|
Time-travel
Time travel is the concept of movement between certain points in time, analogous to movement between different points in space by an object or a person, typically with the use of a hypothetical device known as a time machine. Time travel is a widely recognized concept in philosophy and fiction, particularly science fiction. The idea of a time machine was popularized by H. G. Wells' 1895 novel '' The Time Machine''. It is uncertain if time travel to the past is physically possible, and such travel, if at all feasible, may give rise to questions of causality. Forward time travel, outside the usual sense of the perception of time, is an extensively observed phenomenon and well-understood within the framework of special relativity and general relativity. However, making one body advance or delay more than a few milliseconds compared to another body is not feasible with current technology. As for backward time travel, it is possible to find solutions in general relativity that al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Time Travel In Fiction
Time travel is a common theme in fiction, mainly since the late 19th century, and has been depicted in a variety of media, such as literature, television, film, and advertisements. The concept of time travel by mechanical means was popularized in H. G. Wells' 1895 story, '' The Time Machine''. In general, time travel stories focus on the consequences of traveling into the past or the future. The central premise for these stories often involves changing history, either intentionally or by accident, and the ways by which altering the past changes the future and creates an altered present or future for the time traveler upon their return home. In other instances, the premise is that the past cannot be changed or that the future is predetermined, and the protagonist's actions turn out to be either inconsequential or intrinsic to events as they originally unfolded. Some stories focus solely on the paradoxes and alternate timelines that come with time travel, rather than time traveli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
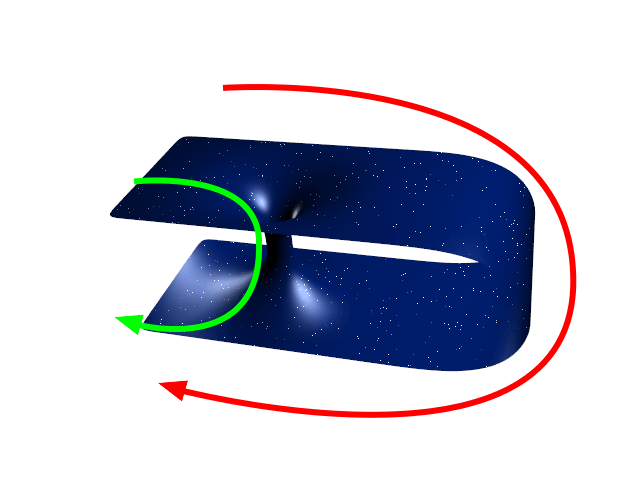
Wormhole
A wormhole ( Einstein-Rosen bridge) is a hypothetical structure connecting disparate points in spacetime, and is based on a special solution of the Einstein field equations. A wormhole can be visualized as a tunnel with two ends at separate points in spacetime (i.e., different locations, different points in time, or both). Wormholes are consistent with the general theory of relativity, but whether wormholes actually exist remains to be seen. Many scientists postulate that wormholes are merely projections of a fourth spatial dimension, analogous to how a two-dimensional (2D) being could experience only part of a three-dimensional (3D) object. Theoretically, a wormhole might connect extremely long distances such as a billion light years, or short distances such as a few meters, or different points in time, or even different universes. In 1995, Matt Visser suggested there may be many wormholes in the universe if cosmic strings with negative mass were generated in the early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Mechanics Of Time Travel
Until recently, most studies on time travel are based upon classical general relativity. Coming up with a quantum version of time travel requires physicists to figure out the time evolution equations for density states in the presence of closed timelike curves (CTC). Novikov had conjectured that once quantum mechanics is taken into account, self-consistent solutions always exist for all time machine configurations, and initial conditions. However, it has been noted such solutions are not unique in general, in violation of determinism, unitarity and linearity. The application of self-consistency to quantum mechanical time machines has taken two main routes. Novikov's rule applied to the density matrix itself gives the Deutsch prescription. Applied instead to the state vector, the same rule gives nonunitary physics with a dual description in terms of post-selection. Deutsch's prescription In 1991, David Deutsch came up with a proposal for the time evolution equations, with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Fiction
Science fiction (sometimes shortened to Sci-Fi or SF) is a genre of speculative fiction which typically deals with imaginative and futuristic concepts such as advanced science and technology, space exploration, time travel, parallel universes, extraterrestrial life, sentient artificial intelligence, cybernetics, certain forms of immortality (like mind uploading), and the singularity. Science fiction predicted several existing inventions, such as the atomic bomb, robots, and borazon, whose names entirely match their fictional predecessors. In addition, science fiction might serve as an outlet to facilitate future scientific and technological innovations. Science fiction can trace its roots to ancient mythology. It is also related to fantasy, horror, and superhero fiction and contains many subgenres. Its exact definition has long been disputed among authors, critics, scholars, and readers. Science fiction, in literature, film, television, and other media, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Payasi
Pāyāsi or Paesi is a legendary king mentioned in the ancient Buddhist and Jain texts of India. In these legends, he appears as a materialist who orders several experiments to conclude that the soul does not exist. A Jain or Buddhist monk proves him wrong in a debate, and converts him to their faith. Legends According to Buddhist and Jain legends, Paesi ordered several cruel experiments to conclude that the soul does not exist. For example, he had a thief thrown alive in a brass pot, with a brass lid soldered over it, to see how his soul could escape after his death. Buddhist and Jain works mention similar accounts of other people conducting such experiments to deny the existence of soul. In all these accounts,a Buddhist or Jain monk defeats the person denying the existence of the soul in a debate. E.g. in Haribhadra's ''Samaraichcha Katha'' (''Samarditya Katha''), a man named Pingakesa states that a robber sentenced to death had been put in a sealed iron vessel, but no soul wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kakudmi
Kakudmi (nominative case, stem Kakudmin), sometimes also called Raivata, is a character within Hindu Mythology. Kakudmi was the King of Kusasthali, son of Revata, and father of Revati, who married Balarama. Within Hinduism, his account is given within a number of existing texts such as the Mahabharata, the Harivaṃśa, the Devi Bhagavatam and the Bhagavata Purana. Lineage Kakudmi was a descendant of Surya, the deity of the Sun. Surya's son was Vaivasvata Manu. Vaivasvata Manu had powerful son named Ikshvaku. Ikshvaku had one hundred sons of whom Vikuksi was the eldest. Vikuksi had many sons of whom S'aryâti was one. King S'aryâti had three sons, namely Uttânabarhi, Ânarta and Bhûrishena. Ânarta's eldest son was Revata. Revata constructed the city of Kusasthali and ruled from there. Revata had one hundred sons of whom Kakudmi (also called Raivata, son of Revata) was the eldest. Personality Kakudmi was of pure character and a benevolent ruler. He had one very beauti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahma
Brahma ( sa, ब्रह्मा, Brahmā) is a Hindu god, referred to as "the Creator" within the Trimurti, the trinity of supreme divinity that includes Vishnu, and Shiva.Jan Gonda (1969)The Hindu Trinity Anthropos, Bd 63/64, H 1/2, pp. 212–226. He is associated with creation, knowledge, and the '' Vedas''. Brahma is prominently mentioned in creation legends. In some '' Puranas'', he created himself in a golden embryo known as the Hiranyagarbha. Brahma is frequently identified with the Vedic god Prajapati.;David Leeming (2005), The Oxford Companion to World Mythology, Oxford University Press, , page 54, Quote: "Especially in the Vedanta Hindu Philosophy, Brahman is the Absolute. In the Upanishads, Brahman becomes the eternal first cause, present everywhere and nowhere, always and never. Brahman can be incarnated in Brahma, in Vishnu, in Shiva. To put it another way, everything that is, owes its existence to Brahman. In this sense, Hinduism is ultimately monotheistic or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Routledge
Routledge () is a British multinational publisher. It was founded in 1836 by George Routledge, and specialises in providing academic books, journals and online resources in the fields of the humanities, behavioural science, education, law, and social science. The company publishes approximately 1,800 journals and 5,000 new books each year and their backlist encompasses over 70,000 titles. Routledge is claimed to be the largest global academic publisher within humanities and social sciences. In 1998, Routledge became a subdivision and imprint of its former rival, Taylor & Francis Group (T&F), as a result of a £90-million acquisition deal from Cinven, a venture capital group which had purchased it two years previously for £25 million. Following the merger of Informa and T&F in 2004, Routledge became a publishing unit and major imprint within the Informa "academic publishing" division. Routledge is headquartered in the main T&F office in Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxfords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pāli Canon
The Pāli Canon is the standard collection of scriptures in the Theravada Buddhist tradition, as preserved in the Pāli language. It is the most complete extant early Buddhist canon. It derives mainly from the Tamrashatiya school. During the First Buddhist Council, three months after the parinibbana of Gautama Buddha in Rajgir, Ananda recited the Sutta Pitaka, and Upali recited the Vinaya Pitaka. The Arhats present accepted the recitations and henceforth the teachings were preserved orally by the Sangha. The Tipitaka that was transmitted to Sri Lanka during the reign of King Asoka were initially preserved orally and were later written down on palm leaves during the Fourth Buddhist Council in 29 BCE, approximately 454 years after the death of Gautama Buddha. The claim that the texts were "spoken by the Buddha", is meant in this non-literal sense. The existence of the bhanaka tradition existing until later periods, along with other sources, shows that oral traditio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mahākāśyapa
Mahākāśyapa ( pi, Mahākassapa) was one of the principal disciples of Gautama Buddha. He is regarded in Buddhism as an enlightened disciple, being foremost in ascetic practice. Mahākāśyapa assumed leadership of the monastic community following the '' paranirvāṇa'' (death) of the Buddha, presiding over the First Buddhist Council. He was considered to be the first patriarch in a number of Early Buddhist schools and continued to have an important role as patriarch in the Chan and Zen traditions. In Buddhist texts, he assumed many identities, that of a renunciant saint, a lawgiver, an anti-establishment figure, but also a "guarantor of future justice" in the time of Maitreya, the future Buddhahe has been described as "both the anchorite and the friend of mankind, even of the outcast". In canonical Buddhist texts in several traditions, Mahākāśyapa was born as Pippali in a village and entered an arranged marriage with a woman named Bhadra-Kapilānī. Both of them aspired ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gautama Buddha
Siddhartha Gautama, most commonly referred to as the Buddha, was a wandering ascetic and religious teacher who lived in South Asia during the 6th or 5th century BCE and founded Buddhism. According to Buddhist tradition, he was born in Lumbini, in what is now Nepal, to royal parents of the Shakya clan, but renounced his home life to live as a wandering ascetic ( sa, śramaṇa). After leading a life of begging, asceticism, and meditation, he attained enlightenment at Bodh Gaya in what is now India. The Buddha thereafter wandered through the lower Indo-Gangetic Plain, teaching and building a monastic order. He taught a Middle Way between sensual indulgence and severe asceticism, leading to Nirvana, that is, freedom from ignorance, craving, rebirth, and suffering. His teachings are summarized in the Noble Eightfold Path, a training of the mind that includes meditation and instruction in Buddhist ethics such as right effort, mindfulness, and '' jhana''. He di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rip Van Winkle
"Rip Van Winkle" is a short story by the American author Washington Irving, first published in 1819. It follows a Dutch-American villager in colonial America named Rip Van Winkle who meets mysterious Dutchmen, imbibes their liquor and falls asleep in the Catskill Mountains. He awakes 20 years later to a very changed world, having missed the American Revolution. The concept is ancient, including the 70-year nap by Choni HaMeA-Gail. Irving, inspired by a conversation on nostalgia with his American expatriate brother-in-law, wrote his story while temporarily living in Birmingham, England. It was published in his collection, '' The Sketch Book of Geoffrey Crayon, Gent.'' While the story is set in New York's Catskill Mountains near where Irving later took up residence, he admitted, "When I wrote the story, I had never been on the Catskills." Plot Rip Van Winkle, a Dutch-American man with a habit of avoiding useful work, lives in a village at the foot of New York's Catskill Mounta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.jpg)
