|
Trials Of The Knights Templar
The downfall of the Knights Templar was initiated by King Philip IV of France. Philip, who was heavily in debt due to his lavish policies and military endeavours, saw the Templars as a way of alleviating his financial hardship and at the same time eliminating a powerful rival. In addition, the Templars were difficult to control by secular authorities due to their international networks and their special rights, which placed them directly under the Church, which Philip perceived as a threat. At the same time, Philip had been embroiled in a bitter conflict with Pope Pope Boniface VIII, Boniface VIII over the question of the division of power between the Church and the Crown. After Boniface's death and the election of the French Pope Pope Clement V, Clement V, Philip saw his opportunity to further extend his control over ecclesiastical affairs. On Friday 13 October 1307, Philip had numerous Templars arrested in Kingdom of France, France, including the Grand Master Jacques de Molay. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Templars On Stake
The Poor Fellow-Soldiers of Christ and of the Temple of Solomon, mainly known as the Knights Templar, was a Military order (religious society), military order of the Catholic Church, Catholic faith, and one of the most important military orders in Western Christianity. They were founded in 1118 to defend pilgrims on their way to Jerusalem, with their headquarters located there on the Temple Mount, and existed for nearly two centuries during the Middle Ages. Officially endorsed by the Catholic Church by such decrees as the papal bull ''Omne datum optimum'' of Pope Innocent II, the Templars became a favoured charity throughout Christendom and grew rapidly in membership and power. The Templar knights, in their distinctive white mantle (monastic vesture), mantles with a red Christian cross, cross, were among the most skilled fighting units of the Crusades. They were prominent in Christian finance; non-combatant members of the order, who made up as much as 90% of their members, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Order Of St
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to: * A socio-political or established or existing order, e.g. World order, Ancien Regime, Pax Britannica * Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood * Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of different ways * Hierarchy, an arrangement of items that are represented as being "above", "below", or "at the same level as" one another * an action or inaction that must be obeyed, mandated by someone in authority People * Orders (surname) Arts, entertainment, and media * ''Order'' (film), a 2005 Russian film * ''Order'' (album), a 2009 album by Maroon * "Order", a 2016 song from '' Brand New Maid'' by Band-Maid * ''Orders'' (1974 film), a film by Michel Brault * "Orders" (''Star Wars: The Clone Wars'') Business * Blanket order, a purchase order to allow multiple delivery dates over a period of time * Money order or postal orde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
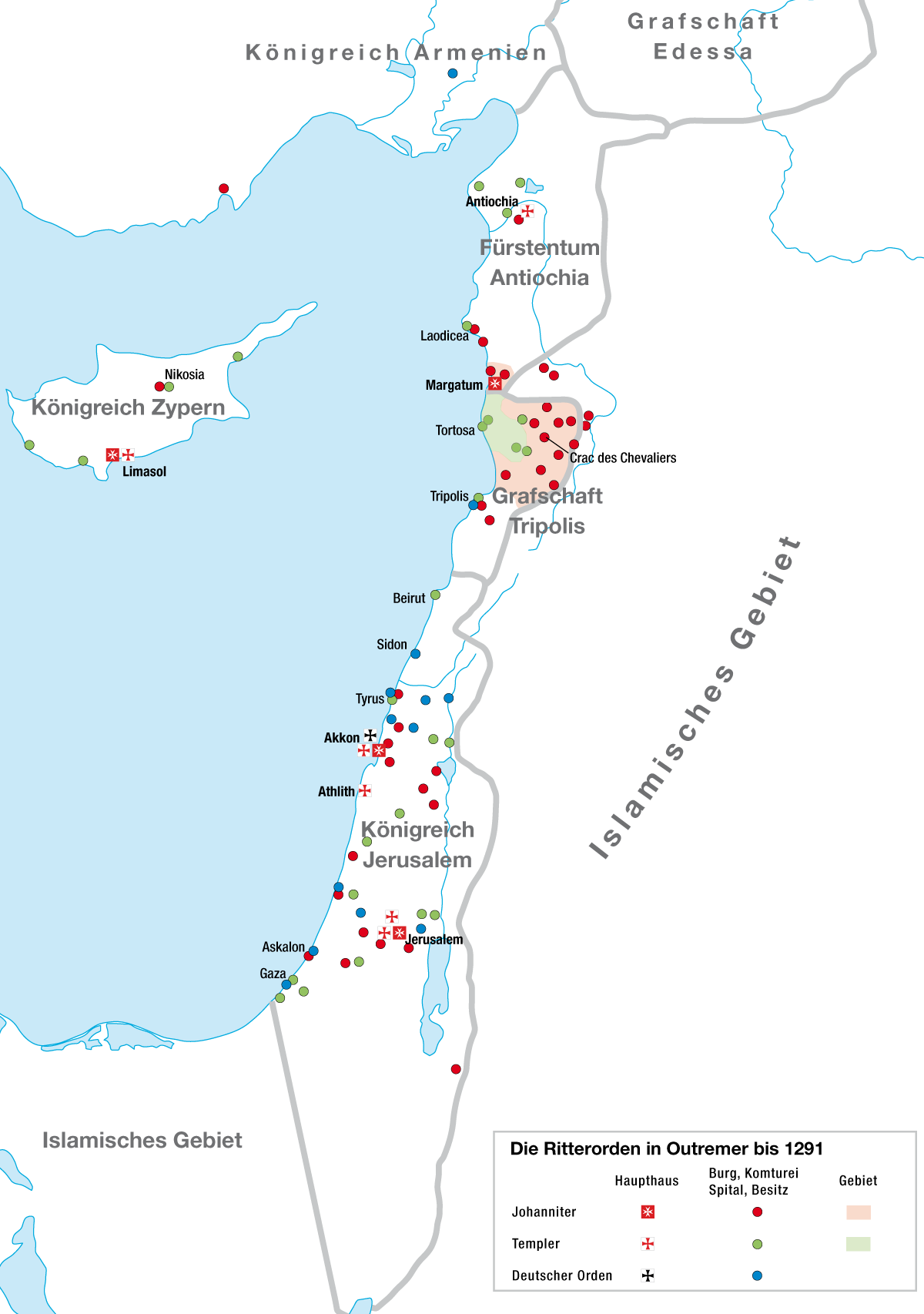
Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and at times directed by the Papacy during the Middle Ages. The most prominent of these were the campaigns to the Holy Land aimed at reclaiming Jerusalem and its surrounding territories from Muslim rule. Beginning with the First Crusade, which culminated in the Siege of Jerusalem (1099), capture of Jerusalem in 1099, these expeditions spanned centuries and became a central aspect of European political, religious, and military history. In 1095, after a Byzantine request for aid,Helen J. Nicholson, ''The Crusades'', (Greenwood Publishing, 2004), 6. Pope Urban II proclaimed the first expedition at the Council of Clermont. He encouraged military support for List of Byzantine emperors, Byzantine emperor Alexios I Komnenos, AlexiosI Komnenos and called for an armed pilgrimage to Jerusalem. Across all social strata in Western Europe, there was an enthusiastic response. Participants came from all over Europe and had a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obedience, Poverty And Chastity
In Christianity, the three evangelical counsels, or counsels of perfection, are chastity, poverty (or perfect charity), and obedience. As stated by Jesus in the canonical gospels, they are counsels for those who desire to become "perfect" (, ). The Catholic Church interprets this to mean that they are not binding upon all, and hence not necessary conditions to attain eternal life (heaven), but that they are " acts of supererogation", "over and above" the minimum stipulated in the biblical commandments. Catholics who have made a public profession to order their lives by the evangelical counsels, and confirmed this by public vows before their competent church authority (the act of religious commitment known as a profession), are recognised as members of the consecrated life. Consecrated life There are early forms of religious vows in the monastic traditions. The Rule of Saint Benedict (ch. 58.17) indicates that the newly received promise stability, fidelity to monastic life, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercian
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly influential Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Bernard of Clairvaux, Saint Bernard, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of their cowl, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme Abbey, Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098. The first three abbots were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and Stephen Harding. Bernard helped launch a new era when he entered the monastery in the early 1110s with 30 companions. By the end of the 12th century, the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin Rule
The Latin Rule was a document with 72 clauses attributed to Bernard de Clairvaux and Hugues de Payens. It is also known as the "Specific Behavior for the Templar Order". It outlines the ideal behavior of a knight. The rule borrowed from the ''Rule of Saint Augustine'', but was mostly inspired by the ''Rule of Saint Benedict'' (Latin: ''Regula Sancti Benedicti''). It was, however, adapted for use by active, primarily military, knights, rather than cloistered monks. For example, the fasts were less severe so that they did not interfere with combat. The original rule was written in 1128 and added to the minutes of the Council of Troyes in 1129. However, in about 1138 under the direction of Robert de Craon, second grand master of the order (1136–1149), the rule was translated into French and modified. Later, it was expanded to include 609 articles, notably covering such things as hierarchy and justice within the order. See also *Knights Templar *Rule of Saint Augustine *Rule of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernard Of Clairvaux
Bernard of Clairvaux, Cistercians, O.Cist. (; 109020 August 1153), venerated as Saint Bernard, was an abbot, Mysticism, mystic, co-founder of the Knights Templar, and a major leader in the reform of the Benedictines through the nascent Cistercians, Cistercian Order. Bernard was sent to found Clairvaux Abbey only a few years after becoming a monk at Cîteaux Abbey, Cîteaux. In the year 1128, Bernard attended the Council of Troyes (1129), Council of Troyes, at which he traced the outlines of the Rule of the Knights Templar, which soon became an ideal of Christian nobility. On the death of Pope Honorius II in 1130, a schism arose in the church. Bernard was a major proponent of Pope Innocent II, arguing effectively for his legitimacy over the Antipope Anacletus II. The eloquent abbot advocated crusades in general and convinced many to participate in the unsuccessful Second Crusade, notably through a famous sermon at Council of Vézelay, Vézelay (1146). Bernard was canonized just ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Catholic Church
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization.Gerald O'Collins, O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 Catholic particular churches and liturgical rites#Churches, ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and Eparchy, eparchies List of Catholic dioceses (structured view), around the world, each overseen by one or more Bishops in the Catholic Church, bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the Papal supremacy, chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Order (society)
A military order () is a Christianity, Christian religious society of Knight, knights. The original military orders were the Knights Templar, the Knights Hospitaller, the Order of the Holy Sepulchre (Catholic), Order of the Holy Sepulchre, the Order of Santiago, Order of Saint James, the Order of Calatrava, and the Teutonic Order, Teutonic Knights. They arose in the Middle Ages in association with the Crusades - in the Holy Land, the Baltic states, Baltics, and the Iberian Peninsula, Iberian peninsula; their members being initially dedicated to the protection of Christians , Christian pilgrims, and eventually to the defence of the Crusader states and the conquest of non-Christian or even non-Western Christianity , Catholic lands. They are the predecessors of Order of chivalry, chivalric orders. Most members of military orders were Laity, laymen who took religious vows, such as of Evangelical counsels, poverty, chastity, and obedience, according to Monasticism, monastic ideals. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Council Of Troyes In 1129
The Council of Troyes was convened by Bernard of Clairvaux on 13 January 1129 in the city of Troyes. The council, largely attended by French clerics, was assembled to hear a petition by Hugues de Payens, head of the Knights Templar. Pope Honorius II did not attend the council, sending the papal legate, Matthew, cardinal-bishop of Albano. The council addressed issues concerning the Templar Order and a dispute between the bishop of Paris and king of France. Background Founded by Hugues de Payens in 1119, the Knights Templar had gained the backing of King Baldwin II of Jerusalem at the Council of Nablus in 16 January 1120. In 1126, Baldwin had commissioned two clerics to speak with Bernard of Clairvaux seeking papal recognition and a Rule for the Templar Order. Later, Baldwin sent Hugues to Europe to convince Fulk of Anjou to marry his daughter Melisende and to raise an army for a crusade against Damascus. Hugues's other objectives were to gain papal recognition, recruit members f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hugues De Payens
, commonly known in French as or ( – 24 May 1136), was the co-founder and first Grand Master of the Knights Templar. Origin and early life The Latin text of William of Tyre's ''History of Deeds Done Beyond the Sea'', dated , calls him , without any geographical reference. William's history was translated into French in the early 13th century, by an anonymous author who added that Hugh was from "," “near Troyes." The 12th-century author Walter Map also noted that Hugh was named "Payns, from a village of that name in Burgundy.” Hugh is therefore assumed to have come from the village of Payns, about 10km from Troyes, in Champagne (eastern France). is mentioned as a witness to a donation by Count Hugh of Champagne in a document of 1085–90, indicating that the man was at least sixteen by this date—a legal adult and thus able to bear witness to legal documents—and so born no later than 1070. The same name appears on a number of other charters up to 1113 also relat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon's Temple
Solomon's Temple, also known as the First Temple (), was a biblical Temple in Jerusalem believed to have existed between the 10th and 6th centuries Common Era, BCE. Its description is largely based on narratives in the Hebrew Bible, in which it was commissioned by biblical king Solomon before being destroyed during the Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC), Siege of Jerusalem by Nebuchadnezzar II of the Neo-Babylonian Empire in 587 BCE. No excavations are allowed on the Temple Mount, and no positively identified remains of the destroyed temple have been found. Most modern scholars agree that the First Temple existed on the Temple Mount in Jerusalem by the time of the Babylonian siege, and there is significant debate among scholars over the date of its construction and the identity of its builder. The Hebrew Bible, specifically within the Books of Kings, Book of Kings, includes a detailed narrative about the construction's ordering by Solomon, the penultimate ruler of the Kingdom of Israel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |