|
Trial Frame
A trial frame is a tool used by ophthalmic professionals like ophthalmologists and optometrists. It is basically an adjustable spectacle frame with multiple cells, used to hold corrective lenses, and other accessories in subjective refraction (finding the correct spectacle power) and retinoscopy. Uses To measure a patient's refractive error, squint and presbyopia, it is used to hold lenses, prism or other tools like pinhole occluder. The cells of the trial frame allow holding lenses in correct position. Although phoropters, which contains lenses allow a quicker refraction, the trial frame help to test near vision at the patient's preferred working distance and position. Since it is portable, a trial frame is ideal for vision and refraction screening during home (domiciliary) visits and outreach camps. Since it allows more natural vision, trial frame refraction is preferred for patients with low vision patients. Parts An ideal trial frame have minimum 3 cells, one each for ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visual Acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of visual perception, vision, but technically rates an animal's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity depends on optical and neural factors. Optical factors of the eye influence the sharpness of an image on its retina. Neural factors include the health and functioning of the retina, of the neural pathways to the brain, and of the interpretative faculty of the brain. The most commonly referred-to visual acuity is ''distance acuity'' or ''far acuity'' (e.g., "20/20 vision"), which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a far distance. This ability is compromised in people with myopia, also known as short-sightedness or near-sightedness. Another visual acuity is ''Near visual acuity, near acuity'', which describes someone's ability to recognize small details at a near distance. This ability is compromised in people with hyperopia, also known as long-sightedness or far-sightedness. A com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
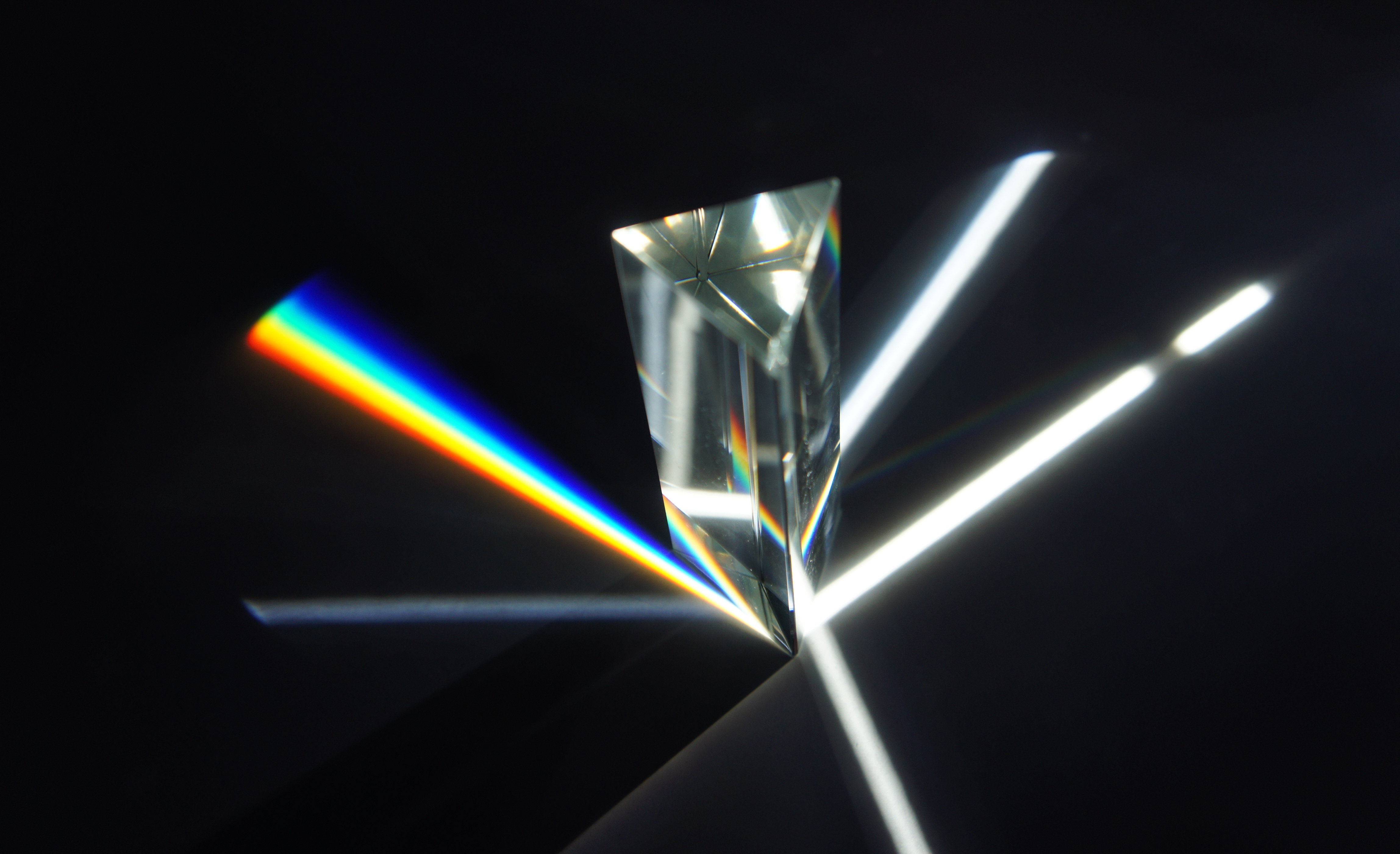
Prism (optics)
An optical prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that are designed to refract light. At least one surface must be angled—elements with two parallel surfaces are ''not'' prisms. The most familiar type of optical prism is the triangular prism, which has a triangular base and rectangular sides. Not all optical prisms are geometric prisms, and not all geometric prisms would count as an optical prism. Prisms can be made from any material that is transparent to the wavelengths for which they are designed. Typical materials include glass, acrylic and fluorite. A dispersive prism can be used to break white light up into its constituent spectral colors (the colors of the rainbow) to form a spectrum as described in the following section. Other types of prisms noted below can be used to reflect light, or to split light into components with different polarizations. Types Dispersive ''Dispersive prisms'' are used to break up light into its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many inc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maddox Rod
The Maddox rod test can be used to subjectively detect and measure a latent, manifest, horizontal or vertical strabismus for near and distance. The test is based on the principle of diplopic projection. Dissociation of the deviation is brought about by presenting a red line image to one eye and a white light to the other, while Prism (optics), prisms are used to superimpose these and effectively measure the angle of deviation (horizontal and vertical). The strength of the Prism (optics), prism is increased until the streak of the light passes through the centre of the Prism (optics), prism, as the strength of the Prism (optics), prism indicates the amount of deviation present. The Maddox rod is a handheld instrument composed of red parallel plano convex cylinder Lens (optics), lens, which refracts light rays so that a point source of light is seen as a line or streak of light. Due to the optical properties, the streak of light is seen perpendicular to the axis of the cylinder. E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interpupillary Distance
Pupillary distance (PD), more correctly known as interpupillary distance (IPD) is the distance in millimeters between the centers of each pupil. Interpupillary Distance Classifications Distance PD is the separation between the visual axes of the eyes in their primary position, as the subject fixates on an infinitely distant object. Near PD is the separation between the visual axes of the eyes, at the plane of the spectacle lenses, as the subject fixates on a near object at the intended working distance. Intermediate PD is at a specified plane in between distance and near. Monocular PD refers to the distance between either the right or left visual axis to the bridge of the nose, which may be slightly different for each eye due to anatomical variations but always sums up to the binocular PD. For people who need to wear prescription eyeglasses, glasses, consideration of monocular PD measurement by an optician helps to ensure that the Lens (optics), lenses will be located in the optim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. The lens and cornea of an eye without astigmatism are nearly spherical, with only a single radius of curvature, and any refractive errors present can be corrected with simple glasses. In an eye with astigmatism, either the lens or the cornea is slightly egg-shaped, with higher curvature in one direction than the other. This gives distorted or blurred vision at any distance and requires corrective lenses that apply different optical powers at different rotational angles. Astigmatism can lead to symptoms that include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at night. Astigmatism often is present at birth, but can change or develop later in life. If it occurs in early life and is left untreated, it may result in amblyopia. The cause of astigmatism is unclear, although it is believed to be partly related to genetic factors. The underlying mechanism involves an irregular c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low Vision
Visual or vision impairment (VI or VIP) is the partial or total inability of visual perception. In the absence of treatment such as corrective eyewear, assistive devices, and medical treatment, visual impairment may cause the individual difficulties with normal daily tasks, including reading and walking. The terms ''low vision'' and ''blindness'' are often used for levels of impairment which are difficult or impossible to correct and significantly impact daily life. In addition to the various permanent conditions, fleeting temporary vision impairment, amaurosis fugax, may occur, and may indicate serious medical problems. The most common causes of visual impairment globally are uncorrected refractive errors (43%), cataracts (33%), and glaucoma (2%). Refractive errors include near-sightedness, far-sightedness, presbyopia, and astigmatism (eye), astigmatism. Cataracts are the most common cause of blindness. Other disorders that may cause visual problems include age-related macular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phoropter
A phoropter or refractor is an ophthalmic testing device. It is commonly used by eye care professionals during an eye examination, and contains different lenses used for refraction of the eye during sight testing, to measure an individual's refractive error and determine their eyeglass prescription. Dictionary.comDefinition of "phoropter" American Heritage Stedman's Medical Dictionary. Retrieved 10-10-10. It also is used to measure the patients' Heterophoria, phorias and ductions, which are characteristics of binocularity. Typically, the patient sits behind the phoropter, and looks through it at an eye chart placed at optical infinity (20 feet or 6 metres), then at near (16 inches or 40 centimetres) for individuals needing reading glasses. The eye care professional then changes lens (optics), lenses and other settings, while asking the patient for subjective feedback on which settings gave the best visual perception, vision. The patient's habitual prescription or an automat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pinhole Occluder
A pinhole occluder is an opaque disk with one or more small holes through it, used by ophthalmologists, orthoptists and optometrists to test visual acuity. The occluder is a simple way to focus light, as in a pinhole camera, temporarily removing the effects of refractive errors such as myopia. Because light passes only through the center of the eye's lens, defects in the shape of the lens (errors of refraction) have no effect while the occluder is used. In this way, the ophthalmologist, orthoptist or optometrist can estimate the maximum improvement in a patient's vision that can be attained by lenses to correct errors of refraction. This can be used to distinguish visual defects caused by refractive error, which improve when the occluder is used, from other problems, which do not. The pinhole occluder can also be used in testing visual acuity in mydriatic patients. In this case, the pinhole occluder compensates for the inability to contract the iris assisting the eye in obtain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device that focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements''), usually arranged along a common axis. Lenses are made from materials such as glass or plastic and are ground, polished, or molded to the required shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly focus or disperse waves and radiation other than visible light are also called "lenses", such as microwave lenses, electron lenses, acoustic lenses, or explosive lenses. Lenses are used in various imaging devices such as telescopes, binoculars, and cameras. They are also used as visual aids in glasses to correct defects of vision such as myopia and hypermetropia. History The word '' lens'' comes from , the Latin name of the lentil (a seed of a lentil p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmologist
Ophthalmology (, ) is the branch of medicine that deals with the diagnosis, treatment, and surgery of eye diseases and disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. In the United States, following graduation from medical school, one must complete a four-year residency in ophthalmology to become an ophthalmologist. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat ailments, such as eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care—medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many incl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Presbyopia
Presbyopia is a physiological insufficiency of optical Accommodation (vertebrate eye), accommodation associated with the aging of the human eye, eye; it results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as age-related farsightedness (or as age-related long sight in the UK), it affects many adults over the age of 40. A common sign of presbyopia is difficulty in reading small print, which results in having to hold reading material farther away. Other symptoms associated can be headaches and eyestrain. Different people experience different degrees of problems. Other types of refractive errors may exist at the same time as presbyopia. This condition is similar to hypermetropia or far-sightedness, which starts in childhood and exhibits similar symptoms of blur in the vision for close objects. Presbyopia is a typical part of the aging process. It occurs due to age-related changes in the Lens (anatomy), lens (decreased elasticity and increased h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |