|
Trace (linguistics)
Syntactic movement is the means by which some theories of syntax address discontinuities. Movement was first postulated by structuralist linguists who expressed it in terms of ''discontinuous constituents'' or ''displacement''. Some constituents appear to have been displaced from the position in which they receive important features of interpretation. The concept of movement is controversial and is associated with so-called ''transformational'' or ''derivational'' theories of syntax (such as transformational grammar, government and binding theory, minimalist program). Representational theories (such as head-driven phrase structure grammar, lexical functional grammar, construction grammar, and most dependency grammars), in contrast, reject the notion of movement and often instead address discontinuities with other mechanisms including graph reentrancies, feature passing, and type shifters. Illustration Movement is the traditional means of explaining discontinuities such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discontinuity (linguistics)
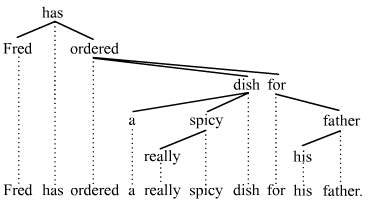
In linguistics, a discontinuity occurs when a given word or phrase is separated from another word or phrase that it modifies in such a manner that a direct connection cannot be established between the two without incurring crossing lines in the tree structure. The terminology that is employed to denote discontinuities varies depending on the theory of syntax at hand. The terms ''discontinuous constituent'', ''displacement'', ''long distance dependency'', ''unbounded dependency'', and ''projectivity violation'' are largely synonymous with the term ''discontinuity''. There are various types of discontinuities, the most prominent and widely studied of these being topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, and extraposition. Natural languages vary with respect to the types of discontinuities that they permit. The fixed word order of English allows for relatively few discontinuities compared to, for instance, the Slavic languages, which are much more permissive. Even compared to a closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discontinuity (linguistics)
In linguistics, a discontinuity occurs when a given word or phrase is separated from another word or phrase that it modifies in such a manner that a direct connection cannot be established between the two without incurring crossing lines in the tree structure. The terminology that is employed to denote discontinuities varies depending on the theory of syntax at hand. The terms ''discontinuous constituent'', ''displacement'', ''long distance dependency'', ''unbounded dependency'', and ''projectivity violation'' are largely synonymous with the term ''discontinuity''. There are various types of discontinuities, the most prominent and widely studied of these being topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, and extraposition. Natural languages vary with respect to the types of discontinuities that they permit. The fixed word order of English allows for relatively few discontinuities compared to, for instance, the Slavic languages, which are much more permissive. Even compared to a closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Contraction (grammar)
A contraction is a shortened version of the spoken and written forms of a word, syllable, or word group, created by omission of internal letters and sounds. In linguistic analysis, contractions should not be confused with crasis, abbreviations and initialisms (including acronyms), with which they share some semantic and phonetic functions, though all three are connoted by the term "abbreviation" in layman’s terms. Contraction is also distinguished from morphological clipping, where beginnings and endings are omitted. The definition overlaps with the term portmanteau (a linguistic ''blend''), but a distinction can be made between a portmanteau and a contraction by noting that contractions are formed from words that would otherwise appear together in sequence, such as ''do'' and ''not'', whereas a portmanteau word is formed by combining two or more existing words that all relate to a singular concept that the portmanteau describes. English English has a number of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the island of Great Britain. Existing on a dialect continuum with Scots, and then closest related to the Low Saxon and Frisian languages, English is genealogically West Germanic. However, its vocabulary is also distinctively influenced by dialects of France (about 29% of Modern English words) and Latin (also about 29%), plus some grammar and a small amount of core vocabulary influenced by Old Norse (a North Germanic language). Speakers of English are called Anglophones. The earliest forms of English, collectively known as Old English, evolved from a group of West Germanic (Ingvaeonic) dialects brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the 5th century and further mutated by Norse-speaking Viking settlers starting in the 8 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Category
In linguistics, an empty category, which may also be referred to as a covert category, is an element in the study of syntax that does not have any phonological content and is therefore unpronounced.Kosta, Peter, and Krivochen, Diego Gabriel. ''Eliminating Empty Categories: A Radically Minimalist View on Their Ontology and Justification''. Frankfurt: Peter Lang GmbH, 2013. Print. Empty categories exist in contrast to overt categories which are pronounced. When representing empty categories in tree structures, linguists use a null symbol (∅) to depict the idea that there is a mental category at the level being represented, even if the word(s) are being left out of overt speech. The phenomenon was named and outlined by Noam Chomsky in his 1981 LGB framework, and serves to address apparent violations of locality of selection — there are different types of empty categories that each appear to account for locality violations in different environments. Empty categories are present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subcategorization (linguistics)
In linguistics, subcategorization denotes the ability/necessity for lexical items (usually verbs) to require/allow the presence and types of the syntactic arguments with which they co-occur. The notion of subcategorization is similar to the notion of valency, although the two concepts (subcategorization and valency) stem from different traditions in the study of syntax and grammar. Argument structure Argument structure is the list of selected arguments associated with a lexical category, such as a verb (SKS, 2015). When every predicate, otherwise known as a verb, is used, it selects a specific set of arguments that need to be fulfilled to create a well-formed sentence (Kroger, 2005). These are arguments such as AGENT, PATIENT, EXPERIENCER, THEME, RECIPIENT, and STIMULUS. To illustrate this, the sentence ''The adults asked if the cats would pee on the sofa'', has been broken down into its semantic roles and argument selections below. It is necessary to understand the fundame ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catena (linguistics)
In linguistics, a catena (English pronunciation: , plural catenas or catenae; from Latin for "chain") is a unit of syntax and morphology, closely associated with dependency grammars. It is a more flexible and inclusive unit than the constituent and may therefore be better suited than the constituent to serve as the fundamental unit of syntactic and morphosyntactic analysis. The catena has served as the basis for the analysis of a number of phenomena of syntax, such as idiosyncratic meaning, ellipsis mechanisms (e.g. gapping, stripping, VP-ellipsis, pseudogapping, sluicing, answer ellipsis, comparative deletion), predicate-argument structures, and discontinuities (topicalization, wh-fronting, scrambling, extraposition, etc.). The catena concept has also been taken as the basis for a theory of morphosyntax, i.e. for the extension of dependencies into words; dependencies are acknowledged between the morphs that constitute words. While the catena concept has been applied main ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
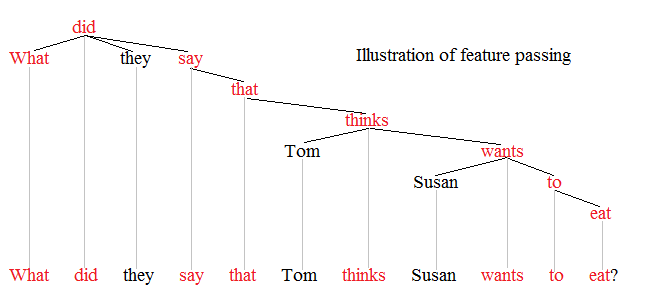
Feature Passing 1
Feature may refer to: Computing * Feature (CAD), could be a hole, pocket, or notch * Feature (computer vision), could be an edge, corner or blob * Feature (software design) is an intentional distinguishing characteristic of a software item (in performance, portability, or—especially—functionality) * Feature (machine learning), in statistics: individual measurable properties of the phenomena being observed Science and analysis * Feature data, in geographic information systems, comprise information about an entity with a geographic location * Features, in audio signal processing, an aim to capture specific aspects of audio signals in a numeric way * Feature (archaeology), any dug, built, or dumped evidence of human activity Media * Feature film, a film with a running time long enough to be considered the principal or sole film to fill a program ** Feature length, the standardized length of such films * Feature story, a piece of non-fiction writing about news * Radio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government (linguistics)
In grammar and theoretical linguistics, government or rection refers to the relationship between a word and its dependents. One can discern between at least three concepts of government: the traditional notion of case government, the highly specialized definition of government in some generative models of syntax, and a much broader notion in dependency grammars. Traditional case government In traditional Latin and Greek (and other) grammars, government is the control by verbs and prepositions of the selection of grammatical features of other words. Most commonly, a verb or preposition is said to "govern" a specific grammatical case if its complement must take that case in a grammatically correct structure (see: case government). For example, in Latin, most transitive verbs require their direct object to appear in the accusative case, while the dative case is reserved for indirect objects. Thus, the phrase ''I see you'' would be rendered as ''Te video'' in Latin, using the accusativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Movement Paradox
A movement paradox is a phenomenon of grammar that challenges the transformational approach to syntax. The importance of movement paradoxes is emphasized by those theories of syntax (e.g. lexical functional grammar, head-driven phrase structure grammar, construction grammar Construction grammar (often abbreviated CxG) is a family of theories within the field of cognitive linguistics which posit that constructions, or learned pairings of linguistic patterns with meanings, are the fundamental building blocks of human ..., most dependency grammars) that reject movement, i.e. the notion that Discontinuity (linguistics), discontinuities in syntax are explained by the movement of Constituent (linguistics), constituents. Syntactic movement Given a transformational approach to syntax, the following related sentences are explained in terms of Syntactic movement, movement: ::a. We talked about the fact that he was sick for days. ::b. The fact that he was sick, we talked about ___ f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Locality (linguistics)
In linguistics, locality refers to the proximity of elements in a linguistic structure. Constraints on locality limit the span over which rules can apply to a particular structure. Theories of transformational grammar use syntactic locality constraints to explain restrictions on argument selection, syntactic binding, and syntactic movement. Where locality is observed Locality is observed in a number of linguistic contexts, and most notably with: # Selection of arguments; this is regulated by the projection principle # Binding of two DPs; this is regulated by binding theory # Displacement of wh-phrases; this is regulated by wh-movement Selection The projection principle requires that lexical properties — in particular argument structure properties such as thematic roles — be "projected" onto syntactic structures. Together with Locality of Selection, which forces lexical properties to be projected within a local projection (as defined by X-bar theory), the projection princi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |