|
Trigonometric Function
In mathematics, the trigonometric functions (also called circular functions, angle functions or goniometric functions) are real functions which relate an angle of a right-angled triangle to ratios of two side lengths. They are widely used in all sciences that are related to geometry, such as navigation, solid mechanics, celestial mechanics, geodesy, and many others. They are among the simplest periodic functions, and as such are also widely used for studying periodic phenomena through Fourier analysis. The trigonometric functions most widely used in modern mathematics are the sine, the cosine, and the tangent functions. Their multiplicative inverse, reciprocals are respectively the cosecant, the secant, and the cotangent functions, which are less used. Each of these six trigonometric functions has a corresponding Inverse trigonometric functions, inverse function, and an analog among the hyperbolic functions. The oldest definitions of trigonometric functions, related to right-an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Domain Of A Function
In mathematics, the domain of a function is the Set (mathematics), set of inputs accepted by the Function (mathematics), function. It is sometimes denoted by \operatorname(f) or \operatornamef, where is the function. In layman's terms, the domain of a function can generally be thought of as "what x can be". More precisely, given a function f\colon X\to Y, the domain of is . In modern mathematical language, the domain is part of the definition of a function rather than a property of it. In the special case that and are both sets of real numbers, the function can be graphed in the Cartesian coordinate system. In this case, the domain is represented on the -axis of the graph, as the projection of the graph of the function onto the -axis. For a function f\colon X\to Y, the set is called the ''codomain'': the set to which all outputs must belong. The set of specific outputs the function assigns to elements of is called its ''Range of a function, range'' or ''Image (mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Function Composition
In mathematics, the composition operator \circ takes two function (mathematics), functions, f and g, and returns a new function h(x) := (g \circ f) (x) = g(f(x)). Thus, the function is function application, applied after applying to . (g \circ f) is pronounced "the composition of and ". Reverse composition, sometimes denoted f \mapsto g , applies the operation in the opposite order, applying f first and g second. Intuitively, reverse composition is a chaining process in which the output of function feeds the input of function . The composition of functions is a special case of the composition of relations, sometimes also denoted by \circ. As a result, all properties of composition of relations are true of composition of functions, such as #Properties, associativity. Examples * Composition of functions on a finite set (mathematics), set: If , and , then , as shown in the figure. * Composition of functions on an infinite set: If (where is the set of all real numbers) is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Exponentiation
In mathematics, exponentiation, denoted , is an operation (mathematics), operation involving two numbers: the ''base'', , and the ''exponent'' or ''power'', . When is a positive integer, exponentiation corresponds to repeated multiplication of the base: that is, is the product (mathematics), product of multiplying bases: b^n = \underbrace_.In particular, b^1=b. The exponent is usually shown as a superscript to the right of the base as or in computer code as b^n. This binary operation is often read as " to the power "; it may also be referred to as " raised to the th power", "the th power of ", or, most briefly, " to the ". The above definition of b^n immediately implies several properties, in particular the multiplication rule:There are three common notations for multiplication: x\times y is most commonly used for explicit numbers and at a very elementary level; xy is most common when variable (mathematics), variables are used; x\cdot y is used for emphasizing that one ta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Positive Integer
In mathematics, the natural numbers are the numbers 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on, possibly excluding 0. Some start counting with 0, defining the natural numbers as the non-negative integers , while others start with 1, defining them as the positive integers Some authors acknowledge both definitions whenever convenient. Sometimes, the whole numbers are the natural numbers as well as zero. In other cases, the ''whole numbers'' refer to all of the integers, including negative integers. The counting numbers are another term for the natural numbers, particularly in primary education, and are ambiguous as well although typically start at 1. The natural numbers are used for counting things, like "there are ''six'' coins on the table", in which case they are called ''cardinal numbers''. They are also used to put things in order, like "this is the ''third'' largest city in the country", which are called ''ordinal numbers''. Natural numbers are also used as labels, like jersey numbers on a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Functional Notation
In mathematics, a function from a set to a set assigns to each element of exactly one element of .; the words ''map'', ''mapping'', ''transformation'', ''correspondence'', and ''operator'' are sometimes used synonymously. The set is called the domain of the function and the set is called the codomain of the function. Functions were originally the idealization of how a varying quantity depends on another quantity. For example, the position of a planet is a ''function'' of time. Historically, the concept was elaborated with the infinitesimal calculus at the end of the 17th century, and, until the 19th century, the functions that were considered were differentiable (that is, they had a high degree of regularity). The concept of a function was formalized at the end of the 19th century in terms of set theory, and this greatly increased the possible applications of the concept. A function is often denoted by a letter such as , or . The value of a function at an element of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
History Of The Function Concept
The mathematical concept of a function dates from the 17th century in connection with the development of calculus; for example, the slope dy/dx of a graph at a point was regarded as a function of the ''x''-coordinate of the point. Functions were not explicitly considered in antiquity, but some precursors of the concept can perhaps be seen in the work of medieval philosophers and mathematicians such as Oresme. Mathematicians of the 18th century typically regarded a function as being defined by an analytic expression. In the 19th century, the demands of the rigorous development of analysis by Karl Weierstrass and others, the reformulation of geometry in terms of analysis, and the invention of set theory by Georg Cantor, eventually led to the much more general modern concept of a function as a single-valued mapping from one set to another. Functions before the 17th century In the 12th century, mathematician Sharaf al-Din al-Tusi analyzed the equation in the form stating that t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
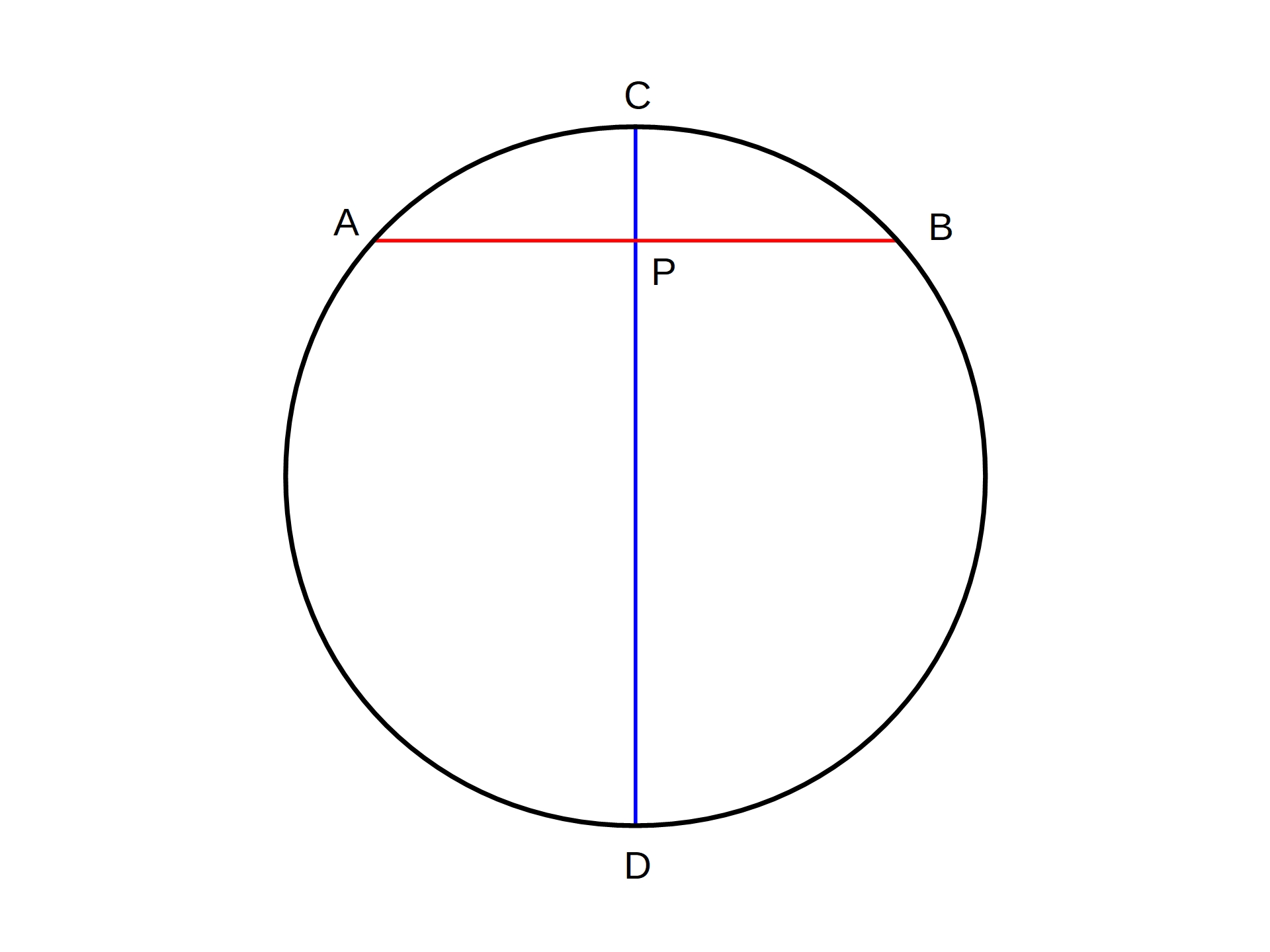 |
Circular Arc
A circular arc is the arc of a circle between a pair of distinct points. If the two points are not directly opposite each other, one of these arcs, the minor arc, subtends an angle at the center of the circle that is less than radians (180 degrees); and the other arc, the major arc, subtends an angle greater than radians. The arc of a circle is defined as the part or segment of the circumference of a circle. A straight line that connects the two ends of the arc is known as a '' chord'' of a circle. If the length of an arc is exactly half of the circle, it is known as a '' semicircular arc''. Length The length (more precisely, arc length) of an arc of a circle with radius ''r'' and subtending an angle ''θ'' (measured in radians) with the circle center — i.e., the central angle — is : L = \theta r. This is because :\frac=\frac. Substituting in the circumference :\frac=\frac, and, with ''α'' being the same angle measured in degrees, since ''θ'' = , the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Line Segment
In geometry, a line segment is a part of a line (mathematics), straight line that is bounded by two distinct endpoints (its extreme points), and contains every Point (geometry), point on the line that is between its endpoints. It is a special case of an ''arc (geometry), arc'', with zero curvature. The length of a line segment is given by the Euclidean distance between its endpoints. A closed line segment includes both endpoints, while an open line segment excludes both endpoints; a half-open line segment includes exactly one of the endpoints. In geometry, a line segment is often denoted using an overline (vinculum (symbol), vinculum) above the symbols for the two endpoints, such as in . Examples of line segments include the sides of a triangle or square. More generally, when both of the segment's end points are vertices of a polygon or polyhedron, the line segment is either an edge (geometry), edge (of that polygon or polyhedron) if they are adjacent vertices, or a diagonal. Wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Complex Plane
In mathematics, the complex plane is the plane (geometry), plane formed by the complex numbers, with a Cartesian coordinate system such that the horizontal -axis, called the real axis, is formed by the real numbers, and the vertical -axis, called the imaginary axis, is formed by the imaginary numbers. The complex plane allows for a geometric interpretation of complex numbers. Under addition, they add like vector (geometry), vectors. The multiplication of two complex numbers can be expressed more easily in polar coordinates: the magnitude or ' of the product is the product of the two absolute values, or moduli, and the angle or ' of the product is the sum of the two angles, or arguments. In particular, multiplication by a complex number of modulus 1 acts as a rotation. The complex plane is sometimes called the Argand plane or Gauss plane. Notational conventions Complex numbers In complex analysis, the complex numbers are customarily represented by the symbol , which can be sepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Series (mathematics)
In mathematics, a series is, roughly speaking, an addition of Infinity, infinitely many Addition#Terms, terms, one after the other. The study of series is a major part of calculus and its generalization, mathematical analysis. Series are used in most areas of mathematics, even for studying finite structures in combinatorics through generating functions. The mathematical properties of infinite series make them widely applicable in other quantitative disciplines such as physics, computer science, statistics and finance. Among the Ancient Greece, Ancient Greeks, the idea that a potential infinity, potentially infinite summation could produce a finite result was considered paradoxical, most famously in Zeno's paradoxes. Nonetheless, infinite series were applied practically by Ancient Greek mathematicians including Archimedes, for instance in the Quadrature of the Parabola, quadrature of the parabola. The mathematical side of Zeno's paradoxes was resolved using the concept of a limit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |