|
Tetrabamate
Tetrabamate (Atrium, G Tril, Sevrium) is a combination drug formulation of febarbamate, difebarbamate, and phenobarbital which was marketed in France and Spain and was used to treat anxiety and alcohol withdrawal-associated muscle tremors, agitation, and depression. It was largely, but not completely discontinued on April 4, 1997 after over 30 years of use due to reports of hepatitis and acute liver failure Acute liver failure is the appearance of severe complications rapidly after the first signs (such as jaundice) of liver disease, and indicates that the liver has sustained severe damage (loss of function of 80–90% of liver cells). The complicati .... The decision to restrict the use of the drug had been long-awaited. References {{GABAAR PAMs Anxiolytics Barbiturates Carbamates Drug rehabilitation Hepatotoxins Muscle relaxants Sedatives Withdrawn drugs Combination drugs GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Difebarbamate
Difebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation Formulation is a term used in various senses in various applications, both the material and the abstract or formal. Its fundamental meaning is the putting together of components in appropriate relationships or structures, according to a formul ... referred to as tetrabamate (Atrium, Sevrium). See also * Febarbamate References {{GABAAR PAMs Barbiturates Carbamates Sedatives Muscle relaxants GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Febarbamate
Febarbamate ( INN; Solium, Tymium), also known as phenobamate, is an anxiolytic and tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe by itself and as part of a combination drug formulation called tetrabamate. See also * Difebarbamate Difebarbamate (INN) is a tranquilizer of the barbiturate and carbamate families which is used in Europe as a component of a combination drug formulation Formulation is a term used in various senses in various applications, both the material ... References Barbiturates Carbamates Muscle relaxants Pyrimidines Sedatives GABAA receptor positive allosteric modulators Anxiolytics {{musculoskeletal-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
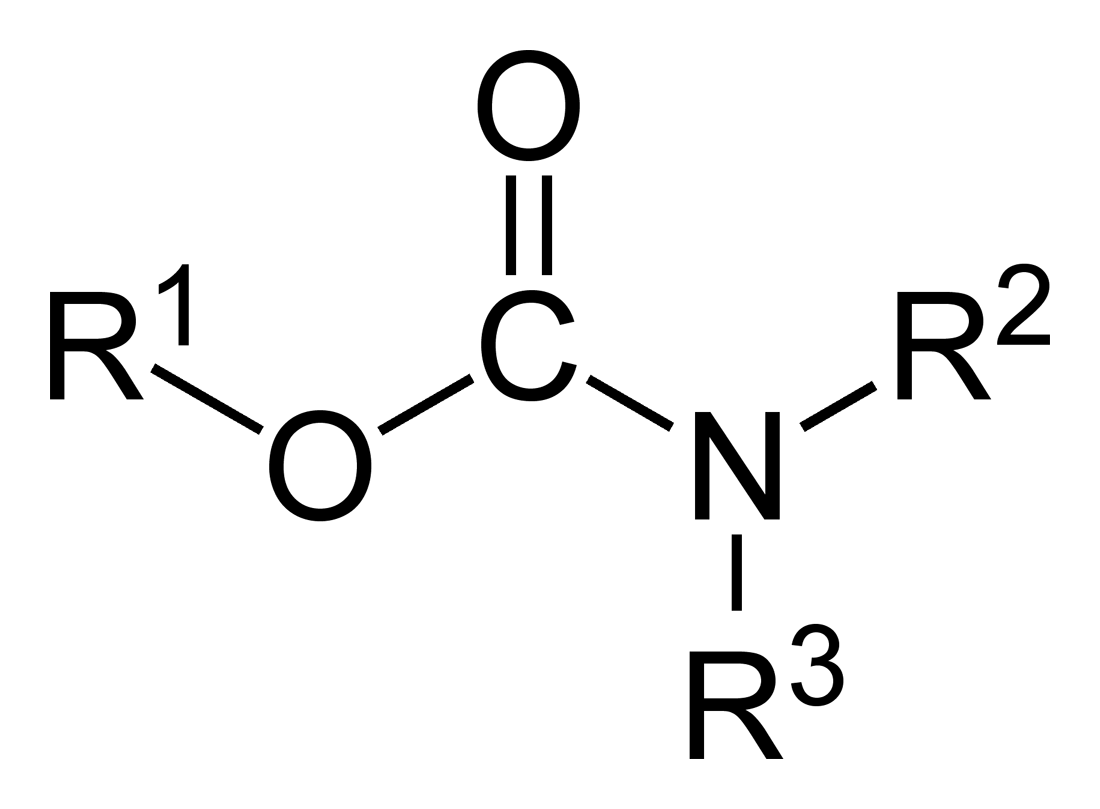
Carbamate
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate imm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Withdrawn Drugs
Drugs or medicines may be withdrawn from commercial markets because of risks to patients, but also because of commercial reasons (e.g. lack of demand and relatively high production costs). Where risks or harms is the reason for withdrawal, this will usually have been prompted by unexpected adverse effects that were not detected during Phase III clinical trials, i.e. they were only made apparent from postmarketing surveillance data collected from the wider community over longer periods of time. This list is not limited to drugs that were ever approved by the FDA. Some of them (lumiracoxib, rimonabant, tolrestat, ximelagatran and ximelidine, for example) were approved to be marketed in Europe but had not yet been approved for marketing in the US, when side effects became clear and their developers pulled them from the market. Some drugs in this list (e.g. LSD) were never approved for marketing in the US or Europe. Significant withdrawals Withdrawn clinical trial drugs * RG7795, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Withdrawn Drugs
Withdrawal means "an act of taking out" and may refer to: * Anchoresis (withdrawal from the world for religious or ethical reasons) * ''Coitus interruptus ''Coitus interruptus'', also known as withdrawal, pulling out or the pull-out method, is a method of birth control in which a man, during sexual intercourse, withdraws his penis from a woman's vagina prior to ejaculation and then directs his ej ...'' (the withdrawal method) * Drug withdrawal * Social withdrawal * Taking of money from a bank * Water withdrawal * Withdrawal (military) * Withdrawal reflex * ''Withdrawal'', Twista/ Do or Die EP * "Withdrawals" (Tyler Farr song) See also * * {{disambiguation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sedatives
A sedative or tranquilliser is a substance that induces sedation by reducing irritability or excitement. They are CNS depressants and interact with brain activity causing its deceleration. Various kinds of sedatives can be distinguished, but the majority of them affect the neurotransmitter gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). In spite of the fact that each sedative acts in its own way, most produce relaxing effects by increasing GABA activity. This group is related to hypnotics. The term ''sedative'' describes drugs that serve to calm or relieve anxiety, whereas the term ''hypnotic'' describes drugs whose main purpose is to initiate, sustain, or lengthen sleep. Because these two functions frequently overlap, and because drugs in this class generally produce dose-dependent effects (ranging from anxiolysis to loss of consciousness) they are often referred to collectively as ''sedative-hypnotic'' drugs. Sedatives can be used to produce an overly-calming effect ( alcohol being t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muscle Relaxants
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxant, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxant, [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hepatotoxins
Hepatotoxicity (from ''hepatic toxicity'') implies chemical-driven liver damage. Drug-induced liver injury is a cause of acute and chronic liver disease caused specifically by medications and the most common reason for a drug to be withdrawn from the market after approval. The liver plays a central role in transforming and clearing chemicals and is susceptible to the toxicity from these agents. Certain medicinal agents, when taken in overdoses (e.g. paracetamol) and sometimes even when introduced within therapeutic ranges (e.g. halothane), may injure the organ. Other chemical agents, such as those used in laboratories and industries, natural chemicals (e.g., microcystins), and herbal remedies (two prominent examples being kava, mechanism unknown, and comfrey, through its pyrrolizidine alkaloid content) can also induce hepatotoxicity. Chemicals that cause liver injury are called hepatotoxins. More than 900 drugs have been implicated in causing liver injury (see LiverTox, exte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drug Rehabilitation
Drug rehabilitation is the process of medical or psychotherapeutic treatment for dependency on psychoactive substances such as alcohol, prescription drugs, and street drugs such as cannabis, cocaine, heroin or amphetamines. The general intent is to enable the patient to confront substance dependence, if present, and stop substance misuse to avoid the psychological, legal, financial, social, and physical consequences that can be caused. Treatment includes medication for depression or other disorders, counseling by experts and sharing of experience with other addicts. Psychological dependency Psychological dependency is addressed in many drug rehabilitation programs by attempting to teach the person new methods of interacting in a drug-free environment. In particular, patients are generally encouraged, or possibly even required, to not associate with peers who still use the addictive substance. Twelve-step programs encourage addicts not only to stop using alcohol or other drugs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carbamates
In organic chemistry, a carbamate is a category of organic compounds with the general formula and structure , which are formally derived from carbamic acid (). The term includes organic compounds (e.g., the ester ethyl carbamate), formally obtained by replacing one or more of the hydrogen atoms by other organic functional groups; as well as salts with the carbamate anion (e.g. ammonium carbamate). Polymers whose units are joined by carbamate groups are an important family of plastics, the polyurethanes. Properties While carbamic acids are unstable, many carbamate esters or ionic) are stable and well known. Equilibrium with carbonate and bicarbonate In water solutions, the carbamate anion slowly equilibrates with the ammonium cation and the carbonate or bicarbonate anions: : : Calcium carbamate is soluble in water, whereas calcium carbonate is not. Adding a calcium salt to an ammonium carbamate/carbonate solution will precipitate some calcium carbonate im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Barbiturates
Barbiturates are a class of depressant drugs that are chemically derived from barbituric acid. They are effective when used medically as anxiolytics, hypnotics, and anticonvulsants, but have physical and psychological addiction potential as well as overdose potential among other possible adverse effects. They have been used recreationally for their anxiolytic and sedative effects, and are thus controlled in most countries due to the risks associated with such use. Barbiturates have largely been replaced by benzodiazepines and nonbenzodiazepines ("Z-drugs") in routine medical practice, particularly in the treatment of anxiety disorders and insomnia, because of the significantly lower risk of overdose, and the lack of an antidote for barbiturate overdose. Despite this, barbiturates are still in use for various purposes: in general anesthesia, epilepsy, treatment of acute migraines or cluster headaches, acute tension headaches, euthanasia, capital punishment, and assisted s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anxiolytics
An anxiolytic (; also antipanic or antianxiety agent) is a medication or other intervention that reduces anxiety. This effect is in contrast to anxiogenic agents which increase anxiety. Anxiolytic medications are used for the treatment of anxiety disorders and their related psychological and physical symptoms. Nature of anxiety Anxiety is a naturally-occurring emotion and an innate response of the body to the environmental stimuli. Mild to moderate anxiety would increase level of performance. However, when anxiety levels exceed the tolerability of a person, anxiety disorders may occur. People with anxiety disorders can exhibit fear responses such as defensive behaviors, high levels of alertness and negative emotions, without external stimuli which induce anxiety within an individual. Those with anxiety disorders are also often found to have concurrent psychological disorders, most commonly depression. Anxiety disorders are divided into 6 types in clinical recognition. They are a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |