|
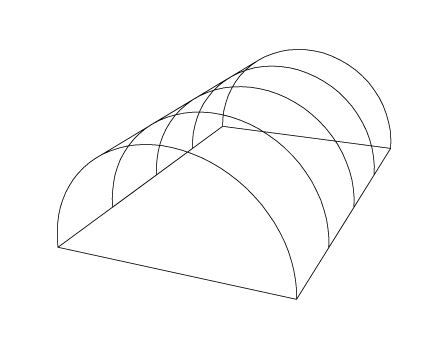
Transverse Arch
In architecture, a transverse arch is an arch in a vaulted building that goes across the barrel vault. A series of transverse arches sitting on tops of the columns on the sides of the nave was typical in the churches of Romanesque architecture (common since Carolingian times). By analogy, the term is also used to describe the transverse ribs of a groined vault and for any crosswise arch in modern buildings. An arc that goes in transverse direction, but carries an exposed wall on top, dividing the vault into compartments, is called a diaphragm arch. In the historical buildings, the transverse arches provide support for purlins and roof ridge beams. They also subdivide the nave into bays. The springings of the arch are typically pinned to supports using wooden or steel ties, but the bulk of lateral thrust is terminated in the abutments. File:Kerkplattegrond gordelboog en travee.png, The transverse arches are highlighted in green on a plan of a church File:Voûte en berceau C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of morphology concerned with the study of the internal structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine, and is often studied alongside physiology. Anatomy is a complex and dynamic field that is constantly evolving as discoveries are made. In recent years, there has been a significant increase in the use of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Bay (architecture)
In architecture, a bay is the space between architectural elements, or a recess or compartment. The term ''bay'' comes from Old French ''baie'', meaning an opening or hole."Bay" ''Online Etymology Dictionary''. http://www.etymonline.com/index.php?allowed_in_frame=0&search=bay&searchmode=none accessed 3/10/2014 __NOTOC__ Examples # The spaces between post (structural), posts, columns, or buttresses in the length of a building, the division in the widths being called aisle, aisles. This meaning also applies to overhead vaults (between rib vault, ribs), in a building using a vaulted structural system. For example, the Gothic architecture period's Chartres Cathedral has a nave (main interior space) that is '' "seven bays long." '' Similarly in timber framing a bay is the space between posts in the transverse direction of the building and aisles run longitudinally."Bay", n.3. def. 1-6 and "Bay", n.5 def 2. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) © Oxford Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Banz Abbey
Banz Abbey (), now known as Banz Castle (), is a former Benedictine monastery, since 1978 a part of the town of Bad Staffelstein north of Bamberg, Bavaria, southern Germany. History The abbey was founded in about 1070 by Countess Alberada of Schweinfurt and her husband, Count Hermann of Habsburg-Kastl, and until the secularisation of 1803 was the oldest monastery on the upper Main. In the late Middle Ages and until 1575 only members of the nobility were accepted as monks. After the Thirty Years' War the abbey had to be rebuilt. The abbots Eucharius Weiner and Kilian Düring commissioned Johann Leonhard Dientzenhofer and after his death in 1707, his brother Johann Dientzenhofer. Construction began in 1698. The church, built in Baroque style, was consecrated in 1719. The interior is built, not with right angles, but with a series of ellipses. The main altar, the chancel and the statues of saints in the church and on the façade are by Balthasar Esterbauer; the ceiling fres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Würzburg Residence
The Würzburg Residence (German: ''Würzburger Residenz'') is a palace in Würzburg, Germany. Johann Lukas von Hildebrandt and Maximilian von Welsch, representatives of the Austrian/Southern German Baroque style, were involved in the construction, as well as Robert de Cotte and Germain Boffrand, who were followers of the French style. Balthasar Neumann, court architect of the Bishop of Würzburg, was the principal architect of the Residence, which was commissioned by the Prince-Bishop of Würzburg Johann Philipp Franz von Schönborn and his brother Friedrich Carl von Schönborn in 1720, and completed in 1744. The Venetian painter Giovanni Battista Tiepolo, assisted by his son, Domenico, painted frescoes in the building. Interiors considered masterworks of Baroque/Rococo or Neoclassical architecture and art include the grand staircase, the chapel, and the Imperial Hall. The building was reportedly called the "largest parsonage in Europe" by Napoleon. It was heavily dama ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Cross-ribbed Vault
A rib vault or ribbed vault is an architectural feature for covering a wide space, such as a church nave, composed of a framework of crossed or diagonal arched ribs. Variations were used in Roman architecture Ancient Roman architecture adopted the external language of classical ancient Greek architecture for the purposes of the ancient Romans, but was different from Greek buildings, becoming a new architectural style. The two styles are often con ..., Byzantine architecture, Islamic architecture, Romanesque architecture, and especially Gothic architecture. Thin stone panels fill the space between the ribs. This greatly reduced the weight and thus the outward thrust of the vault. The ribs transmit the load downward and outward to specific points, usually rows of columns or piers. This feature allowed architects of Gothic cathedrals to make higher and thinner walls and much larger windows. It is a type of arcuated, or arched, Vault (architecture), vault in which the sever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abbey Of Fontenay
The Abbey of Fontenay is a former Cistercian abbey located in the commune of Marmagne, near Montbard, in the département of Côte-d'Or in France. It was founded by Saint Bernard of Clairvaux in 1118, and built in the Romanesque style. It is one of the oldest and most complete Cistercian abbeys in Europe, and became a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1981. Of the original complex comprising church, dormitory, cloister, chapter house, caldarium, refectory, dovecote and the so-called "forge", all remain intact except the refectory and are well maintained. The Abbey of Fontenay, along with other Cistercian abbeys, forms a connecting link between Romanesque and Gothic architecture. History Foundation of the order In the late 11th century during the heyday of the great church of Cluny III (a magnificent Benedictine monastery in Cluny, France), although Cluny had numerous followers, Saint Robert of Molesme, the subsequent founder of Cîteaux Abbey, led a strong reaction against it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abbey Church Of Sainte-Foy
The Abbey Church of Sainte-Foy in Conques, France, was a popular stop for pilgrims traveling the Way of St. James to Santiago de Compostela, in what is now Spain. The main draw for medieval pilgrims at Conques were the remains of Saint Faith, Sainte-Foy, a young woman martyred during the fourth century. The relics of Sainte-Foy arrived in Conques through theft in 866. After unsuccessful attempts to acquire the relics of Saint Vincent of Saragossa and then the relics of St. Vincent Pompejac in Agen, the abbey authorities set their sights on the relics of Sainte-Foy at the ancient St. Faith's Church, Sélestat. The Conques abbey opened a priory next to the shrine in Sélestat. A monk from Conques posed as a loyal monk in Agen for nearly a decade in order to get close enough to the relics to steal them. The abbey church has been a listed monument since 1840. Architecture The original monastery building at Conques was an eighth-century oratory built by monks fleeing the Saracens in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abutments
An abutment is the Bridge#Structure types, substructure at the ends of a bridge Span (architecture), span or dam supporting its Bridge#Structure types, superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining walls to resist lateral movement of the earthen cut and fill, fill of the bridge approach. Multi-span bridges require pier (architecture), piers to support ends of spans unsupported by abutments. Dam abutments are generally the sides of a valley or gorge, but may be artificial in order to support arch dams such as Kurobe Dam in Japan. The civil engineering term may also refer to the structure supporting one side of an arch, or masonry used to resist the lateral forces of a vault (architecture), vault.Pevsner, N. (1970) ''Cornwall''; 2nd ed. Harmondsworth: Penguin; p. 245 The impost (architecture), impost or abacus (architecture), abacus of a column in classical architecture may al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Thrust (arch)
An arch is a curved vertical structure span (engineering), spanning an open space underneath it. Arches may support the load above them, or they may perform a purely decorative role. As a decorative element, the arch dates back to the 4th millennium BC, but structural load-bearing arches became popular only after their adoption by the Ancient Romans in the 4th century Anno Domini, BC. Arch-like structures can be horizontal, like an arch dam that withstands the horizontal hydrostatic pressure load. Arches are usually used as supports for many types of Vault (architecture), vaults, with the barrel vault in particular being a continuous arch. Extensive use of arches and vaults characterizes an arcuated construction, as opposed to the trabeated system, where, like in the architectures of ancient Greece, China, and Japan (as well as the modern steel-framed technique), Post and lintel, posts and beams dominate. Arches had several advantages over the lintel, especially in the masonr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tie (engineering)
A tie, strap, tie rod, eyebar, guy-wire, suspension cables, or wire ropes, are examples of linear structural components designed to resist tension. It is the opposite of a strut or column, which is designed to resist compression. Ties may be made of any tension resisting material. Application in wood construction In wood-frame construction ties are generally made of galvanized steel. Wood framing ties generally have holes allowing them to be fastened to the wood structure by nails or screws. The number and type of nails are specific to the tie and its use. The manufacturer generally specifies information as to the connection method for each of their products. Among the most common wood framing ties used is the hurricane tie or seismic tie used in the framing of wooden structures where wind uplift or seismic overturning is a concern. Hurricane tie A hurricane tie (also known as hurricane clip or strip) is used to help make a structure (specifically wooden structures) more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Springer (architecture)
In architecture, a springer (sometimes springing) is the lowest voussoir (wedge-shaped structural element) on each side of an arch. Since it is the bottom-most element of the arch, it is where the arch support terminates at the respond. It rests on the impost or pier of the arch, that is, the topmost part of the abutment An abutment is the substructure at the ends of a bridge span or dam supporting its superstructure. Single-span bridges have abutments at each end that provide vertical and lateral support for the span, as well as acting as retaining walls ..., from which the arch arises. Usually, the springer is located at the bottom of an arch curve. The "delayed" springing (when the curvature starts noticeably above the support) is a trait of a stilted arch, common in Romanesque and Gothic architecture. References Sources * * External links * contains many examples of the stilted arch Arches and vaults {{architecturalelement-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Purlin
A purlin (or historically purline, purloyne, purling, perling) is a longitudinal, horizontal, structural member in a roof. In traditional timber framing there are three basic types of purlin: purlin plate, principal purlin, and common purlin. Purlins also appear in steel frame construction. Steel purlins may be painted or greased for protection from the environment. Etymology Information on the origin of the term "purlin" is scant. The Oxford Dictionary suggests a French origin, with the earliest quote using a variation of ''purlin'' in 1447, though the accuracy of this claim has been disputed. In wood construction Purlin plate A purlin plate in wood construction is also called an "arcade plate" in European English, "under purlin", and "principal purlin". The term plate means a major, horizontal, supporting timber. Purlin plates are beams which support the mid-span of rafter A rafter is one of a series of sloped structural members such as Beam (structure), steel beam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |