|
Tumor Necrosis Factors
The tumor necrosis factor (TNF) superfamily is a protein superfamily of type II transmembrane proteins containing TNF homology domain and forming trimers. Members of this superfamily can be released from the cell membrane by extracellular proteolytic cleavage and function as a cytokine. These proteins are expressed predominantly by immune cells and they regulate diverse cell functions, including immune response and inflammation, but also proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and embryogenesis. The superfamily contains 19 members that bind to 29 members of TNF receptor superfamily. An occurrence of orthologs in invertebrates hints at ancient origin of this superfamily in evolution. The PROSITE pattern of this superfamily is located in a beta sheet The beta sheet, (β-sheet) (also β-pleated sheet) is a common motif of the regular protein secondary structure. Beta sheets consist of beta strands (β-strands) connected laterally by at least two or three backbone hydro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mus Musculus
Mus or MUS may refer to: Abbreviations * MUS, the NATO country code for Mauritius * MUS, the IATA airport code for Minami Torishima Airport * MUS, abbreviation for the Centre for Modern Urban Studies on Campus The Hague, Leiden University, Netherlands * MUS, abbreviation for Medically unexplained physical symptoms * MUS, abbreviation for the Memphis University School * MUS, abbreviation for the Movimiento Unión Soberanista * MUS, abbreviation for Multiple-use water supply system, a low-cost, equitable water supply systems * Mus, abbreviation for Musca, a southern constellation * mus, ISO-639 code for the Muscogee language * Mus., abbreviation used in music degrees such as B.Mus. and M.Mus. * MUs, or million units of energy, used in India for a gigawatt hour People * Anders Mus (fl. 1501–1535), Danish civil servant in Norway * Conny Mus (1950–2010), Dutch journalist, best known as a correspondent for ''RTL Nieuws'' in Israel and the Middle East * Gus Mus (born 1944) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cachexia
Cachexia () is a complex syndrome associated with an underlying illness, causing ongoing muscle loss that is not entirely reversed with nutritional supplementation. A range of diseases can cause cachexia, most commonly cancer, congestive heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, chronic kidney disease, and AIDS. Systemic inflammation from these conditions can cause detrimental changes to metabolism and body composition. In contrast to weight loss from inadequate caloric intake, cachexia causes mostly muscle loss instead of fat loss. Diagnosis of cachexia can be difficult due to the lack of well-established diagnostic criteria. Cachexia can improve with treatment of the underlying illness but other treatment approaches have limited benefit. Cachexia is associated with increased mortality and poor quality of life. The term is from Greek κακός ''kakos'', "bad", and ἕξις ''hexis'', "condition". Causes Cachexia can be caused by diverse medical conditions, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD30 Ligand
CD153 (cluster of differentiation 153) also known as tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNFSF8 gene. CD153 is a cytokine ligand for the TNF receptor CD30. It plays a role in the T cell-dependent anti-mycobacterial ''Mycobacterium'' is a genus of over 190 species in the phylum Actinomycetota, assigned its own family, Mycobacteriaceae. This genus includes pathogens known to cause serious diseases in mammals, including tuberculosis ('' M. tuberculosis'') and ... immune response. References External links * {{gene-9-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
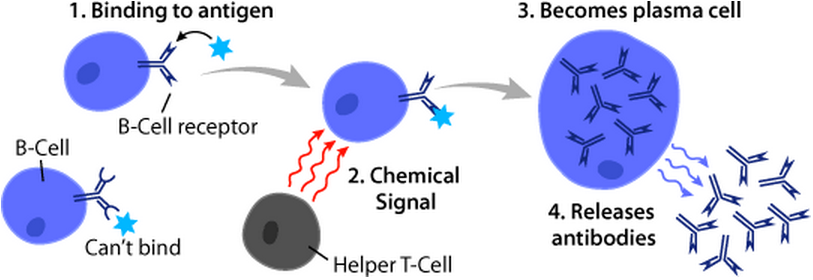
B Cell
B cells, also known as B lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell of the lymphocyte subtype. They function in the humoral immunity component of the adaptive immune system. B cells produce antibody molecules which may be either secreted or inserted into the plasma membrane where they serve as a part of B-cell receptors. When a naïve or memory B cell is activated by an antigen, it proliferates and differentiates into an antibody-secreting effector cell, known as a plasmablast or plasma cell. Additionally, B cells present antigens (they are also classified as professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs)) and secrete cytokines. In mammals, B cells mature in the bone marrow, which is at the core of most bones. In birds, B cells mature in the bursa of Fabricius, a lymphoid organ where they were first discovered by Chang and Glick, which is why the 'B' stands for bursa and not bone marrow as commonly believed. B cells, unlike the other two classes of lymphocytes, T cell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD70
CD70 (Cluster of Differentiation 70) is a protein that in humans is encoded by ''CD70'' gene. CD70 is a ligand for CD27. Clinical significance The CD70 protein is expressed on highly activated lymphocytes (like in T- and B-cell lymphomas). It is therefore suggested that anti-CD70 antibodies might be a possible treatment for CD70 positive lymphomas as normal lymphocytes have low CD70 expression. Drug development ARGX-110 is a CD70-specific antibody that is currently under investigation for the treatment of hematological malignancies. It is being developed by the Belgian company arGEN-X. In December 2013 a first part of a phase 1b trial was completed. In January 2014 a safety and efficacy phase of the study started. Vorsetuzumab mafodotin is a CD70-targeted antibody-drug conjugate that started clinical trials for renal cell carcinoma. See also * Cluster of differentiation The cluster of differentiation (also known as cluster of designation or classification determinant an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antigen-presenting Cell
An antigen-presenting cell (APC) or accessory cell is a cell that displays antigen bound by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins on its surface; this process is known as antigen presentation. T cells may recognize these complexes using their T cell receptors (TCRs). APCs process antigens and present them to T-cells. Almost all cell types can present antigens in some way. They are found in a variety of tissue types. Professional antigen-presenting cells, including macrophages, B cells and dendritic cells, present foreign antigens to helper T cells, while virus-infected cells (or cancer cells) can present antigens originating inside the cell to cytotoxic T cells. In addition to the MHC family of proteins, antigen presentation relies on other specialized signaling molecules on the surfaces of both APCs and T cells. Antigen-presenting cells are vital for effective adaptive immune response, as the functioning of both cytotoxic and helper T cells is dependent on APCs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adaptive Immune System
The adaptive immune system, also known as the acquired immune system, is a subsystem of the immune system that is composed of specialized, systemic cells and processes that eliminate pathogens or prevent their growth. The acquired immune system is one of the two main immunity (medical), immunity strategies found in vertebrates (the other being the innate immune system). Like the innate system, the adaptive immune system includes both humoral immunity components and cell-mediated immunity components and destroys invading pathogens. Unlike the innate immune system, which is pre-programmed to react to common broad categories of pathogen, the adaptive immune system is highly specific to each particular pathogen the body has encountered. Adaptive immunity creates immunological memory after an initial response to a specific pathogen, and leads to an enhanced response to future encounters with that pathogen. Antibody, Antibodies are a critical part of the adaptive immune system. Adap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CD40 Ligand
CD154, also called CD40 ligand or CD40L, is a protein that is primarily expressed on activated T cells and is a member of the TNF superfamily of molecules. It binds to CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many effects depending on the target cell type. In total CD40L has three binding partners: CD40, α5β1 integrin and αIIbβ3. CD154 acts as a costimulatory molecule and is particularly important on a subset of T cells called T follicular helper cells (TFH cells). On TFH cells, CD154 promotes B cell maturation and function by engaging CD40 on the B cell surface and therefore facilitating cell-cell communication. A defect in this gene results in an inability to undergo immunoglobulin class switching and is associated with hyper IgM syndrome. Absence of CD154 also stops the formation of germinal centers and therefore prohibiting antibody affinity maturation, an important process in the adaptive immune system. History In 1991, three groups reported discoveri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
T Cell
A T cell is a type of lymphocyte. T cells are one of the important white blood cells of the immune system and play a central role in the adaptive immune response. T cells can be distinguished from other lymphocytes by the presence of a T-cell receptor (TCR) on their cell surface. T cells are born from hematopoietic stem cells, found in the bone marrow. Developing T cells then migrate to the thymus gland to develop (or mature). T cells derive their name from the thymus. After migration to the thymus, the precursor cells mature into several distinct types of T cells. T cell differentiation also continues after they have left the thymus. Groups of specific, differentiated T cell subtypes have a variety of important functions in controlling and shaping the immune response. One of these functions is immune-mediated cell death, and it is carried out by two major subtypes: CD8+ "killer" and CD4+ "helper" T cells. (These are named for the presence of the cell surface proteins CD8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OX40 Ligand
OX40L is the ligand for OX40 (also known as CD134 or TNFRSF4) and is stably expressed on many antigen-presenting cells such as DC2s (a subtype of dendritic cells), macrophages, and activated B lymphocytes. The OX40 molecule, conversely, is present on the surface of activated T lymphocytes (mainly CD4+ T cells), but also on NK cells, NKT cells, and neutrophils. The ligation of OX40-OX40L is a source of survival signal for T cells and enables the development of memory T cells. Signaling through these two molecules also leads to polarization towards Th2 immune response even in an environment with low levels of IL-4 cytokine. OX40L is also present on the surface of many non-immune cells, for example, endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. The surface expression of OX40L is induced by many pro-inflammatory mediators, such as TNF-α, e.g. produced by mast cells, IFN-γ and PGE2 (prostaglandin E2). OX40L has also been designated CD252 (cluster of differentiation 252). Var ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lymphotoxin Beta
Lymphotoxin-beta (LT-beta) also known as tumor necrosis factor C (TNF-C) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''LTB'' gene. Function Lymphotoxin beta is a type II membrane protein of the TNF family. It anchors lymphotoxin-alpha to the cell surface through heterotrimer formation. The predominant form on the lymphocyte A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include natural killer cells (which function in cell-mediated, cytotoxic innate immunity), T cells (for cell-mediated, cytotoxic ad ... surface is the lymphotoxin-alpha 1/beta 2 complex (e.g. 1 molecule alpha/2 molecules beta) and this complex is the primary ligand for the lymphotoxin-beta receptor. The minor complex is lymphotoxin-alpha 2/beta 1. LTB is an inducer of the inflammatory response system and involved in normal development of lymphoid tissue. Lymphotoxin-beta isoform b is unable to complex with lymphotoxin-alpha suggesting a fu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |