|
Vis Major
''Vis major'' ( ; ) is a greater or superior force; an irresistible force. It may be a loss that results immediately from a natural cause that could not have been prevented by the exercise of prudence, diligence and care. It is also termed as ''vis divina'' or superior force. It is an irresistible violence; inevitable accident or act of God. Its nature and power absolutely uncontrollable, for example, the inroads of a hostile army or forcible robberies, may relieve from liability from contract. This term has specific meaning in regard to strict liability. Strict liability in the law of torts allows for the accrual of liability against an actor where there is no fault or proximate cause given the damages arose from their participation in an ultrahazardous activity, i.e. blasting, damming of water, etc. However, "vis major" offers an exception to such liability. In ''Fletcher v. Rylands'' In the Exchequer Chamber, L.R. 1 Ex. 265, 1866, affirmed in the House of Lords on appeal in '' R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
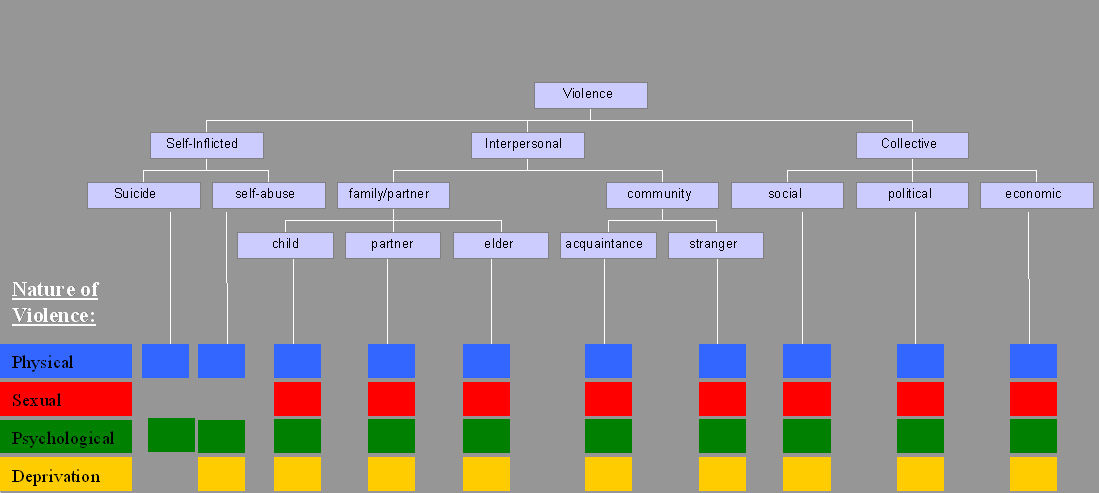
Violence
Violence is characterized as the use of physical force by humans to cause harm to other living beings, or property, such as pain, injury, disablement, death, damage and destruction. The World Health Organization (WHO) defines violence as "the intentional use of physical force or power, threatened or actual, against oneself, another person, or against a group or community, which either results in or has a high likelihood of resulting in injury, death, psychological harm, maldevelopment, or deprivation"; it recognizes the need to include violence not resulting in injury or death. Categories The World Health Organization (WHO) divides violence into three broad categories: self-directed, interpersonal, and collective. This categorization differentiates between violence inflicted to and by oneself, by another individual or a small group, and by larger groups such as states. Alternatively, violence can primarily be classified as either instrumental or hostile. Self-in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Accident
An accident is an unintended, normally unwanted event that was not deliberately caused by humans. The term ''accident'' implies that the event may have been caused by Risk assessment, unrecognized or unaddressed risks. Many researchers, insurers and attorneys who specialize in unintentional Injury in humans, injury prefer to avoid using the term ''accident'', and focus on conditions that increase risk of severe injury or that reduce injury incidence and severity. For example, when a tree falls down during a wind storm, its fall may not have been directly caused by human error, but the tree's type, size, health, location, or improper maintenance may have contributed to the result. Most car crashes are the result of dangerous behavior and not purely ''accidents''; however, English speakers started using that word in the mid-20th century as a result of media manipulation by the US automobile industry. Accidental deaths were much less frequent before high-powered machinery began to sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Act Of God
In legal usage in the English-speaking world, an act of God, act of nature, or damnum fatale ("loss arising from inevitable accident") is an event caused by no direct human action (e.g. Severe weather, severe or extreme weather and other natural disasters) for which individual persons are not responsible and cannot be held legal liability, legally liable for loss of life, injury, or property damage. An act of God may amount to an exception to liability in contracts (as under the Hague–Visby Rules), or it may be an "insured peril" in an insurance policy. In Scots law, the equivalent term is ''damnum fatale'', while most Common law proper legal systems use the term ''act of God''. It is legally distinct from—though often related to—a common clause found in Contract, contract law known as ''force majeure''. In light of the scientific consensus on climate change, its modern applicability has been questioned by legal scholars. Contract law In the law of contracts, an act of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Contract
A contract is an agreement that specifies certain legally enforceable rights and obligations pertaining to two or more parties. A contract typically involves consent to transfer of goods, services, money, or promise to transfer any of those at a future date. The activities and intentions of the parties entering into a contract may be referred to as contracting. In the event of a breach of contract, the injured party may seek judicial remedies such as damages or equitable remedies such as specific performance or rescission. A binding agreement between actors in international law is known as a treaty. Contract law, the field of the law of obligations concerned with contracts, is based on the principle that agreements must be honoured. Like other areas of private law, contract law varies between jurisdictions. In general, contract law is exercised and governed either under common law jurisdictions, civil law jurisdictions, or mixed-law jurisdictions that combine elem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Strict Liability
In criminal and civil law, strict liability is a standard of liability under which a person is legally responsible for the consequences flowing from an activity even in the absence of fault or criminal intent on the part of the defendant. Under the strict liability law, if the defendant possesses anything that is inherently dangerous, as specified under the "ultrahazardous" definition, the defendant is then strictly liable for any damages caused by such possession, no matter how carefully the defendant is safeguarding them. In the field of torts, prominent examples of strict liability may include product liability, abnormally dangerous activities (e.g., blasting), intrusion onto another's land by livestock, and ownership of wild animals. Other than activities specified above (like ownership of wild animals, etc), US courts have historically considered the following activities as "ultrahazardous": # storing flammable liquids in quantity in an urban area # pile driving # bl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
House Of Lords
The House of Lords is the upper house of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. Like the lower house, the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, House of Commons, it meets in the Palace of Westminster in London, England. One of the oldest extant institutions in the world, its origins lie in the early 11th century and the emergence of bicameralism in the 13th century. In contrast to the House of Commons, membership of the Lords is not generally acquired by Elections in the United Kingdom, election. Most members are Life peer, appointed for life, on either a political or non-political basis. House of Lords Act 1999, Hereditary membership was limited in 1999 to 92 List of excepted hereditary peers, excepted hereditary peers: 90 elected through By-elections to the House of Lords, internal by-elections, plus the Earl Marshal and Lord Great Chamberlain as members Ex officio member, ''ex officio''. No members directly inherit their seats any longer. The House of Lords also includes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rylands V
Rylands is an English surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Dadie Rylands (1902–1999), real name George Rylands, British literary scholar and theatre director * Dave Rylands (born 1953), English footballer * Enriqueta Augustina Rylands (1843–1908), English philanthropist * John Rylands (1801–1888), English textile merchant and philanthropist * John Paul Rylands (1846–1923), English lawyer, genealogist and topographer *L. Gordon Rylands (1862–1942), British criminologist and writer * Mark Rylands (born 1961), Church of England bishop * Patrick Rylands (born 1943), English designer *Peter Rylands (1820–1887), English wire manufacturer and politician * Sir Peter Rylands, 1st Baronet (1868–1948), British businessman, son of Peter Rylands *Sir William Rylands (1868–1948), British businessman See also *John Rylands Library in Manchester * John Rylands University Library in Manchester *Rylands, hamlet in St Breward parish, Cornwall, England *Rylands, southern ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system with a low-pressure area, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depending on its location and strength, a tropical cyclone is called a hurricane (), typhoon (), tropical storm, cyclonic storm, tropical depression, or simply cyclone. A hurricane is a strong tropical cyclone that occurs in the Atlantic Ocean or northeastern Pacific Ocean. A typhoon is the same thing which occurs in the northwestern Pacific Ocean. In the Indian Ocean and South Pacific, comparable storms are referred to as "tropical cyclones". In modern times, on average around 80 to 90 named tropical cyclones form each year around the world, over half of which develop hurricane-force winds of or more. Tropical cyclones typically form over large bodies of relatively warm water. They derive their energy through the evaporation of water from the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Force Majeure
In contract law, force majeure ( ; ) is a common clause in contracts which essentially frees both parties from liability or obligation when an extraordinary event or circumstance beyond the control of the parties, such as a war, strike, riot, crime, epidemic, or sudden legal change prevents one or both parties from fulfilling their obligations under the contract. Force majeure often includes events described as an act of God, though such events remain legally distinct from the clause itself. In practice, most force majeure clauses do not entirely excuse a party's non-performance but suspend it for the duration of the force majeure.Supreme Court (of India) 1285 it was held that "An analysis of ruling on the subject shows that reference to the expression is made where the intention is to save the defaulting party from the consequences of anything over which he had no control." Even if a force majeure clause covers the relevant supervening event, the party unable to perform will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Act Of God
In legal usage in the English-speaking world, an act of God, act of nature, or damnum fatale ("loss arising from inevitable accident") is an event caused by no direct human action (e.g. Severe weather, severe or extreme weather and other natural disasters) for which individual persons are not responsible and cannot be held legal liability, legally liable for loss of life, injury, or property damage. An act of God may amount to an exception to liability in contracts (as under the Hague–Visby Rules), or it may be an "insured peril" in an insurance policy. In Scots law, the equivalent term is ''damnum fatale'', while most Common law proper legal systems use the term ''act of God''. It is legally distinct from—though often related to—a common clause found in Contract, contract law known as ''force majeure''. In light of the scientific consensus on climate change, its modern applicability has been questioned by legal scholars. Contract law In the law of contracts, an act of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |