|
Trilateral Retinoblastoma
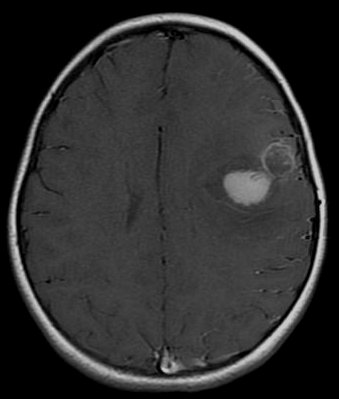
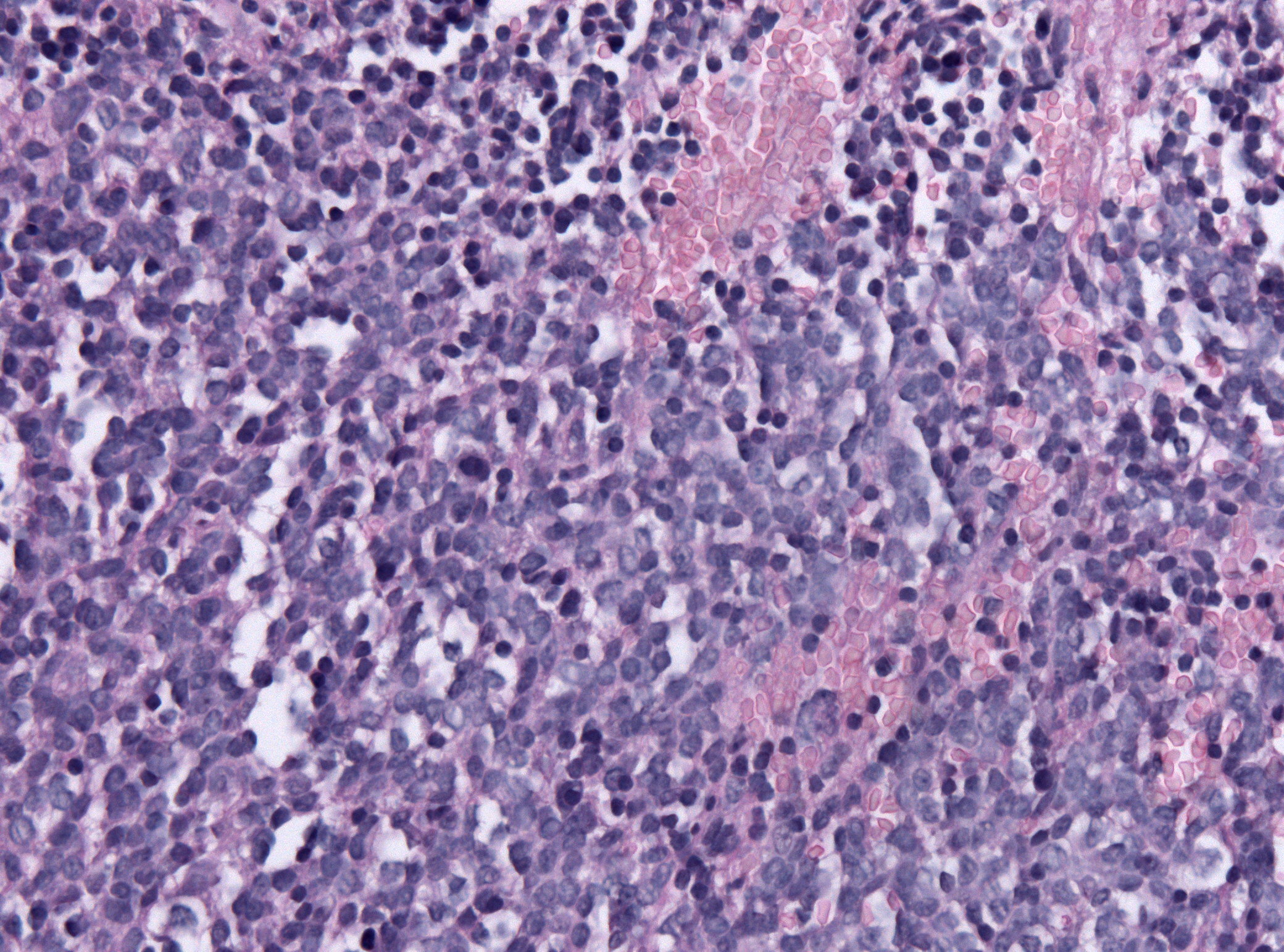
Trilateral retinoblastoma is a malignant midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor occurring in patients with inherited uni- or bilateral retinoblastoma. In most cases trilateral retinoblastoma presents itself as pineoblastoma (pineal TRb). In about a fourth of the cases the tumor develops in another intracranial region, most commonly sella turcica, supra- or parasellar (non-pineal TRb), but there are reported cases with non-pineal TRb in the 3rd ventricle. In most cases pineal TRb is diagnosed before the age of 5, but after the diagnosis of retinoblastoma. Non-pineal TRb, however, is often diagnosed simultaneous with retinoblastoma. Prognosis of patients with trilateral retinoblastoma is dismal, only a few patients have survived more than 5 years after diagnosis; all survivors were diagnosed with small tumors in a subclinical stage. Recent advances in (high-dose) chemotherapy treatment regimens and early detection have improved survival of patients with trilateral retinoblastoma. Se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oncology
Oncology is a branch of medicine that deals with the study, treatment, diagnosis and prevention of cancer. A medical professional who practices oncology is an ''oncologist''. The name's etymological origin is the Greek word ὄγκος (''ónkos''), meaning "tumor", "volume" or "mass". Oncology is concerned with: * The diagnosis of any cancer in a person (pathology) * Therapy (e.g. surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy and other modalities) * Follow-up of cancer patients after successful treatment * Palliative care of patients with terminal malignancies * Ethical questions surrounding cancer care * Screening efforts: ** of populations, or ** of the relatives of patients (in types of cancer that are thought to have a hereditary basis, such as breast cancer) Diagnosis Medical histories remain an important screening tool: the character of the complaints and nonspecific symptoms (such as fatigue, weight loss, unexplained anemia, fever of unknown origin, paraneoplasti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor is a malignant (cancerous) neural crest tumor. It is a rare tumor, usually occurring in children and young adults under 25 years of age. The overall 5 year survival rate is about 53%. It gets its name because the majority of the cells in the tumor are derived from neuroectoderm, but have not developed and differentiated in the way a normal neuron would, and so the cells appear "primitive".PNET belongs to the Ewing family of tumors. Genetics Using gene transfer of SV40 large T-antigen in neuronal precursor cells of rats, a brain tumor model was established. The PNETs were histologically indistinguishable from the human counterparts and have been used to identify new genes involved in human brain tumor carcinogenesis. The model was used to confirm p53 as one of the genes involved in human medulloblastomas, but since only about 10% of the human tumors showed mutations in that gene, the model can be used to identify the other binding partners of SV40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively found in young children. Though most children survive this cancer, they may lose their vision in the affected eye(s) or need to have the eye removed. Almost half of children with retinoblastoma have a hereditary genetic defect associated with retinoblastoma. In other cases, it is caused by a congenital mutation in the chromosome 13 gene 13q14 ( retinoblastoma protein). Signs and symptoms Retinoblastoma is universally known as the most intrusive intraocular cancer among children. The chance of survival and preservation of the eye depends fully on the severity. Retinoblastoma is extremely rare as there are only about 200 to 300 cases every year in the United States. Looking at retinoblastoma globally, only 1 in about 15,000 children have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all primary CNS neoplasms. Epidemiology Pineoblastomas typically occur at very young ages. One study found the average age of presentation to be 4.3 years, with peaks at age 3 and 8. Another cites cases to more commonly occur in patients under 2 years of age. Rates of occurrence for males and females are similar, but may be slightly more common in females. One study found incidence of pineoblastoma to be increased in black patients compared to white patients by around 71%. This difference was most apparent in patients aged 5 to 9 years old. Pathophysiology The pineal gland is a small organ in the center of the brain that is responsible for controlling melatonin secretion. Several tumors can occur in the area of the pineal gland, with the most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sella Turcica
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa. Structure The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa. The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae. Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes. Development It is widely belie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Primitive Neuroectodermal Tumor
Primitive neuroectodermal tumor is a malignant (cancerous) neural crest tumor. It is a rare tumor, usually occurring in children and young adults under 25 years of age. The overall 5 year survival rate is about 53%. It gets its name because the majority of the cells in the tumor are derived from neuroectoderm, but have not developed and differentiated in the way a normal neuron would, and so the cells appear "primitive".PNET belongs to the Ewing family of tumors. Genetics Using gene transfer of SV40 large T-antigen in neuronal precursor cells of rats, a brain tumor model was established. The PNETs were histologically indistinguishable from the human counterparts and have been used to identify new genes involved in human brain tumor carcinogenesis. The model was used to confirm p53 as one of the genes involved in human medulloblastomas, but since only about 10% of the human tumors showed mutations in that gene, the model can be used to identify the other binding partners of SV40 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Retinoblastoma
Retinoblastoma (Rb) is a rare form of cancer that rapidly develops from the immature cells of a retina, the light-detecting tissue of the eye. It is the most common primary malignant intraocular cancer in children, and it is almost exclusively found in young children. Though most children survive this cancer, they may lose their vision in the affected eye(s) or need to have the eye removed. Almost half of children with retinoblastoma have a hereditary genetic defect associated with retinoblastoma. In other cases, it is caused by a congenital mutation in the chromosome 13 gene 13q14 ( retinoblastoma protein). Signs and symptoms Retinoblastoma is universally known as the most intrusive intraocular cancer among children. The chance of survival and preservation of the eye depends fully on the severity. Retinoblastoma is extremely rare as there are only about 200 to 300 cases every year in the United States. Looking at retinoblastoma globally, only 1 in about 15,000 children have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pineoblastoma
Pineoblastoma is a malignant tumor of the pineal gland. A pineoblastoma is a supratentorial midline primitive neuroectodermal tumor. Pineoblastoma can present at any age, but is most common in young children. They account for 0.001% of all primary CNS neoplasms. Epidemiology Pineoblastomas typically occur at very young ages. One study found the average age of presentation to be 4.3 years, with peaks at age 3 and 8. Another cites cases to more commonly occur in patients under 2 years of age. Rates of occurrence for males and females are similar, but may be slightly more common in females. One study found incidence of pineoblastoma to be increased in black patients compared to white patients by around 71%. This difference was most apparent in patients aged 5 to 9 years old. Pathophysiology The pineal gland is a small organ in the center of the brain that is responsible for controlling melatonin secretion. Several tumors can occur in the area of the pineal gland, with the most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endocrine Neoplasia
The endocrine system is a messenger system comprising feedback loops of the hormones released by internal glands of an organism directly into the circulatory system, regulating distant target organs. In vertebrates, the hypothalamus is the neural control center for all endocrine systems. In humans, the major endocrine glands are the thyroid gland and the adrenal glands. The study of the endocrine system and its disorders is known as endocrinology. Glands that signal each other in sequence are often referred to as an axis, such as the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. In addition to the specialized endocrine organs mentioned above, many other organs that are part of other body systems have secondary endocrine functions, including bone, kidneys, liver, heart and gonads. For example, the kidney secretes the endocrine hormone erythropoietin. Hormones can be amino acid complexes, steroids, eicosanoids, leukotrienes, or prostaglandins. The endocrine system can be contrasted to b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |