|
Through-hole Technology
In electronics, through-hole technology (also spelled "thru-hole") is a manufacturing scheme in which leads on the components are inserted through holes drilled in printed circuit boards (PCB) and soldered to pads on the opposite side, either by manual assembly (hand placement) or by the use of automated insertion mount machines. History Through-hole technology almost completely replaced earlier electronics assembly techniques such as point-to-point construction. From the second generation of computers in the 1950s until surface-mount technology (SMT) became popular in the mid 1980s, every component on a typical PCB was a through-hole component. PCBs initially had tracks printed on one side only, later both sides, then multi-layer boards were in use. Through holes became plated-through holes (PTH) in order for the components to make contact with the required conductive layers. Plated-through holes are no longer required with SMT boards for making the component connection ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
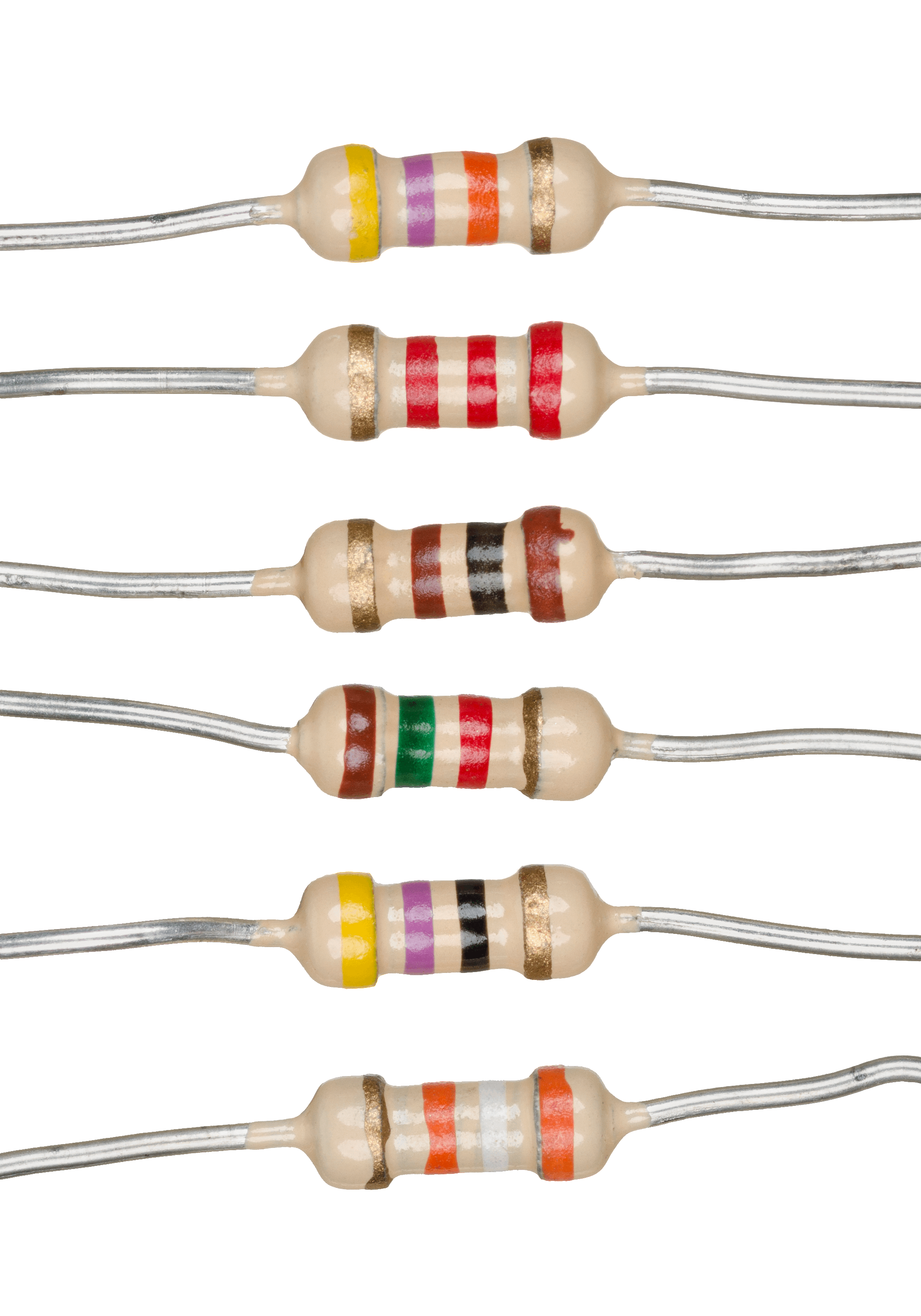
Resistors (1)
A resistor is a passivity (engineering), passive terminal (electronics), two-terminal electronic component, electrical component that implements electrical resistance as a circuit element. In electronic circuits, resistors are used to reduce current flow, adjust signal levels, to Voltage divider, divide voltages, Biasing, bias active elements, and terminate transmission lines, among other uses. High-power resistors that can dissipate many watts of electrical power as heat may be used as part of motor controls, in power distribution systems, or as test loads for electric generator, generators. Fixed resistors have resistances that only change slightly with temperature, time or operating voltage. Variable resistors can be used to adjust circuit elements (such as a volume control or a lamp dimmer), or as sensing devices for heat, light, humidity, force, or chemical activity. Resistors are common elements of electrical networks and electronic circuits and are ubiquitous in Electron ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point-to-point Wiring
Point-to-point construction is a non-automated method of construction of electronics circuits widely used before the use of printed circuit boards (PCBs) and automated assembly gradually became widespread following their introduction in the 1950s. Circuits using thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) were relatively large, relatively simple (the number of large, hot, expensive devices which needed replacing was minimised), and used large sockets, all of which made the PCB less obviously advantageous than with later complex semiconductor circuits. Point-to-point construction is still widespread in power electronics where components are bulky and serviceability is a consideration, and to construct prototype equipment with few or heavy electronic components. A common practice, especially in older point-to-point construction, is to use the leads of components such as resistors and capacitors to bridge as much of the distance between connections as possible, reducing the need to add additio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electrolytic Capacitor
An electrolytic capacitor is a polarized capacitor whose anode or positive plate is made of a metal that forms an insulating oxide layer through anodization. This oxide layer acts as the dielectric of the capacitor. A solid, liquid, or gel electrolyte covers the surface of this oxide layer, serving as the cathode or negative plate of the capacitor. Due to their very thin dielectric oxide layer and enlarged anode surface, electrolytic capacitors have a much higher capacitance-voltage (CV) product per unit volume than ceramic capacitors or film capacitors, and so can have large capacitance values. There are three families of electrolytic capacitor: aluminum electrolytic capacitors, tantalum electrolytic capacitors, and niobium electrolytic capacitors. The large capacitance of electrolytic capacitors makes them particularly suitable for passing or bypassing low-frequency signals, and for storing large amounts of energy. They are widely used for decoupling or noise filtering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanical Shock
A mechanical or physical shock is a sudden acceleration caused, for example, by impact, drop, kick, earthquake, or explosion. Shock is a transient physical excitation. Shock describes matter subject to extreme rates of force with respect to time. Shock is a vector that has units of an acceleration (rate of change of velocity). The unit ''g'' (or g) represents multiples of the acceleration of gravity and is conventionally used. A shock pulse can be characterised by its peak acceleration, the duration, and the shape of the shock pulse (half sine, triangular, trapezoidal, etc.). The shock response spectrum is a method for further evaluating a mechanical shock. Shock measurement Shock measurement is of interest in several fields such as *Propagation of heel shock through a runner's body *Measure the magnitude of a shock need to cause damage to an item: fragility. *Measure shock attenuation through athletic flooring *Measuring the effectiveness of a shock absorber *Measuring the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vibration
Vibration is a mechanical phenomenon whereby oscillations occur about an equilibrium point. The word comes from Latin ''vibrationem'' ("shaking, brandishing"). The oscillations may be periodic, such as the motion of a pendulum—or random, such as the movement of a tire on a gravel road. Vibration can be desirable: for example, the motion of a tuning fork, the reed in a woodwind instrument or harmonica, a mobile phone, or the cone of a loudspeaker. In many cases, however, vibration is undesirable, wasting energy and creating unwanted sound. For example, the vibrational motions of engines, electric motors, or any mechanical device in operation are typically unwanted. Such vibrations could be caused by imbalances in the rotating parts, uneven friction, or the meshing of gear teeth. Careful designs usually minimize unwanted vibrations. The studies of sound and vibration are closely related. Sound, or pressure waves, are generated by vibrating structures (e.g. v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reliability Engineering
Reliability engineering is a sub-discipline of systems engineering that emphasizes the ability of equipment to function without failure. Reliability describes the ability of a system or component to function under stated conditions for a specified period of time. Reliability is closely related to availability, which is typically described as the ability of a component or system to function at a specified moment or interval of time. The reliability function is theoretically defined as the probability of success at time t, which is denoted R(t). This probability is estimated from detailed (physics of failure) analysis, previous data sets or through reliability testing and reliability modelling. Availability, testability, maintainability and maintenance are often defined as a part of "reliability engineering" in reliability programs. Reliability often plays the key role in the cost-effectiveness of systems. Reliability engineering deals with the prediction, prevention and mana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SMT Placement Equipment
Surface-mount technology (SMT) component placement systems, commonly called pick-and-place machines or P&Ps, are robotic machines which are used to place surface-mount devices (SMDs) onto a printed circuit board (PCB). They are used for high speed, high precision placing of a broad range of electronic components, like capacitors, resistors, integrated circuits onto the PCBs which are in turn used in computers, consumer electronics as well as industrial, medical, automotive, military and telecommunications equipment. Similar equipment exists for through-hole components. This type of equipment is sometimes also used to package microchips using the flip chip method. History 1980s and 1990s During this time, a typical SMT assembly line employed two different types of pick-and-place (P&P) machines arranged in sequence. The unpopulated board was fed into a rapid placement machine. These machines, sometimes called chip shooters, place mainly low-precision, simple package compon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass Production
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods. The term ''mass production'' was popularized by a 1926 article in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' supplement that was written based on correspondence with Ford Motor Company. ''The New York Times'' used the term in the title of an article that appeared before publication of the ''Britannica'' article. The concepts of mass production are applied to various kinds of products: from fluids and particulates handled in bulk ( food, fuel, chemicals and mined minerals), to parts and assemblies of parts (household appliances and automobiles). Some mass production techniques, such as standardized sizes and production lines, predate the Industrial Revolution by many centuries; howe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Deprecated
In several fields, especially computing, deprecation is the discouragement of use of some terminology, feature, design, or practice, typically because it has been superseded or is no longer considered efficient or safe, without completely removing it or prohibiting its use. Typically, deprecated materials are not completely removed to ensure legacy compatibility or back up practice in case new methods are not functional in an odd scenario. It can also imply that a feature, design, or practice will be removed or discontinued entirely in the future. Etymology In general English usage, the infinitive "to deprecate" means "to express disapproval of (something)". It derives from the Latin verb ''deprecari'', meaning "to ward off (a disaster) by prayer". In current technical usage, for one to state that a feature is deprecated is merely a recommendation against using it. It is still possible to produce a program or product without heeding the deprecation. Software While a deprecated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample, model, or release of a product built to test a concept or process. It is a term used in a variety of contexts, including semantics, design, electronics, and software programming. A prototype is generally used to evaluate a new design to enhance precision by system analysts and users. Prototyping serves to provide specifications for a real, working system rather than a theoretical one. In some design workflow models, creating a prototype (a process sometimes called materialization) is the step between the formalization and the evaluation of an idea. A prototype can also mean a typical example of something such as in the use of the derivation 'prototypical'. This is a useful term in identifying objects, behaviours and concepts which are considered the accepted norm and is analogous with terms such as stereotypes and archetypes. The word ''prototype'' derives from the Greek , "primitive form", neutral of , "original, primitive", from πρῶτ� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Breadboard
A breadboard, solderless breadboard, or protoboard is a construction base used to build semi-permanent prototypes of electronic circuits. Unlike a perfboard or stripboard, breadboards do not require soldering or destruction of tracks and are hence reusable. For this reason, breadboards are also popular with students and in technological education. A variety of electronic systems may be prototyped by using breadboards, from small analog and digital circuits to complete central processing units (CPUs). Compared to more permanent circuit connection methods, modern breadboards have high parasitic capacitance, relatively high resistance, and less reliable connections, which are subject to jostle and physical degradation. Signaling is limited to about 10 MHz, and not everything works properly even well below that frequency. History In the early days of radio, amateurs nailed bare copper wires or terminal strips to a wooden board (often literally a bread cutting board) and solde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Short Circuit
A short circuit (sometimes abbreviated to short or s/c) is an electrical circuit that allows a current to travel along an unintended path with no or very low electrical impedance. This results in an excessive current flowing through the circuit. The opposite of a short circuit is an " open circuit", which is an infinite resistance between two nodes. Definition A short circuit is an abnormal connection between two nodes of an electric circuit intended to be at different voltages. This results in an electric current limited only by the Thévenin equivalent resistance of the rest of the network which can cause circuit damage, overheating, fire or explosion. Although usually the result of a fault, there are cases where short circuits are caused intentionally, for example, for the purpose of voltage-sensing crowbar circuit protectors. In circuit analysis, a ''short circuit'' is defined as a connection between two nodes that forces them to be at the same voltage. In an 'id ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)

_shock_trials.jpg)



