|
Xanthoma
A xanthoma (pl. xanthomas or xanthomata) (condition: xanthomatosis) is a deposition of yellowish cholesterol-rich material that can appear anywhere in the body in various disease states. They are cutaneous manifestations of lipidosis in which lipids accumulate in large foam cells within the skin. They are associated with hyperlipidemias, both primary and secondary types. Tendon xanthomas are associated with type II hyperlipidemia, chronic Biliary tract#Pathology, biliary tract obstruction, primary biliary cirrhosis, sitosterolemia and the rare metabolic disease cerebrotendineous xanthomatosis. Palmar xanthomata and tuberoeruptive xanthomata (over knees and elbows) occur in type III hyperlipidemia. Etymology The term xanthoma stems from Greek ξανθός (xanthós) 'yellow', and -ωμα -oma, a suffix forming nouns indicating a mass or tumor. Types Xanthelasma A xanthelasma is a sharply demarcated yellowish collection of cholesterol underneath the skin, usually on or around ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerebrotendineous Xanthomatosis
Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX), also called cerebral cholesterosis, is a rare inborn bile acid metabolism disorder caused by autosomal-recessive mutations in the CYP27A1 gene. CTX is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including neurological and non-neurological issues. The average age of symptom onset is 19 years, with central nervous system symptoms being the first indications. Neurological characteristics include Parkinsonism, epilepsy, dystonia, progressive ataxia, palatal myoclonus, intellectual disability, dementia, and psychiatric symptoms. CTX often results in cataracts during childhood. Adults with CTX often experience optic disk paleness and other ocular problems. Clinical symptoms include cardiovascular disease and premature atherosclerosis, with patients experiencing elevated levels of 27-hydroxycholesterol and decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. CTX patients often experience osteoporosis and recurrent bone fractures, with gait abnormalities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Xanthoma Variants Associated With Hyperlipoproteinemia Subtypes
When the cholesterol levels in the body rise above the normal level, a number of skin lesions can occur. Xanthomas are one of types of skin lesions that may occur in this situation. Other systemic conditions may also occur with increased levels of cholesterol in the blood. See also *List of cutaneous conditions * List of contact allergens *List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer * List of cutaneous conditions associated with internal malignancy * List of cutaneous conditions caused by mutations in keratins * List of cutaneous conditions caused by problems with junctional proteins * List of dental abnormalities associated with cutaneous conditions * List of genes mutated in cutaneous conditions * List of histologic stains that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions * List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous conditions * List of inclusion bodies that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions *List of kerati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyperlipidemia
Hyperlipidemia is abnormally high levels of any or all lipids (e.g. fats, triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids) or lipoproteins in the blood. citing: and The term ''hyperlipidemia'' refers to the laboratory finding itself and is also used as an umbrella term covering any of various acquired or genetic disorders that result in that finding. Hyperlipidemia represents a subset of dyslipidemia and a superset of hypercholesterolemia. Hyperlipidemia is usually chronic and requires ongoing medication to control blood lipid levels. Lipids (water-insoluble molecules) are transported in a Apolipoprotein, protein Lipoprotein, capsule. The size of that capsule, or lipoprotein, determines its density. The lipoprotein density and type of apolipoproteins it contains determines the fate of the particle and its influence on metabolism. Hyperlipidemias are divided into primary and secondary subtypes. Primary hyperlipidemia is usually due to genetic causes (such as a mutation in a recepto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthoma Disseminatum
Xanthoma disseminatum is a rare cutaneous condition that preferentially affects males in childhood, characterized by the insidious onset of small, yellow-red to brown papules and nodules that are discrete and disseminated. It is a histiocytosis syndrome. See also * Non-X histiocytosis * List of cutaneous conditions Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function o ... References External links Monocyte- and macrophage-related cutaneous conditions {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xanthoma Diabeticorum
Xanthoma diabeticorum is a cutaneous condition that may result in young persons who are unresponsive to insulin. See also * Xanthoma * Skin lesion A skin condition, also known as cutaneous condition, is any medical condition that affects the integumentary system—the organ system that encloses the body and includes skin, nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this ... References Skin conditions resulting from errors in metabolism {{Cutaneous-condition-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
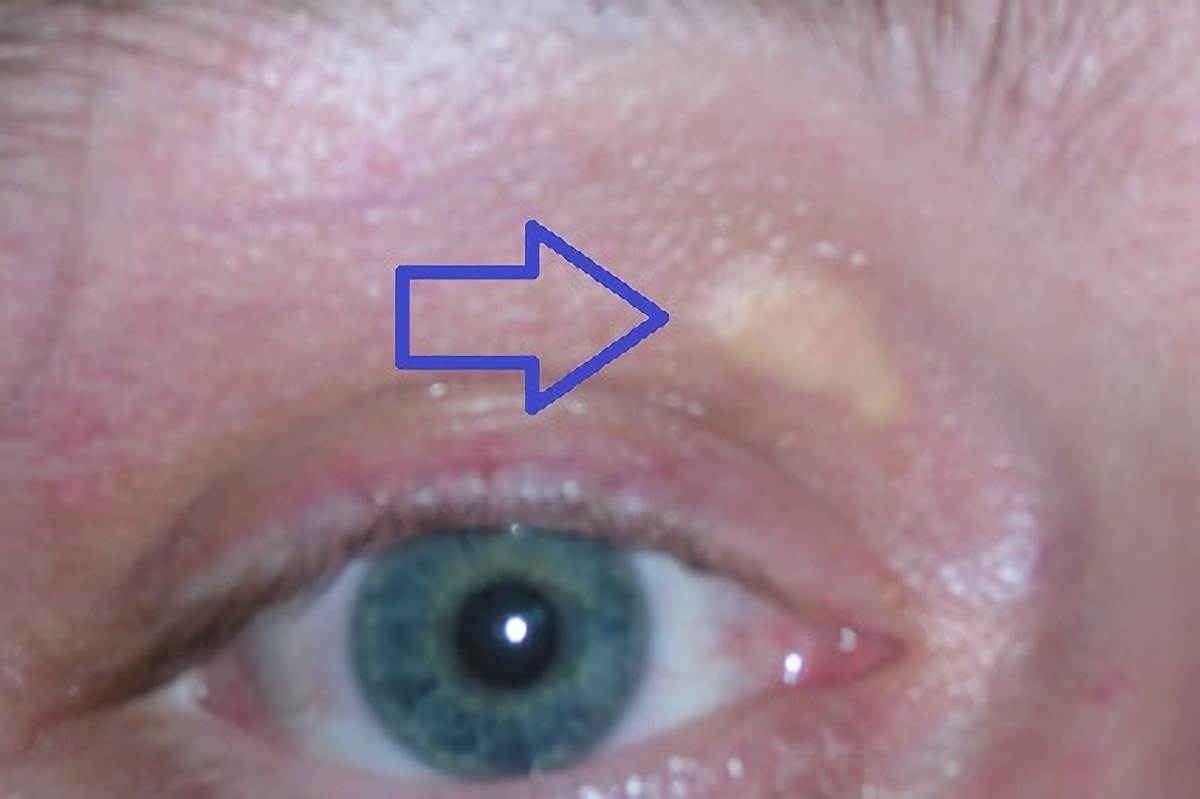
Xanthelasma
Xanthelasma is a sharply demarcated yellowish deposit of cholesterol underneath the skin. It usually occurs on or around the eyelids (''xanthelasma palpebrarum'', abbreviated XP). While they are neither harmful to the skin nor painful, these minor growths may be disfiguring and can be removed. There is a growing body of evidence for the association between xanthelasma deposits and blood low-density lipoprotein levels and increased risk of atherosclerosis. A xanthelasma may be referred to as a xanthoma when becoming larger and nodular, assuming tumorous proportions. Xanthelasma is often classified simply as a subtype of xanthoma. Diagnosis Xanthelasma in the form of XP can be diagnosed from clinical impression, although in some cases it may need to be distinguished (differential diagnosis) from other conditions, especially necrobiotic xanthogranuloma, syringoma, palpebral sarcoidosis, sebaceous hyperplasia, Erdheim–Chester disease, lipoid proteinosis ( Urbach–Wiethe di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitosterolemia
Sitosterolemia, also known as phytosterolemia, is a rare autosomal recessively inherited lipid metabolic disorder. It is characterized by hyperabsorption and decreased biliary excretion of dietary sterols (including the phytosterol beta-sitosterol). Healthy persons absorb only about 5% of dietary plant sterols, but sitosterolemia patients absorb 15% to 60% of ingested sitosterol without excreting much into the bile. It's named after the most abundant phytosterol in the diet, sitosterol, though other phytosterols are also involved. The phytosterol campesterol is more readily absorbed than sitosterol. Sitosterolemia patients develop hypercholesterolemia, tendon and tuberous xanthomas, premature development of atherosclerosis, and abnormal hematologic and liver function test results. Signs and symptoms Sitosterolemia may share several clinical characteristics with the well-characterized familial hypercholesterolemia (FH), such as the development of tendon xanthomas in the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipidosis
A lipid storage disorder (or lipidosis) is any one of a group of inherited metabolic disorders in which harmful amounts of fats or lipids accumulate in some body cells and tissues. People with these disorders either do not produce enough of one of the enzymes needed to metabolize and break down lipids or, they produce enzymes that do not work properly. Over time, the buildup of fats may cause permanent cellular and tissue damage, particularly in the brain, peripheral nervous system, liver, spleen, and bone marrow. Inside cells under normal conditions, lysosomes convert, or metabolize, lipids and proteins into smaller components to provide energy for the body. Classification Disorders that store this intracellular material are part of the lysosomal storage diseases family of disorders. Sphingolipidoses Many lipid storage disorders can be classified into the subgroup of sphingolipidoses, as they relate to sphingolipid metabolism. Members of this group include Niemann-Pick diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
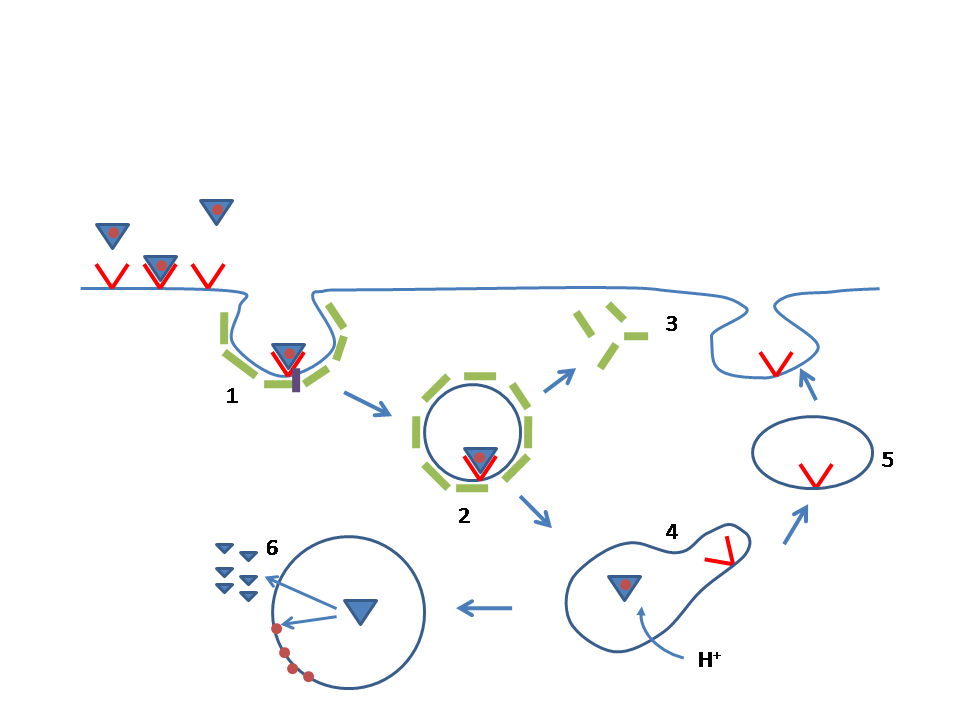
Familial Hypercholesterolemia
Familial hypercholesterolemia (FH) is a genetic disorder characterized by high cholesterol levels, specifically very high levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL cholesterol), in the blood and early cardiovascular diseases. The most common mutations diminish the number of functional LDL receptors in the liver or produce abnormal LDL receptors that never go to the cell surface to function properly (abnormal trafficking). Since the underlying body biochemistry is slightly different in individuals with FH, their high cholesterol levels are less responsive to the kinds of cholesterol control methods which are usually more effective in people without FH (such as dietary modification and statin tablets). Nevertheless, treatment (including higher statin doses and PCSK9 inhibitors) is usually effective. FH is classified as a type 2 familial dyslipidemia. There are five types of familial dyslipidemia (not including subtypes), and each are classified from both the altered l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |