|
Transpiration Stream
In plants, the transpiration stream is the uninterrupted stream of water and solutes which is taken up by the roots and transported via the xylem to the leaves where it evaporates into the air/ apoplast-interface of the substomatal cavity. It is driven by capillary action and in some plants by root pressure. The main driving factor is the difference in water potential between the soil and the substomatal cavity caused by transpiration. Transpiration Transpiration can be regulated through stomatal closure or opening. It allows for plants to efficiently transport water up to their highest body organs, regulate the temperature of stem and leaves and it allows for upstream signaling such as the dispersal of an apoplastic alkalinization during local oxidative stress. Summary of water movement: #Soil #Roots and Root Hair #Xylem #Leaves #Stomata #Air Osmosis The water passes from the soil to the root by osmosis. The long and thin shape of root hairs maximizes surface area so tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transpiration Overview
Transpiration is the process of water movement through a plant and its evaporation from aerial parts, such as leaf, leaves, Plant stem, stems and flowers. It is a passive process that requires no energy expense by the plant. Transpiration also cools plants, changes osmotic pressure of cells, and enables Mass flow (life sciences), mass flow of Plant nutrition, mineral nutrients. When water uptake by the roots is less than the water lost to the Atmosphere of Earth, atmosphere by evaporation, plants close small pores called stomata to decrease water loss, which slows down nutrient uptake and decreases CO2 absorption from the atmosphere limiting metabolic processes, photosynthesis, and growth. Water and nutrient uptake Water is necessary for plants, but only a small amount of water taken up by the roots is used for growth and metabolism. The remaining 97–99.5% is lost by transpiration and guttation. Water with any dissolved mineral nutrients is absorbed into the roots by osmosis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts of the plants such as stems and leaves, but it also transports plant nutrition, nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "wood"; the best-known wood organism is plants, though it is found throughout a plant. The term was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858. Structure The most distinctive xylem cell (biology), cells are the long tracheary elements that transport water. Tracheids and vessel elements are distinguished by their shape; vessel elements are shorter, and are connected together into long tubes that are called ''vessels''. Wood also contains two other type of cells: Ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma and ground tissue#Fibres, fibers. Xylem can be found: * in vascular bundles, present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffusion
Diffusion is the net movement of anything (for example, atoms, ions, molecules, energy) generally from a region of higher concentration to a region of lower concentration. Diffusion is driven by a gradient in Gibbs free energy or chemical potential. It is possible to diffuse "uphill" from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, as in spinodal decomposition. Diffusion is a stochastic process due to the inherent randomness of the diffusing entity and can be used to model many real-life stochastic scenarios. Therefore, diffusion and the corresponding mathematical models are used in several fields beyond physics, such as statistics, probability theory, information theory, neural networks, finance, and marketing. The concept of diffusion is widely used in many fields, including physics (Molecular diffusion, particle diffusion), chemistry, biology, sociology, economics, statistics, data science, and finance (diffusion of people, ideas, data and price v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root Hair
Soil biology Root hairs or absorbent hairs, are outgrowths of epidermal cells, specialized cells at the tip of a plant root. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and are only rarely branched. They are found in the region of maturation, of the root. Root hair cells improve plant water absorption by increasing root surface area to volume ratio which allows the root hair cell to take in more water. The large vacuole inside root hair cells makes this intake much more efficient. Root hairs are also important for nutrient uptake as they are main interface between plants and Mycorrhiza, mycorrhizal fungi. Function The function of all root hairs is to collect water and mineral nutrients in the soil to be sent throughout the plant. In roots, most water absorption happens through the root hairs. The length of root hairs allows them to penetrate between soil particles and prevents harmful bacterial organisms from entering the plant through the xylem vessels. Increasing the surface are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
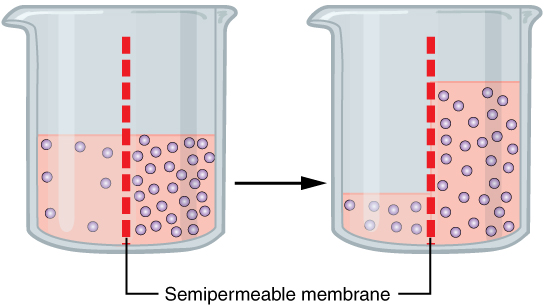
Osmosis
Osmosis (, ) is the spontaneous net movement or diffusion of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane, selectively-permeable membrane from a region of high water potential (region of lower solute concentration) to a region of low water potential (region of higher solute concentration), in the direction that tends to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides. It may also be used to describe a physical process in which any solvent moves across a selectively permeable membrane (permeable to the solvent, but not the solute) separating two solutions of different concentrations. Osmosis can be made to do Work (physics), work. Osmotic pressure is defined as the external pressure required to prevent net movement of solvent across the membrane. Osmotic pressure is a colligative properties, colligative property, meaning that the osmotic pressure depends on the molar concentration of the solute but not on its identity. Osmosis is a vital process in biology, bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial root, aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Types of Roots (major rooting system) Plants exhibit two main root system types: ''taproot'' and ''fibrous'', with variations like adventitious, aerial, and buttress roots, each serving specific functions. Taproot System Characterized by a single, main root growing vertically downward, with smaller lateral roots branching off. Examples. Dandelions, carrots, and many dicot plants. Fibrous RootSystem Consists of a network of thin, branching roots that spread out from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stomata
In botany, a stoma (: stomata, from Greek ''στόμα'', "mouth"), also called a stomate (: stomates), is a pore found in the epidermis of leaves, stems, and other organs, that controls the rate of gas exchange between the internal air spaces of the leaf and the atmosphere. The pore is bordered by a pair of specialized parenchyma cells known as guard cells that regulate the size of the stomatal opening. The term is usually used collectively to refer to the entire stomatal complex, consisting of the paired guard cells and the pore itself, which is referred to as the stomatal aperture. Air, containing oxygen, which is used in respiration, and carbon dioxide, which is used in photosynthesis, passes through stomata by gaseous diffusion. Water vapour diffuses through the stomata into the atmosphere as part of a process called transpiration. Stomata are present in the sporophyte generation of the vast majority of land plants, with the exception of liverworts, as well as so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leaves
A leaf (: leaves) is a principal appendage of the stem of a vascular plant, usually borne laterally above ground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, stem, flower, and fruit collectively form the shoot system. In most leaves, the primary photosynthetic tissue is the palisade mesophyll and is located on the upper side of the blade or lamina of the leaf, but in some species, including the mature foliage of ''Eucalyptus'', palisade mesophyll is present on both sides and the leaves are said to be isobilateral. The leaf is an integral part of the stem system, and most leaves are flattened and have distinct upper ( adaxial) and lower ( abaxial) surfaces that differ in color, hairiness, the number of stomata (pores that intake and output gases), the amount and structure of epicuticular wax, and other features. Leaves are mostly green in color due to the presence of a compound called chlorop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Root
In vascular plants, the roots are the plant organ, organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the surface of the soil, but roots can also be aerial root, aerial or aerating, that is, growing up above the ground or especially above water. Function The major functions of roots are absorption of water, plant nutrition and anchoring of the plant body to the ground. Types of Roots (major rooting system) Plants exhibit two main root system types: ''taproot'' and ''fibrous'', with variations like adventitious, aerial, and buttress roots, each serving specific functions. Taproot System Characterized by a single, main root growing vertically downward, with smaller lateral roots branching off. Examples. Dandelions, carrots, and many dicot plants. Fibrous RootSystem Consists of a network of thin, branching roots that spread out from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xylem
Xylem is one of the two types of transport tissue (biology), tissue in vascular plants, the other being phloem; both of these are part of the vascular bundle. The basic function of the xylem is to transport water upward from the roots to parts of the plants such as stems and leaves, but it also transports plant nutrition, nutrients. The word ''xylem'' is derived from the Ancient Greek word (), meaning "wood"; the best-known wood organism is plants, though it is found throughout a plant. The term was introduced by Carl Nägeli in 1858. Structure The most distinctive xylem cell (biology), cells are the long tracheary elements that transport water. Tracheids and vessel elements are distinguished by their shape; vessel elements are shorter, and are connected together into long tubes that are called ''vessels''. Wood also contains two other type of cells: Ground tissue#Parenchyma, parenchyma and ground tissue#Fibres, fibers. Xylem can be found: * in vascular bundles, present in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soil
Soil, also commonly referred to as earth, is a mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, water, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms. Some scientific definitions distinguish dirt from ''soil'' by restricting the former term specifically to displaced soil. Soil consists of a solid collection of minerals and organic matter (the soil matrix), as well as a porous phase that holds gases (the soil atmosphere) and water (the soil solution). Accordingly, soil is a three- state system of solids, liquids, and gases. Soil is a product of several factors: the influence of climate, relief (elevation, orientation, and slope of terrain), organisms, and the soil's parent materials (original minerals) interacting over time. It continually undergoes development by way of numerous physical, chemical and biological processes, which include weathering with associated erosion. Given its complexity and strong internal connectedness, soil ecologists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |