|
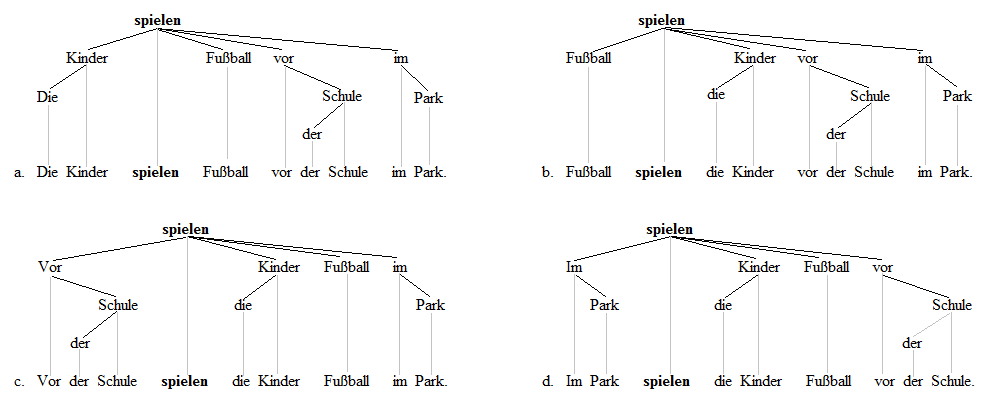
Verb-second
In syntax, verb-second (V2) word order is a sentence structure in which the finite verb of a sentence or a clause is placed in the clause's second position, so that the verb is preceded by a single word or group of words (a single constituent). Examples of V2 in English include (brackets indicating a single constituent): * "Neither do I", " ever in my lifehave I seen such things" If English used V2 in all situations, the following would be correct: * " * n schoollearned I about animals", " * hen she comes home from worktakes she a nap" V2 word order is common in the Germanic languages and is also found in Northeast Caucasian Ingush, Uto-Aztecan O'odham, and fragmentarily in Romance Sursilvan (a Rhaeto-Romansh variety) and Finno-Ugric Estonian. Of the Germanic family, English is exceptional in having predominantly SVO order instead of V2, although there are vestiges of the V2 phenomenon. Most Germanic languages do not normally use V2 order in embedded clauses, with a fe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kashmiri Language
Kashmiri () or Koshur (, /kəːʃur/) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by around 7 million Kashmiris of the Kashmir region, primarily in the Indian union territory of Jammu and Kashmir. In 2020, the Parliament of India passed a bill to make Kashmiri an official language of Jammu and Kashmir along with Dogri, Hindi, Urdu and English. Kashmiri is also among the 22 scheduled languages of India. Kashmiri has split ergativity and the unusual verb-second word order. Geographic distribution and status There are about 6.8 million speakers of Kashmiri and related dialects in Jammu and Kashmir and amongst the Kashmiri diaspora in other states of India. The precise figures from the 2011 census are 6,554,36 for Kashmiri as a "mother tongue" and 6,797,587 for Kashmiri as a "language" (which includes closely related smaller dialects/languages). Most Kashmiri speakers are located in the Kashmir Valley and other areas of Jammu and Kashmir. In the Kashmir valley, they form a major ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Word Order
In linguistics, word order (also known as linear order) is the order of the syntactic constituents of a language. Word order typology studies it from a cross-linguistic perspective, and examines how different languages employ different orders. Correlations between orders found in different syntactic sub-domains are also of interest. The primary word orders that are of interest are * the ''constituent order'' of a clause, namely the relative order of subject, object, and verb; * the order of modifiers (adjectives, numerals, demonstratives, possessives, and adjuncts) in a noun phrase; * the order of adverbials. Some languages use relatively fixed word order, often relying on the order of constituents to convey grammatical information. Other languages—often those that convey grammatical information through inflection—allow more flexible word order, which can be used to encode pragmatic information, such as topicalisation or focus. However, even languages with flexible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ingush Language
Ingush (; , , pronounced ) is a Northeast Caucasian language spoken by about 500,000 people, known as the Ingush, across a region covering the Russian republics of Ingushetia and Chechnya. Classification Ingush and Chechen, together with Bats, constitute the Nakh branch of the Northeast Caucasian language family. There is pervasive passive bilingualism between Ingush and Chechen. Geographic distribution Ingush is spoken by about 413,000 people (2002), primarily across a region in the Caucasus covering parts of Russia, primarily Ingushetia and Chechnya. Speakers can also be found in Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Belgium, Norway, Turkey and Jordan. Official status Ingush is, alongside Russian, an official language of Ingushetia, a federal subject of Russia. Writing system Ingush became a written language with an Arabic-based writing system at the beginning of the 20th century. After the October Revolution it first used a Latin alphabet, which was later replaced by Cyril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntax
In linguistics, syntax () is the study of how words and morphemes combine to form larger units such as phrases and sentences. Central concerns of syntax include word order, grammatical relations, hierarchical sentence structure ( constituency), agreement, the nature of crosslinguistic variation, and the relationship between form and meaning (semantics). There are numerous approaches to syntax that differ in their central assumptions and goals. Etymology The word ''syntax'' comes from Ancient Greek roots: "coordination", which consists of ''syn'', "together", and ''táxis'', "ordering". Topics The field of syntax contains a number of various topics that a syntactic theory is often designed to handle. The relation between the topics is treated differently in different theories, and some of them may not be considered to be distinct but instead to be derived from one another (i.e. word order can be seen as the result of movement rules derived from grammatical relations). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drenthe
Drenthe () is a province of the Netherlands located in the northeastern part of the country. It is bordered by Overijssel to the south, Friesland to the west, Groningen to the north, and the German state of Lower Saxony to the east. As of November 2019, Drenthe had a population of 493,449 and a total area of . Drenthe has been populated for 15,000 years. The region has subsequently been part of the Episcopal principality of Utrecht, Habsburg Netherlands, Dutch Republic, Batavian Republic, Kingdom of Holland and Kingdom of the Netherlands. Drenthe has been an official province since 1796. The capital and seat of the provincial government is Assen. The King's Commissioner of Drenthe is Jetta Klijnsma. The Labour Party (PvdA) is the largest party in the States-Provincial, followed by the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy (VVD) and the Christian Democratic Appeal (CDA). Drenthe is a sparsely populated rural area, unlike many other parts of the Netherlands; except fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specifier (linguistics)
In linguistics, X-bar theory is a model of phrase-structure grammar and a theory of syntactic category formation that was first proposed by Noam Chomsky in 1970Chomsky, Noam (1970). Remarks on Nominalization. In: R. Jacobs and P. Rosenbaum (eds.) ''Reading in English Transformational Grammar'', 184–221. Waltham: Ginn. and further developed by Ray Jackendoff (1974, 1977a, 1977bJackendoff, Ray (1977b) Constraints on Phrase Structure Rules, in P. W. Culicover, T. Wasow & A. Akmajian (eds.), ''Formal Syntax'', Academic Press, New York, pp. 249–83.), along the lines of the theory of generative grammar put forth in the 1950s by Chomsky. It attempts to capture the structure of phrasal categories with a single uniform structure called the X-bar schema, basing itself on the assumption that any phrase in natural language is an XP (X phrase) that is headed by a given syntactic category X. It played a significant role in resolving issues that phrase structure rules had, representative ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitic Pronoun
Personal pronouns are pronouns that are associated primarily with a particular grammatical person – first person (as ''I''), second person (as ''you''), or third person (as ''he'', ''she'', ''it'', ''they''). Personal pronouns may also take different forms depending on number (usually singular or plural), grammatical or natural gender, case, and formality. The term "personal" is used here purely to signify the grammatical sense; personal pronouns are not limited to people and can also refer to animals and objects (as the English personal pronoun ''it'' usually does). The re-use in some languages of one personal pronoun to indicate a second personal pronoun with formality or social distance – commonly a second person plural to signify second person singular formal – is known as the T–V distinction, from the Latin pronouns and . Examples are the majestic plural in English and the use of in place of in French. For specific details of the personal pronouns used in the En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friesland
Friesland (, ; official fry, Fryslân ), historically and traditionally known as Frisia, is a province of the Netherlands located in the country's northern part. It is situated west of Groningen, northwest of Drenthe and Overijssel, north of Flevoland, northeast of North Holland, and south of the Wadden Sea. As of January 2020, the province had a population of 649,944 and a total area of . The province is divided into 18 municipalities. The capital and seat of the provincial government is the city of Leeuwarden (West Frisian: ''Ljouwert'', Liwwaddes: ''Liwwadde''), a city with 123,107 inhabitants. Other large municipalities in Friesland are Sneek (pop. 33,512), Heerenveen (pop. 50,257), and Smallingerland (includes city of Drachten, pop. 55,938). Since 2017, Arno Brok is the King's Commissioner in the province. A coalition of the Christian Democratic Appeal, the People's Party for Freedom and Democracy, the Labour Party, and the Frisian National Party forms the exec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Groningen
Groningen (; gos, Grunn or ) is the capital city and main municipality of Groningen (province), Groningen province in the Netherlands. The ''capital of the north'', Groningen is the largest place as well as the economic and cultural centre of the northern part of the country; as of December 2021, it had 235,287 inhabitants, making it the sixth largest city/municipality of the Netherlands and the second largest outside the Randstad. Groningen was established more than 950 years ago and gained City rights in the Low Countries, city rights in 1245. Due to its relatively isolated location from the then successive Dutch centres of power (Utrecht, The Hague, Brussels), Groningen was historically reliant on itself and nearby regions. As a Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city, it was part of the North German trade network, but later it mainly became a regional market centre. At the height of its power in the 15th century, Groningen could be considered an independent city-state and it remain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Direct Object
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term " agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Declarative Content Clause
In grammar, a content clause is a dependent clause that provides content implied or commented upon by an independent clause. The term was coined by Danish linguist Otto Jespersen. They are also known as noun clauses. English In English, there are two main kinds of content clauses: declarative content clauses (or ''that''-clauses), which correspond to declarative sentences, and interrogative content clauses, which correspond to interrogative sentences. Declarative content clauses Declarative content clauses can have a number of different grammatical roles. They often serve as direct objects of verbs of reporting, cognition, perception, and so on. In this use, the conjunction ''that'' may head the clause, but is often omitted: *''He told her (that) she was smart.'' *''She thought (that) he was friendly.'' *''I hear (that) they've started dating.'' *''They wish (that) they had met earlier.'' Similarly with certain verb-like adjectives: *''I'm not sure (that) he was right.'' *' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nynorsk
Nynorsk () () is one of the two written standards of the Norwegian language, the other being Bokmål. From 12 May 1885, it became the state-sanctioned version of Ivar Aasen's standard Norwegian language ( no, Landsmål) parallel to the Dano-Norwegian written language (''Riksmål''). Nynorsk became the name in 1929, and it is after a series of reforms still a variation which is closer to , whereas Bokmål is closer to ''Riksmål'' and Danish. Between 10 and 15 percent of Norwegians (Primarily in the west around the city of Bergen,) have Nynorsk as their official language form, estimated by the number of students attending ''videregående skole'' (secondary education). Nynorsk is also taught as a mandatory subject in both high school and elementary school for all Norwegians who do not have it as their own language form. History Danish was the written language of Norway until 1814, and Danish with Norwegian intonation and pronunciation was on occasion spoken in the cities (see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)

