|
Tumor-agnostic Minimal Residual Disease
Tumor-agnostic minimal residual disease (MRD) testing, also referred to as tumor-naive, tumor-uninformed, or tumor-agnostic MRD (taMRD) testing, is an approach for detecting minimal residual disease (MRD) using circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) analysis that does not require prior sequencing of a tumor tissue. Instead, these assays analyze a blood plasma sample directly using pre-designed panels targeting molecular alterations commonly found across various cancers or specific cancer types. Tumor-agnostic MRD tests are employed to detect residual cancer cells after treatment, monitor for recurrence, and assess treatment response, particularly when primary tumor tissue is unavailable or when a faster turnaround time is needed. Key approaches include fixed NGS panels and methylation-based assays. Uses Tumor-agnostic MRD assays are utilized in similar clinical contexts as tumor-informed approaches, including post-treatment surveillance, risk stratification, and monitoring therapy res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Minimal Residual Disease
Minimal residual disease (MRD), also known as molecular residual disease, is the medical condition in which small number of cancer cells persist in a patient either during or after treatment when the patient is in Remission (medicine), remission and that cannot be detected with current medical imaging or routine screening options (occult stage of cancer progression). MRD detection is strongly associated with cancer recurrence, often with a lead time of months relative to other forms of clinical evidence. The presence and quantity of MRD are significant because these residual cells can potentially multiply and cause the cancer to relapse, and therefore detecting MRD has significant clinical and Clinical diagnosis, diagnostic potential. Sensitive molecular tests, often minimal invasive and done through a liquid biopsy, are either in development or available to test for MRD. These can measure minute levels of cancer cells in tissue samples, sometimes as low as one cancer cell in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulating Tumor DNA
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is tumor-derived fragmented DNA in the bloodstream that is not associated with cells. ctDNA should not be confused with cell-free DNA ( cfDNA), a broader term which describes DNA that is freely circulating in the bloodstream, but is not necessarily of tumor origin. Because ctDNA may reflect the entire tumor genome, it has gained traction for its potential clinical utility; " liquid biopsies" in the form of blood draws may be taken at various time points to monitor tumor progression throughout the treatment regimen. Recent studies have laid the foundation for inferring gene expression from cfDNA (and ctDNA), with EPIC-seq emerging as a notable advancement. This method has substantially raised the bar for the noninvasive inference of expression levels of individual genes, thereby augmenting the assay's applicability in disease characterization, histological classification, and monitoring treatment efficacy. ctDNA originates directly from the tumor or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Next-generation Sequencing
Massive parallel sequencing or massively parallel sequencing is any of several high-throughput approaches to DNA sequencing using the concept of massively parallel processing; it is also called next-generation sequencing (NGS) or second-generation sequencing. Some of these technologies emerged between 1993 and 1998 and have been commercially available since 2005. These technologies use miniaturized and parallelized platforms for sequencing of 1 million to 43 billion short reads (50 to 400 bases each) per instrument run. Many NGS platforms differ in engineering configurations and sequencing chemistry. They share the technical paradigm of massive parallel sequencing via spatially separated, clonally amplified DNA templates or single DNA molecules in a flow cell. This design is very different from that of Sanger sequencing—also known as capillary sequencing or first-generation sequencing—which is based on electrophoretic separation of chain-termination products produced in indiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DNA Methylation
DNA methylation is a biological process by which methyl groups are added to the DNA molecule. Methylation can change the activity of a DNA segment without changing the sequence. When located in a gene promoter (genetics), promoter, DNA methylation typically acts to repress gene Transcription (genetics), transcription. In mammals, DNA methylation is essential for normal development and is associated with a number of key processes including genomic imprinting, X-chromosome inactivation, repression of transposable elements, aging, and carcinogenesis. As of 2016, two nucleobases have been found on which natural, enzymatic DNA methylation takes place: adenine and cytosine. The modified bases are N6-methyladenine,D. B. Dunn, J. D. Smith: "The occurrence of 6-methylaminopurine in deoxyribonucleic acids". In: ''Biochem J.'' 68(4), Apr 1958, S. 627–636. [//www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13522672?dopt=Abstract PMID 13522672]. . 5-methylcytosineB. F. Vanyushin, S. G. Tkacheva, A. N. Belozers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulating Free DNA
Circulating free DNA (cfDNA) (also known as cell-free DNA) are degraded DNA fragments released to body fluids such as blood plasma, urine, cerebrospinal fluid, etc. Typical sizes of cfDNA fragments reflect chromatosome particles (~165bp), as well as multiples of nucleosomes, which protect DNA from digestion by apoptotic nucleases. The term cfDNA can be used to describe various forms of DNA freely circulating in body fluids, including circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA), cell-free mitochondrial DNA (ccf mtDNA), cell-free fetal DNA (cffDNA) and donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA). Elevated levels of cfDNA are observed in cancer, especially in advanced disease. There is evidence that cfDNA becomes increasingly frequent in circulation with the onset of age. cfDNA has been shown to be a useful biomarker for a multitude of ailments other than cancer and fetal medicine. This includes but is not limited to trauma, sepsis, aseptic inflammation, myocardial infarction, stroke, transplantatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomarker
In biomedical contexts, a biomarker, or biological marker, is a measurable indicator of some biological state or condition. Biomarkers are often measured and evaluated using blood, urine, or soft tissues to examine normal biological processes, pathogenic processes, or pharmacologic responses to a therapeutic intervention. as cited in Biomarkers are used in many scientific fields. Medicine Biomarkers used in the medical field, are a part of a relatively new clinical toolset categorized by their clinical applications. The four main classes are molecular, physiologic, histologic and radiographic biomarkers. All four types of biomarkers have a clinical role in narrowing or guiding treatment decisions and follow a sub-categorization of being either predictive, prognostic, or diagnostic. Predictive Predictive molecular, cellular, or imaging biomarkers that pass validation can serve as a method of predicting clinical outcomes. Predictive biomarkers are used to help optimize ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Single Nucleotide Variants
In genetics and bioinformatics, a single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP ; plural SNPs ) is a germline substitution of a single nucleotide at a specific position in the genome. Although certain definitions require the substitution to be present in a sufficiently large fraction of the population (e.g. 1% or more), many publications do not apply such a frequency threshold. For example, a G nucleotide present at a specific location in a reference genome may be replaced by an A in a minority of individuals. The two possible nucleotide variations of this SNP – G or A – are called alleles. SNPs can help explain differences in susceptibility to a wide range of diseases across a population. For example, a common SNP in the CFH gene is associated with increased risk of age-related macular degeneration. Differences in the severity of an illness or response to treatments may also be manifestations of genetic variations caused by SNPs. For example, two common SNPs in the ''APO ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
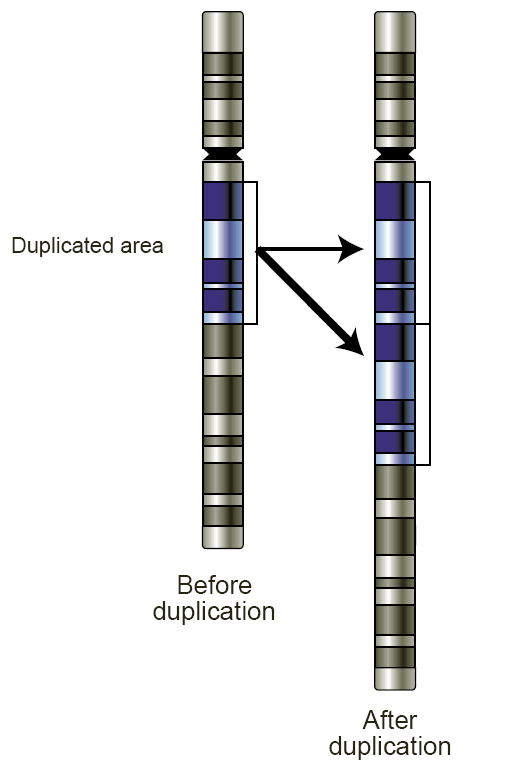
Copy Number Variation
Copy number variation (CNV) is a phenomenon in which sections of the genome are repeated and the number of repeats in the genome varies between individuals. Copy number variation is a type of structural variation: specifically, it is a type of duplication or deletion event that affects a considerable number of base pairs. Approximately two-thirds of the entire human genome may be composed of repeats and 4.8–9.5% of the human genome can be classified as copy number variations. In mammals, copy number variations play an important role in generating necessary variation in the population as well as disease phenotype. Copy number variations can be generally categorized into two main groups: short repeats and long repeats. However, there are no clear boundaries between the two groups and the classification depends on the nature of the loci of interest. Short repeats include mainly dinucleotide repeats (two repeating nucleotides e.g. A-C-A-C-A-C...) and trinucleotide repeats. Lon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Fusion
In genetics, a fusion gene is a hybrid gene formed from two previously independent genes. It can occur as a result of translocation, interstitial deletion, or chromosomal inversion. Fusion genes have been found to be prevalent in all main types of human neoplasia. The identification of these fusion genes play a prominent role in being a diagnostic and prognostic marker. History The first fusion gene was described in cancer cells in the early 1980s. The finding was based on the discovery in 1960 by Peter Nowell and David Hungerford in Philadelphia of a small abnormal marker chromosome in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia—the first consistent chromosome abnormality detected in a human malignancy, later designated the Philadelphia chromosome. In 1973, Janet Rowley in Chicago showed that the Philadelphia chromosome had originated through a translocation between chromosomes 9 and 22, and not through a simple deletion of chromosome 22 as was previously thought. Several ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methylated DNA Immunoprecipitation
Methylated DNA immunoprecipitation (MeDIP or mDIP) is a large-scale (chromosome- or genome-wide) purification technique in molecular biology that is used to enrich for DNA methylation, methylated DNA sequences. It consists of isolating methylated DNA fragments via an antibody raised against 5-methylcytosine (5mC). This technique was first described by Weber M. ''et al.'' in 2005 and has helped pave the way for viable methylome-level assessment efforts, as the purified fraction of methylated DNA can be input to high-throughput DNA detection methods such as high-resolution DNA microarrays (Tiling array#MeDIP-chip, MeDIP-chip) or DNA sequencing#New sequencing methods, next-generation sequencing (MeDIP-seq). Nonetheless, understanding of the methylome remains rudimentary; its study is complicated by the fact that, like other epigenetic properties, patterns vary from cell-type to cell-type. Background DNA methylation, referring to the reversible methylation of the 5 position of cyt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clonal Hematopoiesis
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential, or CHIP, is a common aging-related phenomenon in which hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) or other early blood cell progenitors contribute to the formation of a genetically distinct subpopulation of blood cells. As the name suggests, this subpopulation in the blood is characterized by a shared unique mutation in the cells' DNA; it is thought that this subpopulation is "clonally" derived from a single founding cell and is therefore made of genetic "clones" of the founder. The establishment of a clonal population may occur when a stem or progenitor cell acquires one or more somatic mutations that give it a competitive advantage in hematopoiesis over the stem/progenitor cells without these mutations. Alternatively, clonal hematopoiesis may arise without a driving mutation, through mechanisms such as neutral drift in the stem cell population. Clonal hematopoiesis may occur in people who are completely healthy but has also been found in peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circulating Tumor DNA
Circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA) is tumor-derived fragmented DNA in the bloodstream that is not associated with cells. ctDNA should not be confused with cell-free DNA ( cfDNA), a broader term which describes DNA that is freely circulating in the bloodstream, but is not necessarily of tumor origin. Because ctDNA may reflect the entire tumor genome, it has gained traction for its potential clinical utility; " liquid biopsies" in the form of blood draws may be taken at various time points to monitor tumor progression throughout the treatment regimen. Recent studies have laid the foundation for inferring gene expression from cfDNA (and ctDNA), with EPIC-seq emerging as a notable advancement. This method has substantially raised the bar for the noninvasive inference of expression levels of individual genes, thereby augmenting the assay's applicability in disease characterization, histological classification, and monitoring treatment efficacy. ctDNA originates directly from the tumor or f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |