|
Truckhouse
A truckhouse or truck-house was a type of trading post established by legislation in the colonies of British America to regulate the North American fur trade. Truckhouses were maintained in the early to mid-18th century. Truckhouses in the province of Massachusetts Bay held a monopoly on trade with Indigenous peoples along the Nashua, Merrimack, and Piscataqua rivers. Leach argues that truckhouses "completely dominated" trade in the eastern colonies between 1726 and the 1740s, when King George's War erupted. Despite its dominance, however, the system did not generally turn a profit. Truckhouses sold goods to Indigenous buyers at low prices. The aim of the truckhouse system was to disrupt French diplomatic influence in the area, not primarily to supplement government revenue. It also served as a means of regulating settlers' trade with Indigenous peoples. The Massachusetts General Court, legislature of the province of Massachusetts Bay, established truckhouses by statute in 1699. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Halifax Treaties
The Peace and Friendship Treaties were a series of written documents (or, treaties) that Britain signed bearing the Authority of Great Britain between 1725 and 1779 with various Mi’kmaq, Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet), Abenaki, Penobscot, and Passamaquoddy peoples (i.e., the Wabanaki Confederacy) living in parts of what are now the Maritime and Gaspé region in Canada and the northeastern United States. Primarily negotiated to reaffirm the peace after periods of war and to facilitate trade, these treaties remain in effect to this day. The Peace and Friendship Treaties include the Halifax Treaties. These are 11 treaties signed between 1760 and 1761 by the various bands of the Miꞌkmaq (as well as other Indigenous peoples)There were also Halifax Treaties signed with the Wolastoqiyik (Maliseet) and the Passamaquoddy. and the British in Halifax, Nova Scotia. These agreements ended the conflict that had persisted between the two peoples for 85 years. The Halifax Treaties include both m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Trading Post
A trading post, trading station, or trading house, also known as a factory in European and colonial contexts, is an establishment or settlement where goods and services could be traded. Typically a trading post allows people from one geographic area to exchange for goods produced in another area. Usually money is not used. The barter that occurs often includes an aspect of haggling. In some examples, local inhabitants can use a trading post to exchange what they have (such as locally-harvested furs) for goods they wish to acquire (such as manufactured trade goods imported from industrialized places). Given bulk transportation costs, exchanges made at a trading post for long-distance distribution can involve items which either party or both parties regard as luxury goods. A trading post can consist either of a single building or of an entire town. Trading posts have been established in a range of areas, including relatively remote ones, but most often near an ocean, a ri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
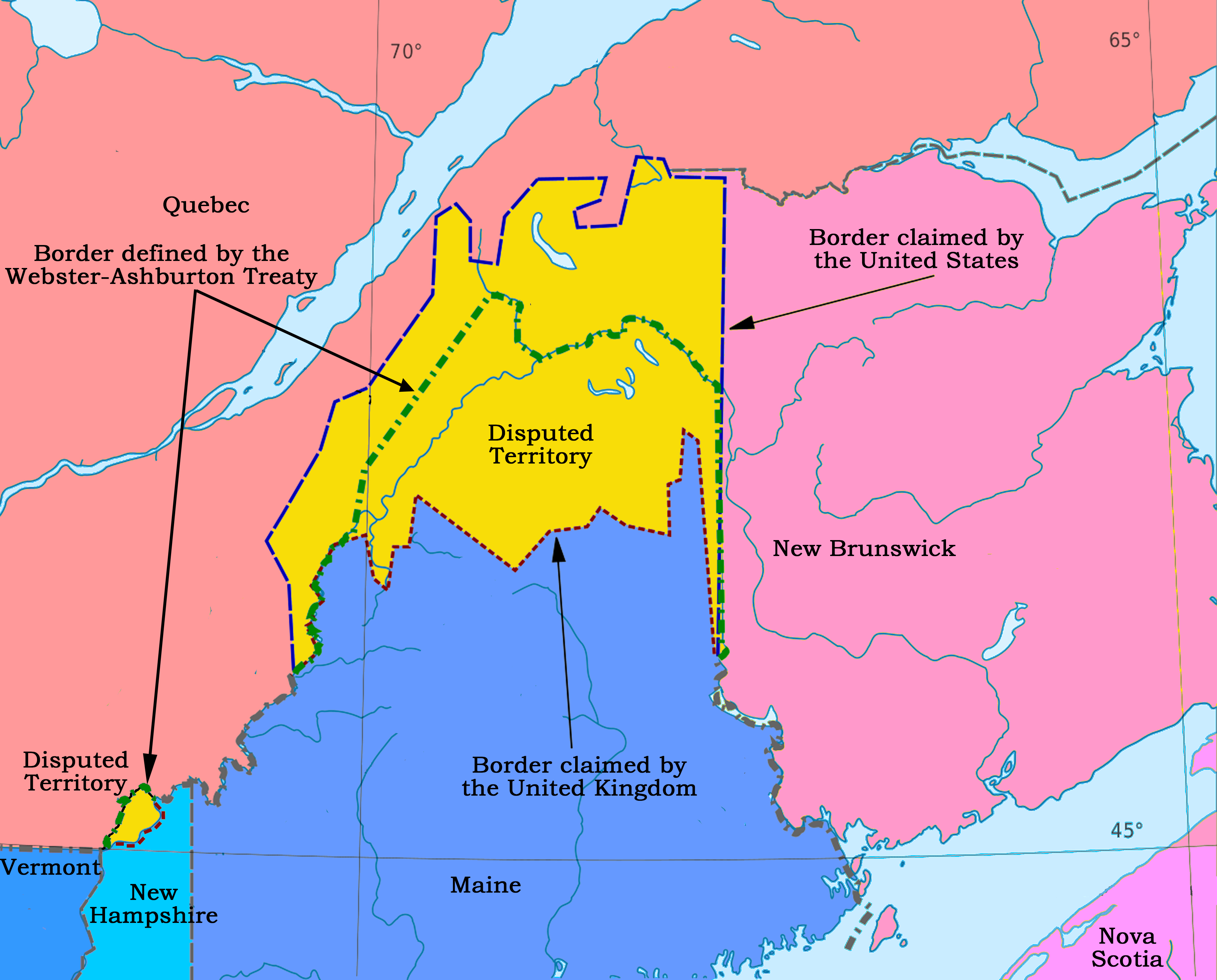
Saint John River (Bay Of Fundy)
The Saint John River (; Maliseet-Passamaquoddy: ''Wolastoq'') is a river flowing within the Dawnland region from headwaters in the Notre Dame Mountains near the Maine-Quebec border through western New Brunswick to the northwest shore of the Bay of Fundy. Eastern Canada's longest river, its drainage basin is one of the largest on the east coast at about . This “River of the Good Wave” and its tributary drainage basin formed the territorial countries of the Wolastoqiyik and Passamaquoddy First Nations (named Wolastokuk and Peskotomuhkatik, respectively) prior to European colonization, and it remains a cultural centre of the Wabanaki Confederacy to this day. The Webster–Ashburton Treaty following the Aroostook War established a border between New Brunswick and Maine following of the river, while a tributary forms of the border between Quebec and Maine. Maine communities along the river include Fort Kent, Madawaska, and Van Buren. New Brunswick settlements through ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada, located on its east coast. It is one of the three Maritime Canada, Maritime provinces and Population of Canada by province and territory, most populous province in Atlantic Canada, with an estimated population of over 1 million as of 2024; it is also the second-most densely populated province in Canada, and second-smallest province by area. The province comprises the Nova Scotia peninsula and Cape Breton Island, as well as 3,800 other coastal islands. The province is connected to the rest of Canada by the Isthmus of Chignecto, on which the province's land border with New Brunswick is located. Nova Scotia's Capital city, capital and largest municipality is Halifax, Nova Scotia, Halifax, which is home to over 45% of the province's population as of the 2021 Canadian census, 2021 census. Halifax is the List of census metropolitan areas and agglomerations in Canada, twelfth-largest census metropolitan area in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Miꞌkmaq
The Mi'kmaq (also ''Mi'gmaq'', ''Lnu'', ''Mi'kmaw'' or ''Mi'gmaw''; ; , and formerly Micmac) are an Indigenous group of people of the Northeastern Woodlands, native to the areas of Canada's Atlantic Provinces, primarily Nova Scotia, New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island, and Newfoundland, and the Gaspé Peninsula of Quebec as well as Native Americans in the northeastern region of Maine. The traditional national territory of the Mi'kmaq is named Mi'kma'ki (or Mi'gma'gi). There are 66,748 Mi'kmaq people in the region as of 2023 (including 25,182 members in the more recently formed Qalipu First Nation in Newfoundland). According to the Canadian 2021 census, 9,245 people claim to speak Mi'kmaq, an Eastern Algonquian language. Once written in Mi'kmaw hieroglyphic writing, it is now written using most letters of the Latin alphabet. The Mi'kmaq, Maliseet, and Pasamaquoddy nations signed a series of treaties known as the Covenant Chain of Peace and Friendship Treaties wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Province Of Pennsylvania
The Province of Pennsylvania, also known as the Pennsylvania Colony, was a British North American colony founded by William Penn, who received the land through a grant from Charles II of England in 1681. The name Pennsylvania was derived from Latin, meaning "Penn's Woods", a reference to William Penn's father Admiral Sir William Penn. History European settlement The Province of Pennsylvania was one of two major Restoration colonies in colonial-era British America. A plan for government of the colony of Pennsylvania was heavily influenced by the ideas and utopian aspirations of English political scientist James Harrington. The proprietary colony's charter remained in the Penn family until the Penns were ousted in 1776 during the American Revolutionary War, and the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania was established as one of the original thirteen states. In June 1776, the Lower counties on the Delaware, a separate colony within the Province of Pennsylvania, broke away from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
New York University Press
New York University Press (or NYU Press) is a university press that is part of New York University New York University (NYU) is a private university, private research university in New York City, New York, United States. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded in 1832 by Albert Gallatin as a Nondenominational .... History NYU Press was founded in 1916 by the then chancellor of NYU, Elmer Ellsworth Brown. Directors * Arthur Huntington Nason, 1916–1932 * No director, 1932–1946 * Jean B. Barr (interim director), 1946–1952 * Filmore Hyde, 1952–1957 * Wilbur McKee, acting director, 1957–1958 * William B. Harvey, 1958–1966 * Christopher Kentera, 1966–1974 * Malcolm C. Johnson, 1974–1981 * Colin Jones, 1981–1996 * Niko Pfund, 1996–2000 * Steve Maikowski, 2001–2014 * Ellen Chodosh, 2014–2024 * Eric Schwartz, 2024–present Notable publications Once best known for publishing '' The Collected Writings of Walt Whitman'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Indian Agent
In United States history, an Indian agent was an individual authorized to interact with American Indian tribes on behalf of the U.S. government. Agents established in Nonintercourse Act of 1793 The federal regulation of Indian affairs in the United States first included development of the position of Indian agent in the Nonintercourse Act of 1793, a revision of the original 1790 law. This required land sales by or from Indians to be federally licensed and permitted. The legislation also authorized the President to "appoint such persons, from time to time, as temporary agents to reside among the Indians," and guide them into acculturation of American society by changing their agricultural practices and domestic activities. Eventually, the U.S. government ceased using the word "temporary" in the Indian agent's job title. Changing role of Indian Agents, 1800–1840s From the close of the 18th century to nearly 1869, Congress maintained the position that it was legally responsible ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Joseph Kellogg (colonist)
Joseph Kellogg was a well-known steamboat captain and businessman of Portland, Oregon. Early life Joseph Kellogg was born in Canada on June 12, 1812. His father Orrin Kellogg (September 4, 1790 – February 14, 1872) was born in St. Albans, Vermont, and his mother Margaret Miller Kellogg was Canadian. After the War of 1812, his family moved first to New York and then to Ohio. Kellogg was trained as a millwright.Hines, H. K., ''An Illustrated History of the State of Oregon'' Chicago: Lewis Pub. Co. 1893, at 1037 In 1847 the Kellogg family crossed the plains to Oregon. They left Wood county, Ohio, November 24, 1847, with horse-drawn wagons. At Cincinnati, Ohio they shipped by steamer to St. Louis, and from there drove to St. Joseph, Missouri where they wintered. Emigration to Oregon In May a company of thirty wagons started on journey across the plains. They had covered wagons and were provided with tin stoves and all the arms and provisions needed for such a journey. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
American Indian Quarterly
The ''American Indian Quarterly'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed academic journal covering studies on the indigenous peoples of North and South America. It is published by the University of Nebraska Press and was established in 1974. The editor-in-chief is Lindsey Claire Smith (Oklahoma State University Oklahoma State University (informally Oklahoma State or OSU) is a public land-grant research university in Stillwater, Oklahoma, United States. The university was established in 1890 under the legislation of the Morrill Act. Originally known ...). External links * University of Nebraska–Lincoln Native American studies American studies journals Academic journals established in 1974 Quarterly journals English-language journals 1974 establishments in Nebraska {{area-journal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dictionary Of Canadian Biography
The ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography'' (''DCB''; ) is a dictionary of biographical entries for individuals who have contributed to the history of Canada. The ''DCB'', which was initiated in 1959, is a collaboration between the University of Toronto and Laval University. Fifteen volumes have so far been published with more than 8,400 biographies of individuals who died or whose last known activity fell between the years 1000 and 1930. The entire print edition is online, along with some additional biographies to the year 2000. Establishment of the project The project was undertaken following a bequest to the University of Toronto from businessman James Nicholson for the establishment of a Canadian version of the United Kingdom's ''Dictionary of National Biography''. In the spring of 1959, George Williams Brown was appointed general editor and the University of Toronto Press, which had been named publisher, sent out some 10,000 announcements introducing the project. Work started in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Samuel Moody
Samuel Moody was a seventeenth century English politician. He was christened at Moulton, Suffolk on 31 March 1592. He was an Alderman in Bury St Edmunds by 1644. He was appointed to the First Suffolk Committee for Scandalous Ministers that year. He was later one of the two MPs for Bury St Edmunds in 1654 and 1656. Samuel was born in Moulton, Suffolk, the son of George Moody and his wife Margaret Chenery. Moody was one of the commissioners who sat on the Suffolk Committees for Scandalous Ministers The Suffolk Committees for Scandalous Ministers were two committees commissioned by the Earl of Manchester between 24 February and 15 March 1644 in accordance with an ordinance published on 22 January 1644. Manchester had been pressing for authori .... References Moody {{1656-England-MP-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |