|
Wolf Fifth
In music theory, the wolf fifth (sometimes also called Procrustean fifth, or imperfect fifth) is a particularly dissonant musical interval spanning seven semitones. Strictly, the term refers to an interval produced by a specific tuning system, widely used in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries: the quarter-comma meantone temperament. More broadly, it is also used to refer to similar intervals (of close, but variable magnitudes) produced by other tuning systems, including Pythagorean and most meantone temperaments. When the twelve notes within the octave of a chromatic scale are tuned using the quarter-comma meantone systems of temperament, one of the twelve intervals apparently spanning seven semitones is actually a diminished sixth, which turns out to be much wider than the in-tune genuine fifths, In mean-tone systems, this interval is usually from C to A or from G to E but can be moved in either direction to favor certain groups of keys. The eleven perfect fifths s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Wolf Fifth
In music theory, the wolf fifth (sometimes also called Procrustean fifth, or imperfect fifth) is a particularly dissonant musical interval spanning seven semitones. Strictly, the term refers to an interval produced by a specific tuning system, widely used in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries: the quarter-comma meantone temperament. More broadly, it is also used to refer to similar intervals (of close, but variable magnitudes) produced by other tuning systems, including Pythagorean and most meantone temperaments. When the twelve notes within the octave of a chromatic scale are tuned using the quarter-comma meantone systems of temperament, one of the twelve intervals apparently spanning seven semitones is actually a diminished sixth, which turns out to be much wider than the in-tune genuine fifths, In mean-tone systems, this interval is usually from C to A or from G to E but can be moved in either direction to favor certain groups of keys. The eleven perfect fifths so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Fifth On C
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the grey wolf or gray wolf, is a Canis, canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of Canis lupus, subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, including the dog and dingo, though grey wolves, as popularly understood, only comprise Wild type, naturally-occurring wild subspecies. The wolf is the largest wild Neontology, extant member of the family Canidae, and is further distinguished from other ''Canis'' species by its less pointed ears and muzzle, as well as a shorter torso and a longer tail. The wolf is nonetheless related closely enough to smaller ''Canis'' species, such as the coyote and the golden jackal, to produce fertile Canid hybrid, hybrids with them. The wolf's fur is usually mottled white, brown, grey, and black, although subspecies in the arctic region may be nearly all white. Of all members of the genus ''Canis'', the wolf is most Generalist and specialist species, specializ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cent (music)
The cent is a logarithmic unit of measure used for musical intervals. Twelve-tone equal temperament divides the octave into 12 semitones of 100 cents each. Typically, cents are used to express small intervals, to check intonation, or to compare the sizes of comparable intervals in different tuning systems. For humans, a single cent is too small to be perceived between successive notes. Cents, as described by Alexander John Ellis, follow a tradition of measuring intervals by logarithms that began with Juan Caramuel y Lobkowitz in the 17th century. Ellis chose to base his measures on the hundredth part of a semitone, \sqrt 200/math>, at Robert Holford Macdowell Bosanquet's suggestion. Making extensive measurements of musical instruments from around the world, Ellis used cents to report and compare the scales employed, and further described and utilized the system in his 1875 edition of Hermann von Helmholtz's ''On the Sensations of Tone''. It has become the standard me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle Of Fifths
In music theory, the circle of fifths (sometimes also cycle of fifths) is a way of organizing pitches as a sequence of perfect fifths. Starting on a C, and using the standard system of tuning for Western music (12-tone equal temperament), the sequence is: C, G, D, A, E, B, F/G, C/D, G/A, D/E, A/B, F, and C. This order places the most closely related key signatures adjacent to one another. Twelve-tone equal temperament tuning divides each octave into twelve equivalent semitones, and the circle of fifths leads to a C seven octaves above the starting point. If the fifths are tuned with an exact frequency ratio of 3:2 (the system of tuning known as just intonation), this is not the case (the circle does not "close"). Definition The circle of fifths organizes pitches in a sequence of perfect fifths, generally shown as a circle with the pitches (and their corresponding keys) in clockwise order. It can be viewed in a counterclockwise direction as a circle of fourths. Harmonic progres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Theory
Music theory is the study of theoretical frameworks for understanding the practices and possibilities of music. '' The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory": The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (key signatures, time signatures, and rhythmic notation); the second is learning scholars' views on music from antiquity to the present; the third is a sub-topic of musicology that "seeks to define processes and general principles in music". The musicological approach to theory differs from music analysis "in that it takes as its starting-point not the individual work or performance but the fundamental materials from which it is built." Music theory is frequently concerned with describing how musicians and composers make music, including tuning systems and composition methods among other topics. Because of the ever-expanding conception of what constitutes music, a more inclusive definition could b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equal Temperament
An equal temperament is a musical temperament or Musical tuning#Tuning systems, tuning system that approximates Just intonation, just intervals by dividing an octave (or other interval) into steps such that the ratio of the frequency, frequencies of any adjacent pair of notes is the same. This system yields Pitch (music), pitch steps perceived as equal in size, due to the logarithmic changes in pitch frequency. In classical music and Western music in general, the most common tuning system since the 18th century has been 12 equal temperament (also known as ''12 tone equal temperament'', ' or ', informally abbreviated as ''12 equal''), which divides the octave into 12 parts, all of which are equal on a logarithmic scale, with a ratio equal to the twelfth root of two, 12th root of 2, (\sqrt[12] ≈ 1.05946). That resulting smallest interval, the width of an octave, is called a semitone or half step. In Western world, Western countries the term ''equal temperamen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Notation
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music. Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods. For example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves, time signatures, key signatures, and noteheads for writing and deciphering pieces. But even so, there are far more systems just that, for instance in professional country music, the Nashville Number System is the main method, and for string instruments such as guitar, it is quite common for tablature to be used by player ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meantone Tuning
Meantone temperaments are musical temperaments; that is, a variety of tuning systems constructed, similarly to Pythagorean tuning, as a sequence of equal fifths, both rising and descending, scaled to remain within the same octave. But rather than using perfect fifths, consisting of frequency ratios of value 3:2, these are ''tempered'' by a suitable factor that narrows them to ratios that are slightly less than 3:2, in order to bring the major or minor thirds closer to the just intonation ratio of 5:4 or 6:5 , respectively. Among temperaments constructed as a sequence of fifths, a regular temperament is one in which all the fifths are chosen to be of the same size. Twelve-tone equal temperament () is obtained by making all semitones the same size, with each equal to one-twelfth of an octave; i.e. with ratios . Relative to Pythagorean tuning, it narrows the perfect fifths by about 2 cents or of a Pythagorean comma to give a frequency ratio of 2^:1. This produces major t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic Equivalence
In music, two written notes have enharmonic equivalence if they produce the same pitch (music), pitch but are musical notation, notated differently. Similarly, written Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, or key signatures are considered enharmonic if they represent identical pitches that are notated differently. The term derives from Latin , in turn from Late Latin , from Ancient Greek (), from ('in') and ('harmony'). Definition The predominant musical tuning, tuning system in Western music is 12 tone equal temperament, twelve-tone equal temperament (12 ), where each octave is divided into twelve equivalent half steps or semitones. The notes F and G are a whole step apart, so the note one semitone above F (F) and the note one semitone below G (G) indicate the same pitch. These written notes are ''enharmonic'', or ''enharmonically equivalent''. The choice of notation for a pitch can depend on its diatonic function, role in harmony; this notation keeps modern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Comma Meantone
Quarter-comma meantone, or -comma meantone, was the most common meantone temperament in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries, and was sometimes used later. In this system the perfect fifth is flattened by one quarter of a syntonic comma with respect to its just intonation used in Pythagorean tuning (frequency ratio the result is \tfrac \times \left(\tfrac\right)^ = \sqrt \approx 1.49535, or a fifth of 696.578 cents. (The 12th power of that value is 125, whereas 7 octaves is 128, and so falls 41.059 cents short.) This fifth is then iterated to generate the diatonic scale and other notes of the temperament. The purpose is to obtain justly intoned major thirds (with a frequency ratio equal to It was described by Pietro Aron in his ''Toscanello de la Musica'' of 1523, by saying the major thirds should be tuned to be "sonorous and just, as united as possible". Later theorists Gioseffo Zarlino and Francisco de Salinas described the tuning with mathematical exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
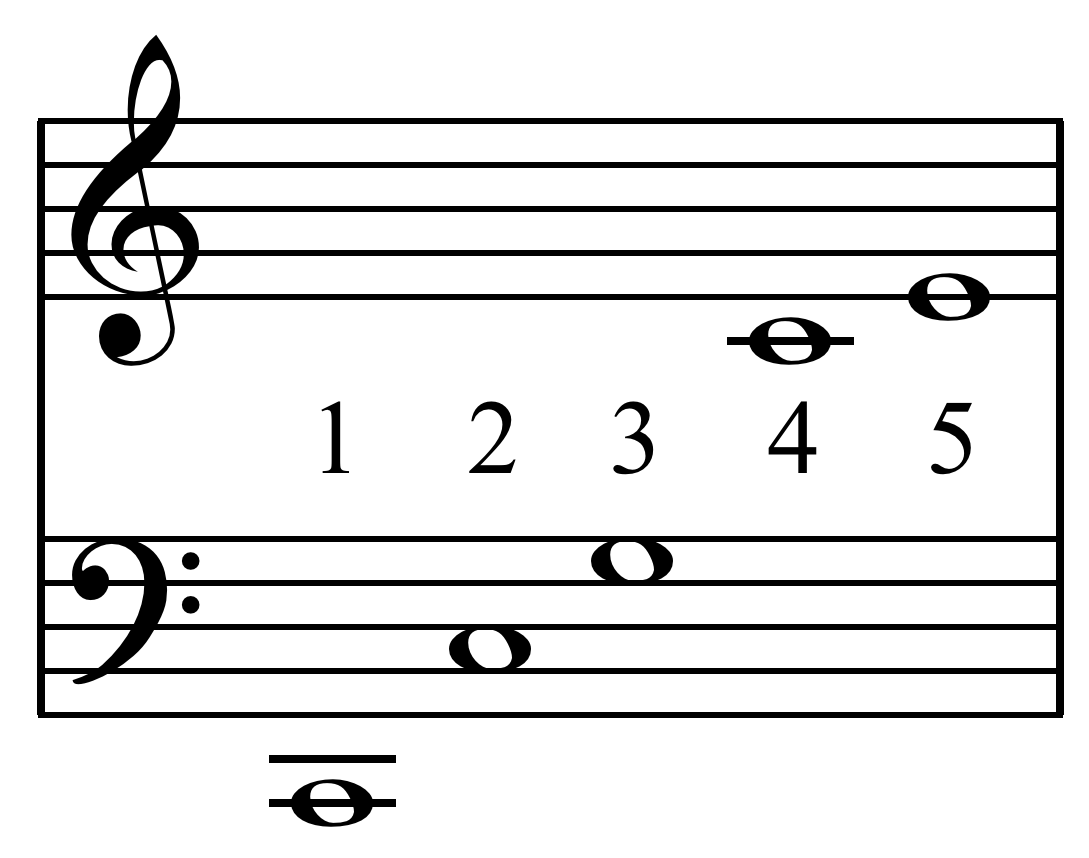
Just Intonation
In music, just intonation or pure intonation is a musical tuning, tuning system in which the space between notes' frequency, frequencies (called interval (music), intervals) is a natural number, whole number ratio, ratio. Intervals spaced in this way are said to be pure, and are called just intervals. Just intervals (and chords created by combining them) consist of tones from a single harmonic series (music), harmonic series of an implied fundamental frequency, fundamental. For example, in the diagram, if the notes G3 and C4 (labelled 3 and 4) are tuned as members of the harmonic series of the lowest C, their frequencies will be 3 and 4 times the fundamental frequency. The interval ratio between C4 and G3 is therefore 4:3, a just fourth (music), fourth. In Western musical practice, bowed instruments such as violins, violas, cellos, and double basses are tuned using pure fifths or fourths. In contrast, keyboard instruments are rarely tuned using only pure intervals—the desire fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diminished Seventh
In classical music from Western culture, a diminished seventh () is an interval (music), interval produced by Diminution, narrowing a minor seventh by a chromatic semitone,Benward & Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice, Vol. I'', p.54. . Specific example of an d7 not given but general example of minor intervals described. and its Inversion (interval), inversion is the augmented second. For instance, the interval from A to G is a minor seventh, ten semitones wide, and both the intervals from A to G, and from A to G are diminished sevenths, spanning nine semitones. Being diminished, it is considered a consonance and dissonance, dissonant interval. The diminished seventh is used quite readily in the minor key, where it is present in the harmonic minor scale between the seventh scale step and the sixth scale step in the octave above. In 12-tone equal temperament, a diminished seventh is equal to nine semitones, a ratio of 29/12:1 (approximately 1.6818), or 900 cents, and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |