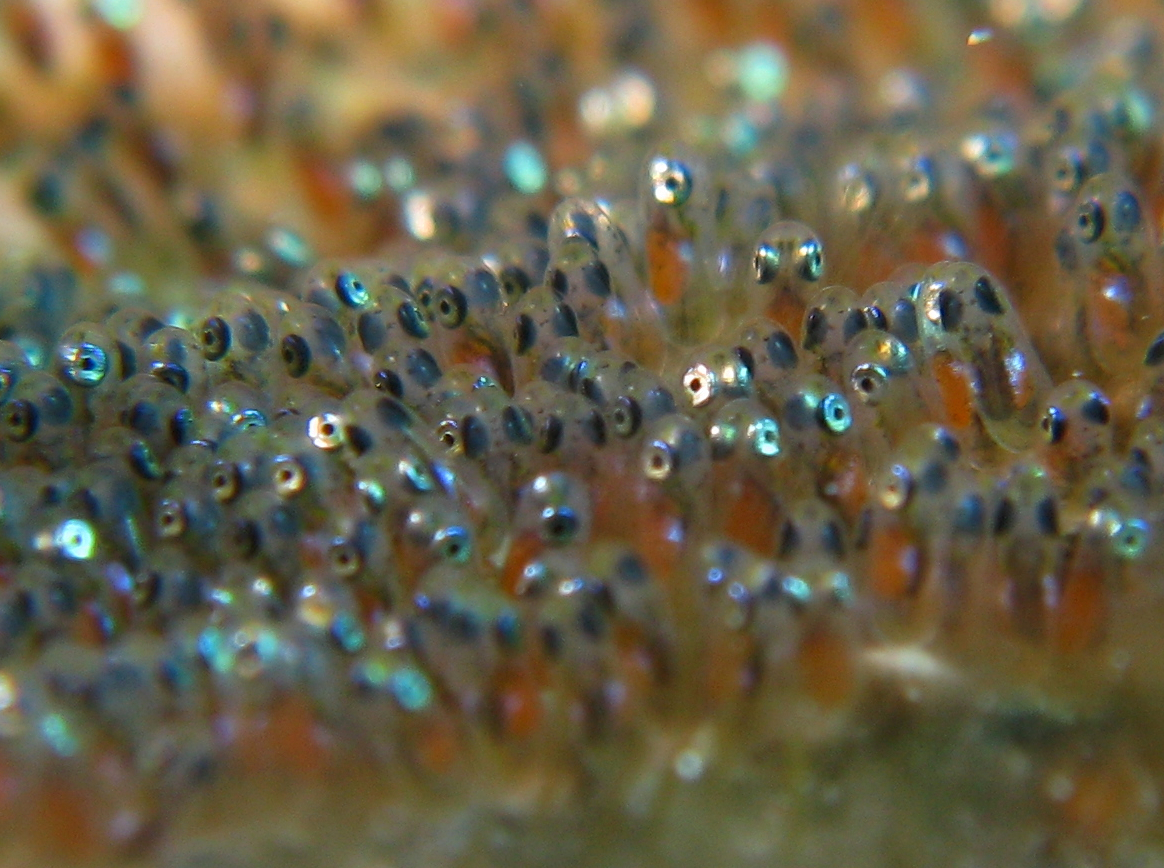
Spawn (biology)
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of freely releasing eggs and sperm into a body of water (fresh or marine); the physical act is known as spawning. The vast majority of aquatic and amphibious animals reproduce through spawning. These include the following groups: * Bony fishes * Crustaceans (such as crabs, shrimps, etc.) *Mollusks (such as oysters, octopus, squid) *Echinoderms (such as sea urchins, sea stars, sea cucumbers, etc.) * Amphibians (such as frogs, toads, salamanders, newts) * Aquatic insects (such as dragonflies, mayflies, mosquitoes) *Coral, which are living colonies of tiny, aquatic organisms—not plants, as they are sometimes perceived to be. Corals, while appearing sedentary or botanical by nature, actually spawn by releasing clouds of sperm and egg cells into the water column, where the two mix. As a general rule, aquatic or semiaquatic reptiles, birds, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sexual Maturity
Sexual maturity is the capability of an organism to reproduce. In humans, it is related to both puberty and adulthood. ''Puberty'' is the biological process of sexual maturation, while ''adulthood'', the condition of being socially recognized as an independent person capable of giving consent and taking responsibility, generally implies sexual maturity (certain disorders of sexual development notwithstanding), but depends on other criteria, defined by specific cultural expectations. Most multicellular organisms are unable to sexually reproduce at birth (animals) or germination (e.g. plants): depending on the species, it may be days, weeks, or years until they have developed enough to be able to do so; in addition, certain cues may trigger an organism to become sexually mature. These may be external, such as drought, or fire, that triggers sexual maturation of certain plants, or internal, such as percentage of body fat (certain animals). Internal cues are not to be confused ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egg (biology)
An egg is an organic vessel grown by an animal to carry a possibly fertilization, fertilized egg cell (a zygote) and to egg incubation, incubate from it an embryo within the egg until the embryo has become an animal fetus that can survive on its own, at which point the animal hatches. Most arthropods, vertebrates (excluding live-bearing mammals), and Mollusca, mollusks lay eggs, although some, such as scorpions, do not. Reptile eggs, bird eggs, and monotreme eggs are laid out of water and are surrounded by a protective eggshell, shell, either flexible or inflexible. Eggs laid on land or in nests are usually kept within a warm and favorable temperature range while the embryo grows. When the embryo is adequately developed it hatches, i.e., breaks out of the egg's shell. Some embryos have a temporary egg tooth they use to crack, pip, or break the eggshell or covering. The largest recorded egg is from a whale shark and was in size. Whale shark eggs typically hatch within the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |