|
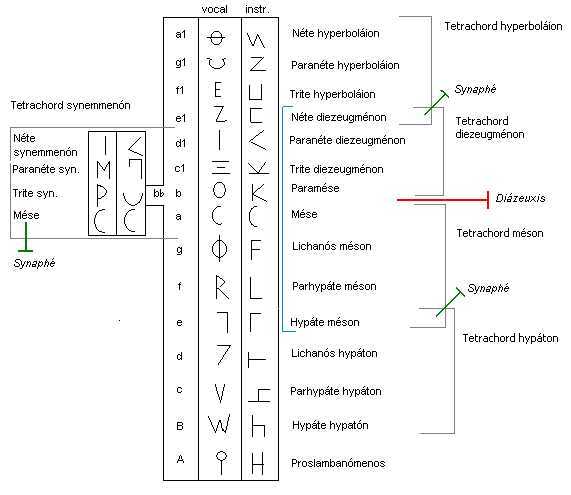
Tetrachord
In music theory, a tetrachord ( el, τετράχορδoν; lat, tetrachordum) is a series of four notes separated by three intervals. In traditional music theory, a tetrachord always spanned the interval of a perfect fourth, a 4:3 frequency proportion (approx. 498 cents)—but in modern use it means any four-note segment of a scale or tone row, not necessarily related to a particular tuning system. History The name comes from ''tetra'' (from Greek—"four of something") and ''chord'' (from Greek ''chordon''—"string" or "note"). In ancient Greek music theory, ''tetrachord'' signified a segment of the greater and lesser perfect systems bounded by ''immovable'' notes ( ); the notes between these were ''movable'' ( ). It literally means ''four strings'', originally in reference to harp-like instruments such as the lyre or the kithara, with the implicit understanding that the four strings produced adjacent (i.e., conjunct) notes. Modern music theory uses the octave as the ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical System Of Ancient Greece
The musical system of ancient Greece evolved over a period of more than 500 years from simple scales of tetrachords, or divisions of the perfect fourth, into several complex systems encompassing tetrachords and octaves, as well as octave scales divided into seven to thirteen intervals. Any discussion of the music of ancient Greece, theoretical, philosophical or aesthetic, is fraught with two problems: there are few examples of written music, and there are many, sometimes fragmentary, theoretical and philosophical accounts. The empirical research of scholars like Richard Crocker, C. André Barbera, and John Chalmers has made it possible to look at the ancient Greek systems as a whole without regard to the tastes of any one ancient theorist. The primary genera they examine are those of Pythagoras and the Pythagorean school, Archytas, Aristoxenos, and Ptolemy (including his versions of the genera of Didymos and Eratosthenes). Overview of the first complete tone system As an initial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus (music)
In the musical system of ancient Greece, genus (Greek: γένος 'genos'' pl. γένη 'genē'' Latin: ''genus'', pl. ''genera'' "type, kind") is a term used to describe certain classes of intonations of the two movable notes within a tetrachord. The tetrachordal system was inherited by the Latin medieval theory of scales and by the modal theory of Byzantine music; it may have been one source of the later theory of the jins of Arabic music. In addition, Aristoxenus (in his fragmentary treatise on rhythm) calls some patterns of rhythm "genera". Tetrachords According to the system of Aristoxenus and his followers— Cleonides, Bacchius, Gaudentius, Alypius, Bryennius, and Aristides Quintilianus—the paradigmatic tetrachord was bounded by the fixed tones ''hypate'' and ''mese'', which are a perfect fourth apart and do not vary from one genus to another. Between these are two movable notes, called ''parhypate'' and ''lichanos''. The upper tone, lichanos, can vary over the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyknon
Pyknon (from el, πυκνόν), sometimes also transliterated as pycnon (from el, πυκνός close, close-packed, crowded, condensed; lat, spissus) in the music theory of Antiquity is a structural property of any tetrachord in which a composite of two smaller intervals is less than the remaining ( incomposite) interval. The makeup of the ''pyknon'' serves to identify the melodic genus (also called "genus of a tetrachord") and the octave species made by compounding two such tetrachords, and the rules governing the ways in which such compounds may be made centre on the relationships of the two ''pykna'' involved. Definition The ''pyknon'' was an important criterion in the classification of melodic genera ( el, γένη τῶν μελῳδουμένων). The Greek word πυκνόν is an adjective meaning "close", "compact", "close-packed", or "crowded". In Ancient Greek music theory, this term is used to describe a pair of intervals within a tetrachord, the sum of which is les ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diatonic Scale
In music theory, a diatonic scale is any heptatonic scale that includes five whole steps (whole tones) and two half steps (semitones) in each octave, in which the two half steps are separated from each other by either two or three whole steps, depending on their position in the scale. This pattern ensures that, in a diatonic scale spanning more than one octave, all the half steps are maximally separated from each other (i.e. separated by at least two whole steps). The seven pitches of any diatonic scale can also be obtained by using a chain of six perfect fifths. For instance, the seven natural pitch classes that form the C-major scale can be obtained from a stack of perfect fifths starting from F: :F–C–G–D–A–E–B Any sequence of seven successive natural notes, such as C–D–E–F–G–A–B, and any transposition thereof, is a diatonic scale. Modern musical keyboards are designed so that the white notes form a diatonic scale, though transpositions of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incomposite Interval
An incomposite interval (; ) is a concept in the Ancient Greek theory of music concerning melodic musical intervals () between neighbouring notes in a tetrachord or scale which, for that reason, do not encompass smaller intervals. ( means "uncompounded".) Aristoxenus (fl. 335 BCE) defines melodically incomposite intervals in the following context: In another place, Aristoxenus clarifies that It is thus not an issue of the voice being physically incapable of singing a note within an incomposite interval. For example, in the enharmonic genus the distance from the neighbouring scale degrees ''lichanos'' () to ''mesē'' () is a ditone—a gap equivalent to the major-third interval between F and A in the modern scale. In such a case the function of the note λιχανός is such that "the 'nature of μελῳδία' somehow requires that it should leap forward at least as far as μέση, without touching down anywhere in between. Any smaller distance is melodically impossible or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quarter Tone
A quarter tone is a pitch halfway between the usual notes of a chromatic scale or an interval about half as wide (aurally, or logarithmically) as a semitone, which itself is half a whole tone. Quarter tones divide the octave by 50 cents each, and have 24 different pitches. Quarter tone has its roots in the music of the Middle East and more specifically in Persian traditional music. However, the first evidenced proposal of quarter tones, or the quarter-tone scale (24 equal temperament), was made by 19th-century music theorists Heinrich Richter in 1823 Julian Rushton, "Quarter-Tone", ''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', second edition, edited by Stanley Sadie and John Tyrrell (London: Macmillan, 2001). and Mikhail Mishaqa about 1840. Composers who have written music using this scale include: Pierre Boulez, Julián Carrillo, Mildred Couper, George Enescu, Alberto Ginastera, Gérard Grisey, Alois Hába, Ljubica Marić, Charles Ives, Tristan Murail, K ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tone Row
In music, a tone row or note row (german: Reihe or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets are sometimes found. History and usage Tone rows are the basis of Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique and most types of serial music. Tone rows were widely used in 20th-century contemporary music, like Dmitri Shostakovich's use of twelve-tone rows, "without dodecaphonic transformations." A tone row has been identified in the A minor prelude, BWV 889, from book II of J.S. Bach's '' The Well-Tempered Clavier'' (1742) and by the late eighteenth century it is found in works such as Mozart's C major String Quartet, K. 157 (1772), String Quartet in E-flat major, K. 428, String Quintet in G minor, K. 516 (1790), and the Symphony in G minor, K. 550 (1788). Beethoven also used the technique but, on the whole, "Mozart seems to hav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lyre
The lyre () is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute-family of instruments. In organology, a lyre is considered a yoke lute, since it is a lute in which the strings are attached to a yoke that lies in the same plane as the sound table, and consists of two arms and a crossbar. The lyre has its origins in ancient history. Lyres were used in several ancient cultures surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. The earliest known examples of the lyre have been recovered at archeological sites that date to c. 2700 BCE in Mesopotamia. The oldest lyres from the Fertile Crescent are known as the eastern lyres and are distinguished from other ancient lyres by their flat base. They have been found at archaeological sites in Egypt, Syria, Anatolia, and the Levant. The round lyre or the Western lyre also originated in Syria and Anatolia, but was not as widely used and eventually died out ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Intense Chromatic Tetrachord
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quadr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy Soft Chromatic Tetrachord
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the '' Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Quad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. (Boston: McGraw-Hill). Vol. I: p. 56. . This ratio, also known as the " pure" perfect fifth, is chosen because it is one of the most consonant and easiest to tune by ear and because of importance attributed to the integer 3. As Novalis put it, "The musical proportions seem to me to be particularly correct natural proportions." Alternatively, it can be described as the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the generator is the ratio 3:2 (i.e., the untempered perfect fifth), which is ≈702 cents wide. The system dates to Ancient Mesopotamia; see . The system is named, and has been widely misattributed, to Ancient Greeks, notably Pythagoras (sixth century BC) by modern authors of music theory, while Ptolemy, and later Boethius, ascribed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enharmonic Tetrachord Pythagorean Tuning
In modern musical notation and tuning, an enharmonic equivalent is a note, interval, or key signature that is equivalent to some other note, interval, or key signature but "spelled", or named differently. The enharmonic spelling of a written note, interval, or chord is an alternative way to write that note, interval, or chord. The term is derived from Latin ''enharmonicus'', from Late Latin ''enarmonius'', from Ancient Greek ἐναρμόνιος (''enarmónios''), from ἐν (''en'') and ἁρμονία (''harmonía''). Definition For example, in any twelve-tone equal temperament (the predominant system of musical tuning in Western music), the notes C and D are ''enharmonic'' (or ''enharmonically equivalent'') notes. Namely, they are the same key on a keyboard, and thus they are identical in pitch, although they have different names and different roles in harmony and chord progressions. Arbitrary amounts of accidentals can produce further enharmonic equivalents, such as B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |