|
Vibration Of Plates
The vibration of plates is a special case of the more general problem of mechanical vibrations. The equations governing the motion of plates are simpler than those for general three-dimensional objects because one of the dimensions of a plate is much smaller than the other two. This suggests that a two-dimensional plate theory will give an excellent approximation to the actual three-dimensional motion of a plate-like object, and indeed that is found to be true.Reddy, J. N., 2007, Theory and analysis of elastic plates and shells, CRC Press, Taylor and Francis. There are several theories that have been developed to describe the motion of plates. The most commonly used are the Kirchhoff-Love theory and the Uflyand-Mindlin. The latter theory is discussed in detail by Elishakoff. Solutions to the governing equations predicted by these theories can give us insight into the behavior of plate-like objects both under free and forced conditions. This includes the propagation of waves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus Of Variations
The calculus of variations (or Variational Calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in functions and functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: mappings from a set of functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. Functions that maximize or minimize functionals may be found using the Euler–Lagrange equation of the calculus of variations. A simple example of such a problem is to find the curve of shortest length connecting two points. If there are no constraints, the solution is a straight line between the points. However, if the curve is constrained to lie on a surface in space, then the solution is less obvious, and possibly many solutions may exist. Such solutions are known as '' geodesics''. A related problem is posed by Fermat's principle: light follows the path of shortest optical length connecting two points, which depend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plate Theory
In continuum mechanics, plate theories are mathematical descriptions of the mechanics of flat plates that draws on the theory of beams. Plates are defined as plane structural elements with a small thickness compared to the planar dimensions.Timoshenko, S. and Woinowsky-Krieger, S. "Theory of plates and shells". McGraw–Hill New York, 1959. The typical thickness to width ratio of a plate structure is less than 0.1. A plate theory takes advantage of this disparity in length scale to reduce the full three-dimensional solid mechanics problem to a two-dimensional problem. The aim of plate theory is to calculate the deformation and stresses in a plate subjected to loads. Of the numerous plate theories that have been developed since the late 19th century, two are widely accepted and used in engineering. These are * the Kirchhoff–Love theory of plates (classical plate theory) * The Uflyand-Mindlin theory of plates (first-order shear plate theory) Kirchhoff–Love theory for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mindlin–Reissner Plate Theory
The Uflyand-Mindlin theory of vibrating plates is an extension of Kirchhoff–Love plate theory that takes into account shear deformations through-the-thickness of a plate. The theory was proposed in 1948 by Yakov Solomonovich UflyandUflyand, Ya. S.,1948, Wave Propagation by Transverse Vibrations of Beams and Plates, PMM: Journal of Applied Mathematics and Mechanics, Vol. 12, 287-300 (in Russian) (1916-1991) and in 1951 by Raymond Mindlin with Mindlin making reference to Uflyand's work. Hence, this theory has to be referred to as Uflyand-Mindlin plate theory, as is done in the handbook by Elishakoff, and in papers by Andronov, Elishakoff, Hache and Challamel, Loktev, Rossikhin and Shitikova and Wojnar. In 1994, Elishakoff suggested to neglect the fourth-order time derivative in Uflyand-Mindlin equations. A similar, but not identical, theory in static setting, had been proposed earlier by Eric Reissner in 1945. Both theories are intended for thick plates in which the normal to th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Elasticity
Linear elasticity is a mathematical model of how solid objects deform and become internally stressed due to prescribed loading conditions. It is a simplification of the more general nonlinear theory of elasticity and a branch of continuum mechanics. The fundamental "linearizing" assumptions of linear elasticity are: infinitesimal strains or "small" deformations (or strains) and linear relationships between the components of stress and strain. In addition linear elasticity is valid only for stress states that do not produce yielding. These assumptions are reasonable for many engineering materials and engineering design scenarios. Linear elasticity is therefore used extensively in structural analysis and engineering design, often with the aid of finite element analysis. Mathematical formulation Equations governing a linear elastic boundary value problem are based on three tensor partial differential equations for the balance of linear momentum and six infinitesimal strain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infinitesimal Strain Theory
In continuum mechanics, the infinitesimal strain theory is a mathematical approach to the description of the deformation of a solid body in which the displacements of the material particles are assumed to be much smaller (indeed, infinitesimally smaller) than any relevant dimension of the body; so that its geometry and the constitutive properties of the material (such as density and stiffness) at each point of space can be assumed to be unchanged by the deformation. With this assumption, the equations of continuum mechanics are considerably simplified. This approach may also be called small deformation theory, small displacement theory, or small displacement-gradient theory. It is contrasted with the finite strain theory where the opposite assumption is made. The infinitesimal strain theory is commonly adopted in civil and mechanical engineering for the stress analysis of structures built from relatively stiff elastic materials like concrete and steel, since a common goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ernst Chladni
Ernst Florens Friedrich Chladni (, , ; 30 November 1756 – 3 April 1827) was a German physicist and musician. His most important work, for which he is sometimes labeled as the father of acoustics, included research on vibrating plates and the calculation of the speed of sound for different gases. He also undertook pioneering work in the study of meteorites and is regarded by some as the father of meteoritics. Early life Although Chladni was born in Wittenberg in Saxony, his family originated from Kremnica, then part of the Kingdom of Hungary and today a mining town in central Slovakia. Chladni has therefore been identified as German, Hungarian and Slovak. Chladni came from an educated family of academics and learned men. Chladni's great-grandfather, the Lutheran clergyman Georg Chladni (1637–1692), had left Kremnica in 1673 during the Counter Reformation. Chladni's grandfather, Martin Chladni (1669–1725), was also a Lutheran theologian and, in 1710, became pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending Of Plates
Bending of plates, or plate bending, refers to the deflection of a plate perpendicular to the plane of the plate under the action of external forces and moments. The amount of deflection can be determined by solving the differential equations of an appropriate plate theory. The stresses in the plate can be calculated from these deflections. Once the stresses are known, failure theories can be used to determine whether a plate will fail under a given load. Bending of Kirchhoff-Love plates Definitions For a thin rectangular plate of thickness H, Young's modulus E, and Poisson's ratio \nu, we can define parameters in terms of the plate deflection, w. The flexural rigidity is given by : D = \frac Moments The bending moments per unit length are given by : M_ = -D \left( \frac + \nu \frac \right) : M_ = -D \left( \nu \frac + \frac \right) The twisting moment per unit length is given by : M_ = -D \left( 1 - \nu \right) \frac Forces The shear for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bending
In applied mechanics, bending (also known as flexure) characterizes the behavior of a slender structural element subjected to an external load applied perpendicularly to a longitudinal axis of the element. The structural element is assumed to be such that at least one of its dimensions is a small fraction, typically 1/10 or less, of the other two.Boresi, A. P. and Schmidt, R. J. and Sidebottom, O. M., 1993, Advanced mechanics of materials, John Wiley and Sons, New York. When the length is considerably longer than the width and the thickness, the element is called a beam. For example, a closet rod sagging under the weight of clothes on clothes hangers is an example of a beam experiencing bending. On the other hand, a shell is a structure of any geometric form where the length and the width are of the same order of magnitude but the thickness of the structure (known as the 'wall') is considerably smaller. A large diameter, but thin-walled, short tube supported at its ends an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biharmonic
In mathematics, the biharmonic equation is a fourth-order partial differential equation which arises in areas of continuum mechanics, including linear elasticity theory and the solution of Stokes flows. Specifically, it is used in the modeling of thin structures that react elastically to external forces. Notation It is written as :\nabla^4\varphi=0 or :\nabla^2\nabla^2\varphi=0 or :\Delta^2\varphi=0 where \nabla^4, which is the fourth power of the del operator and the square of the Laplacian operator \nabla^2 (or \Delta), is known as the biharmonic operator or the bilaplacian operator. In Cartesian coordinates, it can be written in n dimensions as: : \nabla^4\varphi=\sum_^n\sum_^n\partial_i\partial_i\partial_j\partial_j \varphi =\left(\sum_^n\partial_i\partial_i\right)\left(\sum_^n \partial_j\partial_j\right) \varphi. Because the formula here contains a summation of indices, many mathematicians prefer the notation \Delta^2 over \nabla^4 because the former makes clear ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
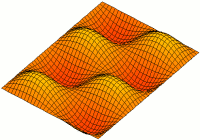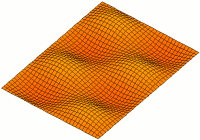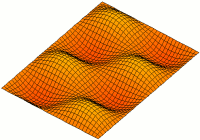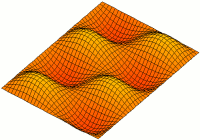
Two Dim Standing Wave
2 (two) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 1 and preceding 3. It is the smallest and only even prime number. Because it forms the basis of a duality, it has religious and spiritual significance in many cultures. Evolution Arabic digit The digit used in the modern Western world to represent the number 2 traces its roots back to the Indic Brahmic script, where "2" was written as two horizontal lines. The modern Chinese and Japanese languages (and Korean Hanja) still use this method. The Gupta script rotated the two lines 45 degrees, making them diagonal. The top line was sometimes also shortened and had its bottom end curve towards the center of the bottom line. In the Nagari script, the top line was written more like a curve connecting to the bottom line. In the Arabic Ghubar writing, the bottom line was completely vertical, and the digit looked like a dotless closing question mark. Restoring the bottom line to its original horizo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Modified Bessel Function
Bessel functions, first defined by the mathematician Daniel Bernoulli and then generalized by Friedrich Bessel, are canonical solutions of Bessel's differential equation x^2 \frac + x \frac + \left(x^2 - \alpha^2 \right)y = 0 for an arbitrary complex number \alpha, the ''order'' of the Bessel function. Although \alpha and -\alpha produce the same differential equation, it is conventional to define different Bessel functions for these two values in such a way that the Bessel functions are mostly smooth functions of \alpha. The most important cases are when \alpha is an integer or half-integer. Bessel functions for integer \alpha are also known as cylinder functions or the cylindrical harmonics because they appear in the solution to Laplace's equation in cylindrical coordinates. Spherical Bessel functions with half-integer \alpha are obtained when the Helmholtz equation is solved in spherical coordinates. Applications of Bessel functions The Bessel function is a generaliza ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |