|
Water Clarity
Water clarity is a descriptive term for how deeply visible light penetrates through water. In addition to light penetration, the term water clarity is also often used to describe underwater visibility. Water clarity is one way that humans measure water quality, along with oxygen concentration and the presence or absence of pollutants and algal blooms. Water clarity governs the health of underwater ecosystems because it impacts the amount of light reaching the plants and animals living underwater. For plants, light is needed for photosynthesis. The clarity of the underwater environment determines the depth ranges where aquatic plants can live. Water clarity also impacts how well visual animals like fish can see their prey. Clarity affects the aquatic plants and animals living in all kinds of water bodies, including rivers, ponds, lakes, reservoirs, estuaries, coastal lagoons, and the open ocean. Water clarity also affects how humans interact with water, from recreation and propert ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Particulate Organic Carbon
Particulate organic matter (POM) is a fraction of total organic matter operationally defined as that which does not pass through a filter pore size that typically ranges in size from 0.053 millimeters (53 μm) to 2 millimeters. Particulate organic carbon (POC) is a closely related term often used interchangeably with POM. POC refers specifically to the mass of carbon in the particulate organic material, while POM refers to the total mass of the particulate organic matter. In addition to carbon, POM includes the mass of the other elements in the organic matter, such as nitrogen, oxygen and hydrogen. In this sense POC is a component of POM and there is typically about twice as much POM as POC. Many statements that can be made about POM apply equally to POC, and much of what is said in this article about POM could equally have been said of POC. Particulate organic matter is sometimes called suspended organic matter, macroorganic matter, or coarse fraction organic matter. When lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or approximately 20% of the water area of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia (continent), Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by the Southern Ocean or Antarctica, depending on the definition in use. The Indian Ocean has large marginal or regional seas, including the Andaman Sea, the Arabian Sea, the Bay of Bengal, and the Laccadive Sea. Geologically, the Indian Ocean is the youngest of the oceans, and it has distinct features such as narrow continental shelf, continental shelves. Its average depth is 3,741 m. It is the warmest ocean, with a significant impact on global climate due to its interaction with the atmosphere. Its waters are affected by the Indian Ocean Walker circulation, resulting in unique oceanic currents and upwelling patterns. The Indian Ocean is ecologically diverse, with important ecosystems such ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal is a rift lake and the deepest lake in the world. It is situated in southern Siberia, Russia between the Federal subjects of Russia, federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast, Irkutsk Oblasts of Russia, Oblast to the northwest and the Republic of Buryatia to the southeast. At —slightly larger than Belgium—Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by area, seventh-largest lake by surface area, as well as the second largest lake in Eurasia after the Caspian Sea. However, because it is also the List of lakes by depth, deepest lake, with a maximum depth of , Lake Baikal is the world's List of lakes by volume, largest freshwater lake by volume, containing of water or 22–23% of the world's fresh surface water, more than all of the North American Great Lakes combined. It is also the world's ancient lake, oldest lake at 25–30 million years, and among the clearest. It is estimated that the lake contains around 19% of the unfrozen fresh water on the planet. Lake Baikal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
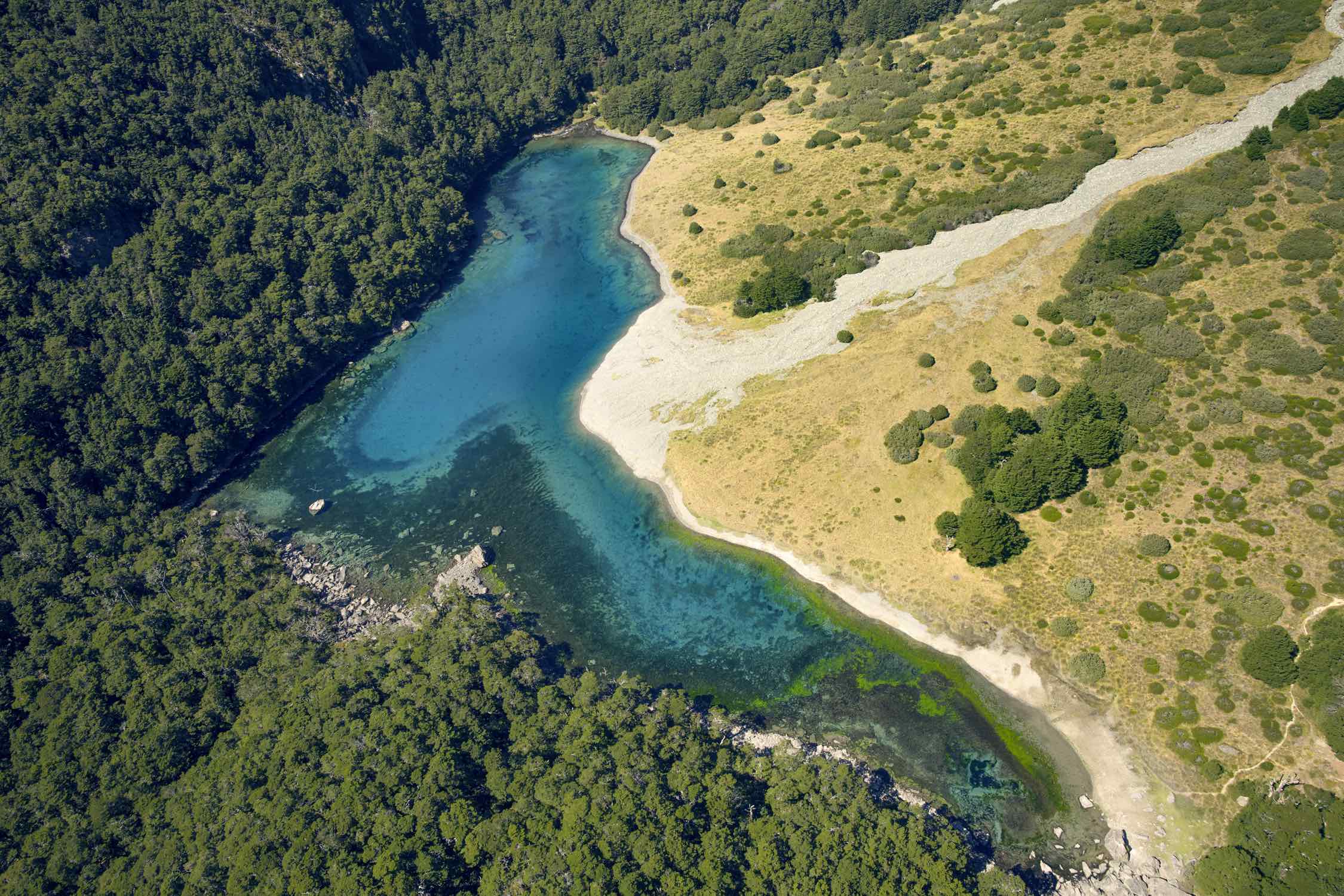
Blue Lake (Tasman)
Rotomairewhenua / Blue Lake is a small lake in Nelson Lakes National Park, in the northern reaches of New Zealand's Southern Alps. Sacred to local Māori, it has the clearest natural fresh water in the world. Description The Blue Lake is drained by the west branch of the Sabine River, which is part of the Buller River system. It is fed by a short upper segment of the Sabine, which in turn is fed by underground seepage through the landslide debris impounding the much larger Lake Constance. Blue Lake is roughly boomerang shaped, running north then northwest, with each arm of the lake stretching some . Its waters are cold, ranging from . Clarity The lake has extremely clear water, and is the clearest natural body of fresh water yet reported. A 2011 study found its visibility ranged from , clearer than the measured for Te Waikoropupu Springs, a previous record holder. For comparison, laboratory measurements show distilled water has a visibility of approximately . Scientists at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pacific Gyre
The Southern Pacific Gyre is part of the Earth's system of rotating ocean currents, bounded by the Equator to the north, Australia to the west, the Antarctic Circumpolar Current to the south, and South America to the east. The center of the South Pacific Gyre is the oceanic pole of inaccessibility, the site on Earth farthest from any continents and productive ocean regions and is regarded as Earth's largest oceanic desert. With an area of 37 million square kilometres, it makes up approximately 10% of the Earth's ocean surface. The gyre, as with Earth's other four gyres, contains an area with elevated concentrations of pelagic plastics, chemical sludge, and other debris known as the South Pacific garbage patch. Sediment flux and accumulation Earth's trade winds and Coriolis force cause the ocean currents in South Pacific Ocean to circulate counterclockwise. The currents act to isolate the center of the gyre from nutrient upwelling, and few nutrients are transported there by th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oligotrophic
An oligotroph is an organism that can live in an environment that offers very low levels of nutrients. They may be contrasted with copiotrophs, which prefer nutritionally rich environments. Oligotrophs are characterized by slow growth, low rates of metabolism, and generally low population density. Oligotrophic environments are those that offer little to sustain life. These environments include deep oceanic sediments, caves, glacial and polar ice, deep subsurface soil, aquifers, ocean waters, and leached soils. Examples of oligotrophic organisms are the cave-dwelling olm; the bacterium " ''Candidatus'' Pelagibacter communis", which is the most abundant organism in the ocean (with an estimated 2 × 1028 individuals in total); and lichens, with their extremely low metabolic rate. Etymology Etymologically, the word "oligotroph" is a combination of the Greek adjective ''oligos'' (ὀλίγος) meaning "few" and the adjective ''trophikos'' (τροφικός) meaning "feeding". Plant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crater Lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ) is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the Western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is a tourist attraction for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fills a caldera that was formed around 7,700 (± 150) years ago by the collapse of the volcano Mount Mazama. No rivers flow into or out of the lake; the evaporation is compensated for by rain and snowfall at a rate such that the total amount of water is replaced every 150 years. With a depth of , the lake is the deepest in the United States. In the world, it ranks eleventh for maximum depth, as well as fifth for mean depth. Crater Lake features two small islands. Wizard Island, located near the western shore of the lake, is a cinder cone about in size. Phantom Ship, a natural rock pillar, is located near the southern shore. Since 2002, one of Oregon's regular-issue license-plate design has featured Crater Lake and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Tahoe
Lake Tahoe (; Washo language, Washo: ''dáʔaw'') is a Fresh water, freshwater lake in the Sierra Nevada of the Western United States, straddling the border between California and Nevada. Lying at above sea level, Lake Tahoe is the largest alpine lake in North America, and at it trails only the five Great Lakes as the List of lakes by volume, largest by volume in the United States. Its depth is , making it the List of lakes by depth, second deepest in the United States after Crater Lake in Oregon (). The lake was formed about two million years ago as part of the Lake Tahoe Basin, and its modern extent was shaped during the Quaternary glaciation, ice ages. It is known for the clarity of its water and the panorama of surrounding mountains on all sides. The area surrounding the lake is also referred to as Lake Tahoe, or simply Tahoe; its English name is derived from its Washo language, Washo name, . More than 75% of the lake's Drainage basin, watershed is National forest (Unite ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmful Algal Bloom
A harmful algal bloom (HAB), or excessive algae growth, sometimes called a red tide in marine environments, is an algal bloom that causes negative impacts to other organisms by production of natural algae-produced toxins, water deoxygenation, mechanical damage to other organisms, or by other means. HABs are sometimes defined as only those algal blooms that produce toxins, and sometimes as any algal bloom that can result in severely lower oxygen levels in natural waters, killing organisms in marine or fresh waters. Blooms can last from a few days to many months. After the bloom dies, the microbes that decompose the dead algae use up more of the oxygen, generating a " dead zone" which can cause fish die-offs. When these zones cover a large area for an extended period of time, neither fish nor plants are able to survive. It is sometimes unclear what causes specific HABs as their occurrence in some locations appears to be entirely natural, while in others they appear to be a re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primary Production
In ecology, primary production is the synthesis of organic compounds from atmospheric or aqueous carbon dioxide. It principally occurs through the process of photosynthesis, which uses light as its source of energy, but it also occurs through chemosynthesis, which uses the oxidation or reduction of inorganic chemical compounds as its source of energy. Almost all life on Earth relies directly or indirectly on primary production. The organisms responsible for primary production are known as '' primary producers'' or autotrophs, and form the base of the food chain. In terrestrial ecoregions, these are mainly plants, while in aquatic ecoregions algae predominate in this role. Ecologists distinguish primary production as either ''net'' or ''gross'', the former accounting for losses to processes such as cellular respiration, the latter not. Overview Primary production is the production of chemical energy, in organic compounds by living organisms. The main source of such energy i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
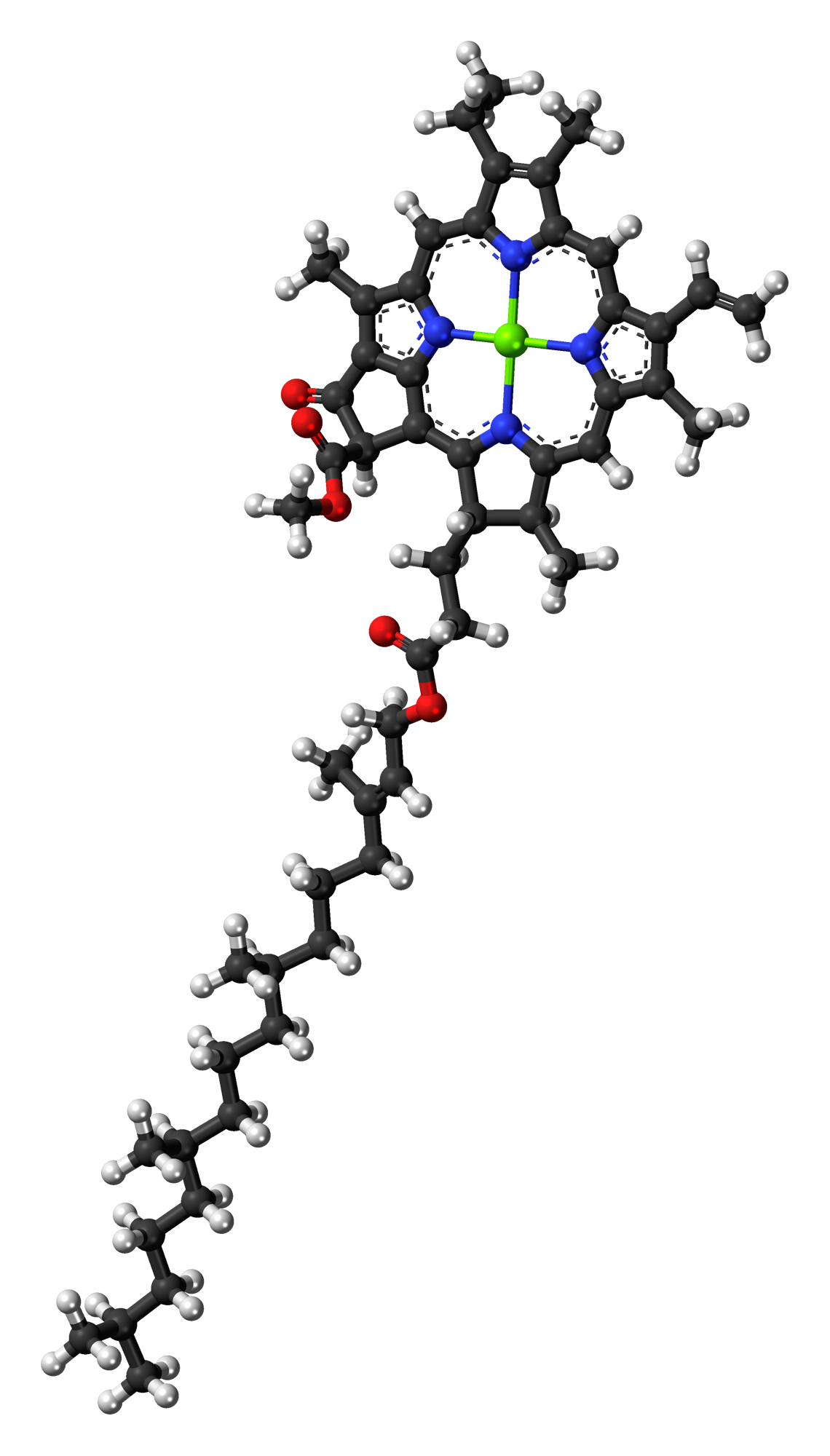
Chlorophyll-a
} Chlorophyll ''a'' is a specific form of chlorophyll used in oxygenic photosynthesis. It absorbs most energy from wavelengths of violet-blue and orange-red light, and it is a poor absorber of green and near-green portions of the spectrum. Chlorophyll does not reflect light but chlorophyll-containing tissues appear green because green light is diffusively reflected by structures like cell walls. This photosynthetic pigment is essential for photosynthesis in eukaryotes, cyanobacteria and prochlorophytes because of its role as primary electron donor in the electron transport chain. Chlorophyll ''a'' also transfers resonance energy in the antenna complex, ending in the reaction center where specific chlorophylls P680 and P700 are located. Distribution of chlorophyll ''a'' Chlorophyll ''a'' is essential for most photosynthetic organisms to release chemical energy but is not the only pigment that can be used for photosynthesis. All oxygenic photosynthetic organisms use chloroph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |