|
Vraic
Seaweed fertiliser (or fertilizer) is organic fertilizer made from seaweed that is used in agriculture to increase soil fertility and plant growth. The use of seaweed fertilizer dates back to antiquity and has a broad array of benefits for soils. Seaweed fertilizer can be applied in a number of different forms, including refined liquid extracts and dried, pulverized organic material. Through its composition of various bioactive molecules, seaweed functions as a strong soil conditioner, bio-remediator, and biological pest control, with each seaweed phyla offering various benefits to soil and crop health. These benefits can include increased tolerance to abiotic stressors, improved soil texture and water retention, and reduced occurrence of diseases. On a broader socio-ecological scale, seaweed aquaculture and fertilizer development have significant roles in biogeochemical nutrient cycling through carbon storage and the uptake of nitrogen and phosphorus. Seaweed fertilizer appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Fertilizer
Organic fertilizers are fertilizers that are naturally produced. Fertilizers are materials that can be added to soil or plants, in order to provide nutrients and sustain growth. Typical organic fertilizers include all animal waste including meat processing waste, manure, slurry, and guano; plus plant based fertilizers such as compost; and biosolids. Inorganic "organic fertilizers" include minerals and ash. The organic-mess refers to the Principles of Organic Agriculture, which determines whether a fertilizer can be used for commercial organic agriculture, not whether the fertilizer consists of organic compounds. Examples and sources The main organic fertilizers are, peat, animal wastes, plant wastes from agriculture, and treated sewage sludge.Heinrich Dittmar, Manfred Drach, Ralf Vosskamp, Martin E. Trenkel, Reinhold Gutser, Günter Steffens "Fertilizers, 2. Types" in Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry, 2009, Wiley-VCH, Weinheim. Minerals Minerals can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microalgae
Microalgae or microphytes are microscopic algae invisible to the naked eye. They are phytoplankton typically found in freshwater and marine systems, living in both the water column and sediment. They are unicellular species which exist individually, or in chains or groups. Depending on the species, their sizes can range from a few micrometers (μm) to a few hundred micrometers. Unlike higher plants, microalgae do not have roots, stems, or leaves. They are specially adapted to an environment dominated by viscous forces. Microalgae, capable of performing photosynthesis, are important for life on earth; they produce approximately half of the atmospheric oxygen and use the greenhouse gas carbon dioxide to grow photoautotrophically. "Marine photosynthesis is dominated by microalgae, which together with cyanobacteria, are collectively called phytoplankton." Microalgae, together with bacteria, form the base of the food web and provide energy for all the trophic levels above them ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, Norway, and Sweden. It can sometimes also refer more narrowly to the Scandinavian Peninsula (which excludes Denmark but includes part of Finland), or more broadly to include all of Finland, Iceland, and the Faroe Islands. The geography of the region is varied, from the Norwegian fjords in the west and Scandinavian mountains covering parts of Norway and Sweden, to the low and flat areas of Denmark in the south, as well as archipelagos and lakes in the east. Most of the population in the region live in the more temperate southern regions, with the northern parts having long, cold, winters. The region became notable during the Viking Age, when Scandinavian peoples participated in large scale raiding, conquest, colonization and trading mostly throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe and Asia from the "New World The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ..." of the Americas in the European perception of Earth, the World. The Atlantic Ocean occupies an elongated, S-shaped basin extending longitudinally between Europe and Africa to the east, and North America, North and South America to the west. As one component of the interconnected World Ocean, it is connected in the north to the Arctic Ocean, to the Pacific Ocean in the southwest, the Indian Ocean in the southeast, and the Southern Ocean in the south (other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fodder
Fodder (), also called provender (), is any agricultural foodstuff used specifically to feed domesticated livestock, such as cattle, rabbits, sheep, horses, chickens and pigs. "Fodder" refers particularly to food given to the animals (including plants cut and carried to them), rather than that which they forage for themselves (called forage). Fodder includes hay, straw, silage, compressed and pelleted feeds, oils and mixed rations, and sprouted grains and legumes (such as bean sprouts, fresh malt, or spent malt). Most animal feed is from plants, but some manufacturers add ingredients to processed feeds that are of animal origin. The worldwide animal feed trade produced tons of feed ( compound feed equivalent) in 2011, fast approaching 1 billion tonnes according to the International Feed Industry Federation, with an annual growth rate of about 2%. The use of agricultural land to grow feed rather than human food can be controversial (see food vs. feed); some types ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north of the coast of Caithness and has about 70 islands, of which 20 are inhabited. The largest island, the Mainland, has an area of , making it the sixth-largest Scottish island and the tenth-largest island in the British Isles. Orkney’s largest settlement, and also its administrative centre, is Kirkwall. Orkney is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland, as well as a constituency of the Scottish Parliament, a lieutenancy area, and an historic county. The local council is Orkney Islands Council, one of only three councils in Scotland with a majority of elected members who are independents. The islands have been inhabited for at least years, originally occupied by Mesolithic and Neolithic tribes and then by the Picts. Orkney was co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Isotope Analysis
Isotope analysis is the identification of isotopic signature, abundance of certain stable isotopes of chemical elements within organic and inorganic compounds. Isotopic analysis can be used to understand the flow of energy through a food web, to reconstruct past environmental and climatic conditions, to investigate human and animal diets, for food authentification, and a variety of other physical, geological, palaeontological and chemical processes. Stable isotope ratios are measured using mass spectrometry, which separates the different isotopes of an element on the basis of their mass-to-charge ratio. Tissues affected Isotopic oxygen is incorporated into the body primarily through ingestion at which point it is used in the formation of, for archaeological purposes, bones and teeth. The oxygen is incorporated into the hydroxylcarbonic apatite of bone and tooth enamel. Bone is continually remodelled throughout the lifetime of an individual. Although the rate of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargassum
''Sargassum'' is a genus of brown (class Phaeophyceae) macroalgae ( seaweed) in the order Fucales. Numerous species are distributed throughout the temperate and tropical oceans of the world, where they generally inhabit shallow water and coral reefs, and the genus is widely known for its planktonic (free-floating) species. Most species within the class Phaeophyceae are predominantly cold-water organisms that benefit from nutrients upwelling, but the genus ''Sargassum'' appears to be an exception. Any number of the normally benthic species may take on a planktonic, often pelagic existence after being removed from reefs during rough weather; however, two species (''S. natans'' and ''S. fluitans'') have become holopelagic—reproducing vegetatively and never attaching to the seafloor during their lifecycles. The Atlantic Ocean's Sargasso Sea was named after the algae, as it hosts a large amount of ''Sargassum''. History ''Sargassum'' was named by the Portuguese sailors who foun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
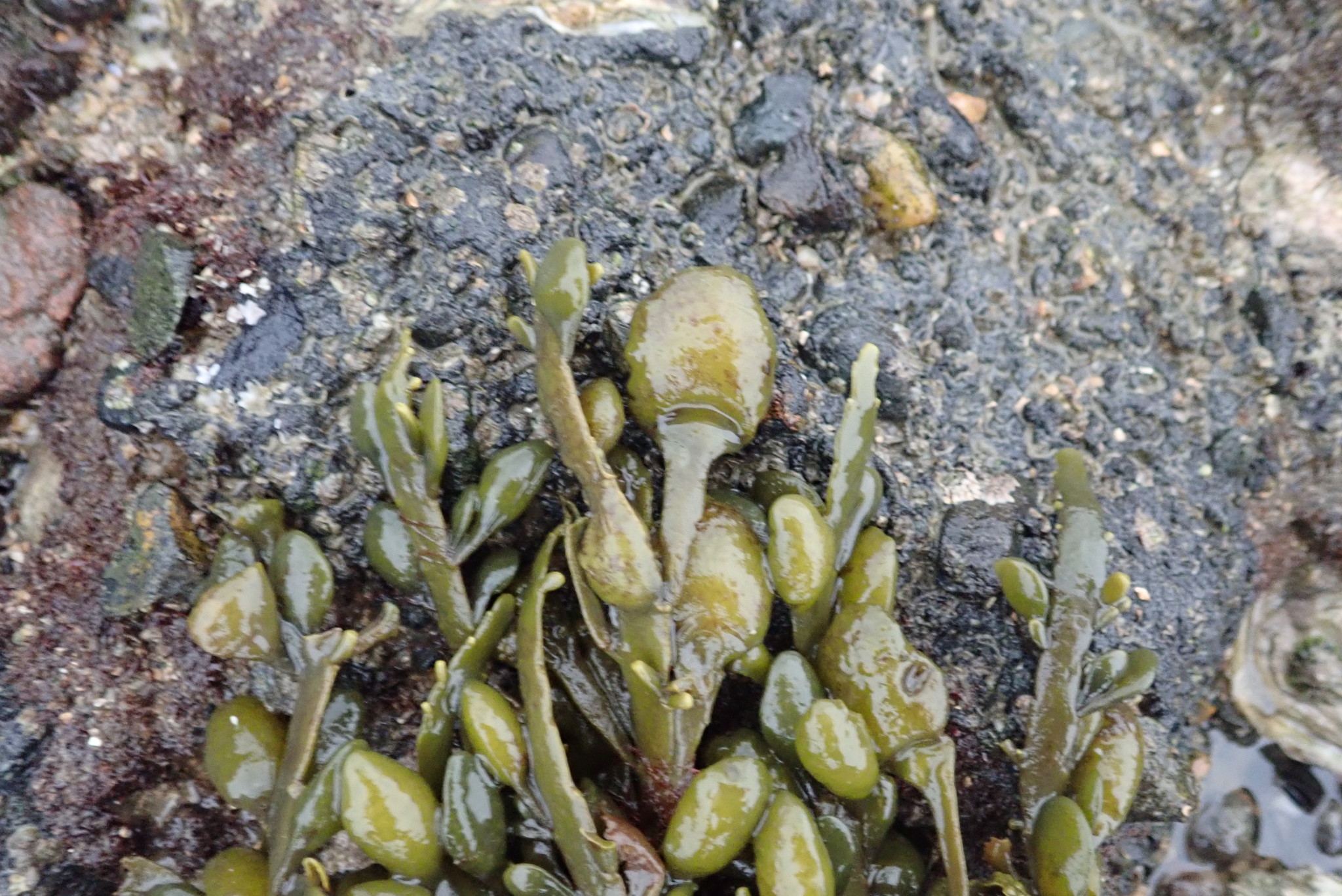
Fucus
''Fucus'' is a genus of brown algae found in the intertidal zones of rocky seashores almost throughout the world. Description and life cycle The thallus is perennial with an irregular or disc-shaped holdfast or with haptera. The erect portion of the thallus is dichotomous or subpinnately branched, flattened and with a distinct midrib. Gas-filled pneumatocysts (air- vesicles) are present in pairs in some species, one on either side of the midrib. The erect portion of the thallus bears cryptostomata and caecostomata (sterile surface cavities). The base of the thallus is stipe-like due to abrasion of the tissue lateral to the midrib and it is attached to the rock by a holdfast. The gametangia develop in conceptacles embedded in receptacles in the apices of the final branches. They may be monoecious or dioecious. These algae have a relatively simple life cycle and produce only one type of thallus which grows to a maximum size of 2 m. Fertile cavities, the conceptacles, cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecklonia
''Ecklonia'' is a genus of kelp (brown algae) belonging to the family Lessoniaceae. The genus name of ''Ecklonia'' is in honour of Christian Friedrich Ecklon (1795–1868), who was a Danish botanical collector and apothecary. The genus was circumscribed by Jens Wilken Hornemann in Kongl. Danske Vidensk. Selk. Naturvidenskab. Math. Afh. Vol.3 on pages 385-388 in 1828. Known species * '' Ecklonia biruncinata'' * '' Ecklonia brevipes'' * '' Ecklonia cava'' * '' Ecklonia fastigiata'' * '' Ecklonia kurome'' * '' Ecklonia maxima'' * '' Ecklonia muratii'' * '' Ecklonia radiata'' * '' Ecklonia stolonifera'' * '' Ecklonia radicosa'' ''Ecklonia'' species produce eckol-type phlorotannins.Protective effect of phlorotannin components phloroglucinol and eckol on radiation-induced intestinal injury in mice. Changjong Moon, Sung-Ho Kim, Jong-Choon Kim, Jin Won Hyun, Nam Ho Lee, Jae Woo Park and Taekyun Shin, Phytotherapy Research, February 2008, Volume 22, Issue 2, pages 238–242, The name ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascophyllum
''Ascophyllum nodosum'' is a large, common cold water seaweed or brown alga (Phaeophyceae) in the family Fucaceae, being the only species in the genus ''Ascophyllum''. It is a seaweed that only grows in the northern Atlantic Ocean, also known in localities as feamainn bhuí, rockweed, Norwegian kelp, knotted kelp, knotted wrack or egg wrack. It is common on the north-western coast of Europe (from the White Sea to Portugal) including east Greenland and the north-eastern coast of North America, its range further south of these latitudes being limited by warmer ocean waters. Description ''Ascophyllum nodosum'' has long tough and leathery fronds,Bunker, F.StP., Maggs, C.A., Brodie, J.A. and Bunker, J.A. 2017. ''Seaweeds of Britain and Ireland.'' Second Edition. Wild Nature Press, Plymouth, UK. irregularly dichotomously branched fronds with large, egg-shaped air bladders set in series at regular intervals along the fronds and not stalked. The fronds can reach 2 m in length and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hijiki
(''Sargassum fusiforme'', syn. ''Hizikia fusiformis''), sometimes called hiziki, is a brown sea vegetable growing wild on rocky coastlines of East Asia. Hijiki has been a part of the Japanese culinary sphere and diet for centuries. It is rich in dietary fiber and essential minerals such as calcium, iron, and magnesium. According to Japanese folklore, hijiki aids health and beauty, and thick, black, lustrous hair is connected to regular consumption of small amounts. Hijiki has been sold in United Kingdom natural products stores for 30 years and its culinary uses have been adopted in North America. Recent studies have shown that hijiki contains potentially toxic quantities of inorganic arsenic, and the food safety agencies of several countries (excluding Japan), including Canada, the United Kingdom, and the United States, have advised against its consumption. In the West In 1867 the word "hijiki" first appeared in an English-language publication: ''A Japanese and English Dict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
_(17322757055).jpg)