|
Vapor Permeation Barrier
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Herring, ''General Chemistry'', Prentice-Hall, 8th ed. 2002, p. 483–86. which means that the vapor can be condensed to a liquid by increasing the pressure on it without reducing the temperature of the vapor. A vapor is different from an aerosol. An aerosol is a suspension of tiny particles of liquid, solid, or both within a gas. For example, water has a critical temperature of , which is the highest temperature at which liquid water can exist at any pressure. In the atmosphere at ordinary temperatures gaseous water (known as water vapor) will condense into a liquid if its partial pressure is increased sufficiently. A vapor may co-exist with a liquid (or a solid). When this is true, the two phases will be in equilibrium, and the gas-partial pressure will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nitrogen Dioxide Gas
Nitrogen dioxide is a chemical compound with the formula . One of several nitrogen oxides, nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas. It is a paramagnetic, bent molecule with C2v point group symmetry. Industrially, is an intermediate in the synthesis of nitric acid, millions of tons of which are produced each year, primarily for the production of fertilizers. Nitrogen dioxide is poisonous and can be fatal if inhaled in large quantities. Cooking with a gas stove produces nitrogen dioxide which causes poorer indoor air quality. Combustion of gas can lead to increased concentrations of nitrogen dioxide throughout the home environment which is linked to respiratory issues and diseases. The LC50 (median lethal dose) for humans has been estimated to be 174 ppm for a 1-hour exposure. It is also included in the NOx family of atmospheric pollutants. Properties Nitrogen dioxide is a reddish-brown gas with a pungent, acrid odor above and becomes a yellowish-brown liquid below . It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles, suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may compose the droplets and crystals. On Earth, clouds are formed as a result of saturation of the air when it is cooled to its dew point, or when it gains sufficient moisture (usually in the form of water vapor) from an adjacent source to raise the dew point to the ambient temperature. Clouds are seen in the Earth's homosphere, which includes the troposphere, stratosphere, and mesosphere. Nephology is the science of clouds, which is undertaken in the cloud physics branch of meteorology. The World Meteorological Organization uses two methods of naming clouds in their respective layers of the homosphere, Latin and common name. Genus types in the troposphere, the atmospheric layer closest to Earth's surface, have Latin names because of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Note (perfumery)
Notes in perfumery are descriptors of scents that can be sensed upon the application of a perfume. Notes are separated into three classes: top/head notes, middle/heart notes, and base/soul notes; which denote groups of scents which can be sensed with respect to the time after the application of a perfume. These notes are created with knowledge of the evaporation process and intended use of the perfume. The presence of one note may alter the perception of another—for instance, the presence of certain base or heart notes will alter the scent perceived when the top notes are strongest, and likewise the scent of base notes in the dry-down will often be altered depending on the smells of the heart notes. The idea of ''notes'' is used primarily for the marketing of fine fragrances. The term is sometimes used by perfumers to describe approximately scents or the perfumery process to laypeople. Volatility grouping Fragrant materials are listed by Poucher in order of volatility and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfume
Perfume (, ) is a mixture of fragrance, fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), Fixative (perfumery), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. Perfumes can be defined as substances that emit and diffuse a pleasant and fragrant odor. They consist of artificial mixtures of aromatic chemicals and essential oils. The 1939 List of Nobel laureates, Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory." Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin and coumarin, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crepuscular Rays Beam Through The Mist Blown From Takkakaw Falls
In zoology, a crepuscular animal is one that is active primarily during the twilight period, being matutinal (active during dawn), vespertine/vespertinal (active during dusk), or both. This is distinguished from diurnal and nocturnal behavior, where an animal is active during the hours of daytime and of night, respectively. Some crepuscular animals may also be active by moonlight or during an overcast day. Matutinal animals are active only after dawn, and vespertine only before dusk. A number of factors affect the time of day an animal is active. Predators hunt when their prey is available, and prey try to avoid the times when their principal predators are at large. The temperature may be too high at midday or too low at night. Some creatures may adjust their activities depending on local competition. Etymology and usage The word ''crepuscular'' derives from the Latin '' crepusculum'' ("twilight"). Its sense accordingly differs from diurnal and nocturnal behavior, which re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
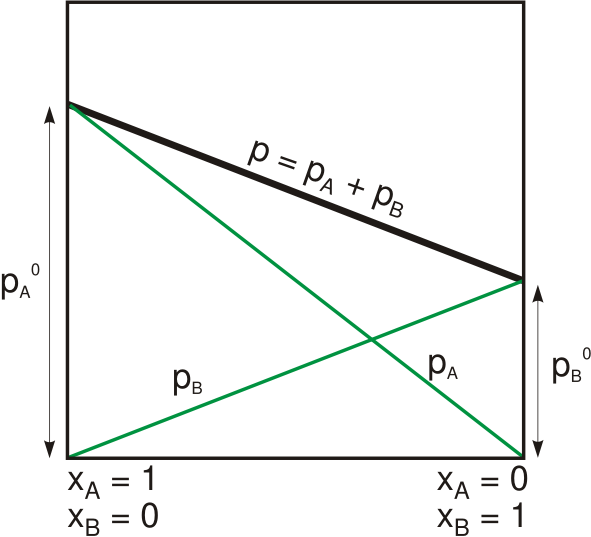
Raoult's Law
Raoult's law ( law) is a relation of physical chemistry, with implications in thermodynamics. Proposed by French chemist François-Marie Raoult in 1887, it states that the partial pressure of each component of an ideal mixture of ''liquids'' is equal to the vapor pressure of the pure component (liquid or solid) multiplied by its mole fraction in the mixture. In consequence, the relative lowering of vapor pressure of a dilute solution of nonvolatile solute is equal to the mole fraction of solute in the solution. Mathematically, Raoult's law for a single component in an ideal solution is stated as : p_i = p_i^\star x_i where p_i is the partial pressure of the component i in the gaseous mixture above the solution, p_i^\star is the equilibrium vapor pressure of the pure component i, and x_i is the mole fraction of the component i in the liquid or solid solution. Where two volatile liquids A and B are mixed with each other to form a solution, the vapor phase consists of both compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level. History The standard atmosphere was originally defined as the pressure exerted by a 760 mm column of mercury at and standard gravity (''g''n = ). It was used as a reference condition for physical and chemical properties, and the definition of the centigrade temperature scale set 100 °C as the boiling point of water at this pressure. In 1954, the 10th General Conference on Weights and Measures (CGPM) adopted ''standard atmosphere'' for general use and affirmed its definition of being precisely equal to dynes per square centimetre (). This defined pressure in a way that is independent of the properties of any particular substance. In addition, the CGPM noted that there had been some misapprehension that the previous definition (from the 9th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Normal Boiling Point
The boiling point of a substance is the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the pressure surrounding the liquid and the liquid changes into a vapor. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A liquid in a partial vacuum, i.e., under a lower pressure, has a lower boiling point than when that liquid is at atmospheric pressure. Because of this, water boils at 100°C (or with scientific precision: ) under standard pressure at sea level, but at at altitude. For a given pressure, different liquids will boil at different temperatures. The normal boiling point (also called the atmospheric boiling point or the atmospheric pressure boiling point) of a liquid is the special case in which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the defined atmospheric pressure at sea level, one atmosphere. At that temperature, the vapor pressure of the liquid becomes sufficient to overcome atmospheric pressure and allow bubbles of v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vapor Being Used In A Cloud Chamber
In physics, a vapor (American English) or vapour (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences) is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical temperature,R. H. Petrucci, W. S. Harwood, and F. G. Herring, ''General Chemistry'', Prentice-Hall, 8th ed. 2002, p. 483–86. which means that the vapor can be condensed to a liquid by increasing the pressure on it without reducing the temperature of the vapor. A vapor is different from an aerosol. An aerosol is a suspension of tiny particles of liquid, solid, or both within a gas. For example, water has a critical temperature of , which is the highest temperature at which liquid water can exist at any pressure. In the atmosphere at ordinary temperatures gaseous water (known as water vapor) will condense into a liquid if its partial pressure is increased sufficiently. A vapor may co-exist with a liquid (or a solid). When this is true, the two phases will be in equilibrium, and the gas-partial pressure will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Binary Boiling Point Diagram New
Binary may refer to: Science and technology Mathematics * Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two values (0 and 1) for each digit * Binary function, a function that takes two arguments * Binary operation, a mathematical operation that takes two arguments * Binary relation, a relation involving two elements * Finger binary, a system for counting in binary numbers on the fingers of human hands Computing * Binary code, the representation of text and data using only the digits 1 and 0 * Bit, or binary digit, the basic unit of information in computers * Binary file, composed of something other than human-readable text ** Executable, a type of binary file that contains machine code for the computer to execute * Binary tree, a computer tree data structure in which each node has at most two children * Binary-coded decimal, a method for encoding for decimal digits in binary sequences Astronomy * Binary star, a star system with two stars in it * Binary planet, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinetic Theory Of Gases
The kinetic theory of gases is a simple classical model of the thermodynamic behavior of gases. Its introduction allowed many principal concepts of thermodynamics to be established. It treats a gas as composed of numerous particles, too small to be seen with a microscope, in constant, random motion. These particles are now known to be the atoms or molecules of the gas. The kinetic theory of gases uses their collisions with each other and with the walls of their container to explain the relationship between the macroscopic properties of gases, such as volume, pressure, and temperature, as well as transport properties such as viscosity, thermal conductivity and mass diffusivity. The basic version of the model describes an ideal gas. It treats the collisions as perfectly elastic and as the only interaction between the particles, which are additionally assumed to be much smaller than their average distance apart. Due to the time reversibility of microscopic dynamics ( microsco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms that are held together by Force, attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions that satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, the distinction from ions is dropped and ''molecule'' is often used when referring to polyatomic ions. A molecule may be homonuclear, that is, it consists of atoms of one chemical element, e.g. two atoms in the oxygen molecule (O2); or it may be heteronuclear, a chemical compound composed of more than one element, e.g. water (molecule), water (two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom; H2O). In the kinetic theory of gases, the term ''molecule'' is often used for any gaseous particle regardless of its composition. This relaxes the requirement that a molecule contains two or more atoms, since the noble gases are individual atoms. Atoms and complexes connected by non-covalent interactions, such as hydrogen bonds or ionic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |