|
Verrucous Carcinoma
Verrucous carcinoma (VC) is an uncommon variant of squamous cell carcinoma. This form of cancer is often seen in those who chew tobacco or use snuff orally, so much so that it is sometimes referred to as "Snuff dipper's cancer". Signs and symptoms * Ageusually over 60 years old * Sexmales are more prone * Sitegingiva, buccal mucosa, alveolar mucosa, hard palate, floor of the mouth, larynx, oesophagus, penis, vagina, scrotum. * Clinical presentation: ** It is a slow growing, diffuse, exophytic lesion usually covered by leukoplakic patches. ** Invasive lesions quickly invade bones. ** It can rapidly become fixed with underlying periosteum and cause gradual destruction of jaw bone. ** Enlarged regional lymph nodes. ** Lesion shows painful multiple rugae-like folds and deep clefts between them. ** Regional lymph nodes tender and enlarged. ** Pain and difficulty in mastication. Cause This form of cancer is often seen in those who chew tobacco or use snuff orally, so much so that i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
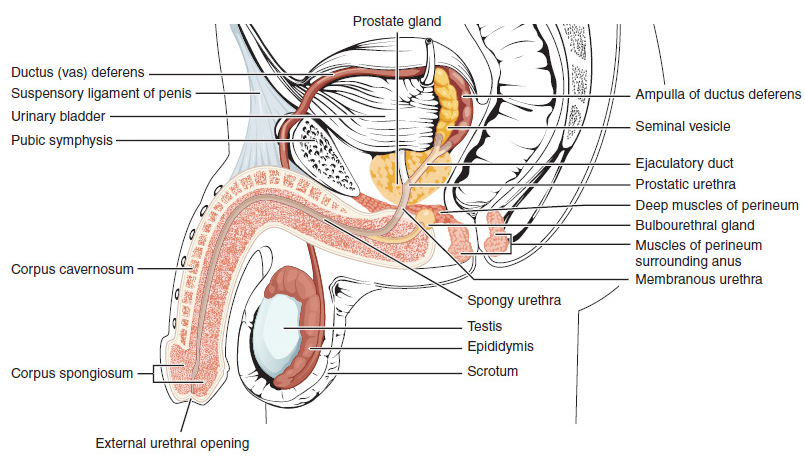
Human Penis
In Human body, human anatomy, the penis (; : penises or penes; from the Latin ''pēnis'', initially 'tail') is an external sex organ (intromittent organ) through which males urination, urinate and ejaculation, ejaculate, as Penis, on other animals. Together with the testes and surrounding structures, the penis functions as part of the male reproductive system. The main parts of the penis are the Root of penis, root, Body of penis, body, the epithelium of the penis, including the shaft skin, and the foreskin covering the glans penis, glans. The body of the penis is made up of three columns of tissue (biology), tissue: two Corpus cavernosum penis, corpora cavernosa on the dorsal side and corpus spongiosum penis, corpus spongiosum between them on the ventral side. The Urethra#Male, urethra passes through the prostate gland, where it is joined by the ejaculatory ducts, and then through the penis. The urethra goes across the corpus spongiosum and ends at the tip of the glans as the o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squamous-cell carcinoma (SCC), also known as epidermoid carcinoma, comprises a number of different types of cancer that begin in squamous cells. These cells form on the surface of the skin, on the lining of hollow organs in the body, and on the lining of the respiratory and digestive tracts. The squamous-cell carcinomas of different body sites can show differences in their presented symptoms, natural history, prognosis, and response to treatment. By body location Human papillomavirus infection has been associated with SCCs of the oropharynx, lung, fingers, and anogenital region. Head and neck cancer About 90% of cases of head and neck cancer (cancer of the mouth, nasal cavity, nasopharynx, throat and associated structures) are due to SCC. Skin Cutaneous squamous-cell carcinoma is the second most common skin cancer, accounting for over 1 million cases in the United States each year. Thyroid Primary squamous-cell carcinoma of the thyroid shows an aggressive biologica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the chief commercial crop is ''N. tabacum''. The more potent variant ''N. rustica'' is also used in some countries. Dried tobacco leaves are mainly used for smoking in cigarettes and cigars, as well as pipes and shishas. They can also be consumed as snuff, chewing tobacco, dipping tobacco, and snus. Tobacco contains the highly addictive stimulant alkaloid nicotine as well as harmala alkaloids. Tobacco use is a cause or risk factor for many deadly diseases, especially those affecting the heart, liver, and lungs, as well as many cancers. In 2008, the World Health Organization named tobacco use as the world's single greatest preventable cause of death. Etymology The English word 'tobacco' originates from the Spanish word ''taba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Snuff (tobacco)
Snuff is a type of smokeless tobacco product made from finely ground or pulverized tobacco leaves. The Old Snuff House of Fribourg & Treyer at the Sign of the Rasp & Crown, No.34 James's Haymarket, London, S.W., 1720, 1920. Author: George Evens and Fribourg & Treyer. Publisher: Nabu Press, London, England. Reproduced 5 August 2010, It is snorted or "sniffed" (alternatively sometimes written as "snuffed") into the nasal cavity, delivering nicotine and a flavored scent to the user (especially if flavoring has been blended with the tobacco). Traditionally, it is sniffed or inhaled lightly after a pinch of snuff is either placed onto the back surface of the hand, held pinched between thumb and index finger, or held by a specially made "snuffing" device. Snuff originated in the Americas and was commonly used in Europe by the 17th century. Traditional snuff production consists of a lengthy, multi-step process, in tobacco snuff mills. The selected tobacco leaves are first subject ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alveolar Mucosa
The oral mucosa is the mucous membrane lining the inside of the mouth. It comprises stratified squamous epithelium, termed "oral epithelium", and an underlying connective tissue termed ''lamina propria''. The oral cavity has sometimes been described as a mirror that reflects the health of the individual. Changes indicative of disease are seen as alterations in the oral mucosa lining the mouth, which can reveal systemic conditions, such as diabetes or vitamin deficiency, or the local effects of chronic tobacco or alcohol use. The oral mucosa tends to heal faster and with less scar formation compared to the skin. The underlying mechanism remains unknown, but research suggests that extracellular vesicles might be involved. Classification Oral mucosa can be divided into three main categories based on function and histology: * ''Lining mucosa'', nonkeratinized stratified squamous epithelium, found almost everywhere else in the oral cavity, including the: ** ''Alveolar mucosa'', the lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alcohol And Cancer
Alcohol may refer to: Common uses * Alcohol (chemistry), a class of compounds * Ethanol, one of several alcohols, commonly known as alcohol in everyday life ** Alcohol (drug), intoxicant found in alcoholic beverages ** Alcoholic beverage Drinks containing alcohol (drug), alcohol are typically divided into three classes—beers, wines, and Distilled beverage, spirits—with alcohol content typically between 3% and 50%. Drinks with less than 0.5% are sometimes considered Non-al ..., an alcoholic drink * Rubbing alcohol, for sanitation and to kill germs Music * "Alcohol", a song by Barenaked Ladies from the 1998 album '' Stunt'' * "Alcohol", a song by Beck from the 1993 single " Loser" * "Alcohol" (Brad Paisley song), 2005 * "Alcohol", a song by Butthole Surfers from the 1993 album '' Independent Worm Saloon'' * "Alcohol", a song by CSS from the 2005 album ''Cansei de Ser Sexy'' * "Alcohol", a song by Gang Green from the 1986 album '' Another Wasted Night'' * "Alcohol", a so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sole (foot)
In humans, the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect. Structure The glabrous skin on the sole of the foot lacks the hair and pigmentation found elsewhere on the body, and it has a high concentration of sweat pores. The sole contains the thickest layers of skin on the body due to the weight that is continually placed on it. It is crossed by a set of creases that form during the early stages of embryonic development. Like those of the palm, the sweat pores of the sole lack sebaceous glands. The sole is a sensory organ by which the ground can be perceived while standing and walking. The subcutaneous tissue in the sole has adapted to deal with the high local compressive forces on the heel and the ball (between the toes and the arch) by developing a system of "pressure chambers." Each chamber is composed of internal fibrofatty tissue covered by external collagen connective tissue. The septa (internal walls) of these chambers are permeated by n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histopathology
Histopathology (compound of three Greek words: 'tissue', 'suffering', and '' -logia'' 'study of') is the microscopic examination of tissue in order to study the manifestations of disease. Specifically, in clinical medicine, histopathology refers to the examination of a biopsy or surgical specimen by a pathologist, after the specimen has been processed and histological sections have been placed onto glass slides. In contrast, cytopathology examines free cells or tissue micro-fragments (as "cell blocks "). Collection of tissues Histopathological examination of tissues starts with surgery, biopsy, or autopsy. The tissue is removed from the body or plant, and then, often following expert dissection in the fresh state, placed in a fixative which stabilizes the tissues to prevent decay. The most common fixative is 10% neutral buffered formalin (corresponding to 3.7% w/v formaldehyde in neutral buffered water, such as phosphate buffered saline). Preparation for h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atypia
Atypia (from Greek language, Greek, ''a'' + ''typos'', without type; a condition of being irregular or nonstandard) is a histopathology, histopathologic term for a structural abnormality in a Cell (biology), cell, i.e. it is used to describe atypical cells. Atypia can be caused by infection or irritation. If, for example it were diagnosed in a Pap smear in the uterus it is more likely to be precancerous. The related concept of dysplasia refers to an abnormality of development, and includes abnormalities on larger, histopathologic scales. Example features Features that constitute atypia have different definitions for different diseases, but often include the following Cell nucleus, nucleus abnormalities: *Enlargement *Pleomorphism (cytology), Pleomorphism *Nuclear polychromasia, which means variability in nuclear chromatin content. Polychromasia otherwise refers to a disease of immature red blood cells. *Numerous mitosis, mitotic figures Examples for Barrett's esophagus In Barret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metastasis
Metastasis is a pathogenic agent's spreading from an initial or primary site to a different or secondary site within the host's body; the term is typically used when referring to metastasis by a cancerous tumor. The newly pathological sites, then, are metastases (mets). It is generally distinguished from cancer invasion, which is the direct extension and penetration by cancer cells into neighboring tissues. Cancer occurs after cells are genetically altered to proliferate rapidly and indefinitely. This uncontrolled proliferation by mitosis produces a primary tumor, primary tumour heterogeneity, heterogeneic tumour. The cells which constitute the tumor eventually undergo metaplasia, followed by dysplasia then anaplasia, resulting in a Malignancy, malignant phenotype. This malignancy allows for invasion into the circulation, followed by invasion to a second site for tumorigenesis. Some cancer cells, known as circulating tumor cells (CTCs), are able to penetrate the walls of lymp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis (skin), epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. Embryology, In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Verrucous Carcinoma Subtypes
Verrucous carcinoma is a type of squamous cell carcinoma that may be associated with HPV infection (may be subtypes 16 or 18, but types 6 and 11 have also been reported, as have HPV negative variants). Several subtypes of verrucous carcinoma have been described. Treatment of verrucous carcinoma with radiation therapy should be avoided due to the risk of anaplastic transformation. See also *List of cutaneous conditions *List of contact allergens *List of cutaneous conditions associated with increased risk of nonmelanoma skin cancer *List of cutaneous conditions associated with internal malignancy *List of cutaneous conditions caused by mutations in keratins *List of cutaneous conditions caused by problems with junctional proteins *List of dental abnormalities associated with cutaneous conditions *List of genes mutated in cutaneous conditions *List of histologic stains that aid in diagnosis of cutaneous conditions *List of immunofluorescence findings for autoimmune bullous con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |