|
Twystron
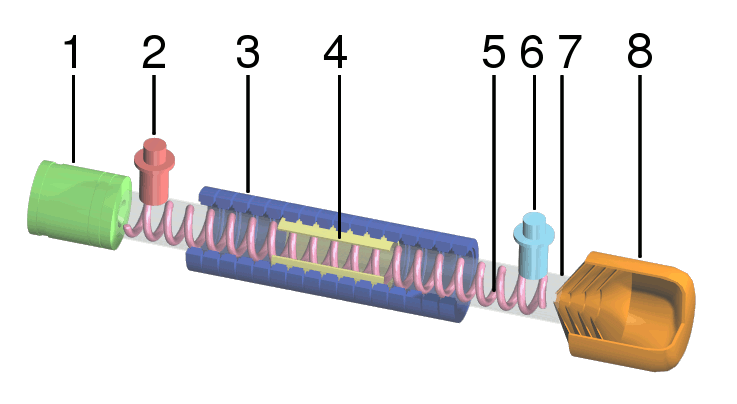
A twystron is a type of microwave-producing vacuum tube most commonly found in high-power radar systems. The name refers to its construction, which combines a traveling wave tube, or TWT, with a klystron, producing a tw-ystron. The name was originally a trademark of Varian Associates, its developer, and was often capitalized. In recent times has become a generic term for any similar design. The twystron amplifies a source signal using a conventional klystron, which consists of a series of cylindrical resonant chambers fed with the source signal. An electron gun at one end of the tube produces electrons that flow through holes in the centers of the resonators. As they pass through the holes, the signal within the resonator causes the electrons to "bunch up", a process known as velocity-modulation. The resulting electron beam is an amplified version of the original signal. In a conventional klystron, this signal is then captured and used as the output. In the twystron, the output in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microwave
Microwave is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths shorter than other radio waves but longer than infrared waves. Its wavelength ranges from about one meter to one millimeter, corresponding to frequency, frequencies between 300 MHz and 300 GHz, broadly construed. A more common definition in radio-frequency engineering is the range between 1 and 100 GHz (wavelengths between 30 cm and 3 mm), or between 1 and 3000 GHz (30 cm and 0.1 mm). In all cases, microwaves include the entire super high frequency, super high frequency (SHF) band (3 to 30 GHz, or 10 to 1 cm) at minimum. The boundaries between far infrared, terahertz radiation, microwaves, and ultra-high-frequency (UHF) are fairly arbitrary and differ between different fields of study. The prefix ' in ''microwave'' indicates that microwaves are small (having shorter wavelengths), compared to the radio waves used in prior radio technology. Frequencies in the micr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It takes the form of an evacuated tubular envelope of glass or sometimes metal containing electrodes connected to external connection pins. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental Electronics, electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current Rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as vacuum phototubes achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light and measurement of its intensity. In both types the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The first, and simplest, vacuum tube, the diode or Flem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radar
Radar is a system that uses radio waves to determine the distance ('' ranging''), direction ( azimuth and elevation angles), and radial velocity of objects relative to the site. It is a radiodetermination method used to detect and track aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, map weather formations, and terrain. The term ''RADAR'' was coined in 1940 by the United States Navy as an acronym for "radio detection and ranging". The term ''radar'' has since entered English and other languages as an anacronym, a common noun, losing all capitalization. A radar system consists of a transmitter producing electromagnetic waves in the radio or microwave domain, a transmitting antenna, a receiving antenna (often the same antenna is used for transmitting and receiving) and a receiver and processor to determine properties of the objects. Radio waves (pulsed or continuous) from the transmitter reflect off the objects and return to the receiver, giving ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Traveling Wave Tube
A traveling-wave tube (TWT, pronounced "twit") or traveling-wave tube amplifier (TWTA, pronounced "tweeta") is a specialized vacuum tube that is used in electronics to amplify radio frequency (RF) signals in the microwave range. It was invented by Andrei Haeff around 1933 as a graduate student at Caltech, and its present form was invented by Rudolf Kompfner in 1942–43. The TWT belongs to a category of "linear beam" tubes, such as the klystron, in which the radio wave is amplified by absorbing power from a beam of electrons as it passes down the tube. Although there are various types of TWT, two major categories are: *''Helix TWT'' - in which the radio waves interact with the electron beam while traveling down a wire helix which surrounds the beam. These have wide bandwidth, but output power is limited to a few hundred watts. *''Coupled cavity TWT'' - in which the radio wave interacts with the beam in a series of cavity resonators through which the beam passes. These functio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klystron
A klystron is a specialized linear-beam vacuum tube, invented in 1937 by American electrical engineers Russell and Sigurd Varian,Pond, Norman H. "The Tube Guys". Russ Cochran, 2008 p.31-40 which is used as an amplifier for high radio frequencies, from ultra high frequency, UHF up into the microwave range. Low-power klystrons are used as oscillators in terrestrial microwave relay communications links, while high-power klystrons are used as output tubes in UHF television transmitters, satellite communication, radar transmitters, and to generate the drive power for modern particle accelerators. In a klystron, an electron beam interacts with radio waves as it passes through cavity resonator, resonant cavities, metal boxes along the length of a tube. The electron beam first passes through a cavity to which the input signal is applied. The energy of the electron beam amplifies the signal, and the amplified signal is taken from a cavity at the other end of the tube. The output signal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Varian Associates
Varian Associates was one of the first high-tech companies in Silicon Valley. It was founded in 1948 by Russell H. and Sigurd F. Varian, William Webster Hansen, and Edward Ginzton to sell the klystron, the first vacuum tube which could amplify electromagnetic waves at microwave frequencies, and other electromagnetic equipment. Varian Associates split into three companies in 1999: Varian Medical Systems, Varian, Inc. and Varian Semiconductor. Incorporation and leadership On April 20, 1948, the Articles of Incorporation were filed, signed by nine directors: Edward Ginzton, who had worked with the Varian brothers since his days as a doctoral student; William Webster Hansen, Richard M. Leonard, an attorney; Leonard I. Schiff, then head of the physics department at Stanford University; H. Myrl Stearns, Russell H. Varian, his wife, Dorothy Varian, Sigurd F. Varian and Paul B. Hunter. The company began with six full-time employees: the Varian brothers, Dorothy, Myrl Stea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
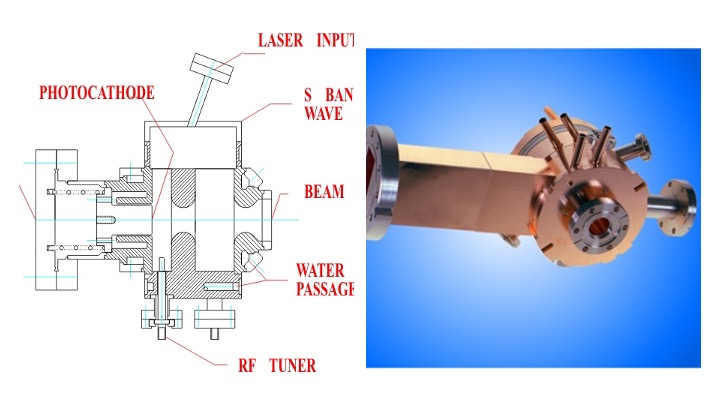
Electron Gun
file:Egun.jpg, Electron gun from a cathode-ray tube file:Vidicon Electron Gun.jpg, The electron gun from an RCA Vidicon video camera tube An electron gun (also called electron emitter) is an electrical component in some vacuum tubes that produces a narrow, collimation, collimated electron beam that has a precise kinetic energy. The largest use is in cathode-ray tubes (CRTs), used in older television sets, computer displays and oscilloscopes, before the advent of flat-panel displays. Electron guns are also used in field-emission display, field-emission displays (FEDs), which are essentially flat-panel displays made out of rows of extremely small cathode-ray tubes. They are also used in microwave linear beam vacuum tubes such as klystrons, inductive output tubes, travelling-wave tubes, and gyrotrons, as well as in scientific instruments such as electron microscopes and particle accelerators. Electron guns may be classified by the type of electric field generation (DC or RF), by e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electron
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up quark, up and down quark, down quarks. Electrons are extremely lightweight particles that orbit the positively charged atomic nucleus, nucleus of atoms. Their negative charge is balanced by the positive charge of protons in the nucleus, giving atoms their overall electric charge#Charge neutrality, neutral charge. Ordinary matter is composed of atoms, each consisting of a positively charged nucleus surrounded by a number of orbiting electrons equal to the number of protons. The configuration and energy levels of these orbiting electrons determine the chemical properties of an atom. Electrons are bound to the nucleus to different degrees. The outermost or valence electron, valence electrons are the least tightly bound and are responsible for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bandwidth (signal Processing)
Bandwidth is the difference between the upper and lower Frequency, frequencies in a continuous Frequency band, band of frequencies. It is typically measured in unit of measurement, unit of hertz (symbol Hz). It may refer more specifically to two subcategories: ''Passband bandwidth'' is the difference between the upper and lower cutoff frequencies of, for example, a band-pass filter, a communication channel, or a signal spectrum. ''Baseband bandwidth'' is equal to the upper cutoff frequency of a low-pass filter or baseband signal, which includes a zero frequency. Bandwidth in hertz is a central concept in many fields, including electronics, information theory, digital communications, radio communications, signal processing, and spectroscopy and is one of the determinants of the capacity of a given communication channel. A key characteristic of bandwidth is that any band of a given width can carry the same amount of information, regardless of where that band is located in the f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frequency Agility
Frequency agility is the ability of a radar system to quickly shift its operating frequency to account for atmospheric effects, jamming, mutual interference with friendly sources, or to make it more difficult to locate the radar broadcaster through radio direction finding. The term can also be applied to other fields, including lasers or traditional radio transceivers using frequency-division multiplexing, but it remains most closely associated with the radar field and these other roles generally use the more generic term "frequency hopping". Description Jamming Radar systems generally operate by sending out short pulses of radio energy and then turning off the broadcaster and listening for the returning echoes from various objects. Because efficient signal reception requires careful tuning throughout the electronics in the transceiver, each operating frequency required a dedicated transceiver. Due to the size of the tube-based electronics used to construct the transceivers, early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extended Interaction Klystron
Extension, extend or extended may refer to: Mathematics Logic or set theory * Axiom of extensionality * Extensible cardinal * Extension (model theory) * Extension (proof theory) * Extension (predicate logic), the set of tuples of values that satisfy the predicate * Extension (semantics), the set of things to which a property applies * Extension (simplicial set) * Extension by definitions * Extensional definition, a definition that enumerates every individual a term applies to * Extensionality Other uses * Extension of a function, defined on a larger domain * Extension of a polyhedron, in geometry * Extension of a line segment (finite) into an infinite line (e.g., extended base) * Exterior algebra, Grassmann's theory of extension, in geometry * Field extension, in Galois theory * Group extension, in abstract algebra and homological algebra * Homotopy extension property, in topology * Kolmogorov extension theorem, in probability theory * Linear extension, in order theory * She ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Electronics
Solid-state electronics are semiconductor electronics: electronic equipment that use semiconductor devices such as transistors, diodes and integrated circuits (ICs). The term is also used as an adjective for devices in which semiconductor electronics that have no moving parts replace devices with moving parts, such as the solid-state relay, in which transistor switches are used in place of a moving-arm electromechanical relay, or the solid-state drive (SSD), a type of semiconductor memory used in computers to replace hard disk drives, which store data on a rotating disk. History The term ''solid-state'' became popular at the beginning of the semiconductor era in the 1960s to distinguish this new technology. A semiconductor device works by controlling an electric current consisting of electrons or holes moving within a solid crystalline piece of semiconducting material such as silicon, while the thermionic vacuum tubes it replaced worked by controlling a current of elect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |